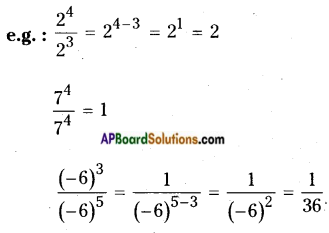
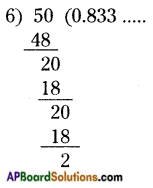Students can go through AP Board 9th Class Maths Notes Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP State Board Syllabus 9th Class Maths Notes Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals
→ A quadrilateral is a simple closed figure bounded by four line segments.
→ The line segments joining any two opposite vertices are called diagonals.
→ The sum of the four interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360° or four right angles.
→ A quadrilateral in which one pair of opposite sides are parallel is called a trapezium.

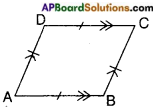
→ A quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel is called a parallelogram.
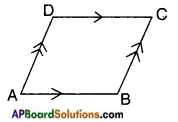
→ A parallelogram in which the adjacent sides are equal is called a rhombus.
![]()
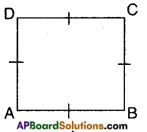
→ A parallelogram in which one angle is right angle is called a rectangle.

→ A parallelogram in which adjacent sides are equal and one angle is right angle is called a square.
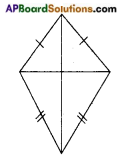
→ A quadrilateral in which the two pairs of adjacent sides are equal is called a ‘kite’.
→ In, a parallelogram
- diagonals bisect each other.
- adjacent/consecutive angles are supplementary.
- opposite angles are equal.
- both pairs of opposite sides are equal.
- diagonal divides the parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
→ In a rhombus, diagonals bisect each other at right angles and the diagonals are unequal.
→ In a square diagonals are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
→ In a rectangle diagonals are equal and bisect each other.
![]()
→ The line segment joining the mid points of two side of a triangle is parallel to third side and also half of it.
→ The line drawn through the mid point of one side of a triangle and parallel to another side will bisect the third side.
→ The intercepts made by the transversal on three or more parallel lines are equal to one another.