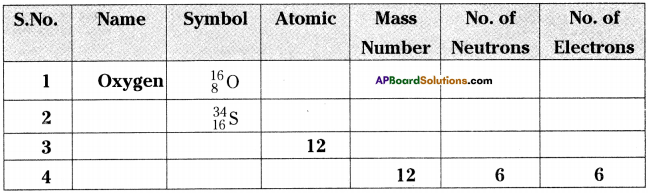
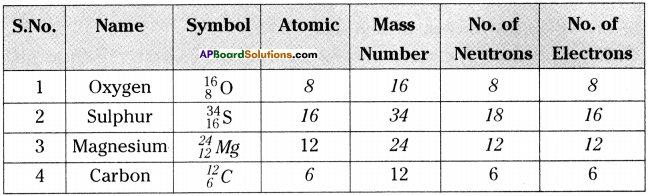
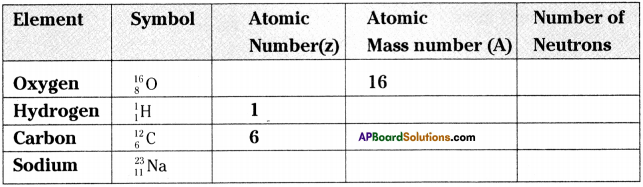
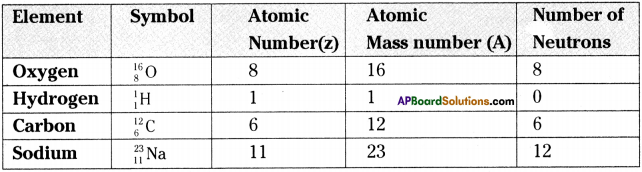
SCERT AP Board 9th Class Social Solutions 24th Lesson Traffic Education Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Solutions 24th Traffic Education
9th Class Social Studies 24th Lesson Traffic Education Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
What documents should a driver carry while driving and what skills are needed to drive safely?
Answer:
The following documents should be carried while driving :
- Driving license
- Registration certificate
- Taxation certificate
- P.U.C. certificate
- Insurance certificate
- Fitness certificate and permit
The following is a basic description of the skills and abilities a driver needs before getting in the driver’s seat. This applies to people of all ages.
Physical skills and abilities :
Driving requires physical strength. It takes a lot of muscle work too.
- Hold the body upright to use and control the steering wheel,
- Maintain sitting balance,
- Control the head, neck, arms and legs, feet and hands.
- To operate a vehicle
Physical and mental stamina and muscle flexibility are needed to :
- sit and drive
- focus constantly on the task of driving.
- twist and turn
- move the head and’ neck side to side, up and down, back and forth.
In addition to these driving requires a clear and alert mind.
![]()
Question 2.
What will happen if someone jumps the traffic signal?
Answer:
Traffic signals help to control traffic. It someone jumps the traffic signal, there is a chance of accident.
Question 3.
Suggest a few steps that are taken in your area for road safety.
Answer:
Road safety is a result of contributing efforts from all the sections the society including both civilians and government officials. In addition to the human sufferings, the estimated costs of the road injuries are a noticeable amount in GNP per annum. So some steps can be fruitful in this direction.
A few important road safety steps :
- Don’t use mobile phone whilst driving.
- Belt up in the back.
- Don’t drink and drive.
- Always adhere to speed limits.
- Take special care about children, senior citizens and pedestrians.
- Don’t drive if tired.
- Pedestrians should walk cautiously.
- Always observe and anticipate other road users.
- Keep your distance and
- Always wear helmets and seat belts.
We follow all these road safety rules in our area.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain mandatory, caution and information traffic signs with examples.
Answer:
1) Mandatory signs :
Mandatory signs are indicated in a circular form. In accordance with the motor vehicle Act 1988, every driver of a motor vehicle shall drive the vehicle in conformity with any indication given by the mandatory signs and not obeying there signs is an offence.
Ex : 1. Stop
2. No Parking
3. Overtaking prohibited
2) Cautionary /Warning signs :
Cautionary signs are meant for cautioning the driver about the hazards lying ahead on the road. Drivers must obey there signs for safety. These signs are indicated in a triangular form
Ex : 1. T -inter section
2. Right hand curve
3. School ahead

3) Information signs:
Informatory signs are erected on the road to provide information on direction, destination, road side facilities etc., to the road users.
Ex : 1. Park this side
2. First aid post
3. Public telephone
![]()
Question 5.
Kamala wants to purchase a new vehicle. Explain her what are the steps to be taken and what documents are to be produced for the registration of a vehicle?
Answer:
The steps to be taken by Kamala in purchasing a car or something else :
- Starting out
- Using incentives and rebates
- Pricing the car
- Finding the exact car you want to buy
- Test driving the car salesman
- If you are trading in your old car
- Negotiating for the best finance options
- Closing the deal
- Reviewing and signing the paper work,
- Inspecting and taking possession of your new car.
Documents to be produced for the registration of a vehicle :
- R.T.O. forms – a) Form 20 b) Form 34
- Pan card , copy of sales certificate
- Address proof
- Insurance cover note
- Person’s authorized signature
- Copy of road worthiness certificate
- Pollution under control certificate
Question 6.
Ramu wants to interchange his vehicle number to other vehicle. Is it correct or not?
Explain, why.
Answer:
No. Ramu cannot interchange his vehicle number to other vehicle.
Reason : Any vehicle registered for its particular registration mark will remain its
identifications and interchange of it is not allowed.
Question 7.
Explain the need of road safety.
Answer:
India loses more than 1,00,000 lives due to road traffic crashes every year. It has a road traffic fatality rate of 16.8 deaths per, 1,00,000 population. Approximately half of all deaths on the country’s roads are among vulnerable road users – motorcyclists, pedestrians and cyclists.
Hence road safety is very important to avoid the accidents and control loss of lives. Road safety ensures that every road user follow traffic rules and thereby avoid traffic jams and deaths due to accidents. For systematic regulation of vehicular traffic, road safety is needed.
![]()
Question 8.
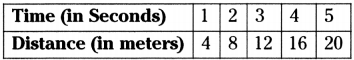
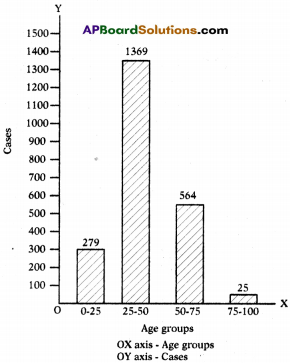
Read the table of page ‘Accident Victims Age’ on page 286, identify the age group for which more number of cases registered and draw a bar graph.
| Age | Cases | Age | Cases |
| 00-05 | 24 | 50-55 | 207 |
| 05-10 | 58 | 55-60 | 138 |
| 10-15 | 40 | 60-65 | 113 |
| 15-20 | 152 | 65-70 | 57 |
| 20-25 | 345 | 70-75 | 49 |
| 25-30 | 380 | 75-80 | 13 |
| 30-35 | 254 | 80-85 | 12 |
| 35-40 | 294 | 85-90 | 0 |
| 40-45 | 226 | 90-95 | 0 |
| 45-50 | 215 | 95-100 | 0 |
Answer:
More number of cases registered age group 35 – 40 years age group.
Question 9.
Read the paras under the title ‘Traffic Chaos’ of page 287 and comment on them.
Traffic Chaos:
You have to go to school on the morning. If you are late, you may miss classes. You are struck in a traffic jam. What will you do?
Students, employees, labourers, teachers, doctors and all are affected by traffic jams. Foot paths (Side walks) are considered a boon for pedestrains. Sometimes motorists drive on these side walks also.
Stray animals, fruit and vegetable seller, private vehicles like cars, autorickshaws are parking at No Parking Zones are the main causes for traffic jams. As there is an increase in population and use of automobiles, there has been a rapid increase in the volume of traffic on roads. To avoid the accidents, one must know the prescribed rules and regulations.
Answer:
Road sense on Indian streets is often completely missing. The Indian traffic conditions are chaotic, the drivers are reckless, and the roads are poor repair conditions.
There is a pecking order for right of way – cows / buffaloes are at the top, trucks and buses are second, and dogs and pedestrians are at the bottom. Two wheelers are pretty low down. Pot holes and speed breaker bends are common and rarely marked. Pedestrians, . animals, bicycles, ox carts and tractors all use the roads.
Question 10.
Collect the data from the traffic police /RTA officials who are nearest to you.
Month : Place :
No. of cases booked :

Analyse the data and discuss in your classroom regarding traffic situations in your area.
Answer:
Month : September Place : Vijayawada
No. of cases booked : 1986

The above data is revealing us the negligence of the vehicle riders and road users. They are to be strictly punished.
9th Class Social Studies 24th Lesson Traffic Education InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why is it compulsory to have a driving license? (Text Book Page No. 288)
Answer:
Yes, it is compulsory to have a driving license. As per Motor Vehicle Act 1988, a valid driving license is necessary to drive any motor vehicle on public roads.
![]()
Question 2.
Observe the given table and answer the questions. (Text Book Page No. 286)
| Age | Cases | Age | Cases |
| 00-05 | 24 | 50-55 | 207 |
| 05-10 | 58 | 55-60 | 138 |
| 10-15 | 40 | 60-65 | 113 |
| 15-20 | 152 | 65-70 | 57 |
| 20-25 | 345 | 70-75 | 49 |
| 25-30 | 380 | 75-80 | 13 |
| 30-35 | 254 | 80-85 | 12 |
| 35-40 | 294 | 85-90 | 0 |
| 40-45 | 226 | 90-95 | 0 |
| 45-50 | 215 | 95-100 | 0 |
1) In which group do you find more cases? Can you say, why.
Answer:
25 – 30. As the people in this age become more independent, they are exposed to risks.
2) How many cases are there in the age group of both 20 – 25 and 25 – 30?
Answer:
345; 380
Question 3.
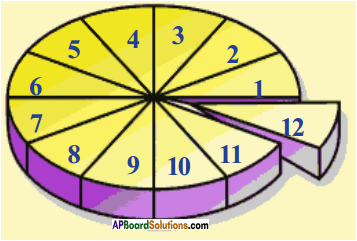
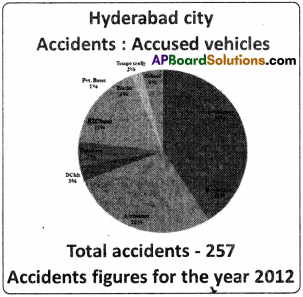
Observe the following pie-chart and answer the following questions. (Text Book Page No. 287)
1) Discuss the data relating to the accidents – accused vehicles in your classroom.
Answer:
Group discussion in classroom
2) Which type of vehicles are accused of more accidents? Can say why?
Answeer:
Two wheelers. Because they are in more number.
3) What are Traffic Rules and regulations? Discuss in your classroom.
Answer:
Traffic rules and regulations of the road are both the laws and the informal rules that may have been developed to facilitate the orderly and timely flow of traffic.
Note : Students should discuss in the classroom.
![]()
Question 4.
With the help of your teacher collect the road surface markings from RTA/Traffic police and discuss the uses of various markings in the classroom. (Text Book Page No. 290)
Answer:
Uses of various markings :
- Road surface markings are used on paved roadways to provide guidance and information to drivers and pedestrians.
- These markings promote road safety.
- These are used to supplement the message of road signs and other devices.
Note : Students should collect road surface markings and discuss in the classroom.