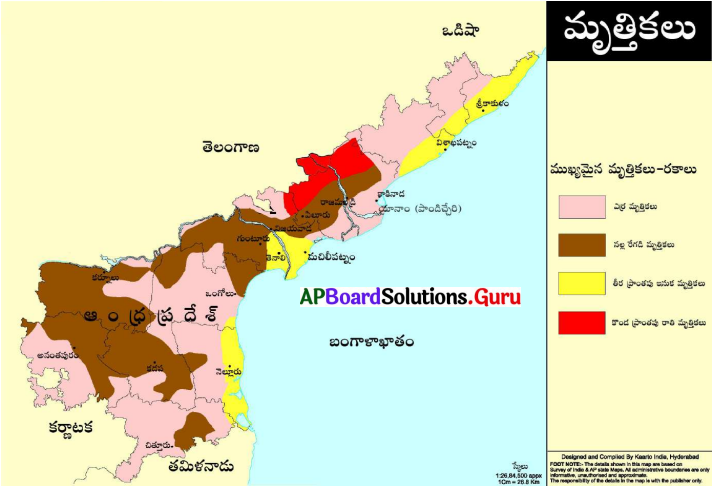
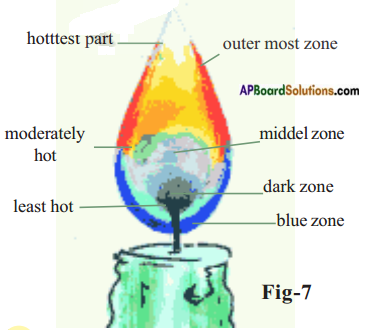
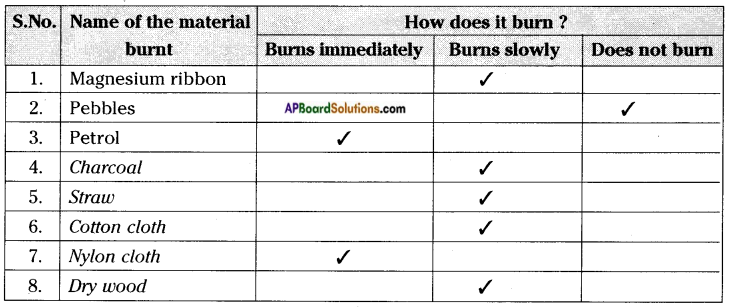
AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Social Studies Important Questions Chapter 21 Performing Arts and Artistes in Modern Times.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Social Studies Important Questions 21st Lesson Performing Arts and Artistes in Modern Times
Question 1.
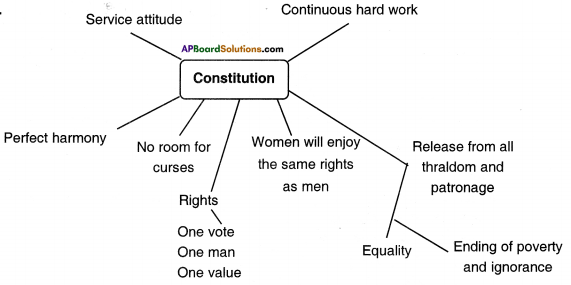
What was the special role of the nattuvanars?
Answer:
The nattuvanars are the dance masters of devadasis. They were usually male children of devadasis. They maintained these traditions from generation to generation. They also trained the new dancers from other castes.
Question 2.
What changes do you see in the position of the artistes and the subject of their performances since the time of the national movement?
Answer:
After the national movement, their condition became worse. Nobody is there to encourage them. As a result the folk artists are facing a decline and crisis of livelihood.
![]()
Question 3.
Is it possible to orient folk arts to new requirements of modern life and revive them?
Answer:
I think it is impossible. Today the life style is very fast. The people who are stuck to the TVs and computers, may not be interested in these arts which are expensive.
Question 4.
Who is Nazar Vali?
Answer:
He was a Burrakatha artist.
Question 5.
Where did Nazar Vali start his profession?
Answer:
He started it with Tenali Balaratna Nataka Samajam.
![]()
Question 6.
Do you think it is important to preserve the folk art traditions when TV and films are becoming the dominant forms of entertainment? Give your reasons
Answer:
I think it is important to preserve it. Our customs and traditions are gifts from our ancestors. Mainly folk arts – These are our traditional entertainment. We should preserve them. They are the soul of nation.
Question 7.
Why do you think the nationalists and communists tried to revive and renew folk arts?
Answer:
Nationalists and communists encouraged these folk arts. They opposed the foreign arts and tried to revive and renew our folk arts.
Question 8.
Do you think institutions like Kalakshetra can help to revive folk arts too?
Answer:
Yes, they can help to revive folk arts too.
But they encourage the rich and the interested people only. They cannot render services to the real hires of the arts. Thus there are mixed results with this type of institutions.
![]()