SCERT AP Board 10th Class Social Solutions 17th Lesson The Making of Independent India’s Constitution Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Social Studies Solutions 17th Lesson The Making of Independent India’s Constitution
10th Class Social Studies 17th Lesson The Making of Independent India’s Constitution Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve your learning
Question 1.
Find the odd one out.
a) Indian Constitution adopts from experiences of freedom struggle.
b) Indian Constitution adopts from already existing Constitutions.
c) Indian Constitution has remained the same since its drafting.
d) Indian Constitution provides principles and provisions for ruling the country.
Answer:
The odd one is ‘c’. It is: Indian Constitution has remained the same since its drafting.
![]()
Question 2.
Correct the false statements:
a) There was unanimity of opinion on all provisions during CA debates.
b) The makers of Constitution represented only certain regions of the country.
c) Constitution provides certain provisions to amend articles in it.
d) Supreme Court of India has said that basic features of Constitution may also be amended.
Answer:
a) There was no unanimity of opinion on all provisions during CA debates.
b) The makers of Constitution represented all the regions of the country.
c) Constitution provides certain provisions to amend articles in it.
d) The Supreme Court of India has said that basic features of Constitution cannot be amended.
Question 3.
Describe the unitary and federal principles of Indian government as discussed in the CA debates.
(OR)
Distinguish between federal and unitary systems. June 2017)
Answer:
Our Constitution reaffirms that India is a unitary and a federal state. The following principles represent the unitary and federal characters.
Unitary Principles :
- Single citizenship,
- The supremacy of the Constitution,
- Residual powers to central governments,
- Single Judiciary,
- Uniformity of fundamental rights,
- Provision for All India Services.
Federal Principles :
- Dual Polity,
- Sovereign Powers to States,
- State Services.
![]()
Question 4.
How does the Constitution reflect the political events of the time? Draw from previous chapters on the freedom struggle.
Answer:
- Indian Constitution adopts from the experience of the freedom struggle.
- It reflects the political events of time.
- It provides for equality, liberty, justice and fraternity.
- It promises adult universal franchise, fundamental rights which were most sought after during freedom struggle.
- It grants single citizenship and independent judiciary to protect the integrity of the country and the rights and liberties of people.
- A reference to the history of British rule and Indian independence struggle provides basic idea of self-governance that emerged into a people’s participative democracy.
- The representatives of princely states declared the First Round table conference that they would join an ‘All India Federation with a Self-Governing British India’. This prefered creation of All India Federation.
Question 5.
What differences would it have made to the making of our Constitution if the Assembly had been elected through universal adult franchise?
Answer:
- It would not have made any difference to the making of our Constitution even if the assembly had been elected through Universal Adult Franchise.
- At that time nearly 86% of the population is illiterate.
- Most of the population was under the poverty line.
- Nothing substantial benefit would have made.
- The Draft Committee chairman himself was one of the greatest intellectuals of all the time in the world.
- So, a better Constitution was already made.
(OR)
- It would be more democratic if the constituent assembly had been elected through universal adult franchise.
- If the assembly members had been elected through universal adult franchise intellectuals would not be elected and better constitution was also not prepared.
![]()
Question 6.
Write a short note on basic principles of Indian Constitution.
Answer:
The Indian Constitution has 8 basic principles.
Sovereignty:
- India is a Sovereign Democratic Republic.
- The Indian people has sovereign (or) supreme power.
Fundamental Rights:
Indian Constitution provide basic fundamental rights to all citizens without discrimination.
Directive Principles:
These are guidelines to frame laws. These are not enforceable by the courts.
Cabinet Government (or) Parliamentary Type of Government:
A Council of Ministers with the Prime Minister as the head to aid and advise the President who shall, in the exercise of his functions, act in accordance with such advice.
Secularism:
Secularism is the basic structure of Indian Constitution. The government respects all religions. It does not uplift or degrade any particular religion.
Socialism:
The world Socialism was added to the preamble by the 42nd amendment- It implies social and economic equality.
Fedaralism:
The Constitution provides a federal structure. The powers are specifically divided between central and state government.
Independent judiciary:
India has an independent and integrated judiciary.
![]()
Question 7.
How has the Constitution defined and changed political institutions in the country?
Answer:
- The Constitution has defined and changed political institutions in the country.
- It provided federal system with union and state government of sovereign power.
- It made the Constitution as the supreme law of land.
- It paves way for strong centre during an emergency.
- It supports multiparty democracy with elections in definite intervals.
- It provided universal Adult Franchise.
- It set up Election Commission for smooth conduct of free and fair elections.
- It adopts single citizenship.
- It provides fundamental rights.
- It adopts directive principles of state policy and fundamental duties.
Conclusion: It defines India as a sovereign, democratic, socialist and secular republic. It has provisions for bringing about social change and defining the relationship between Individual citizen and the state.
Question 8.
While Constitution provides basic principles it is the engagement of people with the system that brings in social change. Do you agree with this statement, give reasons.
Answer:
- Constitution provides basic principles like fundamental rights, the supremacy of the Constitution, etc.
- It is the engagement of people with the system that brings in social change.
- People get good and transparent governance only if they elect good and corrupt free representatives.
- All the schemes of government would be fruitful if they reach genuine beneficiaries.
- Thus, people’s participation brings social change.
10th Class Social Studies 17th Lesson The Making of Independent India’s Constitution InText Questions and Answers
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 232
Question 1.
Complete the following tasks regarding the Indian Constitution.
Task 1: Some significant contributors to the Indian Constitution were:
———-, ———-, ———-.
Answer:
Sri Babu Rajendra Prasad, Acharya Kripalani, Pandit Nehru, Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
Task 2: What are the basic ideals of Indian Constitution as reflected in its Preamble?
Answer:
Basic ideals of Indian Constitution as reflected in the Preamble:
- Justice : Every citizen will have social, economical and political justice.
- Liberty : Every citizen will have the liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship.
- Equality : Every citizen will be provided with the equality of status and of opportunity.
- Fraternity : Citizens of India have been assured about the dignity of the individual and unity, integrity of the nation.
Task 3: Read the following two preambles along with the Indian Preamble and see how they are similar or different. Remember each Constitution also reflects political events around the making of their nations. Try to relate to the political events that may have influenced the thought that went into the Constitution. (You can re-read the background of Japan in chapter 13 and look at page 234 to understand the background of Nepal.)
Answer:
| Preambles of | ||
| Indian Constitution | Nepal Constitution | Japan Constitution |
| Federal Republic | Federal Republic | Peaceful co-operation |
| Multiparty Democracy | Multiparty Democracy | Blessings of liberty |
| Sovereignty | Sovereignty | Sovereignty |
| Fundamental Rights | Fundamental Rights | Trusting in the justice |
| Adult Franchise | Adult Franchise | Faith of the peace-loving people |
| Periodic Elections | Periodic Elections | Banishment of Tyranny and Slavery |
| Independent Judiciary Integrity | Independent Judiciary Integrity | |
The political events that may have influenced the thought that went into the Constitution:
India: The differences in traditional India and disparities in colonial India and political movements shaped the Indian Constitution.
Nepal: The political movements against Monarchy formed the Nepal Constitution.
Japan: The results of World War – II shaped the Japanese Constitution so.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 233 & 234
![]()
Question 2.
Read the Preambles of Nepal and Japan given on Pages 232 and 233 in Textbook and answer the following questions.
a) What do you think is similar or different in the political context of these nations? What were the immediate prior events? Who were the previous rulers?
Answer:
- These nations restrict the monarchy and other forms of governance.
- They are committed to form the government by those who were given mandate in elections.
- They believe their representatives make policies whose fruits are enjoyed by people.
- There were mass movements for democracy in Nepal.
- Japan started new lease of life after war torn image.
- Nepal was ruled by the Monarch.
- Japan was ruled by Pan Asianic rulers.
b) Which Preamble refers to the word gender?
Answer:
- The Preamble of the Constitution of Nepal refers to the word gender.
- It promises to solve the problems relating gender.
c) Which Preamble reflects the desire for peace?
Answer:
- The Preamble of the Japanese Constitution reflects the desire for peace.
- It promises to never visit the horrors of war.
d) How are people’s movements reflected in the Preamble?
Answer:
The Nepalese Constitution reflects the historic struggles and peoples’ movements launched by the people of Nepal at various times since 1951.
e) What is similar or different for Preambles in their reflection of the past?
Answer:
- The Nepalese Constitution refers to abolition of monarchy.
- It also refers to historical struggles and people’s movements.
- The Japanese Constitution refers to the horrors of war.
- It would never like to repeat them and promises to world peace.
f) What types of promises are made up about the future society in the three countries?
Answer:
- In India social, economical, political justice is promised.
- Liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship also promised.
- Equality of status and opportunity also promised.
- Japanese promised a peaceful world.
- They desire to occupy an honoured place in an international society.
- Nepal guaranteed basic rights of the people.
- Nepal expressed full commitment to democratic values.
g) What promises are made about the nature of political system?
Answer:
- Nepal will allow competitive multi-party democratic system, human rights, adult franchise, periodic elections, etc.
- Japan referred Government as a sacred trust of the people who give power to representatives and enjoy benefits of power’
- They try for the banishment of tyranny and slavery, oppression and intolerance for all time from the earth.
- Every Indian get the right to vote at the age of 18 years without discrimination.
h) What promises are made to the citizen of these nations?
Answer:
- Nepal pledges to accomplish the progressive restructuring of the state.
- It also promises to solve the problems relating to class, ethnicity, region and gender.
- Japan desires peace for all time.
- It desires to occupy an honoured place in international society.
- India promised to provide equality, fraternity, justice and fundamental rights to all the people.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 236
![]()
Question 3.
The Constitution of India begins with the statement, “We the people of India…”. Do you think this claim to represent all the people of India was justified?
Answer:
- The claim to represent all the people of India was definitely justified.
- The Constitution was made by the people for the people.
- The draft was printed and made available to the 40 crore people of the country for 8 months.
- There were more than 7,000 changes proposed by the people.
- Out of them above 2000 changes were accepted.
- Thus, the claim is justified.
Question 4.
Do you think all the people of India can participate in the formulation of Constitution for the entire country? Was it important for all people to participate actively in this process or could it have been left to some wise people?
Answer:
- As you can see the Constituent Assembly was not elected through universal adult franchise.
- Only 10% of the population could vote in the provincial election.
- All the people were not necessary to participate actively in the formulation of constitution.
- Because majority of our people are illiterate and they have no knowledge about the constitution.
So, in this situation elites participation is necessary to frame our constitution.
Question 5.
If a Constitution for the entire school had to be drafted, who all should be involved in it and how?
Answer:
- If a Constitution for the entire school had to be drafted the head teacher and all the other teachers should be involved.
- The representative of all classes of the school should also be involved.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 237
![]()
Question 6.
Fill in the blanks.
a) Drafting Committee was appointed roughly ———- days after the Independence.
b) The Assembly first appointed special committees on specific issues like, ———-, ———-, and ———-.
c) The reports of these committees were discussed by the ———- and key decisions were taken by it.
d) The ———- Committee headed by Dr. Ambedkar had to incorporate these decisions.
e) The Draft also drew upon provisions of the ———- passed by the British Government.
f) It was then made available to public for ———- months so that they could criticise and give their suggestions on it.
g) In the Draft Constitution there were ———- Articles and ———- Schedules.
Answer:
a) fifteen,
b) Fundamental rights, Minorities, Tribal Areas,
c) Constituent Assembly,
d) Drafting,
e) Government of India Act, 1935,
f) eight,
g) 395,8.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 238
Question 7.
Fill in the blanks.
a) The powers given to Indian President are more similar to ———-.
b) Constituent Assembly visualised that the Indian President follows the advice of ———-, than ———- of ———-.
Answer:
a) King; England; President; the USA
b) Ministers
Question 8.
What do you think was the difference between the position of the British King and the President of India?
Answer:
- President occupies the same position as the king under the English Constitution.
- His position is not hereditary like king but elected.
- He represents the nation but not rule the nation.
- He generally bound by the advice of Ministers.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 239
![]()
Question 9.
Under federal polity there are more than one government and in the Indian context we have them at ———- and ———- levels. You belong to ———- state while you belong to ———- nation.
Answer:
Central; State; Andhra Pradesh; Indian.
Question 10.
Which type of Constitution gives more powers to the governments at the Centre?
Answer:
- Unitary type of Constitution gives more powers to the governments at the centre.
- Two essential characteristics of a unitary Constitution are the supremacy of the central polity and the absence of subsidiary sovereign polities.
Question 11.
Which type of Constitution gives definite powers to both Central and State governments?
Answer:
- Federal type of Constitution gives definite powers to both Central and State governments.
- A Federal Constitution is marked by the existence of a central polity and subsidiary polities side by side and by each being sovereign in the field assigned to it.
Question 12.
In what ways are Indian states not “administrative units or agencies of the Union Government”?
Answer:
- Indian states are not administrative units or agencies of the union government.
- Because states have sovereign power assigned to them by the Constitution.
- They have elected representatives and they are not the agencies of the union, government.
- They are peripheral entities in the federal system.
Question 13.
Why do you think the framers of the Indian Constitution rejected the idea of dual citizenship (of India and of the state)?
Answer:
- The framers of the Indian Constitution rejected the idea of dual citizenship.
- When there is dual citizen, one is for India and other for the state.
- In such a federal system, rules and laws differ for union and each state.
- It may not be possible to keep them united.
- Our Constitution framers showed uniformity in all basic matters which are essential to maintain the unity of the country.
- So they did not recommend dual citizenship.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 242
Question 14.
Can you point out the main differences between Indian federalism and American federalism?
Answer:
| Indian Federalism | American Federalism |
| 1. Single citizenship. | 1. Dual citizenship |
| 2. Single judiciary | 2. Dual judiciary |
| 3. Uniformity in fundamental, civil and criminal laws. | 3. A duality of legal codes. |
| 4. A common All India Civil Service to main important posts. | 4. A duality of services. |
| 5. No matter of difficulty for a citizen who moved from state to state. | 5. Difficult for a citizen who moved from state to state. |
| 6. India has a parliamentary form of government. | 6. America has a presidential form of government. |
| 7. In India the Loksabha (Lower house) is more powerful. | 7. In America the House of Senate (Upper house) is more powerful. |
| 8. Indian constitution is a rigid and flexible. | 8. American constitution is a only rigid constitution. |
| 9. In India president is nominal head. | 9. In America president has supreme power. |
Question 15.
Does the Indian Constitution allow the states to have their own civil servants (officers)?
Answer:
- The Constitution provides that without depriving the states of their right to form their own civil services, there shall be All Indian Service recruited.
- It is recruited on All India basis with common qualifications, with the uniform scale of pay and the members of which alone could be appointed to the strategic posts throughout the Union.
![]()
Question 16.
Are all officials of a state from the state’s civil services?
Answer:
- No. All officials of a state are not from the state’s civil services.
- Constitution provides for an All India Services for every state in strategic posts.
- They are like Collectors, Superintendents of Police, Secretary, Principle Secretary and Chief Secretary, etc.
Question 17.
In America the judiciary of the Central Government and the judiciary of the states are distinct and separate. In India we have a judiciary in the centre and the states – Explain.
Answer:
- In America the judiciary of the Central Government and that of states are distinct and separate.
- Whereas we have a single judiciary in our country.
- Our judiciary is integrated which is formed with the Supreme Court, all High Courts and other courts.
- We have one jurisdiction and providing remedies in all cases under civil, criminal and constitutional laws.
Question 18.
How were the ideas of Seth and Draft Committee similar or different?
Answer:
- The ideas of Seth and Draft Committee were different.
- He argues that members of CA were not elected by Adult Franchise.
- He says that our Constitution ignores the centrality of villages.
- He opposes Centralization of power as it leads to totalitarian power.
- He desires the decentralization of power to a large extent.
- He believes centralization of power by law leads to Fascism.
Question 19.
Find out what form of autonomy is now being made available to villages after the 73rd amendment of the Constitution.
Answer:
- Villages were provided with the autonomy of forming Grampanchayat.
- Now they are self administered units.
- State Governments shall ensure that direct elections to all seats of Panchayat are conducted.
- The reservation of seats for SCs and STs in proportion to their population and for women reservation seats are not less 1/3 of the total seats.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 244
![]()
Question 20.
Observe the newspaper cutting and answer the following question. What Hems can you read on this page?
 Answer:
Answer:
- This was the first page of ‘The Statesman’ newspaper of January 26th 1950.
- Nehru stated that India emerged as a republic.
- Nehru called for unity and tolerance.
- Soekarno congratulated Indian MPsforthe birth of the republic.
- The preamble of our Constitution is printed.
- Photo of Nehru who was signing on the cabinet assembly was also printed.
- “Today’s programme in Calcutta” was also printed.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 245
![]()
Question 21.
What are the differences of opinion that are being raised in the above debate (‘Debate on Fundamental Rights’ on Page 243 in Textbook)?
Answer:
- The above discussion is about the abolition of untouchability to provide equality as fundamental rights
- Some say untouchability is not a disease itself, but the symptom of disease of caste system.
- So caste system is to abolished.
- Untouchability means different things to different people. So it should be defined clearly.
- Unable to come to a conclusion on definition, it was left for future law makers.
Question 22.
If you were given the choice to participate in the debate, what solution would you suggest?
Answer:
If I have a chance to participate in the debate about untouchability, I will suggest untouchability is a crime however it is in any form in the society. It creates harmess to right to equality. So we should uproot casteism from our society which is main responsible to the untouchability.
Question 23.
Do you think it was a good idea to leave the term undefined in the Constitution? Give reasons for your argument.
Answer:
It was good idea to leave the term “Untouchability” in undefined manner in the Constitution. Because, the word untouchability has different meanings in different places.
So when we are going to use the word ‘untouchability’, we should be in clear manner.
That’s why Article 17 (untouchability is a crime), what says it is correct.
Question 24.
Do you agree with the view that the Constitution should have put an end to all aspects of the caste system instead of just ending untouchability? How do you think it could have been done ?
Answer:
- It would be better if the Constitution had put an end to all aspects of the caste system instead of just ending untouchability.
- Caste system is so deep rooted that to end all the aspects of it may not be that easy.
- But austere efforts and stern action against the practicers of caste system would end it.
10th Class Social Textbook Page No. 246
![]()
Question 25.
What are the examples and explanations you can identify with basic features of Indian Constitution?
Answer:
| Basic features of our constitution | Examples and explanations |
| 1. Form of Government | 1. We have a democratic and parliamentary form of government. |
| 2. Unitary but federal | 2. Central governments are supreme but states are autonomous in their fields. |
| 3. Supremacy of the constitution | 3. Supremacy of the Constitution is the character of unitary form of government. |
| 4. Sovereignty of the nations | 4. We are free in our internal and external affairs. |
| 5. Provision for justice and welfare state | 5. We determine to establish welfare state and provide justice to all people without any discrimination. |
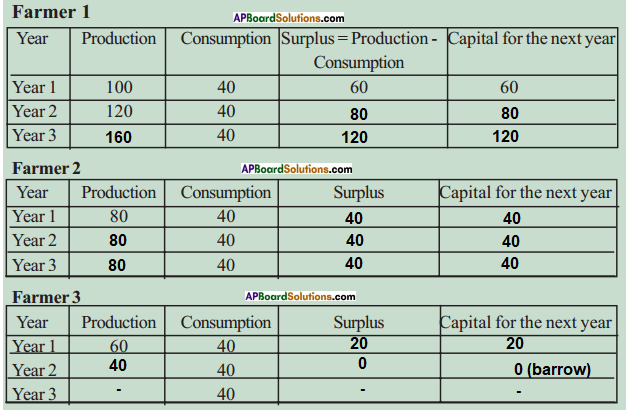
 Many people have argued for localisation of food production rather than food travelling long distances. How is localisation of food connected to the environment ? Find out more about the localisation movement in food and organise a discussion and debate in the classroom.
Many people have argued for localisation of food production rather than food travelling long distances. How is localisation of food connected to the environment ? Find out more about the localisation movement in food and organise a discussion and debate in the classroom.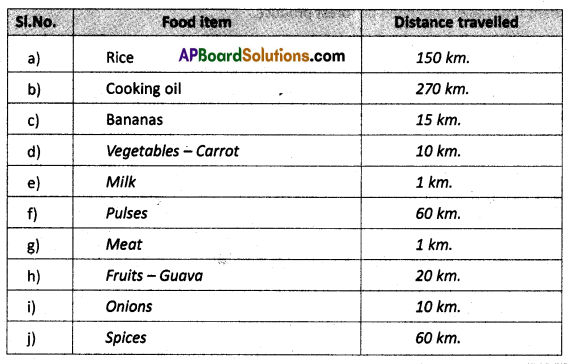
 Answer:
Answer:
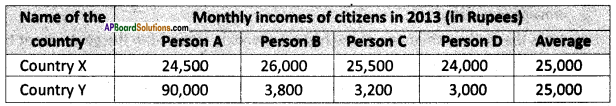
 Write your caption in the context of the environment.
Write your caption in the context of the environment. Answer:
Answer: Write your caption in the context of development.
Write your caption in the context of development. Answer:
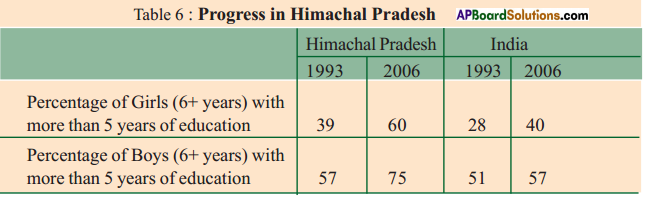
Answer:
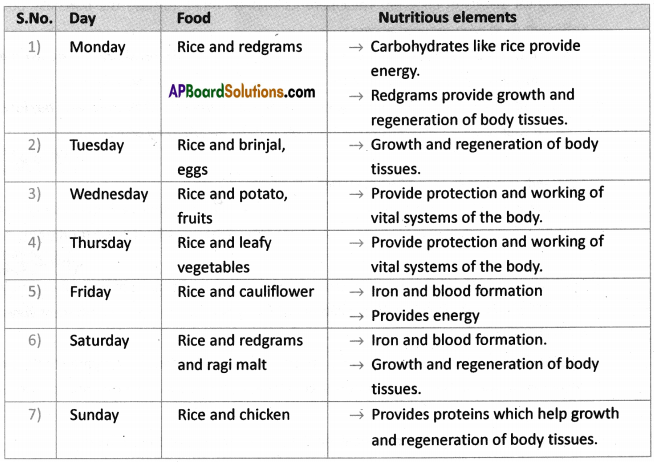
 Answer:
Answer:
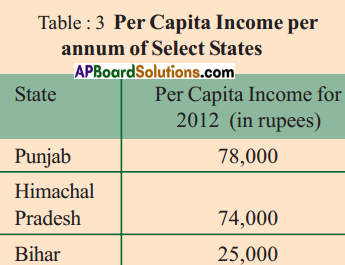
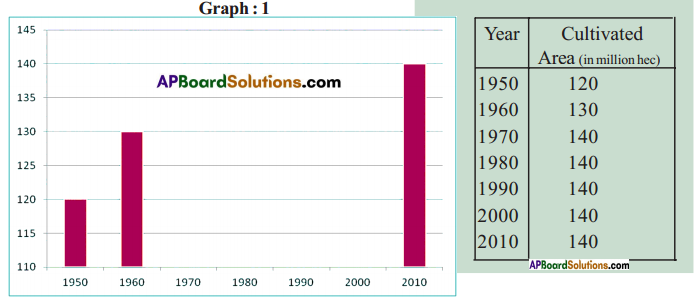
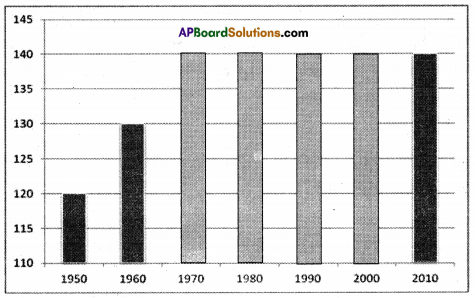
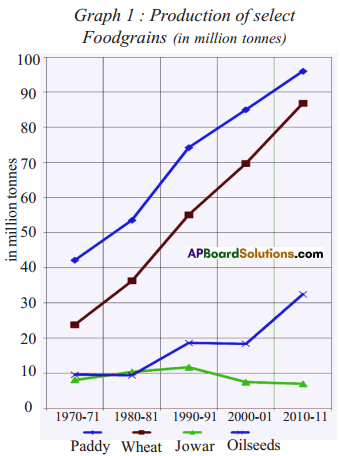 The food grains production has grown over the period 1970-71 to ——–. Paddy production increased from about 40 million tonnes in 1970-71 to about ——– million tonnes in 2010-11. Another important food crop that witnessed rapid increase in production during this 40 years period was ——–. Compared to paddy and wheat the production of ——– did not increase during 1970-2011. This could be due to ——–.
The food grains production has grown over the period 1970-71 to ——–. Paddy production increased from about 40 million tonnes in 1970-71 to about ——– million tonnes in 2010-11. Another important food crop that witnessed rapid increase in production during this 40 years period was ——–. Compared to paddy and wheat the production of ——– did not increase during 1970-2011. This could be due to ——–.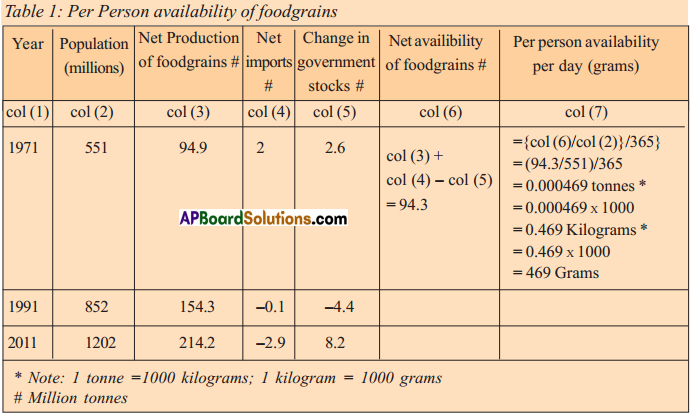 Answer:
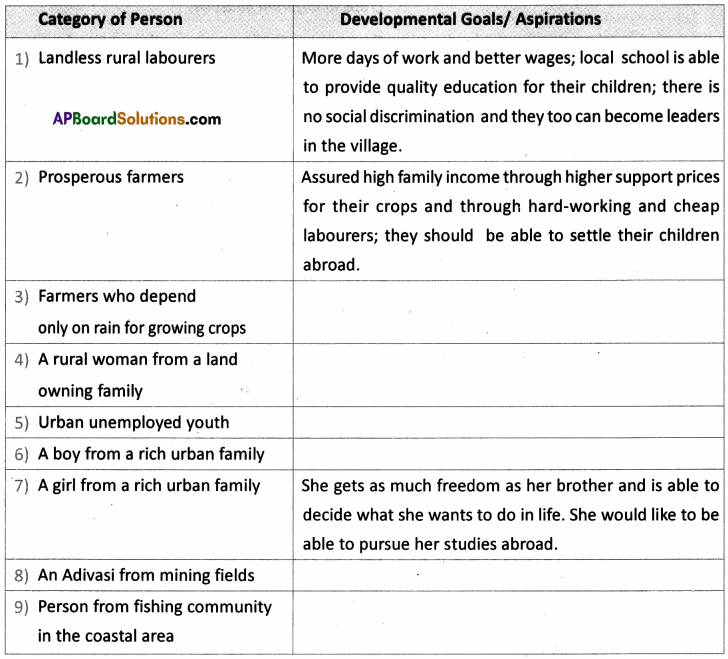
Answer: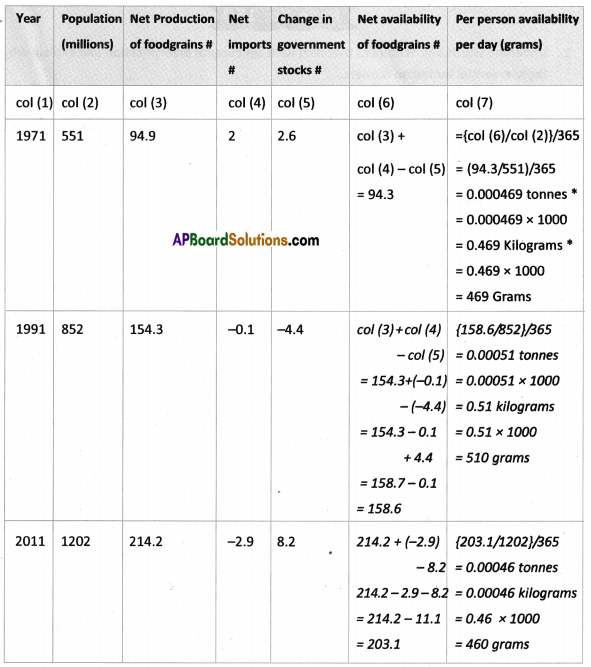
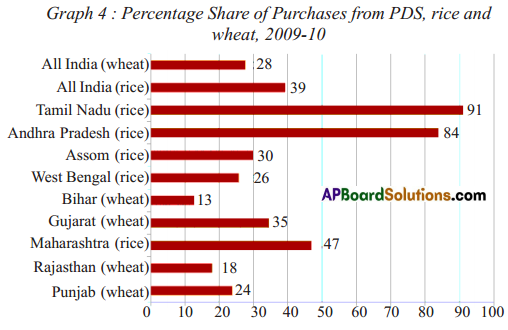
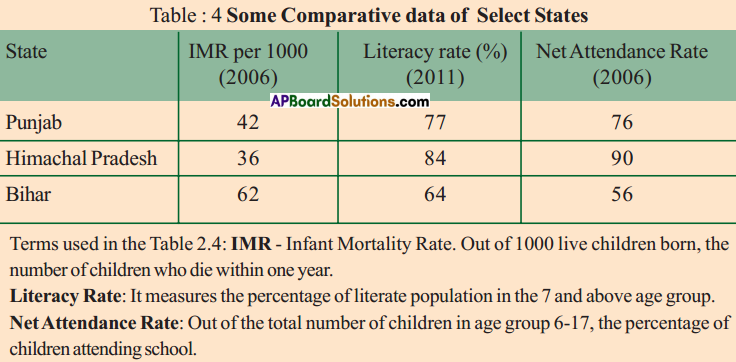
 When weight is plotted against age nearly 45% of children in the country are under weight. It means that they cannot study, work or perform physical activities. They do not grow as quickly as healthy children. Their immune system is weakened. When height is plotted against age 41% of children not up to the height they have to be. It seems their growth is affected and short for their age. They are difficult to cover this. When weight is plotted against height 21% children are not with weight they are supposed to be. With sufficient food they can cover this up.
When weight is plotted against age nearly 45% of children in the country are under weight. It means that they cannot study, work or perform physical activities. They do not grow as quickly as healthy children. Their immune system is weakened. When height is plotted against age 41% of children not up to the height they have to be. It seems their growth is affected and short for their age. They are difficult to cover this. When weight is plotted against height 21% children are not with weight they are supposed to be. With sufficient food they can cover this up.

 Answer:
Answer:
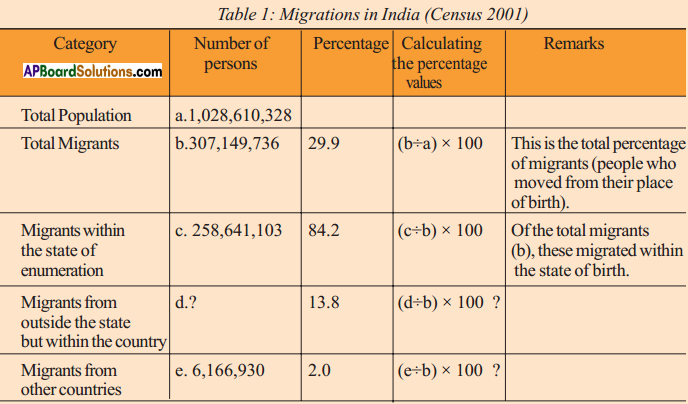 Answer:
Answer: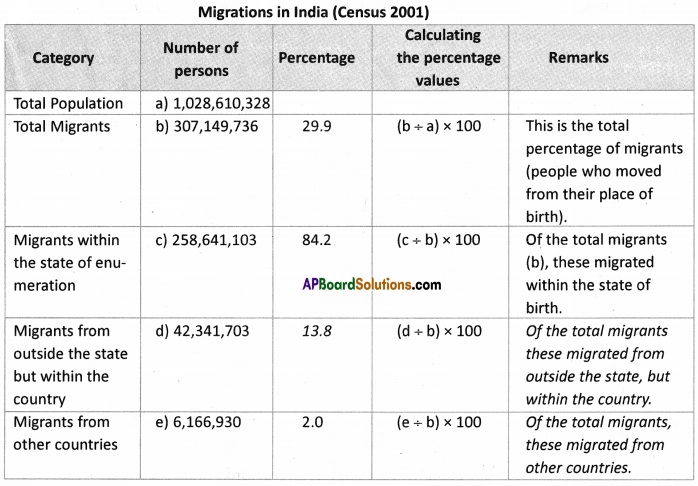
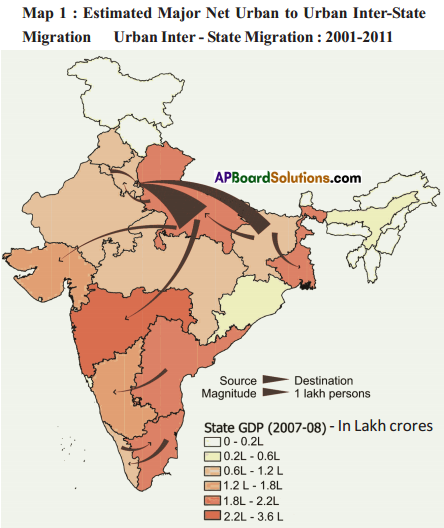 Answer:
Answer: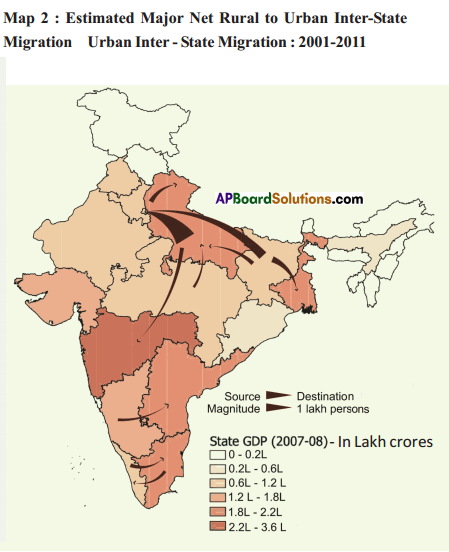 Answer:
Answer: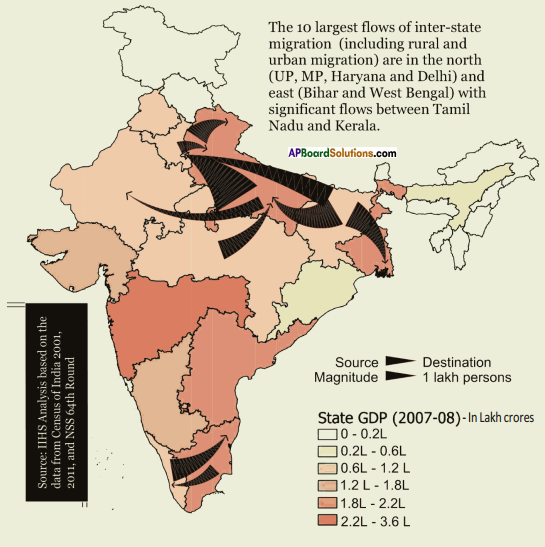 Answer:
Answer: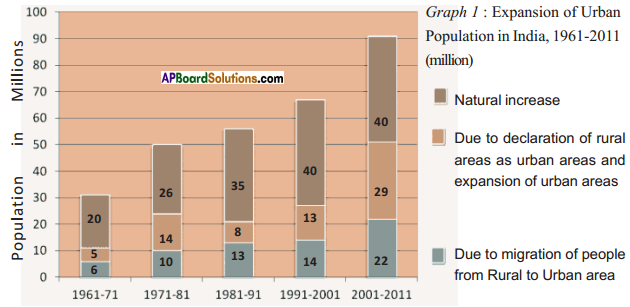 Answer:
Answer: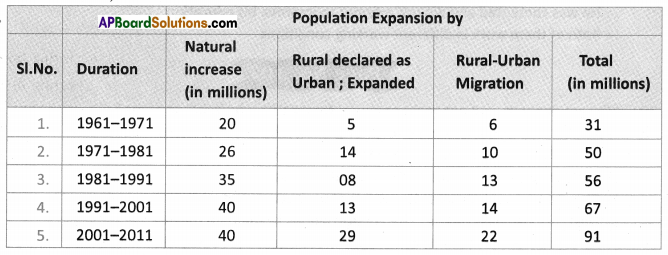
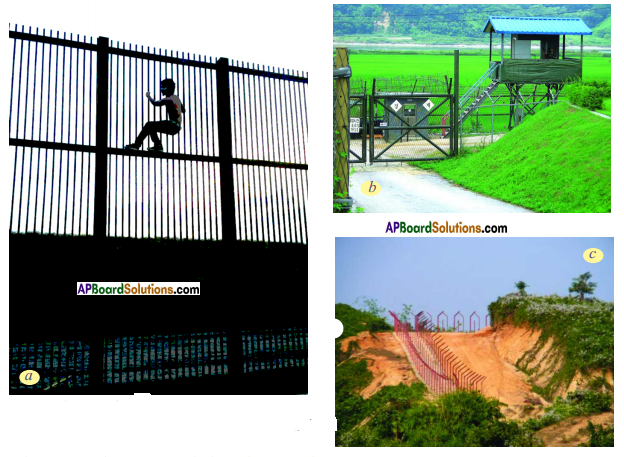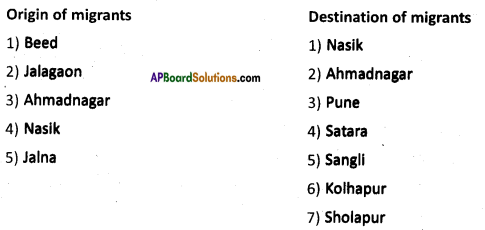
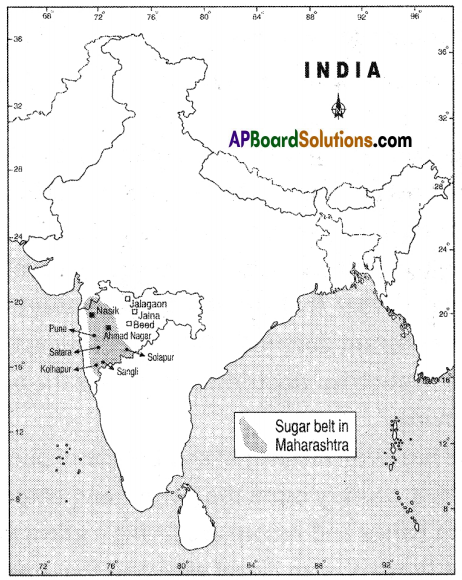
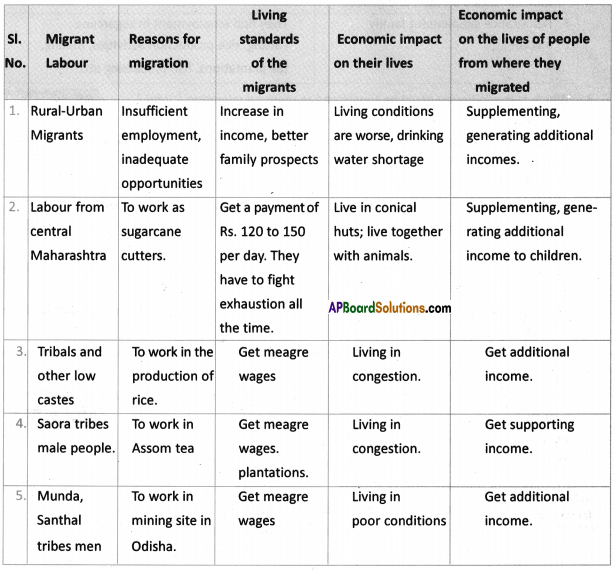
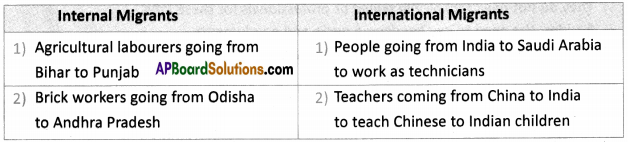
 What do you think of migrants across the border?
What do you think of migrants across the border?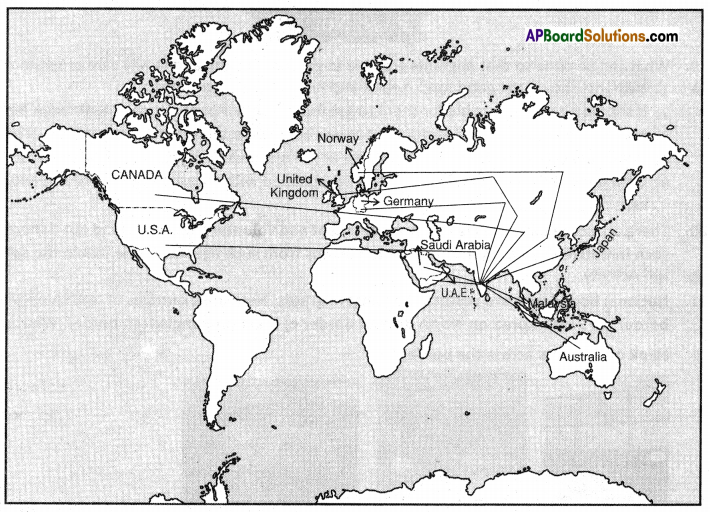






 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: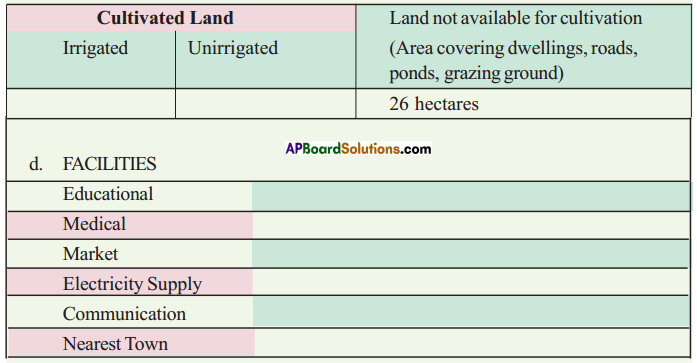
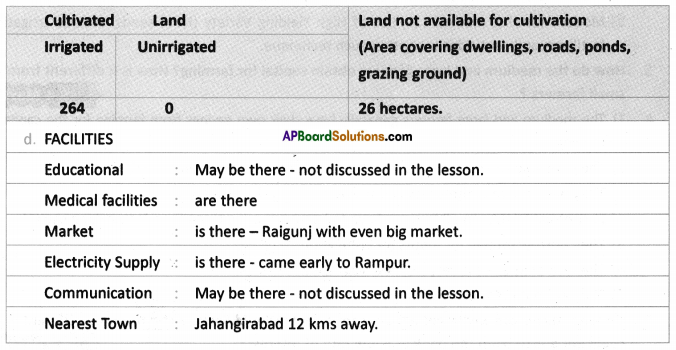
 Answer:
Answer: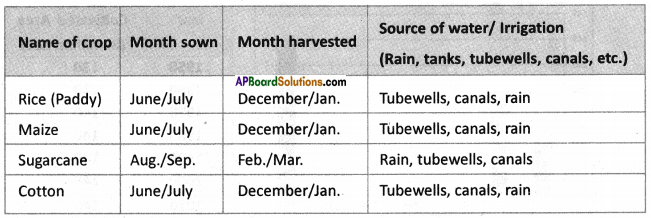
 Answer:
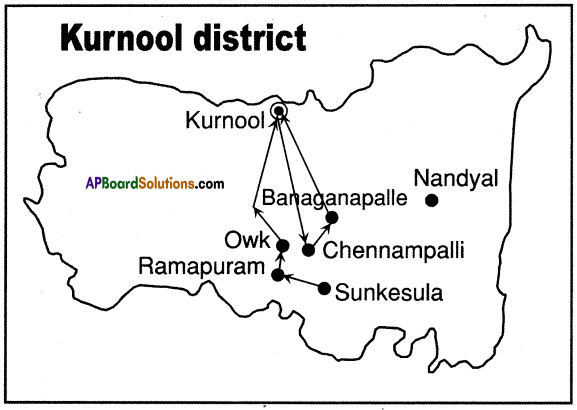
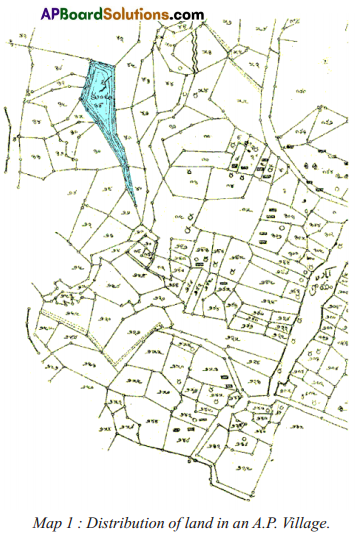
Answer: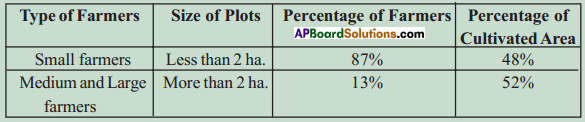 What do the arrows indicate? Would you agree that the distribution of cultivated land is unequal in India? Explain. (OR)
What do the arrows indicate? Would you agree that the distribution of cultivated land is unequal in India? Explain. (OR)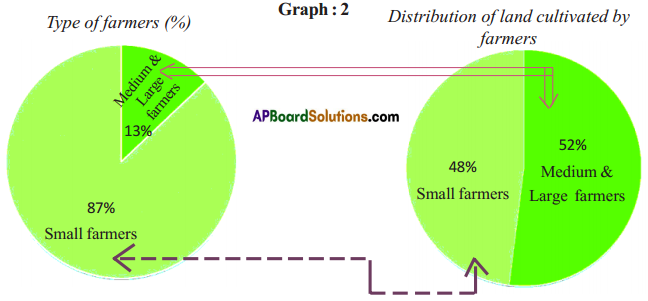 Answer:
Answer: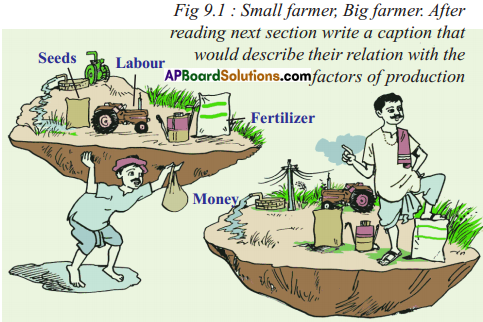 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer:
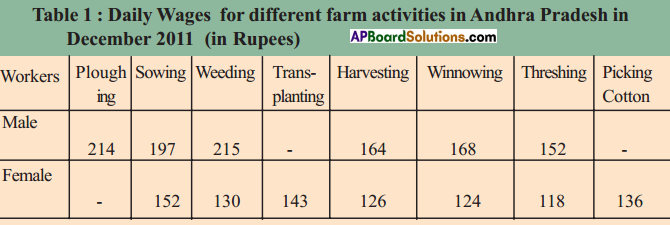 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: