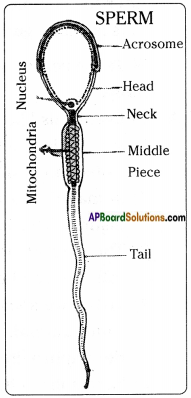
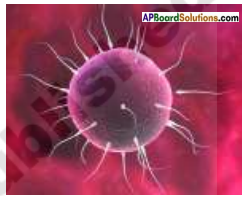
AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Biology Solutions Chapter 11 Why Do We Fall Ill Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Biology Solutions 11th Lesson Why Do We Fall Ill
8th Class Biology 11th Lesson Why Do We Fall Ill Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
A doctor/nurse/health-worker is exposed to more sick people than others in the community. Find out how she/he avoids getting sick herself/himself.
Answer:
- By choosing nutritious food and an active lifestyle, managing stress, using tobacco- free, getting preventive immunizations and screenings and choosing protection measures.
- Maintaining good hygiene:
By washing hands frequently, cleaning their stethoscopes from patient to patient, using gloves. - Recognising the symptoms quicker and knowing what to do can help speedy recovery, easier access to medical care. (E.g.: They can self-prescribe, can ask col¬leagues for help etc.)
![]()
Question 2.
Differentiate the infective and non-infective diseases.
Answer:
- Infectious diseases can be spread from person to person.
Non-infectious diseases can not be spread from person to person. - Infectious diseases are caused by pathogens (microbes) which are disease causing organisms.
The major group of pathogens (microbes) are viruses, bacteria, fungi, single cell organisms like protozoans, multicellular organisms like worms.
Non-infectious diseases are not caused by Pathogens (microbes), but can be caused by physiological malfunctions, environmental or chemical factors, heredity, unknown causes. These are mostly internal, non-infectious causes. - Examples of infectious diseases are Viral, diseases, bacterial etc.
Example for non infectious causes are some cancers caused by genetic abnormali¬ties and high blood pressure caused by excessive weight and lack of exercise.
Question 3.
Why acute disease become chronic disease?
Answer:
- Some diseases last for only very short periods of time and these are called acute diseases.
E.g.: Common Cold lasts only a few days. - Some other diseases or ailments can last for a long time, even as much as a life time and are called chronic diseases.
E.g,: The infection causing elephantiasis, which is very common in some parts of India. - As an example, a cough and cold which all of us have from time to time. Most of us get better and become well within a week or so.
- But if we get infected a chronic disease like tuberculosis of the lungs, it takes over the years to suffer with cough and lose weight and feel tired all the time.
- In other words, we are likely to have prolonged general poor health if we have a chronic disease.
- Chronic diseases therefore have very drastic, longterm effects on people’s health
as compared to acute disease. - One reason might be that, because the person is not well nourished and does not get enough food and it is because of poverty, the acute disease becomes a chronic disease.
Question 4.
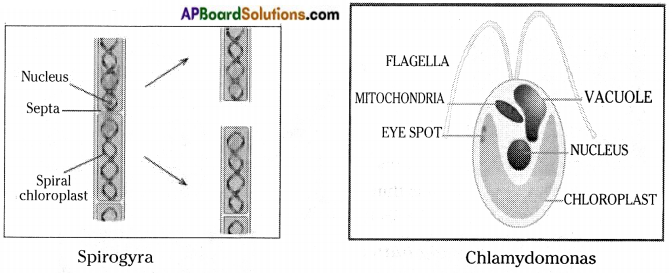
Draw the figure of leishmania and trypanosome.
Answer:

Question 5.
Ramu was effected with small pox. What advice do you give Ramu for not spreading disease?
Answer:
Prevention of Small Pox:
- Isolation of the infected person.
- Surrounding should be kept clean and hygeinic.
- Clothes of the infected person must be washed in hot water and dried in the Sun.
- They should not be used by others.
- Small Pox can be prevented by taking vaccine against it.
- But in 1776 Edward Jenner discovered a vaccine for small pox. Now it is wiped out from our country.
![]()
Question 6.
How do you appreciate for role of vaccine in preventing disease?
Answer:
- Vaccination was discovered by a British doctor called Edward Jenner in the year 1776. Since then, this method has been modified and has become most popular for making people resistant to disease.
- In this process, the disease causing organism are cultured in the laboratory and are collected. They are killed by heat treatment.
- The dead micro-organisms are made into a suspension and injected into humans. The body reacts to these dead micro-organisms as if they are alive and are produces antibodies.
- Next time when the same disease producing micro-organisms enter the body, these antibodies will react and kill them.
- Thus the person is not affected by the disease, even if he is exposed to the disease causing microorganisms. Vaccination also prevents the spread of epidemics.
- At present, vaccines are available for various diseases-Cholera, typhoid, diphtheria, whooping cough, polio, tuberculosis etc. Some of the vaccines if taken once, the immunity persists for life time, while in some cases the immunity will lasts only for limited amount of time.
Question 7.
Prepare a questionnaire to collect the information from your local health worker about spreading of diseases?
Answer:
- What are the causes for a disease?
- Name the organisms that cause diseases.
- Name the diseases caused by virus, bacteria, fungi and protozoans.
- How the infectious agents spread?
- Name the diseases caused by air, water and physical contact.
- What are the symptoms of Typhoid and Jaundice?
- How can we prevent exposure to infectious diseases?
- How do we kill microbes?
- How to get rid of an infection in some one who has the disease?
- What are the treatments for any type of diseases?
- What are the measures taken by Public Health,Programmes to prevent diseases?
- What is immunization? What are antibiotics?
- What is the duty of everyone in the community for the effective prevention of infectious diseases?
![]()
Question 8.
How many times did you fall ill in the last one year? What were the illnesses?
a) Think of one change you could make in your habits in order to avoid any of/ most of the above illnesses.
b) Think of one change you would wish for in your surroundings in order to avoid any of/most of the above illnesses.
Answer:
In the last one year, fall ill for one time with Malaria.
Symptoms:
- It is a communicable disease caused by the Protozoan Plasmodium Falciparum. It is spread by the infected female anopheles mosquito.
- It starts with extreme cold. Patient wants to be covered with heavy blankets. This is followed by fever, as high as 106° F.
- There will be severe head ache and body pains. There will be sweating.
- In children the parasite enter and block the capillaries, supplying blood to the brain. The blood vessels may ruptures child becomes unconscious and may even die.
a) Think of one change you could make in your habits in order to avoid any of/ most of the above illnesses.
Answer:
Preventive measures of malaria:
- To reduce the mosquito population successfully.
- By protecting ourselves from mosquito bites, the spread of malaria can also be prevented.
- Best method is to use mosquito nets while sleeping and by using mosquito proof nets for windows and doors. These nets do not allow mosquitoes to enter the house.
b) Think of one change you would wish for in your surroundings in order to avoid any of/most of the above illnesses.
Answer:
- Preventing water stagnation in water tanks, drainage canals, and discarded vessels lying outside. The stored water tanks should be emptied frequently and filled with fresh water.
- Spraying of insecticides or light oil such as kerosene on stagnant water, especially in drainage water.
- Growing of specific varieties of fishes in stagnant water. They feed on mosquito larvae.
![]()
Question 9.
Conduct a survey in your neighbourhood to find out what the three most common diseases are. Suggest three steps that could be taken by your local authorities to bring down the incidence of these diseases.
Answer:
The most common cause for the spread of diseases in our neighbourhood is by drinking of contaminated water. Polio, Cholera, Typhoid, Jaundice and Amoebiasis and several worms spread through drinking water.
Preventive Measures:
- Drinking water is purified by filtration and chlorination before it is supplied through municipal taps and provide safe drinking water.
- Providing basic sanitation by keeping the surroundings clean.
- Arranging the public health programmes to prevent and control of local diseases by giving immunisation to childhood.
8th Class Biology 11th Lesson Why Do We Fall Ill InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Let us read the wall writings on the panchayat office
Drink boiled water only.
Use mosquito nets.
Keep your surroundings neat and clean.
Do not left water to stagnate.
Eat food when it is hot.
Wash hands before eating food.
Wash hands after toilet.
Use toilets only, not defecate in open.
Keep lids on food vessels.
Wash vegatables before cooking
a) Why local Panchayats display such instructions on the wall?
Answer:
To bring awareness in the local people against diseases.
b) What do we come to know from such instructions?
Answer:
Such infections will spoil the health of people.
c) What would happen if we do not follow the instructions.
Answer:
People who would not follow the instruction may fall sick.
d) In which season do we generally find more mosquitoes? How do they affect us?
Answer:
Generally we find more mosquitoes in rainy season. Mosquitoes cause malaria.
e) What is health ? And when do we fall sick?
Answer:
Health is a state of being well enough to function physically, mentally and socially with optimum efficiency.
When disease causing organisms attack us we fall sick.
![]()
Question 2.
State any two conditions essential for good health.
Answer:
Clean surroundings and fresh air.
Question 3.
State any two conditions essential for being free of disease.
Answer:
Safety food and water and exercise to the body.
Question 4.
Are the answers to the above questions necessarily the same or different? Why?
Answer:
Different.
Question 5.
Do all diseases spread to people coming in contact with a sick person?
Answer:
No, some diseases are infectious and some diseases are non-infectious.
Question 6.
What are the diseases that are not spreading?
Answer:
Non-infectious diseases E.g.: Some cancers, high blood pressure etc.
Question 7.
How would a person develop those diseases that do not spread by contact with a sick person?
Answer:
Non-infectious diseases are some times caused by genetic abnormalities, excessive weight or lack of exercise.
Question 8.
List any three reasons why you would think that you are sick and ought to see a doctor. If only one of these symptoms were present, would you still go to the doctor? Why or why not?
Answer:
Because of not feeling well, unable to do daily work and when feeling uneasy thinking that we are sick we want to see the doctor. If the situation is unbearable then we would like to see the doctor.
![]()
Question 9.
In which of the following case do you think the long-term effects on your health are likely to be most unpleasant?
Answer:
- If in the case of Jaundice, the suffering will be more and it will be cured only by taking medicines. Prescribed by a doctor.
- Because this is the disease for liver, the normal functioning of the liver will be stopped, and feels unpleasant.
8th Class Biology 11th Lesson Why Do We Fall Ill Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
a) Find out what provisions are made by your local authority (Panchayat/ Municipal Corporation) for the supply of clean drinking water.
Answer:
The Panchayat/Municipal Corporation should filter the water and chlorinated before sending through pipes.
b) Are all the people in your locality able to access this?
Answer:
Yes, all the people can access this. The people are avail of this.
Activity – 2
Question 2.
a) Find out how your local authority manages the solid waste generated in your neighbourhood.
Answer:
The solid waste generated in the neighbourhood is collected and disposed.
b) Are these measures adequate?
Answer:
Yes. But still more they can take measures.
c) If not what improvement would you suggest?
Answer:
The authority can announce the public to reduce the waste in the household.
Suitable arrangements will be arranged for the garbage disposal, to prevent accumulation of waste in and around residential areas. This attracts the houseflies and other microbes to spread diseases.
d) What could your family do to reduce the amount of solid waste generated during a day/week from your house?
Answer:
The peels of fruits and vegetables and other waste materials which decay and turns good manure can deposit in the compost pit.
![]()
Activity – 3
Question 3.
Survey your neighbourhood to find out:
a) How many people did suffer from acute diseases during the last three months?
Answer:
More people suffered from acute diseases.
b) How many people did develop chronic diseases during this same period?
Answer:
Very few people develop chronic diseases.
c) And finally, what is the total number of people suffering from chronic diseases in your neighbourhood?
Answer:
One or two.
d) Are these answers to questions (I) and (2) different?
Answer:
Same.
e) Are these answers to questions (2) and (3) different?
Answer:
Same.
f) What do you think could be the reason for these differences? What do you think would be the effect of these differences on the general health of the population?
Answer:
In general people get acute diseases seasonally but chronic diseases are drastic, long term effect because of their poor health.
Activity – 4
![]()
Question 4.
a) Find out how many of in your class had cold/cough/fever recently.
Answer:
One or two or few students.
b) How long did the illness last?
Answer:
The illness lasts for one week.
c) How many of you took antibiotics?
Answer:
Half of the students took antibiotics.
d) How long did they suffer who took antibiotics pills?
Answer:
Seven days.
e) How long did they suffer who did not take antibiotics pills?
Answer:
Seven days.
f) Is there any difference between these two groups?
Answer:
No difference is seen between these two groups.
g) If yes, why ? If not, why not?
Answer:
Because antibiotics do not work against viral infections.
Activity – 5
![]()
Question 5.
Conduct a survey in your locality. Talk to ten families who are well-off and ten who are very poor. Both sets of families should have children who are below five years of age. Measure the heights of these children. Draw a graph of the height of each child against its age for both sets of families.
Families who are well – off
| Name of the child | Age | Heights |
| 1) C. Vivek | 5 | 105 cm |
| 2) B. Ramu | 4 | 99 cm |
| 3) B. Gopi | 4 | 100 cm |
| 4) R. Rahul | 3 | 91 cm |
| 5) B. Somu | 2 | 86 cm |
Families of very poor
| Name of the child | Age | Heights |
| 1) A. Kotaiah | 5 | 100 cm |
| 2) P. Ankalu | 4 | 94 cm |
| 3) B. Srinu | 4 | 92 cm |
| 4) C. Samuel | 3 | 86 cm |
| 5) P. Gopi | 2 | 80 cm |
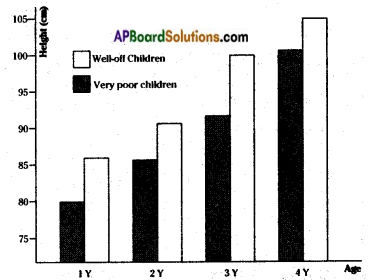
a) Is there any difference between the groups? If yes, Why?
Answer:
Yes, there is a difference between the groups. The children who are sufficient nourishment have good health. Their growth is healthy.
b) If there is no difference, do you think that your findings mean that being well-off or poor does not matter tor health?
Answer:
The functioning of the immune system, like any other system in the body, will not be good if proper and sufficient nourishment and food is not available.
So the availability of proper and sufficient food helps us to be healthy.
Activity – 6
Question 6.
Rabies virus is spread by the bite of infected dogs and other animals. There are anti-rabies vaccines for both humans and animals.
a) Find out the plan of your local authority for the control of rabies in your neighbourhood.
Answer:
Control of Rabies:
- Parental rabies vaccination of owned dogs.
- Sterlization of pet dogs.
- Unwanted dogs should not be abondoned.
- Animal birth control attempt should be made to sterilize the stray dog population or other methods of birth control should be investigated.
- Suitable infrastructure for garbage disposal, to prevent the accumulation of waste in and around residential areas.
![]()
This attracts stray and ownerless dog packs to these areas.
Vaccination:
Sufficient and affordable cell culture vaccine should be available for post exposure treatment.
Mass oral vaccination of the stray dog population.
b) Why we are normally advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick?
Answer:
When we fall sick our normal body functions will be affected the digestion will be slow, so it is advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick.
c) What are the different means by which infectious diseases are spread?
Answer:
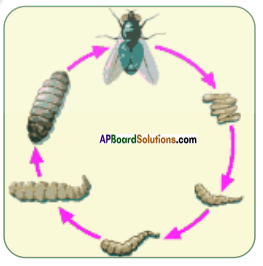
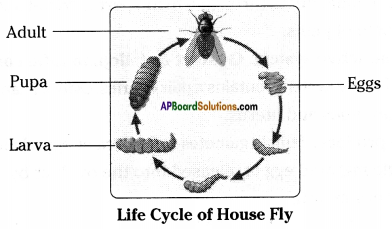
The infectious diseases are spread through contaminated air, water, food and vectors like mosquitoes, flies, cockroaches, snails and even lice.
d) What precautions can you take in your school to reduce the incidence of infec-tious diseases?
Answer:
- Encouraging sick students and staff to stay at home and seek medical attention for several illnesses.
- Facilitating hand hygiene by supplying soap and paper towels and teaching good hand hygiene practicles.
- Cleaning of class room materials and surfaces.
- Daily announcements about preventing infectious diseases.
- Encouraging students and staff to get annual influenza vaccination.
e) What is immunization?
Answer:
The creation of immunity against a particular disease, by vaccination of an organism for the purpose of making it immune to a particular pathogen (disease causing organ¬ism) is called immunisation.
f) What are the immunization programmes available at the nearest health centre in your locality?
Answer:
More children are being protected against vaccine preventable diseases, such as tuberculosis tetanus, pertusis (Whooping cough), diphtheria, polio, measles and now hepatitis – A, B then ever before.
The public health programme of childhood immunisation for preventing infectious diseases.
g) Which of these diseases are the major health problems in your area?
Answer:
Measles and jaundice.