AP State Syllabus AP Board 7th Class Science Solutions Chapter 9 Reflection of Light Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Science Solutions 9th Lesson Reflection of Light
7th Class Science 9th Lesson Reflection of Light Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
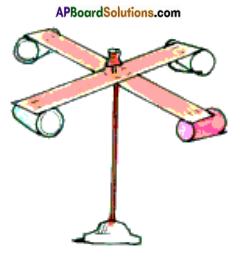
Vidya made a Periscope making slits like this as shown in the figure. Will it work or not? Explain your answer.
Try to make a periscope like this and see whether it works or not?
Answer:
- The periscope does not work.
- The slits made must be parallel to each other.
- If the slits are parallel then the mirror strips placed in them will give reflections property and the image of the object can be seen.
![]()
Question 2.
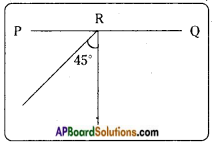
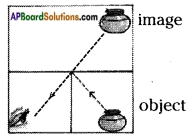
i) Draw reflected ray in the figure given here.
Answer:
- The angle of incidence ∠i = 45° = angle of reflection = ∠r = 45°C
- OR is the incident ray
- RB is the reflected ray
- NR is the normal drawn to the reflecting surface.
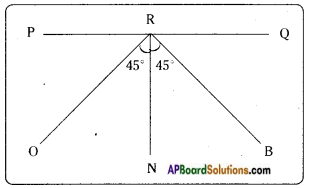
ii) Mark the position of the image in the figure given here by dotted lines.

Answer:
The position of the image is shown by dotted lines.
Question 3.
How do you relate to the angle of reflection and angle of incidence? What will be the angle of reflection when the angle of incidence is i) 60° ii)0°?
Answer:
Angle of incidence ∠i = angle of reflection ∠r
If ∠i = 60° then ∠r = 60°
If ∠i = 0° then ∠r = 0°
![]()
Question 4.
Imagine that your sister is viewing a cricket match on a TV and you are viewing the same cricket match in a mirror which is opposite to the TV. What difference do you notice in the match?
Answer:
- The image of an object in a mirror will have lateral inversion.
- The cricket match my sister is viewing on a T.V. is the object.
- The cricket match I am viewing in a mirror is its image.
- So the match appears to me is a lateral inversion position.
Question 5.
Write the mirror image of your name.
………………………………. (in English)
………………………………. (in Telugu)
Answer:
The student can write his name both in English and Telugu in a lateral inversion way so that it is visible in the right way in the mirror.
Question 6.
You are given the mirror image of a name. Can you find out the actual name?

Place a mirror in front of this figure and check your answer.
Answer:
If this name is seen in a mirror it appears as SURYA.
Question 7.
Get three mirror strips, two rubber bands, card board sheet, translucent paper, and broken bangle pieces and make a Kaleidoscope.
(OR)
Write the procedure of making a Kaleidoscope using the following three mirror strips, two rubber bands, cardboard sheet, translucent paper and broken bangle pieces.
Answer:
1) The student can make a Kaleidoscope with the material supplied.
2) The student can follow the following procedure to make it.
Making a Kaleidoscope :
- Take three mirror strips of the same size.
- Tie these strips with rubber bands to form a triangular tubfe as shown in figure (a).
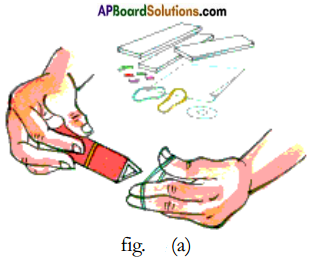
- While tying the strips together, remember to keep their reflecting surfaces facing each other inside the tube.
- Cover one end of the tube with translucent paper using a rubber band.
- Cover the second end with card board sheet and make a hole in it.
- So that we can look inside it. Our kaleidoscope is ready.
- Now put few small pieces of coloured glass bangles inside the. triangular tube as shown in figure (b).

- Look at the bangle pieces through the hole as shown in figure (c).
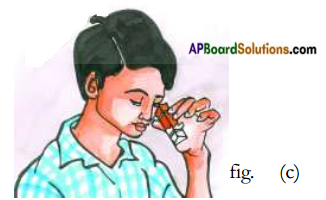
- Shake the kaleidoscope and try to see through the hole slowly rotating it.
- We shall be viewing so many designs and bangle pieces.
![]()
Question 8.
Observe the following figures.
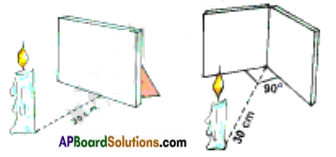
How many images would you observe in the mirrors in the above cases? Write your guesses.
Fig-1 ……………………………
Fig-2 ……………………………
Do experiments and check whether your guesses are correct or not? Give reasons.
Answer:
1) Fig. (a): In fig a: We observe only one image of the candle behind the mirror at a distance of 30 cm. from the mirror.
2) Fig. (b): We observe only 3 images of the candle in the two mirrors arranged at an angle of 90° to each other.
I have done the experiments and my observations are found to be true with my guesses.
Question 9.
Write examples of multiple images formed in your daily life.
Answer:
- In sweet shops mirrors are arranged in such a way that multiple images of the sweets are made visible to the customers.
- In ice-cream parlours and cool drink’s shops also plane mirrors are arranged in parallel on the walls of the room. These mirrors give .multiple images of the customers making them feel that the shop is full of customers.
- In barber’s shop mirrors are arranged in such away that the customer can view his images in all directions.
Question 10.
Observe the figure and identify which type of mirror is used. How do you justify.
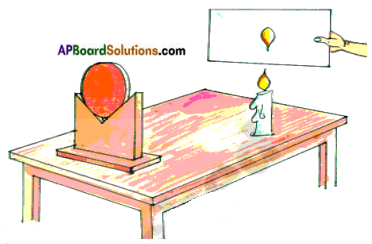
Answer:
- A doncave mirror is used to note the image of the flame of the candle on a screen.
- A concave mirror forms the real image of an object.
- We know images that can be caught on a screen are called real images.
Question 11.
Sai lighted a candle in his house when power went off. His mother placed it in front of a mirror. Sai observed something that excited him. What change would have excited Sai? Some questions came to his mind. Can you guess the questions? Write a few such questions.
Answer:
- When the power is off, the room becomes dark and no object is visible.
- When a lighted candle is put infront of the mirror, light falling from it on all objects are visible in the mirror.
- The following questions are likely to arise in the mind of Sai.
a) Why are only some images of the objects in the room are visible in the mirror?
b) What relation exists between the light of the candle and mirror exists?
c) Why not the images of all objects seen in the mirror.
d) What is important for the visibility of the objects?
![]()
Question 12.
Unexpectedly some water sprinkled on a mirror while Madhu was shaving his face. Did he observe any difference in his image? If yes, explain why?
Answer:
- When water is sprinkled on a mirror the plane surface of the mirror is disturbed.
- So the clarity in the images goes away and due to reflection taking place in a scattered way, the image becomes dull arid unclear.
Question 13.
Imagine that all the houses in your street have elevation with mirrors. Suppose you and your friends are walking in the street. Would you experience any difficulties when you walk through that street? Predict and explain. Is it difficult for birds to live or fly in that street? Why?
Answer:
- We experience difficulties when we walk through the street where all houses have elevation with mirrors.
- Due to the formation of multiple images of the people walking in the street, they often were put to confusion.
- It is difficult for birds to live or fly in that street as the reflections will give confusion to them.
Question 14.
Take an empty toothpaste box and two mirror strips of the required size and make a periscope.
Answer:
Close both ends of the box. Draw squares at both ends. Draw the diagonal to these squares. Slit the diagonals with a blade. The slits should equal to the length of the mirror strips. Fix the mirror strips in these slits. Take care to see that these mirror strips lie parallel to each other, with their reflecting surfaces facing each other. Fix the mirror strips firmly to the box with a few drops of molten wax from a burning candle or fevicol. Cut out two widows on the narrow sides of the box. The windows should open directly on the reflecting surfaces of the mirror strips. Now the periscope is ready to see.
Question 15.
What is the angle between two plane mirrors when there are five images?
Answer:
When the angle between two plane mirrors is 60° then five images of an object are formed in the mirrors.
Question 16.
What is the difference between convex and concave mirrors? Draw the diagrams of concave and convex mirrors.
Answer:
- A concave mirror forms the real image of an object.
- A convex mirror forms the virtual image of an object.
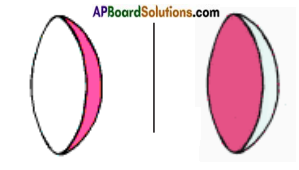
1) Concave mirror
2) Convex mirror- The reflecting surface of the mirror is concave in the case of a concave mirror.
- The reflecting surface of the mirror is convex in the case of a convex mirror.
![]()
Question 17.
Where do you find irregular reflection in daily life? Give some examples.
Answer:
- Irregular reflection is observed in the window glass which is rough.
- Glass mirror on which water is sprinkled. This also makes irregular reflection.
Question 18.
Mirrors help us to see all the objects around us without turning our heads. Write about the role of mirrors in opr life.
Answer:
- Convex mirror is used as a side view mirror in motor vehicles.
- A convex mirror can show the image of a large area as a small image.
- This property of the convex mirror is made use of in seeing all objects behind without turning our head..
- When we stand in between parallel mirrors also we could see our front and back.
- I appreciate the wonderful usefulness of role of mirrors in our life.
Question 19.
Army people can see their enemies while hiding themselves with the help of periscopes. Write about the use of periscope for their security.
Answer:
- If the soldier is infront of his enemy, there will be a danger to his life.
- Army people make use of periscope to see their enemies by hiding themselves.
- This periscope is a gift made by making use of the properties of mirrors.
- I really appreciate the utility of the periscope.
Question 20.
Imagine what would happen if there are no rearview mirrors attached to vehicles and there are no concave mirrors in the headlights of the vehicles. Write about the role of convex and concave mirrors in safe driving.
Answer:
- If there are no rearview mirrors attached to vehicles, it would be impossible for the vehicle drivers to know about the coming vehicles behind him.
- This may lead to accidents.
- If there are no concave mirrors in the headlights of the vehicles, then the light focused by the lights may not have enough intensity.
- This results in not getting a clear vision of long distances during night times when drivers drive their vehicles.
- As a result, drivers cannot travel with the present speed.
- The service rendered by convex and concave mirrors is really wonderful.
Question 21.
While constructing a new house, Kishan’s uncle rejected his wife’s request of glass elevation to the building, saying that “It is harmful to the birds and also ourselves”. Why would you support the decision of Kishan’s uncle?
Answer:
Kishan’s uncle took a good decision which might be appreciable.
Nowadays people prefer the decoration of houses exterior and interior. This may cause more life-threatening to other living forms. If you elevate the house with mirrors, it creates lot of inconvenience to you. The birds, creatures suffer a lot by the reflection and creation of multiple images. The plain mirrors may reflect light during day and night.
So, Kishan’s uncle’s decision is really good and I support it.
![]()
Question 22.
Collect information from your elders and shopkeepers about where we use more mirrors and why?
Answer:
We use more mirrors in
- Sweet shops
- Ice parlours
- Optical shops where spectacles are sold.
- In hair cutting saloons.
Question 23.
Collect information about which objects of your school and home work like a mirror and why? Identify the similarities among those objects.
Answer:
- School bell works like a convex mirror.
- The outer wall of the cylindrical drum made of stainless steel works like a convex mirror.
- The outer portion of the spoon is like a convex mirror where as the inner portion of the spoon is like a concave mirror.






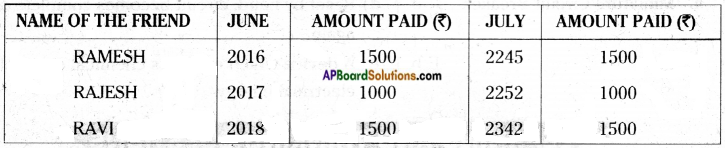
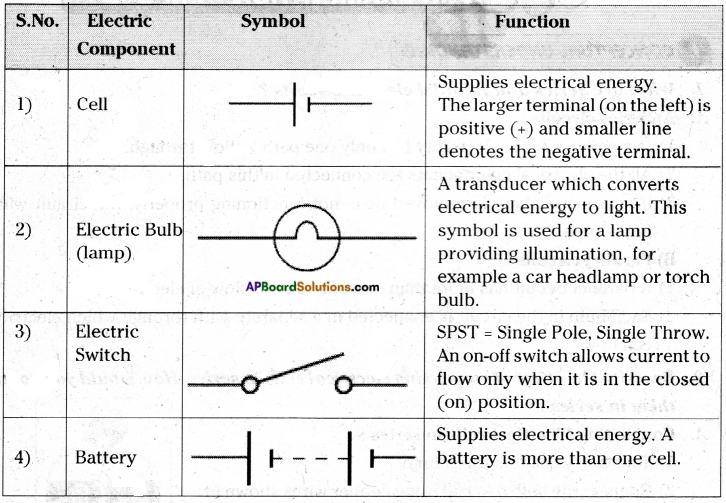







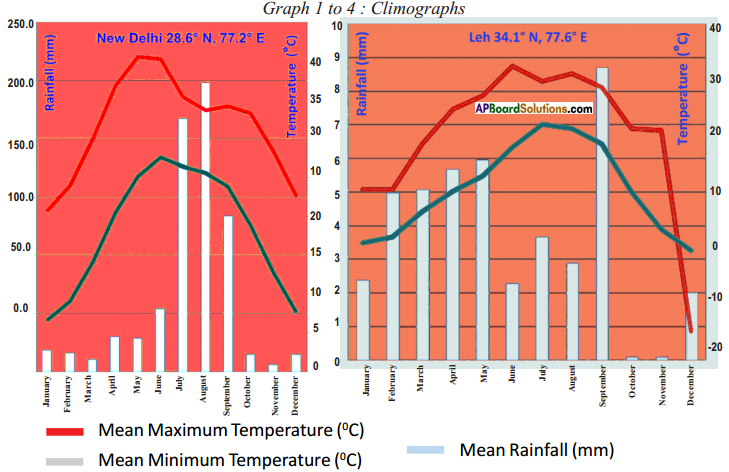
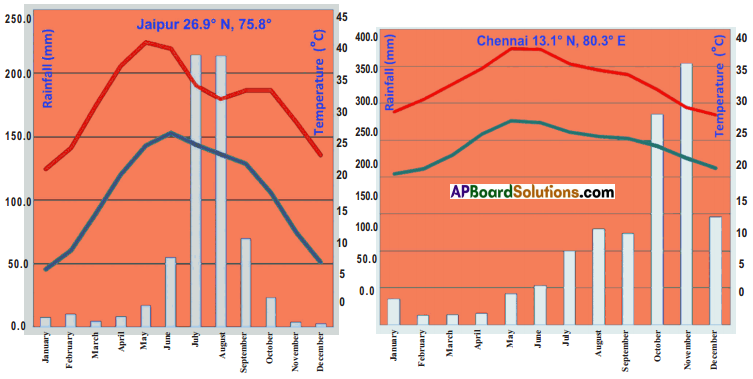
 Answer:
Answer: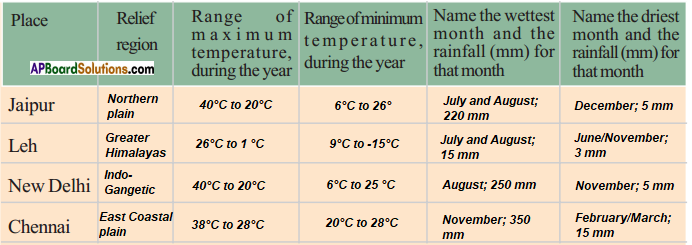
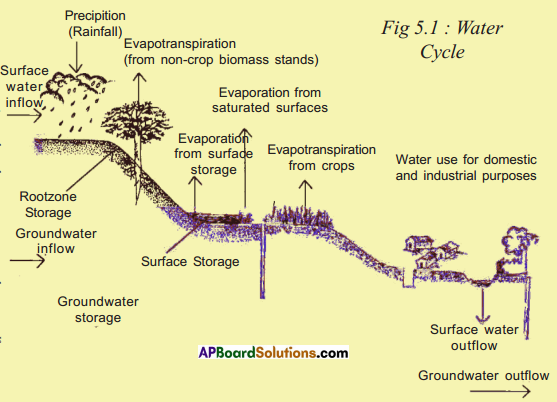
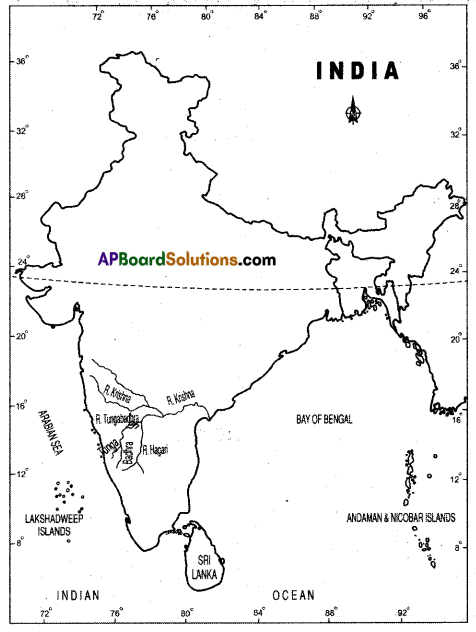
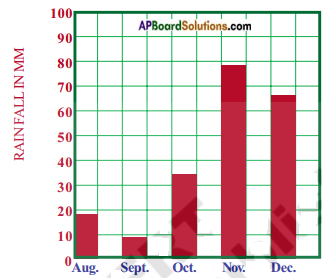
 Sun angles and their impact.
Sun angles and their impact.