Students can go through AP SSC 10th Class Maths Notes Chapter 11 Trigonometry to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Maths Notes Chapter 11 Trigonometry
→ In our daily life, we can measure the heights, distances and slopes by using some mathematical techniques.
→ The mathematical techniques which come under a branch of mathematics is called ‘trigonometry’.
→ “Trigonometry” is the study of relationships between the sides and angles of a triangle.
![]()
→ Early astronomers used to find out the distances of the stars and planets from the Earth. Even today, most of the technologically advanced methods used in engineering and physical sciences are based on trigonometrical concepts.
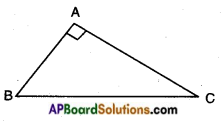
→ Naming the sides in a right triangle:
Let’s take a right triangle ABC as shown in the figure.
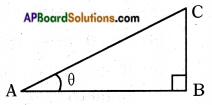
Consider ∠CAB as A where angle ‘A’ is acute.
Since AC is the longest side, it is called “Hypotenuse”.
→ Now observe the position of side BC with respect to angle A. It is opposite to angle ‘A’ and we can call it as “Opposite side of angle A”.
→ And the remaining side AB can be called as “Adjacent side of angle A”.
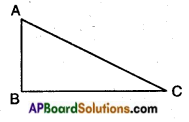
→ Trigonometric Ratios:
The ratios of the sides of a right angled triangle with respect to its acute angles, are called Trigonometric ratios.
→ Consider a right angled triangle ABC having right angle at B as shown in the given figure.
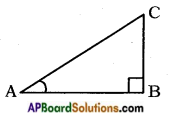
Then, trigonometric ratios of the angle A in right angled triangle ABC are defined as follows:

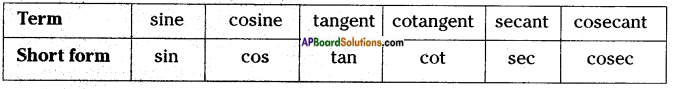
→ There are three more ratios defined in trigonometry which are considered as multiplicative inverse of the above three ratios.
![]()
→ Multiplicative inverse of “sine A” is “cosecant A”.
i.e., cosec A = [latex]\frac{1}{\sin A}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{\text { Hypotenuse }}{\text { Opposite side of the angle } A}[/latex]
→ Multiplicative inverse of “cosine A” is “secant A”.
i.e., sec A = [latex]\frac{1}{\cos A}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{\text { Hypotenuse }}{\text { Adjacent side of the angle } A}[/latex]
→ Multiplicative inverse of “tangent A” is “cot A”.
i.e., cot A = [latex]\frac{1}{\tan A}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{\text { Adjacent side of the angle } A}{\text { Opposite side of the angle } A}[/latex]
Note:
i) The values of the trigonometric ratios of an angle do not vary with the lengths of the sides of the triangles, if the angle remains the same.
ii) Each trigonometric ratio is a real number and has no unit.
iii) “sin θ” is one symbol and sin, cos, tan etc., cannot be separated from θ.
iv) If one of the trigonometric ratios of an acute angle is known, the remaining trigonometric ratios of angle can be easily determined.
v)
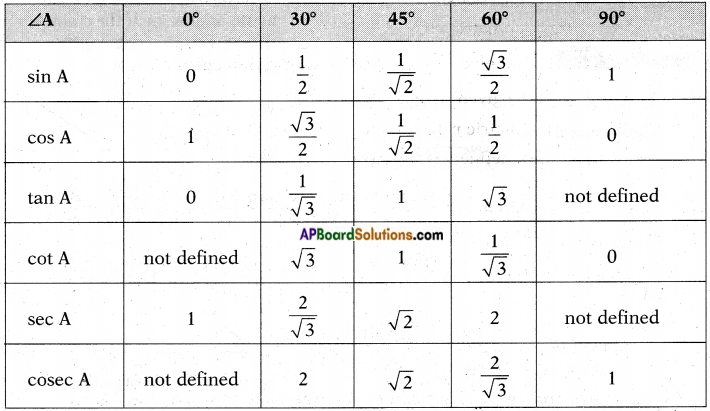
→ Trigonometric ratios of some specific angles:
The values of various trigonometric ratios of 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°.
Note:
i) The values of “sin θ” and “cos θ” always lie between ‘0’ and ‘1’.
ii) In the case of tan θ, the values increase from 0 to ∞ (not determinate).
iii) In the case of cot θ, the values decrease from ∞ to 0.
iv) In the case of cosec θ, the values decrease from ∞ to 1.
v) In the case of sec θ, the values increase from 1 to ∞.
![]()
→ Trigonometric ratios of complementary angles:
Two angles are said to be complementary, if their sum is equal to 90°.
In a right angled triangle, if ∠B = 90°, then ∠A + ∠C = 90° i.e., ∠A and ∠C form a pair of complementary angles.
If ‘θ’ is an acute angle, then we can prove that
sin (90 – θ) = cos θ
cos (90 – θ) = sin θ
tan (90 – θ) = cot θ
cot (90 – θ) = tan θ
sec (90 – θ) = cosec θ
cosec (90 – θ) = sec θ
→ Trigonometric Identity: An identity equation having trigonometric ratios of an angle is called trigonometric identity. It is true for all the values of the angles involved in it.
We have three major trigonometric identities. They are
i) sin2 A + cos2 A = 1
ii) sec2 A – tan2 A = 1
iii) cosec2 A – cot2 A = 1
Note: sin2 θ = (sin θ)2 but sin θ2 ≠ (sin θ)2





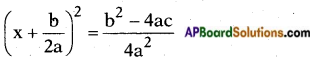
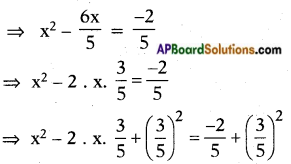
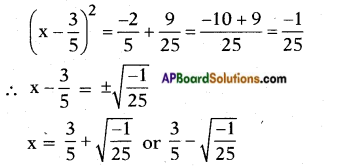
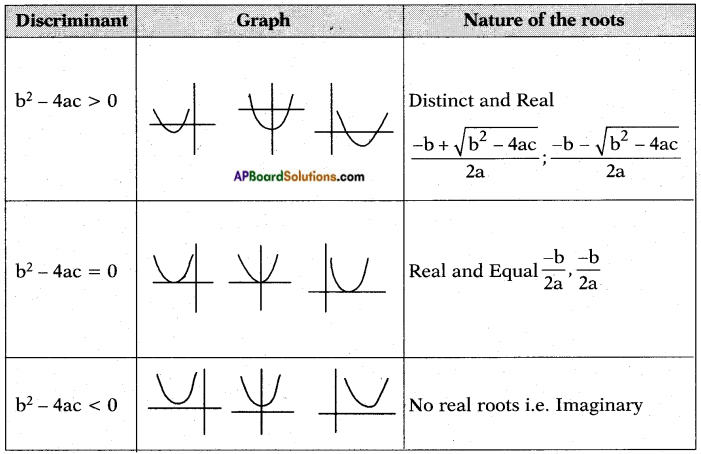
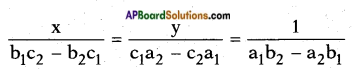
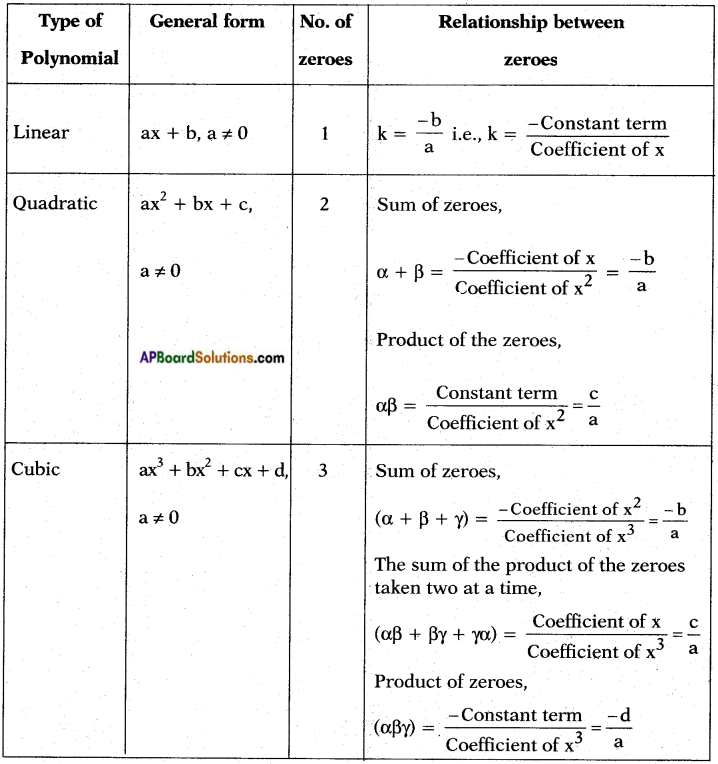
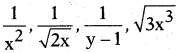 , etc. are not polynomials.
, etc. are not polynomials.