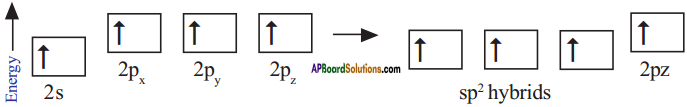
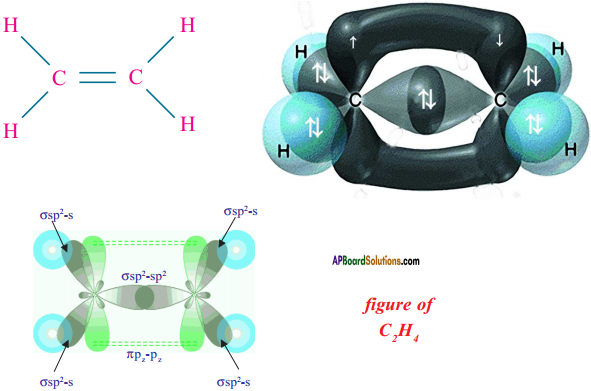
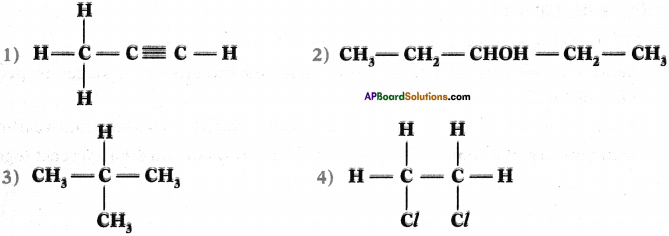
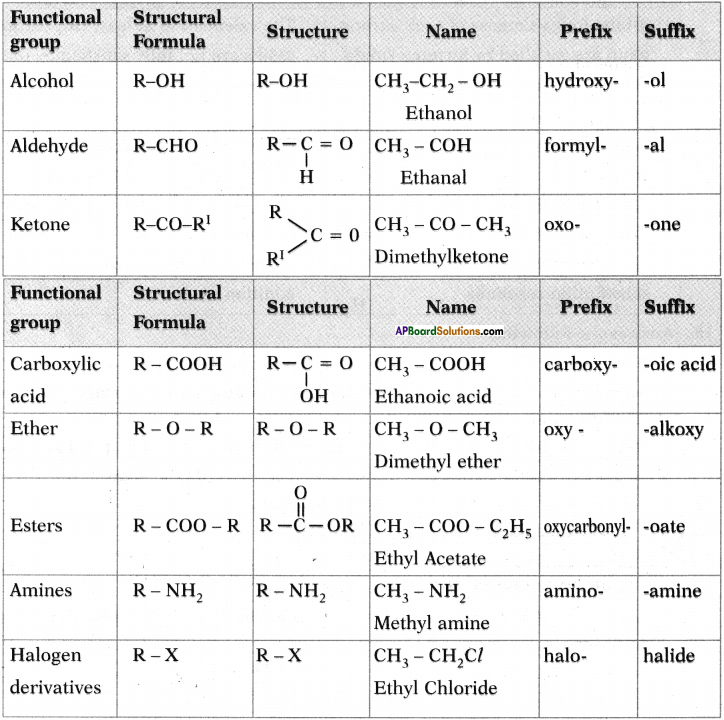
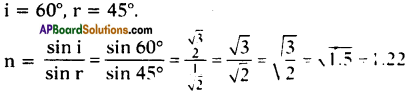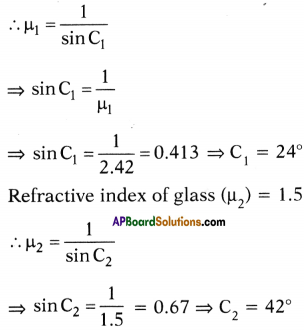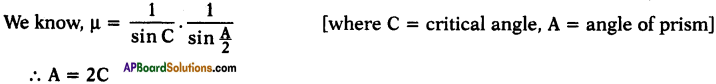AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 2A The Dear Departed Part 1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
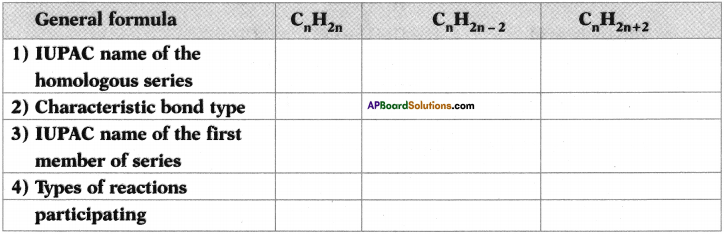
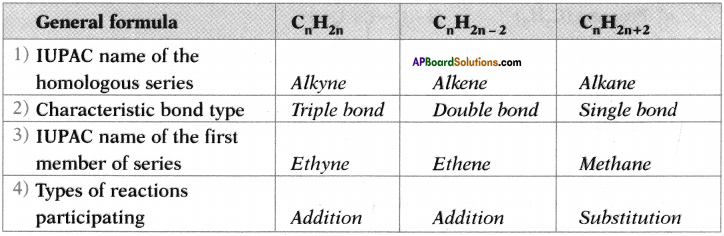
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class English Solutions Chapter 2A The Dear Departed Part 1
10th Class English Chapter 2A The Dear Departed Part 1 Textbook Questions and Answers
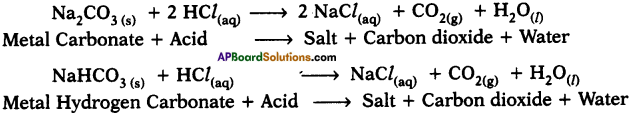
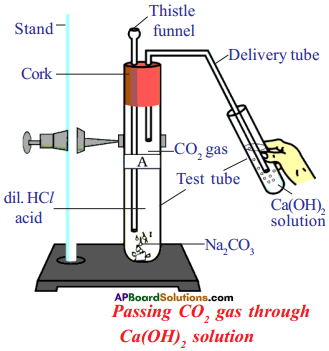
Look at the pictures and answer the questions.

Question 1.
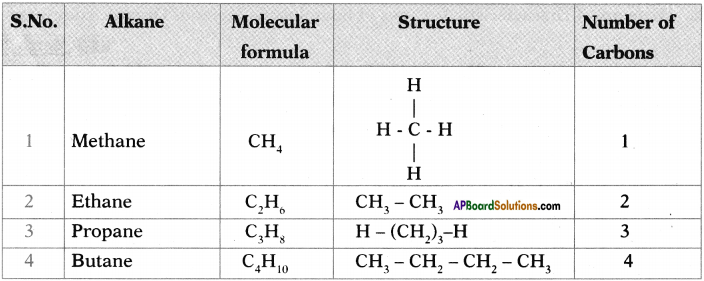
What do you understand from the picture?
Answer:
The rat is pointing a pistol at the cat and intimidating him. I understand that it is a funny picture. One can easily open one’s lips without knowing to smile on seeing this unusual picture.
![]()
Question 2.
Can you recall anything comic associated with these animals?
Answer:
The most popular comic Tom and Jerry’ is associated with them.
‘Tom and Jerry’ is a series of animated cartoon films. We find humour with the rivalry between a cat (Tom) and a mouse (Jerry), Tom’s chasing Jerry and slapstick scenes. “Tom’s making numerous attempts to capture Jerry which leads to destruction” – it creates fun. The scenes such as slicing Tom in half, shutting his head in a window or a door, stuffing Tom’s tail in a mangle, kicking him into a refrigerator, plugging his tail into an electric socket, sticking matches into his feet and lighting them, etc. amuse all the viewers.
(Or)
Yes. I can recall an incident which happened a long time ago in my old house. We used to see many mice in our old house because we stored paddy bags in the house. One day our pet cat jumped on a little mouse which was eating the paddy grains. The little mouse began running. Our cat ran after it. The funny thing was that the mouse did not run away from the place. It began running around the paddy bags. After some time both the cat and the mouse stopped running as they were tired much. At that stage 1 interfered and drove the cat away to save the life of the rat.
Question 3.
Can you imagine, what may be the conversation between the rat and the cat?
Answer:
Conversation between the rat and the cat:
Rat : Hands up!
Cat : Don’t shoot me. I will not eat you.
Rat : No, I don’t believe you. You are cruel.
Cat : Believe me. I decided not to eat rats.
Rat : I don’t believe you. You ran after me yesterday, didn’t you?
Cat : Yes. But not to kill you.
Rat : Then, why?
Cat : I just wanted to tell that I would not kill you thereafter.
Well, how did you get the pistol?
Rat : I stole it from the owner of the house last night.
Cat : Ok. Do you know how to shoot with it?
Rat : I will not tell you.
Cat : Ok. Bye.
Rat : Bye.
![]()
Comprehension
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What qualities of Mrs. Slater have you noticed?
Answer:
Mrs. Slater is unscrupulous, greedy, deceitful, dishonest, selfish, impolite and insensitive. She unfairly claims her father s things. This shows her unscrupulous and dishonest manner. She has shifted her father’s bureau and clock from his room before her sister’s arrival. Hence 1 can say Mrs. Slater is greedy. She wants to deceive her sister by pinching their father’s things. 1 can say that she is impolite and insensitive as she doesn’t even wait for her father s funeral and has started dividing things between them (the two sisters).
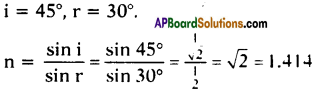
Question 2.
Why does Mrs. Slater decide to shift the bureau from her father’s room before the arrival of the Jordans? How does Henry react to the suggestion?
Answer:
Mrs. Slater wants to own her father’s bureau as he likes it very much. After her father’s death, she decides to shift the bureau to sitting room before the arrival of the Jordans. She thinks that her sister will lay a claim to it. At first, Henry is shocked at her decision. He feels that the two sisters should amicably divide their father’s things. Henry suggests her that it is not a good thing pinching her father’s things in an unfair way. Moreover, Henry is worried about the arrival of the Jordans while they are shifting the bureau.
Question 3.
Why do the Jordans take a long time to get to the house of the Slaters? What does it show about the two sisters’ attitude towards each other?
Answer:
I think the Jordans are late as they have bought mourning dresses to wear before they come to Slater’s house. They are not sorrowful at their father’s death but they are worried about their appearances and how they can come out to each other. In their relationship, we don’t find any kind of emotions and sisterly love.
Question 4.
Ben appreciates his father-in-law saying, ‘It’s a good thing he did’. Later, he calls him a ‘drunken old beggar’. Why does he change his opinion about his father-in-law?
Answer:
Ben appreciates his father-in-law saying it’s a good thing he did’ when he comes to know from Mrs. Slater that the old man has gone out to pay his insurance premium on the day of his death. Later, he comes to know that he has not paid the premium and therefore calls him a drunken old beggar’. Ben has changed his opinion about his father-in-law when be realises that he hasn’t paid premium because, now after his death, they can t claim the insurance company.
Question 5.
What made Mr.Henry feel shocked to hear Victoria say ‘Are you planning to pinch it ?’?
Answer:
When Victoria asked Slaters “Are you planning to pinch it ?”, Mr. Henry felt shocked. He thought that Victoria was innocent. But when she asked him the above question, Mr. Henry came to know that Victoria had wisdom beyond her age. He actually didn’t expect that question from his little daughter.He came to know that she was a precocious girl and had the ability to distinguish between good and bad.
![]()
The Dear Departed Part 1 Summary in English
The one-act play “The Dear Departed” by William Stanley Houghton is a satirical play that explores family relationships and the falsehood and hypocrisy and greed that often lie beneath it. The story exposes the sad fact that human beings often become dehumanized in the face of greed and minor material gains. This play satirizes the degradation of moral values in respect and care within the members of the family itself. This story clearly reveals how elderly people are mistreated. Stanley Houghton uses various literary devices to criticize basic human characteristics in his play. He uses irony, sarcasm, humour and a twist in the plot to criticize human traits. He tries to bring out the qualities of the two daughters called Mrs. Slater and Mrs. Jordan towards their father. He tries to show how the sisters are interested in the property of their father rather than to show true care and affection towards their father.
The story begins with Mrs. Slater telling her daughter, Victoria to change her dress before the arrival of her sister (Slater’s sister) Elizabeth and Elizabeth’s husband, Ben. Mrs. Slater’s husband, Henry has sent them a telegram with the message of the death of his father-in-law and Elizabeth and Ben are coming to talk over the old man’s affairs. Henry wonders if they would come at all because Elizabeth has said that she would never set foot in their house again. But Mrs. Slater says that her sister will come fast enough after her share of what their father has left. Mrs. Slater asks her husband to wear the new slippers of her father. She also suggests that they should replace their shabby old chest of drawers with the valuable bureau of her father which is in his bedroom. He agrees to do it after some hesitation. Mrs. Slater wants to do it before their arrival.
Mrs. Slater fastens the door and she and her husband carry the old chest of drawers upstairs. Henry is shocked when Victoria asks him if they are pinching grandpa’s bureau. He replies that grandpa has given it to her mother before his death. Mrs. Slater carries a handsome clock and puts it on the mantelpiece. Mrs. Slater and her husband carry the pretty old-fashioned bureau downstairs and put it in the place of the chest of drawers. At the same time Victoria ushers in Mrs. Jordan and Ben. Mrs. Jordan goes straight to Mrs. Slater and kisses her and the men shake hands. Mrs. Jordan remarks that their father has gone at last. Mrs. Slater replies that he is seventy-two a fortnight the previous Sunday. She tells them that the old man has been merry that morning and has gone out to pay his insurance. Ben and Mrs. Jordan remark that it is a good thing on his part.
According to Mrs. Slater, their father is found dead when she takes up a bit of something for him on tray.
Ben and Mrs. Jordan don’t want to look at the old man ; they prefer to have tea and so Mrs. Slater gets tea ready. They think of publishing the announcement of the death of the old man in the papers. Then they decide to look through the old man’s things and make a list of them. Mrs. Jordan tells that the old man has promised his gold watch to their Jimmy. Then Victoria tells them that grandpa hasn’t paid his insurance. Ben calls him “the drunken old beggar”. Both the sisters complain that they have to put up with their father for all those years. Then Mrs. Slater asks Victoria to go and bring the bunch of keys from grandpa’s room. Victoria is afraid to go but she does. After some time, she gets back very scared and tells them that grandpa is getting up. They are transfixed with amazement. The vigorous and well coloured old man Abel Merry weather comes in.
![]()
The Dear Departed Part 1 Glossary
lay (v): (here) to put the cloth, plates, knives, forks etc. on a table, ready for a meal
vigorous (adj): using a lot of energy and strength or determination
plump (adj): slightly fat in a fairly pleasant way
vulgar adj): rude and offensive
get her own way (idiom): persuade other people to allow you to do what you want
D’ye: Do you (used in awkward situations)
amazed (adj): very surprised
ages (n): long time
stooping (adj): bent towards and down
drooping (adj): hanging or bending down
come after (phr.v.): to look for someone to get something from them
worn out (adj): too old or damaged to be used
break down (phr.v.): stop working in a successful way
trifle (n): something unimportant or not valuable
precocious (adj): Intelligent/gifted/talented
bureau (n): a writing desk with drawers
drive a liard bargain (idiom): work hard to negotiate agreements in on&s own favour
startled (v): made someone suddenly surprised or slightly shocked
stupefied (adj): so surprised, tired or bored thai one cant think clearly
daft (adj): stupid/silly
shabby (adj): untidy and bad
fasten (v): to firmly close a window, door etc. so that it will not open
pinch (w): steal
mantelpiece (n): a shelf projecting from the wail over the fireplace
usher (v): lead/show the way/welcome
appeal: be attractive
stagger (v): to walk or move unsteadily, almost falling over
complacent (adj): sell-satisfied/unconcerned
mourning (n): feeling of sadness to miss someone after they have died
fortnight (n): two weeks
chirpily (adv): cheerfully and actively
snug (adj): warm and comfortable
wipe (v): to rub a surface with something in order to remove liquid, dirt, etc.
look through (phr.v.): look for something
overdue (adj): not paid by the expected time
annoy (v): to make someone feel slightly angry and unhappy about something
put up with (phr.v.): to accept an unpleasant situation or person without complaining
swindling (v): cheating somebody for property or money
reluctantly (adv): unwillingly

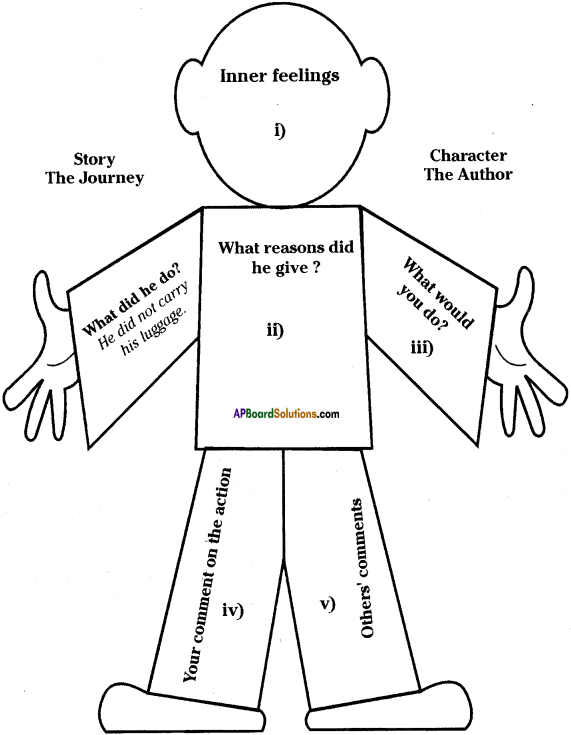

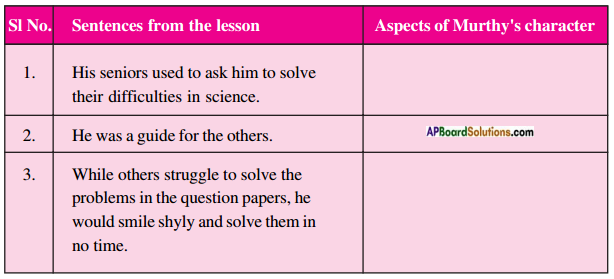
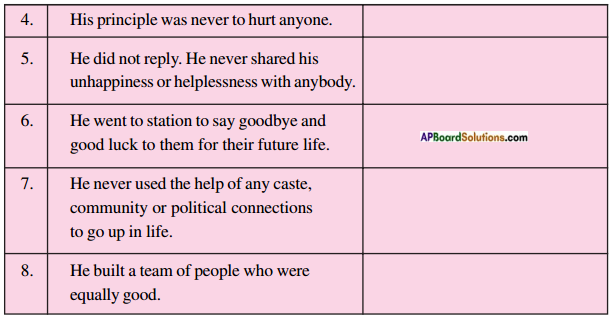
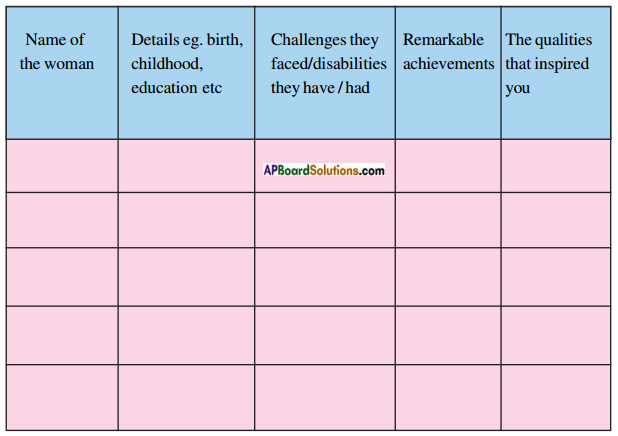

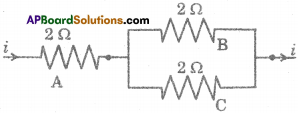

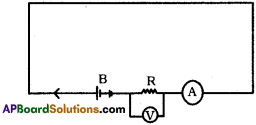

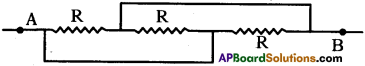
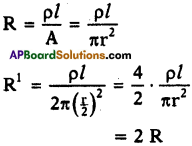
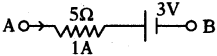

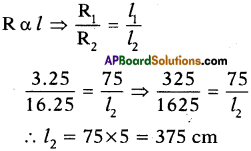
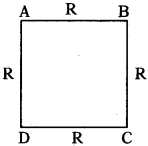
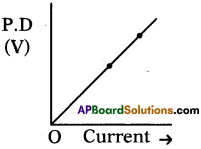
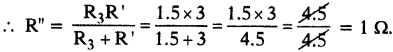
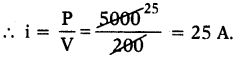
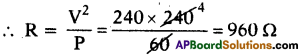

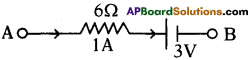
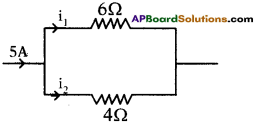
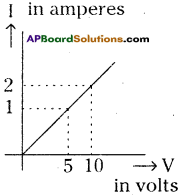

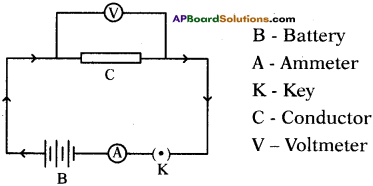
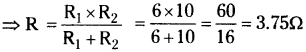

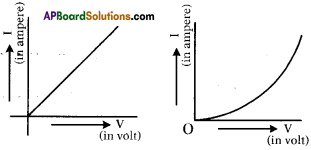
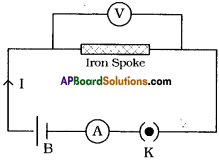
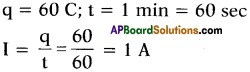


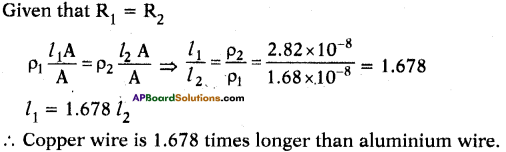
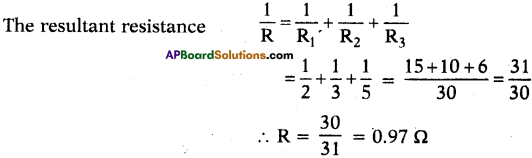
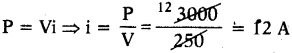
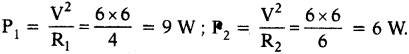
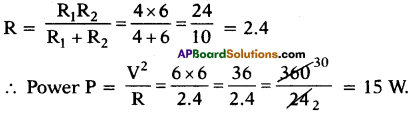
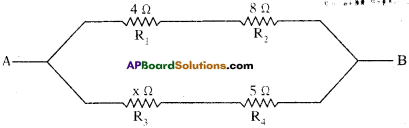
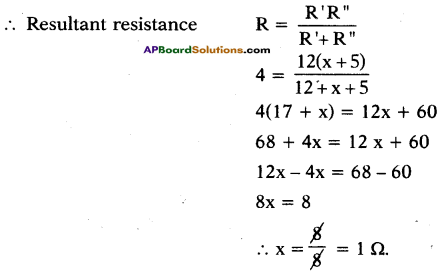

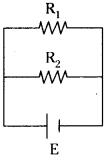
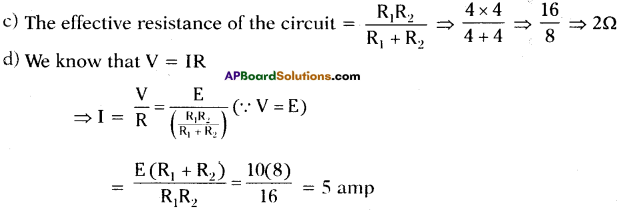
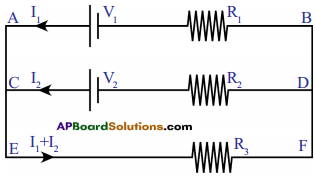
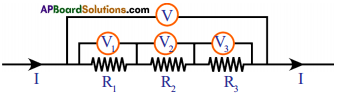
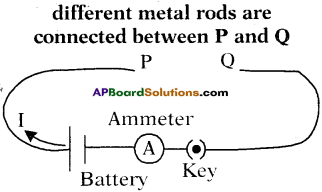


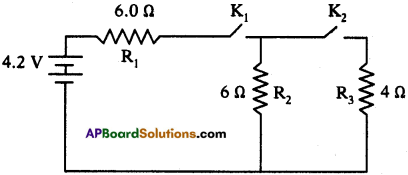
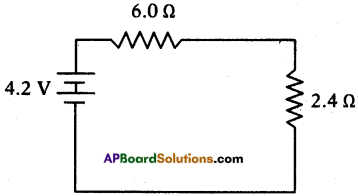
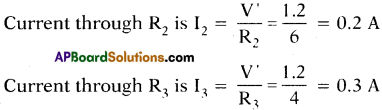
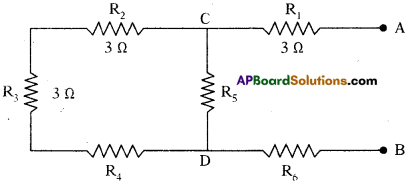
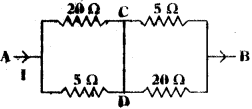
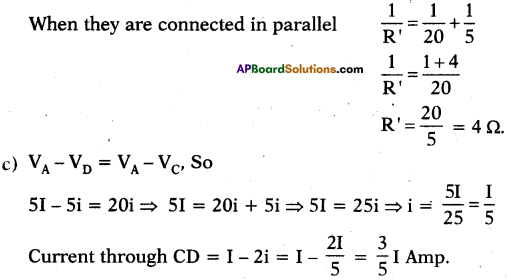
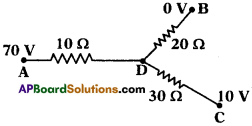
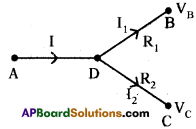


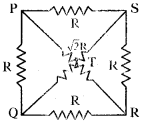
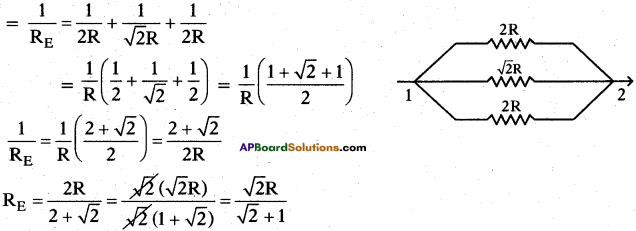
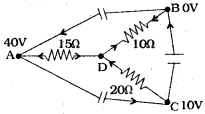
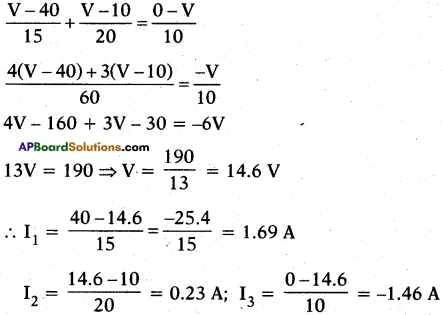
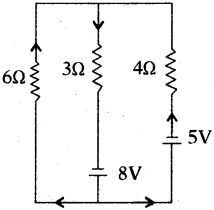
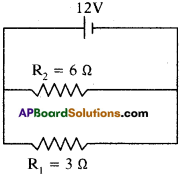
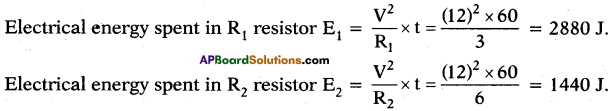
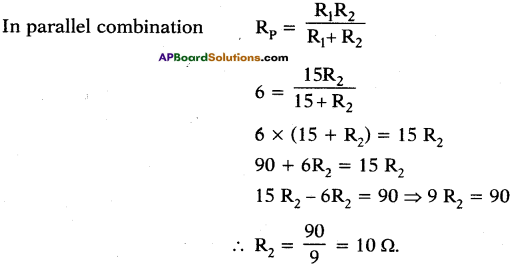

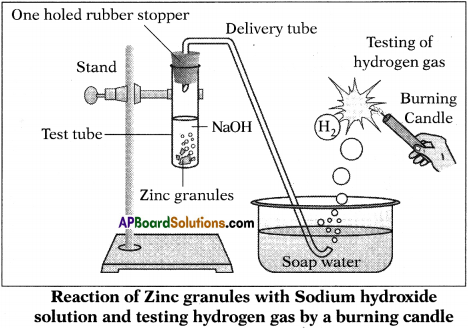

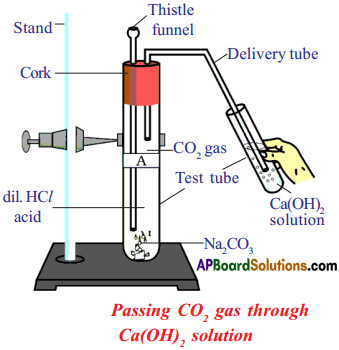
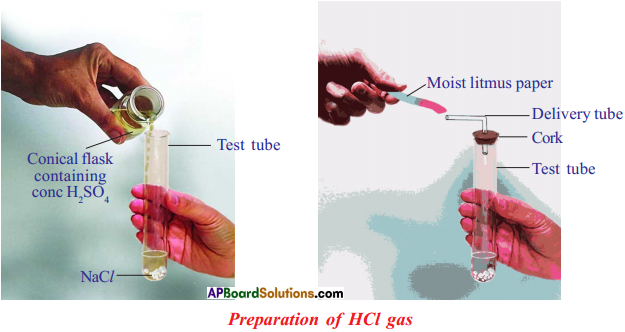
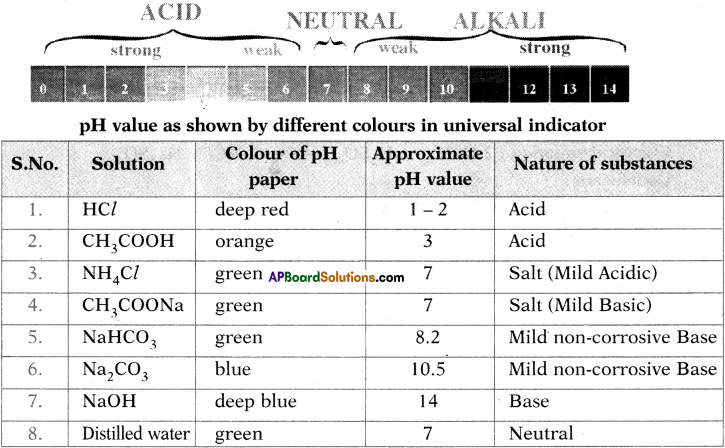



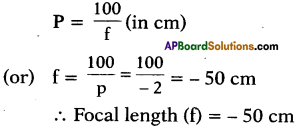


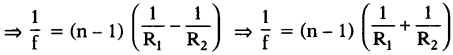
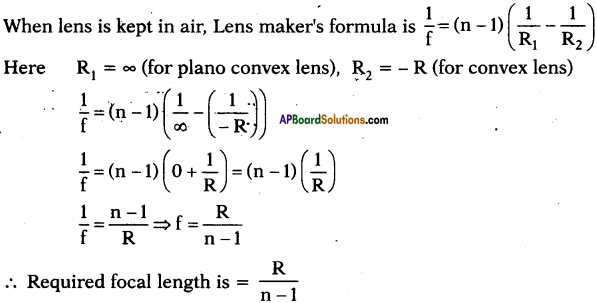
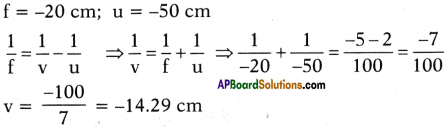
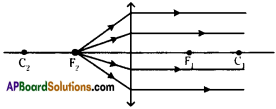
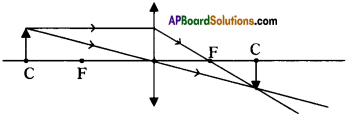
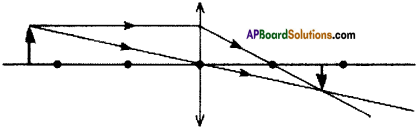
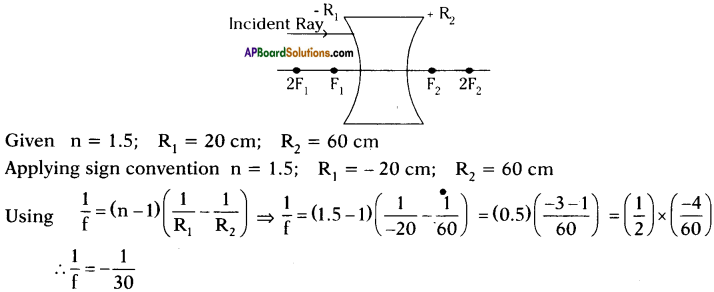



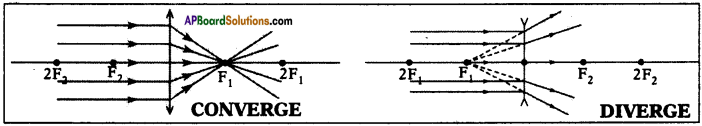
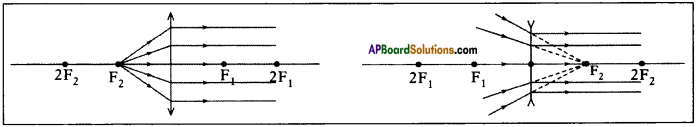
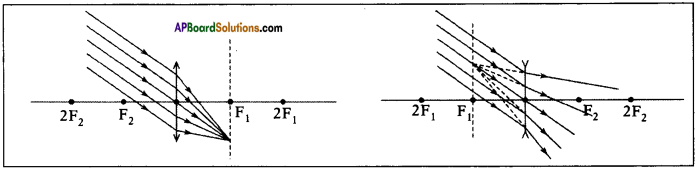
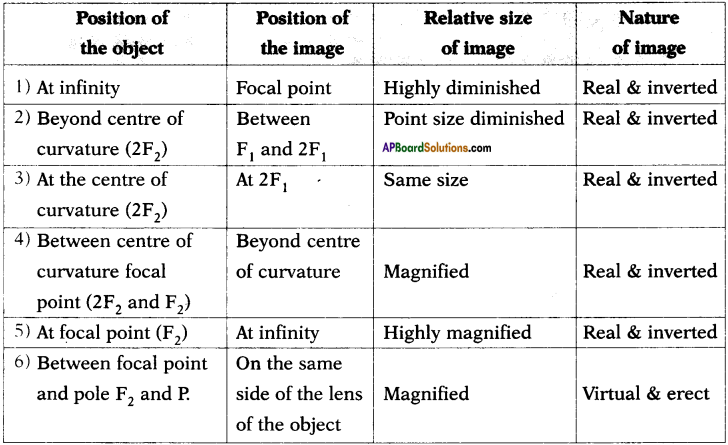


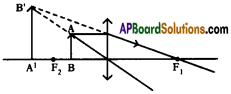

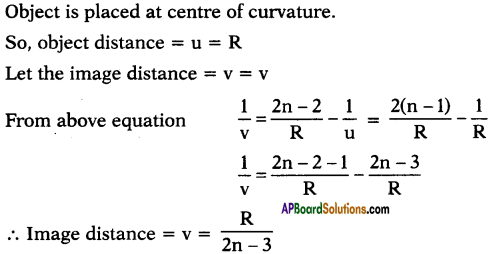


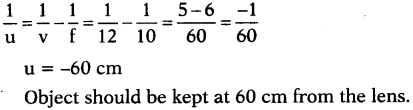
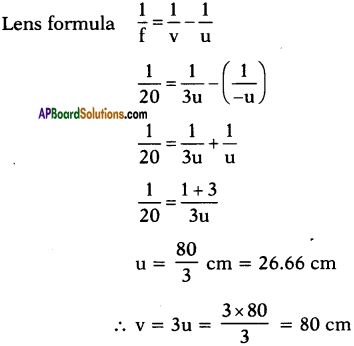








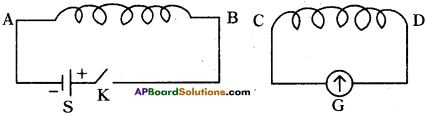
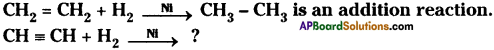
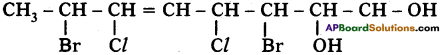
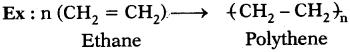


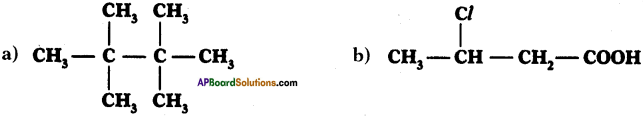
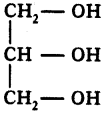
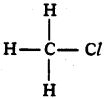
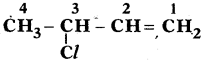
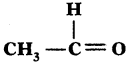
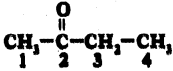
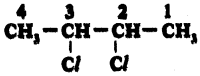
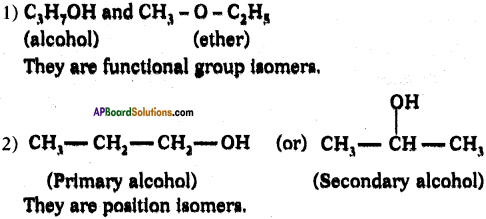






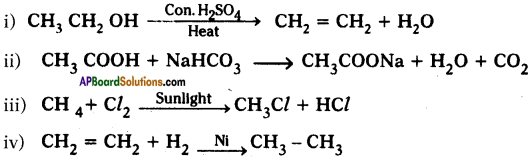
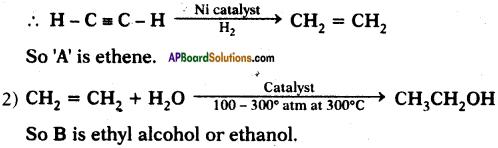

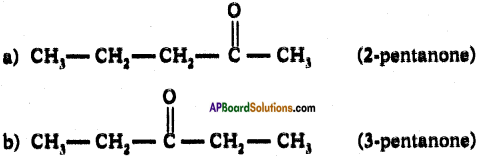

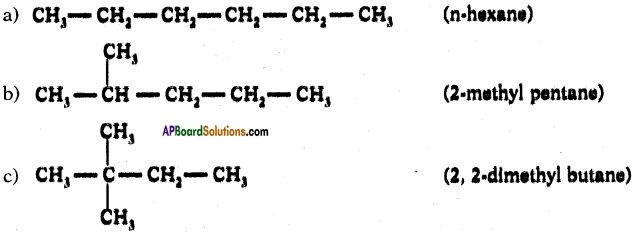
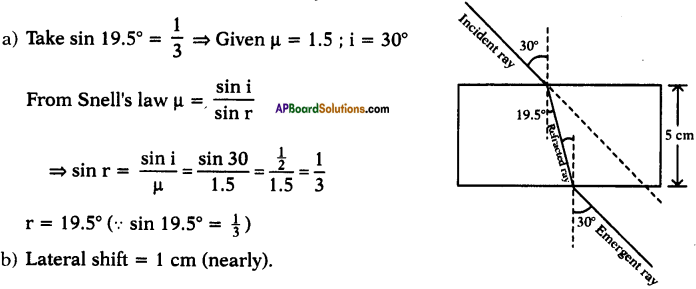
 (AP June 2017)
(AP June 2017)