SCERT AP Board 8th Class Social Solutions 19th Lesson Social and Religious Reform Movements Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Social Studies Solutions 19th Lesson Social and Religious Reform Movements
8th Class Social Studies 19th Lesson Social and Religious Reform Movements Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve your learning
![]()
Question 1.
Do you agree with “Western education and Christian Missionaries influenced the Social and Religious reform movement in India”. Why?
Answer:
Yes. I can agree with this statement.
Reasons: Many Christian missionaries came to India along with the European companies to preach Christianity in India. They severely criticised the existing religious practices and beliefs and tried to persuade people to adopt Christianity. At the same time they also established many educational institutions, hospitals and charity services with the view of serving the poor and needy. This helped in spreading many new ideas among people.
Soon a lively debate ensued between the missionaries and leaders of Hinduism and Islam as each tried to defend their own religious ideas. Such debates helped people not only to understand each others ideas but also encouraged them to enquire into the original and basic tenets of their own religions. Several European scholars studied the ancient literature of India, translated them and published them as books. (Since they studied books of the eastern countries they were called ‘Orientalists’.) Now these books are available for all to study.
As the ancient Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu, Persian and Arabic books got translated into European languages, the rich and diverse cultural heritage of the country was recognized by all. This enabled the people with new ideas to reinterpret their own religions better.
e.g.:
- Rammohan Roy condemned idol worship.
- Vivekananda asked to adopt some of the positive qualities of European culture like freedom and respect for women, work ethic, technology etc.
- Swami Dayananda rejected all later additions to Hindu religion.
- Sir Syed Ahmed Khan worked for the spread of modern education and social reforms among the Muslims.
- The minimum age for marriage was raised to the 14 years.
- Rammohan Roy fought against ‘Sati’.
- Law was made to encourage widow remarriages.
- Many established schools for girls.
![]()
Question 2.
What was the importance of printifig press in the development of reform movement?
Answer:
The Europeans introduced printing press in India. It made possible the appearance of many newspapers and magazines. Books were also published in different Indian languages. This made books accessible to a large number of people at a very low cost. People could now carry on debates and discussions through these newspapers, magazines and books and easily reach out to large number of people.
Question 3.
The main idea behind religious reform was to end complex rituals, worshipping of many gods and idol worship, purdah system. Do you think people have accepted these reforms ? Explain.
Answer:
People have accepted these reforms temporarily.
Reasons:
- Now there was no existence of Brahmo Samaj. The members of it followed ‘Bhakti Path.’
- Arya Samaj also accepted Vedic religion at the end.
- At present, the Hindus are worshipping many Gods and their idols.
- Complex rituals: People have accepted some of the rituals which are easy to follow.
Question 4.
Why do you think people like Ramabai paid special attention to the condition of widows?
Answer:
Many writings tell us about the pitiful conditions of the widows in their families. They suffered because they had no economic freedom and education. The people like Ramabai thought that “it was the biggest sin to endure the ill deeds and not oppose them.” So, they paid special attention to the condition of widows.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the role of Raja Rammohan Roy as a social reformer in India in 19th century.
Answer:
Raja Rammohan Roy was born in Bengal in 1772. He was a great scholar of Sanskrit, Persian, English, and knew Arabic, Latin and Greek.
He also studied several religious philosophies like Hinduism, Islam, Christianity and Sufism. Having studied various religious books he was convinced that there is only one God and that worshipping of idols and making sacrifices were incorrect. He was convinced that all great religions had the same common beliefs and it was incorrect to criticise the religions of others. He also believed that we should accept a religious belief only if it is rational and if it is beneficial to people.
He rejected the authority of priests and called upon people to study the original books of their religions. He published his ideas in magazines and books using the new technology of printing to reach out to maximum number of people.
In 1828 Rammohan Roy founded the Brahmo Samaj – an assembly of all those who believed in an universal religion based on the principle of One Supreme God. After the death of Rammohan Roy in 1833, the Brahmo movement was led by Devendranath Tagore and Keshav Chandra Sen. They popularised their ideas by lecturing all over India.
Question 6.
What was the main concern of Sir Syed Ahmad Khan in promoting English creation?
Answer:
- Sir Syed Ahmed Khan was convinced that the bitterness between Muslims and the British must end.
- In order to progress, Muslims should participate in government and get larger share in government jobs.
- He thought that this was possible only through modern education.
- This was the main concern of Sir Syed Ahmed Khan in promoting English education.
![]()
Question 7.
Different leaders thought of different ways in which the ‘untouchable’ castes can be made the equals with all others. Make a table with the suggestions of leaders like Phule, Bhagya Reddy Varma, Narayana Guru, Ambedkar and Gandhiji.
Answer:
Phule:
- He opened a special school for the Mahar and Maang castes.
- He wrote many books on caste discrimination.
- They set up Satya Shodhak Samaj for low caste children.
- He encouraged to conduct marriage and death ceremonies without the Brahmins.
Bhagya Reddy Varma :
- He called upon Dalits to call themselves ‘Adi Andhras’.
- To spread awareness in dalits he started ‘Jagan Mitra Mandali’.
- He opened special schools.
- He opposed religious misdeeds on dalit girls.
- He encouraged Buddhism.
Narayana Guru:
- He preached the idea of ‘One Jathi, One God and One Religion for all’.
- He called upon the Ezhava community to give up several aspects of their low caste status.
- He set up temples where no caste discrimination would be practised and very simple rituals would be followed without Brahmin priests.
- He even said that building schools for children was more important than building temples.
Ambedkar:
- He led many agitations for dalits.
- He argued that the dalits should vote separately for dalit candidates to the legislatures.
- Overcoming numerous social and financial obstacles, Ambedkar became one of the first dalits to obtain college education in India.
- He founded an Independent Labour Party to represent the interests of the dalits.
- Ambedkar was appointed as the Chairman of the Constitution Drafting Committee, charged by the assembly to write India’s new constitution.
Gandhiji:
Around 1932 Gandhiji started a movement against untouchability. He called the ‘untouchable’ castes as Harijans or ‘People of God’. He wanted to ensure them equal access to temples, water sources and schools. This campaign was taken up by Congress in a big way and helped to bring millions of Dalits into the national movement.
![]()
Question 8.
Why does caste remain such a controversial issue today? What do you think was the most important movement against caste in colonial times?
Answer:
In addition to that one feels one’s caste is great. So caste is an important pillar in some celebrations of families. No caste, even higher or lower, people will agree to cross these limitations.
Bringing this ‘caste’ into social issues is causing many problems, e.g.: A dispute between two persons is created as a dispute between two castes.
I think the movement led by Satya Shodhak Samaj was the most important movement against caste in colonial times.
Question 9.
What did Ambedkar want to achieve through the temple entry movement?
Answer:
Ambedkar wanted to say that ‘All are equal before God and everyone has rights on God”.
Question 10.
How in your opinion were the movements of social reform effective in ridding Indian society of social evils? What social evils do you find today ? Which reform movements should be started to combact them ?
Answer:
The movements of social reforms were effective in ridding Indian society of social evils. These movements banned Sati and child marriages. These encouraged women education, school education and widow remarriages.
We find the following social evils today:
- Corruption
- Religionism,
- Casteism
- Dowry
- Regionalism etc.
Today there is a silence in our society. No politician is working against these evils. Nobody is thinking of these.
The educated should think of these evils and respond. Otherwise, no reforms are introduced. The governments also should think of these issues.
![]()
Question 11.
Create a poster that reflects girls education and its importance.
Answer:
Poster on Girls’ Education
Despite all tall claims by the government and nagging by voluntary organizations, a vast majority of the girls are yet illiterate in India. During the last four decades since independence, much is being done to emancipate women. Education of girls is one of the basic features of the plan. Many schools and colleges are founded for girls.
Education has led to their economic independence and equality with the menfolk. They have now an honoured position in society and have secured their rights from the reluctant men but all this is confined chiefly to the urban areas. In rural areas most of the peopte-are-sWtfr against girls’ education.
Every village must have a girls’ school, or if that is not possible owing to lack of funds, parents should be persuaded to admit their daughters to boys’ schools thus promoting co-education.
Furthermore, the extreme poverty of the Indian masses makes it imperative that education for girls should be free up to the matriculation standard. If facilities for female education are provided in every village, it will also be possible to make it compulsory.
Special legislation should then be enacted to deal with parents who neglect the education of their daughters. This compulsion would be essential in early stages because most villagers are still too ignorant to understand the value of education for girls.
Question 12.
What qualities of Social Reformers you liked? Why?
Answer:
Qualities of Social Reformers I liked:
- The reformers took recourse to propaganda in the Indian language to reach the masses.
- They also used novels, dramas, short stories, poetry, the press and the cinema to spread their views.
- Indian women played an active and important role in the struggle for independence of the country.
Reason: Due to the hardwork of these reformists and other individuals many superstitious disappeared.
8th Class Social Studies 19th Lesson Social and Religious Reform Movements InText Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
What were the similarities and differences between the views of Rammohan Roy and Swami Vivekananda and Dayananda Saraswati ? (Textbook Page No. 213)
Compare the religious views of Ram Mohan Roy, Vivekananda and Dayananda and point out the similarities and differences among them.
(OR)
Compare the religious views of Rammohan Roy, Vivekananda and Dayananda, and point out the similarities and differences among them.
Answer:
Similarities:
- All the three believed the Hindu Dharmic Literature.
- They told that the best things of all the religions should be followed by all.
- They opted social service as their ideal hobby.
Differences:
| Dayananda | Rammohan Roy | Vivekananda |
| 1) He rejected the orthodox Hindu religion. | 1) He treated all the religions equal. | 1) He treated Hindu religion as best of all. |
| 2) He set up Arya Samaj. | 2) He set up Brahmo Samaj. | 2) He set up Ramakrishna Mission. |
| 3) He treated all the religions are false and gave a call to the people to return to Vedic Hindu religions. | 3) He asked people to have faith in only one god. | 3) He wanted to revive a reformed Hindu religion. He wanted the people to leave superstitions and to follow the Hindu religion. |
![]()
Question 2.
How do you think were the early reformers influenced by European culture and Christianity? (Textbook Page No. 213)
Answer:
- The early reformers were influenced by the positive qualities of European culture like freedom and respect for women, work ethic, technology etc. So they worked hard to abolish ‘Sati’ and child marriages and to encourage widow remarriages etc.
- The persons who were influenced with their religion, propagated new systems like worshipping one Supreme God.
- They were all educated in English. They studied many subjects for knowledge. So they encouraged English education and establishment of schools.
Thus the early reformers were influenced by European culture and Christianity.
Question 3.
Do you see any similarities between the DAV schools and the MAO college? (Textbook Page No. 214)
Answer:
| DAV (Dayananda Anglo Vedic) Schools |
MAO (Mohammedan Anglo Oriental) college |
| 1) These were established by the followers of Swami Dayananda. | 1) This was established by Sir Syed Ahmed Khan. |
| 2) To educate children in modern subjects and at the same time keep them in touch with their religion and culture. | 2) It sought to teach English and science but in an Islamic atmosphere. |
| 3) At the end they felt that they should focus on teaching Vedic religion and not modern subjects and counter the influence of other religions. | 3) It later developed into the Aligarh Muslim University. |
Question 4.
Do you think these demands are necessary even today? (Textbook Page No. 219)
Answer:
I do not think so.
Reasons: The Government of India is providing the ‘low’ castes with ‘reservations’ in all the sectors like education, employment etc.
All these people are educated equally with others and doing their jobs. They are participating and are in good positions in politics also. So I think these demands are not necessary today.
![]()
Question 5.
Compare the efforts of Narayana Guru and Jyotiba Phule. What similarities and differences do you see between them? (Textbook Page No. 219)
Answer:
Similarities:
- Both opposed the caste system.
- Both established many schools.
- Both opposed the supremacy of Brahmins.
Differences:
| Narayana Guru | Jhotiba Phule |
| 1. He was a religious leader. | 1. He was a social reformist. |
| 2. He set up temples where no caste discrimination would be practised and very simple rituals would be followed without Brahmin priests. | 2. He campaigned for special schools, colleges and hostels for the children of ‘low’ castes where the teachers too would be from ‘low’ castes. |
| 3. He actively criticized caste system and called for end to all forms of caste discriminations. | 3. He called upon the low castes to conduct marriage and death ceremonies without the Brahmins. |
Question 6.
Recall the teachings of Buddha with regard to the caste system. (Textbook Page No. 220)
Answer:
Buddha preached that ‘All are equal’. He opposed caste and religious discriminations. He treated all his followers equal.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the similarities and differences in the approaches of Gandhiji and Ambedkar towards dalits? (Textbook Page No. 221)
Answer:
Similarities:
- Both worked for Dalits.
- Both were the members of Congress Party.
Differences:
| Gandhiji | Ambedkar |
| 1) Being a person of higher caste, he fought for dalits. | 1) He fought for dalits as a dalit. |
| 2) He reserved some seats in elections to dalits. | 2) He argued that the dalits should vote separately for dalit candidates to the legislatures. |
| 3) He fought for dalits from Congress. | 3) He set up Independent Labour Party for dalits. |
| 4) He continued himself in Hindu religion and fought for dalits. | 4) He lost his faith in Hinduism and converted to Buddhism at the end of his life. |
Question 8.
In what way do you think printing helped in the spread of these new ideas? (Textbook Page No. 213)
Answer:
The Europeans introduced printing press in India. It made possible the appearance of many newspapers and magazines. Books were also published in different Indian languages. This made books accessible to a large number of people at a very low cost. People could now carry on debates and discussions through these newspapers, magazines and books and easily reach out to large number of people.
Thus the printing helped in the spread of these new ideas.
![]()
Question 9.
If you had to choose between a DAV school, Gurukul School and a government run school, which one would you prefer to go to and why? (Textbook Page No. 213)
Answer:
I would prefer the government school.
Reason:
- Here the teaching-learning process would be in a secular way.
- All the students here would be treated equally.
Question 10.
You may have noticed that all the reformers tried to reinterpret the ancient religious books in order to defend their reformist ideas. Look at the examples of all the major reformers and see how they did this. (Textbook Page No. 214)
Answer:
1) Raja Rammohan Roy:
He studied several religious philosophies like Hinduism, Islam, Christianity and Sufism. Having studied various religious books he was convinced that there is only one God and that worshipping of idols and making sacrifices were incorrect. He was convinced that all great religions had the same common beliefs and it was incorrect to criticise the religions of others. He also believed that we should accept a religious belief only if it is rational and if it is beneficial to people. He rejected the authority of priests and called upon people to study the original books of their religions. He published his ideas in magazines and books using the new technology of printing to reach out to maximum number of people.
2) Swami Vivekananda:
He believed that Hindu religion was superior to all others. He emphasized the teachings of Upanishadas which were being translated and printed in large numbers.
3) Swami Dayananda Saraswathi:
He studied the Vedas and was convinced that they contained the true religion and he rejected all later additions to Hindu religion like many gods and goddesses, idol and temple worship and Brahmanic priesthood and caste system. He advocated worshipping one Supreme God through simple rituals and recitation of Vedic mantras. He rejected all other religions as false religions and wanted Hindus who had converted to other religions to return to Hinduism based on the Vedas.
![]()
Question 11.
Do you find any religious idea advocated by the above reformers which was not part of the Bhakti Movement? (Textbook Page No. 214)
Answer:
No. All the reformers advocated the religious ideas of the Bhakti Movement only.
Question 12.
Some people thought this situation (No place inside the classroom) was better than the total lack of education for untouchable people. Would you agree with this view? (Textbook Page No. 218)
Answer:
Yes. I do agree with them.
Jyothiba Phule and Ambedkar faced and ignored such situations and studied well. So they were able to pave the way to the next generations. Otherwise there will be the same situation at present.
Question 13.
Do you think dalits have equal access to temples, water sources and schools today? What problems do they still face? (Textbook Page No. 221)
Answer:
At present dalits have equal access to temples, water sources and schools. To say frankly they have equal access and reservations also. So we can say that there were no social problems to them.
Question 14.
Write a dialogue between supporters and opposers of widow remarriage. (Textbook Page No. 215)
1856 – At the time of first widow remarriage – Calcutta.
- Srikanth Chattarji: Wow, this should be a golden page in the history of our nation. Here is an end to the problems of women. May God bless the women!
- Mukhesh Bandopadhyaya: How dare you to talk like this Srikanth babu? This gives us several punishments in the hell. Arey – A marriage to widow.
How could this be possible? A woman will go to some other’s family to develop their family, again to some other family. How could they do this?
Oh God! Please save us and save our country. - Rajya Laxmi: Today is really a wonderful day. Child marriages and widowships etc., were curses on us. We have to work in our maternal and mother-in-law’s houses freely without any feelings. So this is a good beginning for us. We are very grateful to the God.
![]()
Question 15.
Do you think today equal importance is given to the education of girls or do girls still face discrimination? (Textbook Page No. 217)
Answer:
Equal importance is given to girls education with boys. To be frank the girl enrolment is more than boys in some schools and collges. But in some families girls face discrimination, mostly in some backward states.
Question 16.
What problems do girls face in getting educated which boys do not face? (Textbook Page No. 217)
Answer:
- Girls are not encouraged for higher education.
- Girls are not permitted to far off places for education.
- Some courses are only meant for boys.
Question 17.
To what extent has the treatment of widows changed today? (Textbook Page No. 218)
Answer:
We can say that the attitude of the society is changed. Widows are treated equally with other women. Their elders are only arranging remarriages for them. Men are also taking a step forward to marry them. They are treated equally except in some religious traditions like marriages etc.
Question 18.
Do dalit girls and Muslim girls face special problems in education even today? (Textbook Page No. 218)
Answer:
Nowadays we seldom hear such a news from newspapers that dalit girls are facing some problems from others. They are also receiving education in classrooms along with others. Muslim girls also have separate schools. They are also studying without problems.
Question 19.
Find out about some important women leaders of the freedom struggle – Kalpana Dutt, Aruna Asaf Ali, Captain Lakshmi Sehgal, Sarojini Naidu, Kamladevi Chattopadhyaya, etc. (Textbook Page No. 220)
Answer:
1. Kalpana Dutt:
27.07.1913
08.02.1995.
She was later known as Kalpana Joshi. She was a member of prominent Republican Army in Chittagang and participated in the well known Chittagong Armoury Raid case 1930. Later she joined Communist Party of India.
2) Aruna Asaf Ali:
16.07.1908
27.09.1996
She played a leading role during the Quit India Movement. She unfurled the national flag at the Gowalia tank Maidan to signify the commencement of the Quit India Movement and became a legend for thousands of youth that rose to emulate her.
She was awarded Lenin Prize for Peace in 1975, Jawaharlal Nehru Award for Interna¬tional Understanding – 1991 and Bharata Ratna – 1998.
3) Captain Lakshmi Sehgal:
24.10.1914
23.07.2012.
In 1943 she met Netaji in Singapore. Their meeting changed her life. She started Rani of Jhansi Regiment. Then she became as Captain Lakshmi Sehgal. She was arrested by the British in May 1945.
4) Sarojini Naidu:
13.02.1879
02.03.1949.
The Nightingale of India – she was the second Indian woman to become the President of Indian National Congress. Her birthday was celebrated as Women’s Day in India.
She joined the movement in 1905 – Partition of Bengal. She came into contact with many people.
5) Kamaladevi Chattopadhyaya:
03.04.1903
29.10.1988.
She was a social reformer and freedom fighter. She joined the movement in 1923 during Non-Cooperation Movement. She was the first Indian woman to be arrested.
![]()
Question 20.
Why do you think was there bitterness between the Muslims and the British after 1857? (Textbook Page No. 214)
Answer:
Mohammadans invaded India many times from 6 AD/7AD. Later they occupied and ruled India till the arrival of the Britishers. Nearly 1200 years they ruled India. Even though there were some native rulers, they were small in number. After 1857, India was under the control of the British queen’s rule. Mohammadans were also treated as Indians. So, there was bitter¬ness between the Muslims and the British after 1857.
Question 21.
Why do you think was it important to get the government to pass laws for social reform? (Textbook Page No. 215)
Answer:
Some persons might have reformistic views. Some might reject them. So the people in the society could not follow these ideas. Even though they followed, they might be rejected by the society. So it was important to get the government to pass laws for social reforms.
Question 22.
Imagine that you are one of the students sitting in the school veranda and listening to the classes. What kind of questions would be raising in your mind ? (Textbook Page No. 218)
Answer:
- Why should I sit here?
- Why I am not allowed to sit inside?
- Did I do any mistake
- Why I am an untouchable?
- Is it my mistake, taking birth in this caste?
- Why shouldn’t they touch me?
![]()
Question 23.
Why do you think he (Jyotiba Phule) insisted on ‘low’ caste teachers to teach such students? (Textbook Page No. 219)
Answer:
Teachers of higher castes ill-treated and hurted the low caste students. They showed discrimination in the castes. In these conditions the process of learning might not be perfect. The teachers of low castes could not hurt these students. So he insisted on low caste teachers to teach such students.
Question 24.
How would the feeling that the dalits were the orginal inhabitants of Andhra Pradesh have helped in boosting the confidence of the dalits ? (Textbook Page No. 220)
Answer:
The feeling would raise the confidence in dalits. This confidence would strengthen them in fighting against the discrimination. That led them to their success.
Question 25.
Did all women get the right to vote in independent India? (Textbook Page No. 220)
Answer:
Yes, all women get the right to vote in independent India.
![]()
Question 26.
Create a poster that reflects on social Reforms.
Answer:
Poster on Social Reforms
Sometimes society becomes full of evils and vices. It is guided by blind faith and superstition. People do not try to know the relation between cause and effect. They believe in imaginary ghosts and spirits as the prime-mover of all social actions. They believe in animal sacrifice to please the deities. They also once believed in the human sacrifice. The social vices like child wives were in existence. The widows were not allowed to marry again. The wives were compelled to be burnt with their dead husbands and so on. Untouchability disabled a big section of people. In order to eradicate all these things social reforms were necessary. Social reforms are necessary at all times in order to get the society purged off any vice that creeps into it.
Great reformers are born to reform the society and to reform the religion. Because many times religion is the basis of the social behavior. Martin Luther in Germany and John Wicliff in great Britain were the great reformers in 18th century. In India we got Raja Rammohan Roy, Ishwar Chadra Vidyasagar, Swami Dayananda Saraswati, Ramakrishna, Paramhamsa, Swami Vivekananda, Mahatma Gandhi as the great reformers. In ancient times we had Gautama Buddha and Mahavir as the great religious and social reformers. In Orissa Mr. Madhusudan Das, Pandit Nilakantha Das and Acharya Harihar Das made attempt to reform the society.
Social reform is necessary, time and often. So we must reform our society whenever it is necessary. Social reform should base on science and morality. Social reform cannot be made by legislation, force or imposition. It can be made only by effective public education, though the necessity of legislation cannot be altogether ruled out.
![]()
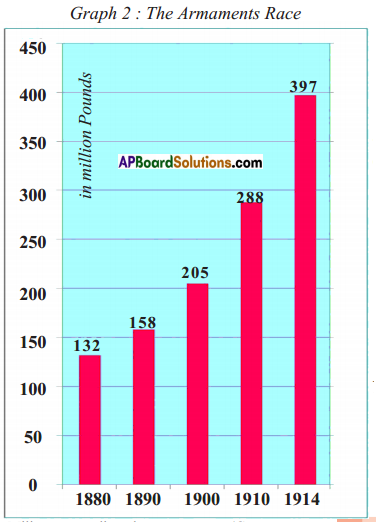
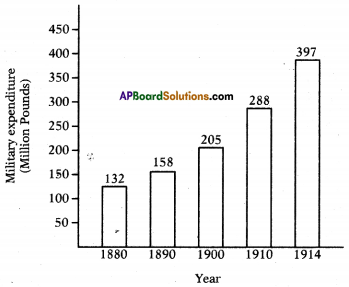
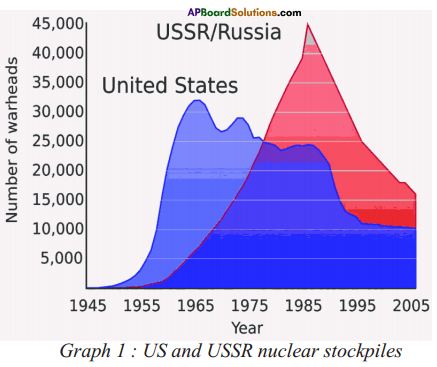 a) During 1955-2005, which country had the highest number of warheads?
a) During 1955-2005, which country had the highest number of warheads?
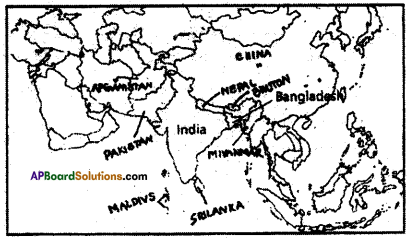 A) Write any two countries which are sharing boundary with India on the North-eastern side.
A) Write any two countries which are sharing boundary with India on the North-eastern side.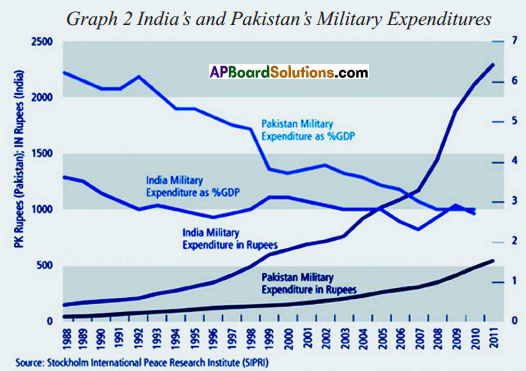 1. Which country had spent more on Military Expenditure in its GDP?
1. Which country had spent more on Military Expenditure in its GDP?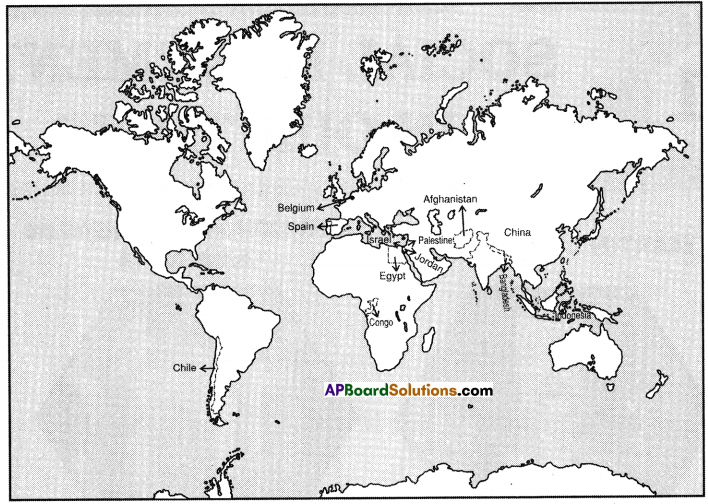


 Answer:
Answer: Write a caption on the above cartoon in the contest of forest. (Textbook Page No. 50)
Write a caption on the above cartoon in the contest of forest. (Textbook Page No. 50)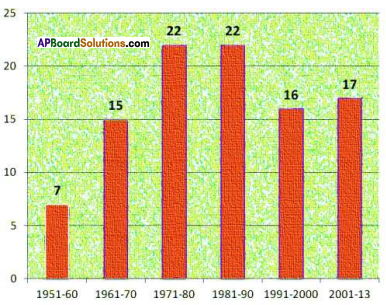
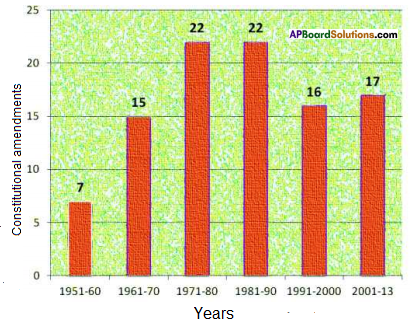
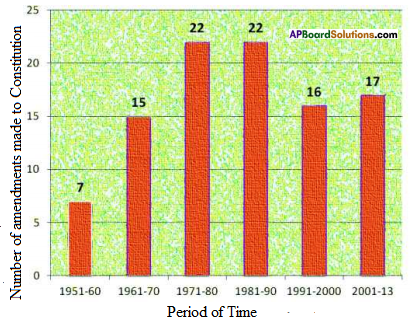
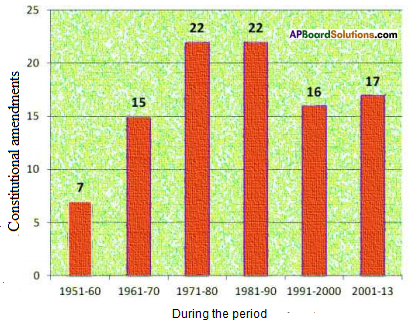 Now answer the following questions.
Now answer the following questions.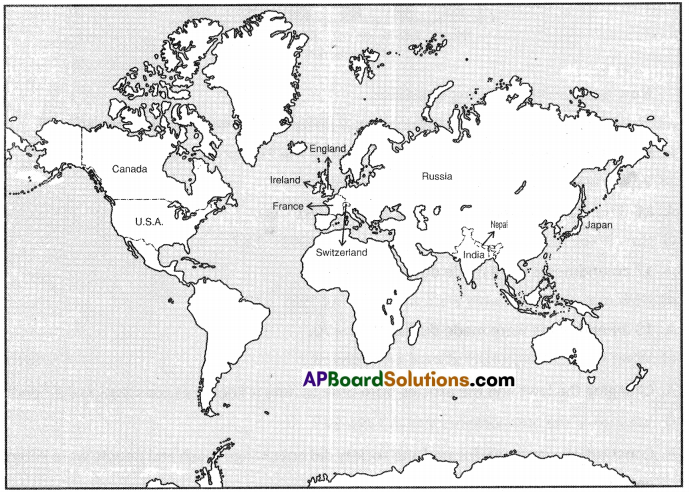








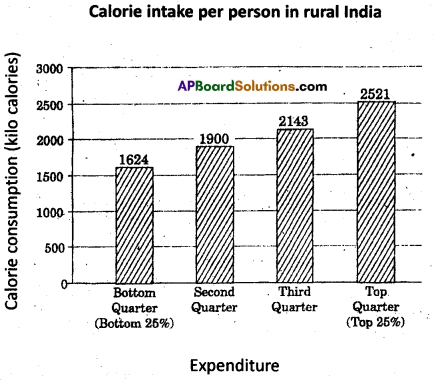 a) What percentage of people in rural India are consuming more calories than are required?
a) What percentage of people in rural India are consuming more calories than are required?


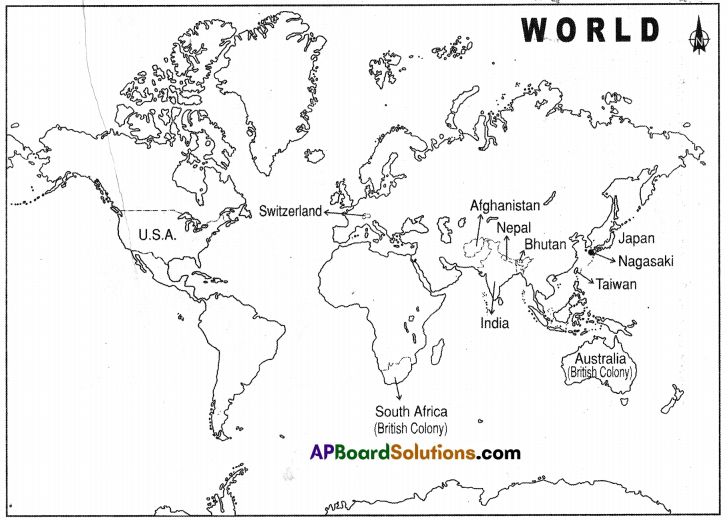
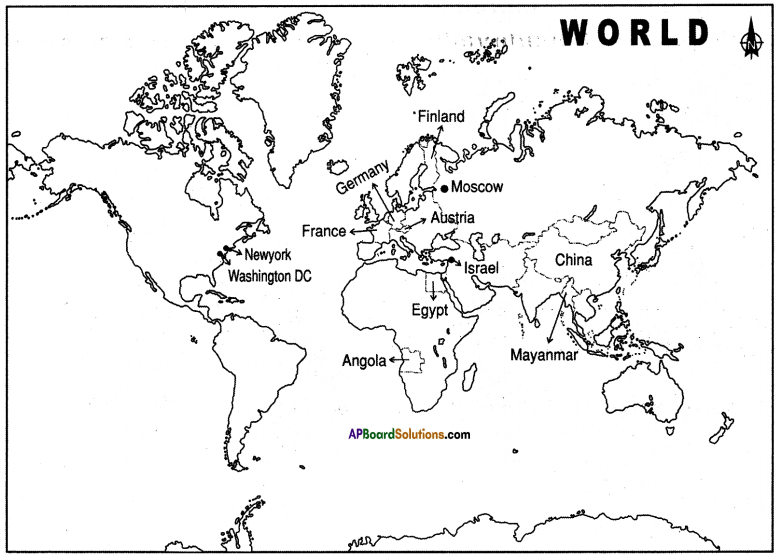
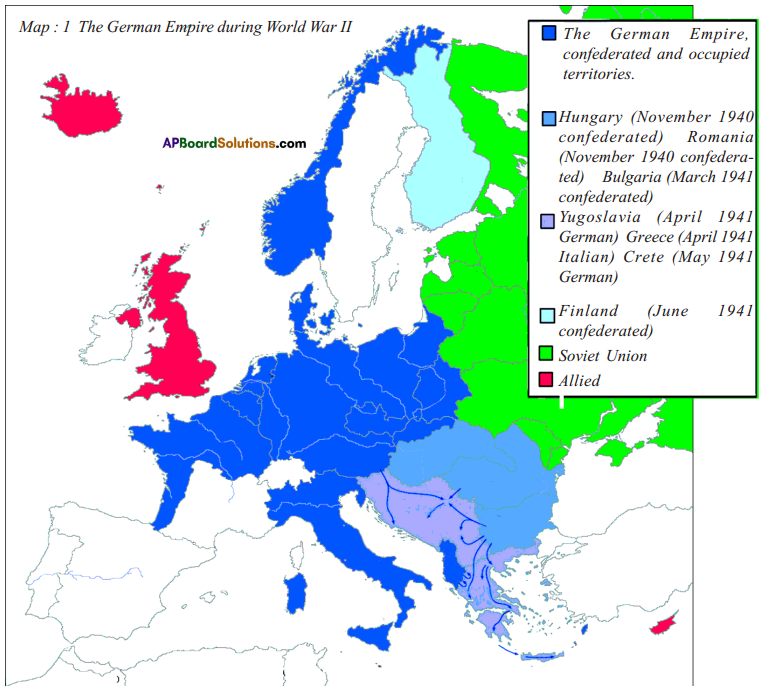 a) Name two countries that did not fall under the German Empire.
a) Name two countries that did not fall under the German Empire. List out the Axis Power group and Central Allies group.
List out the Axis Power group and Central Allies group.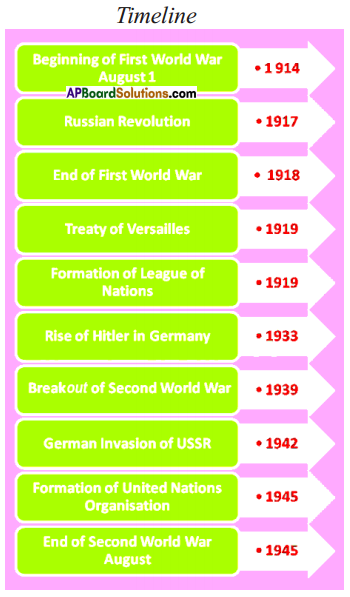 a) What was the immediate cause of World War-ll?
a) What was the immediate cause of World War-ll?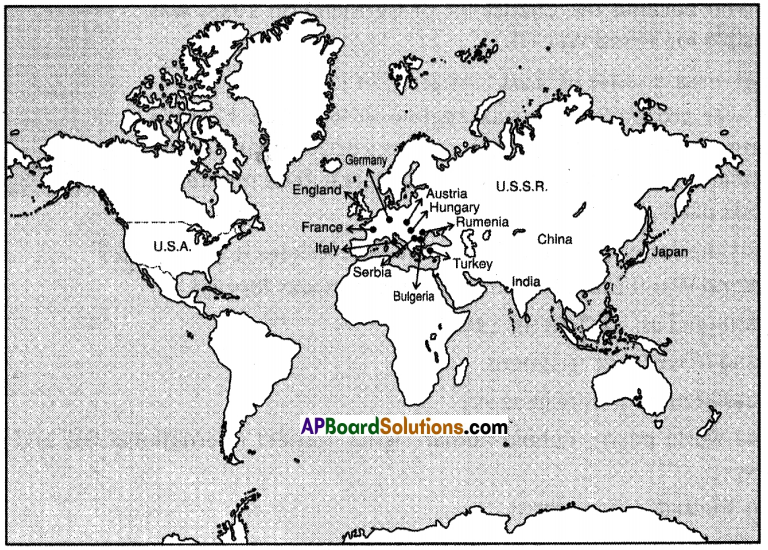
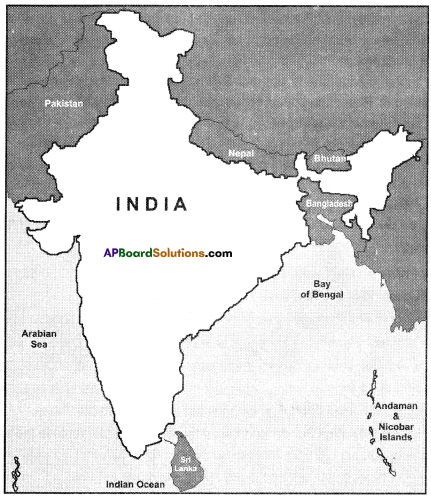 Both Pakistan and Bangladesh are our neighbouring countries.
Both Pakistan and Bangladesh are our neighbouring countries.