Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 1st Lesson Concept of Business Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 1st Lesson Concept of Business
Essay Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Business. What are its characteristics? [A.P. Mar. 2019, 17]
Answer:
The term Business refers to “the state of being busy”. Every individual is engaged in some activities to fulfill his/her set of needs and wants. All these activities are intended to satisfy human needs. Business is one of the human economic activities.
Business – Definitions :
“A human activity directed towards producing or acquiring wealth through buying and selling of goods.” -L.H. Haney
“Business is an institution organized and operated to provide goods and services to society under the incentive of private gain.” -B.O. Wheeler
“Business is a sum of all activities involved in the production and distribution of goods and services for private profits.” – Keith and Carlo
Business – Characteristics :
Following are the essential characteristics of the business.
- Creation of utilities
- Deals with goods and services
- Continuity in dealings
- Sale, transfer or exchange
- Profit motive
- Risk and uncertainty
- Economic activity
- Art as well as science
1) Creation of utilities :
Business makes goods more useful to satisfy human wants. It adds to production, the utilities of person, time, place, form, knowledge, etc. Businessman is able to satisfy the customer’s demands effectively and economically with the help of business transactions.
2) Deals with goods and services :
Business deals with goods and services. The goods may be consumer goods such as cloths, soaps, milk, shoes, furniture, etc. They may be industrial goods such as machinery, equipment, etc. which are used for further production. Business also deals with services such as transport, warehousing, banking, insurance, etc.
3) Continuity in dealings :
Dealings in goods and services become business only if undertaken on a regular basis. A single isolated transaction of purchase and sale does not constitute business. Recurring or repeated transactions of purchase and sale constitutes business. E.g.: If a person sells his old scooter or a car, it is not business though the seller gets money in exchange. But if he opens a shop and sells scooters or cars regularly, it will become business. Therefore, regularity of dealings in an essential feature of business.
4) Sale, transfer or exchange :
In a business activity there should be two parties i.e. a buyer and a seller. There should be exchange, sale, transfer of goods or services between these two parties for money. For instance, cooking food for personal consumption does not constitute business. But cooking food and selling it to others for a price becomes business. E.g.: Students’ mess.
5) Profit motive:
The primary objective of business is to earn profits. Profits are essential for the survival as well as growth of business. Profits must, however, be earned through legal and fair means. Business should never exploit society to make money.
6) Risk and uncertainty :
Profit is the reward for assuming risk. Risk implies uncertainty of profit or the possibility of loss. Risk is a part and parcel of business. Business enterprises function in uncertain and uncontrollable environment. E.g.: Changes in customers’ tastes and fashions, demand, competition, government policies, etc. create risk. Flood, fire, earthquake, strike by employees, theft, etc. also cause loss. A businessman can reduce risks through correct forecasting and insurance. But all risks cannot be eliminated.
7) Economic activity:
Business is primarily an economic function. It involves production and distribution of goods and services for the satisfaction of human wants. However, business is a part of society and it reflects on aspiration, values and beliefs of people. Therefore, business may be described as a socio-economic function.
8) Art as well as science :
Business is an art because it requires personal skills and experience. It is also a science because it is based on certain principles and laws.
The above mentioned features are common to all business enterprises irrespec¬tive of their nature, size and form of ownership.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the objectives of a business.
Answer:
Objectives of business mean the purposes for which business is established and carried on. Proper selection of objectives is essential for the success of a business. Therefore, every businessman must select and define his business objectives carefully and clearly.
Objectives of business are classified as given below.

1) Economic Objectives:
Business is basically an economic activity. Therefore, its primary objectives are economic in nature. The main economic objectives of business are as follows.
i) Earning profits :
Every business enterprise’s main object is profit. It is the hope of earning profits that inspires people to start business. Profit is essential for the survival of every business unit. Profit also serves as the barometer of stability, efficiency and progress of a business enterprise.
ii) Creating customers :
Profits arise from the businessman’s efforts to satisfy the needs and wants of customers. A businessman can earn profits only when there are enough customers to buy and pay for his goods and services. The customer is the foundation of business and keeps it in existence. Business exists to satisfy the wants, tastes and preferences of customers.
iii) Innovation :
Innovation refers to “creation of new things resulting from the study and experimentation, research and development”. In these days of competition a business can be successful only when it creates new designs, better machines, improved techniques, new varieties, etc. Modern science and technology have created a great scope for innovation in the business world.
2) Social Objectives:
Business does not exist in a vaccum. It is a part of society. It cannot survive and grow without the support of society. So, business must have some social objectives. They are given below.
i) Supplying desired goods at reasonable prices :
Business is expected to supply the goods and services required by the society. Goods and services should be of good quality and these should be supplied at reasonable prices. It is also the social obligation of business toaKoid malpractices tike smuggling, black makreting and misleading advertising.
ii) Fair Remuneration to employees:
Employees must be given fair compensation for their work. In addition to wages and salary a reasonable part of profits should be distribuited among employees by way of bonus. Such sharing of profits will help to increase the motivation and efficiency of employees.
It is the obligation of business to provide healthy and safe work environment for employees. Employees work day and night to ensure smooth functioning of business. It is, therefore, the duty of employers to provide hygienic working and living conditions for workers.
iii) Employment generation :
Business should provide opportunities for gainful employment to members of the society. In a country like India unemployment has become a serious problem and no government can offer jobs to all. Therefore, provision of adequate and full employment opportunities is a significant service to society.
iv) Social welfare :
Business should provide support to social, cultural and reli¬gious organisations. Business enterprises can build schools, colleges, libraries, dharamshalas, hospitals, sports bodies and research institutions. They can help non-government organisations (NGOs) like CRY (Child Relief and You), Help Age, and others which render services to weaker sections of society.
v) Payment of government dues :
A business should not shut its eyes to its obligations towards the government. Therefore, business owes it to the government to pay its tax dues honestly and in time. It must also dutifully abide by the laws of the land.
3) Human Objectives:
i) Labour welfare :
Business must recognise the dignity of labour and human factor should be given due recognition. Adequate provisions should be made for their health, safety and social security.
ii) Developing human resources :
Employees must be provided with the opportunities for developing new skills and attitudes. This can be done by training the employees and conducting workshops on skill development and attitude. Human resources are the most valuable asset of business and their development will help in the growth of business.
iii) Participative management :
Employees should be allowed to take part in decision making process of business. This will help in the development of employees. Workers’ participation in management will usher in industrial democracy.
iv) Labour – Management cooperation :
Business should strive for creating and maintaining cordial employer- employee relations so as to ensure peace and progress, in industry.
4) National Objectives:
i) Optimum utilisation of resources :
Business should use the nation’s resources in the best possible manner. Judicious allocation and optimum utilisation of scarce resources is essential for rapid and balanced economic growth of the country. Business should produce goods in accordance with national priorities and interests. It should minimise the wastage of scarce natural resources.
ii) National self-reliance :
It is the duty of business to help the government in increasing exports and in reducing dependence on imports. This will help a country to achieve economic independence. .
iii) Development of small scale industries :
Big business firms are expected to encourage growth of small scale industries which are necessary for generating employment. Small scale firms can be developed as ancillaries which provide inputs to large scale industries.
iv) Development of backward areas :
Business is expected to give preference to the industrialisation of backward regions of the country. Balanced regional development is necessary for peace and progress in the country. It will also help to raise standard of living in backward areas. Government offers special incen¬tives to the businessmen who set up factories in notified backward areas.
Question 3.
Discuss the social responsibility of business.
Answer:
Business organisations are obliged to consider social impact of their decisions. The obligation of any business to protect and serve public interest is known as social responsibility of business. Any responsibility business has, particularly towards members of the society with whom they interact or towards the society in general called is social responsibility.
The Concept of Social Responsibility:
Every business operates within a society. It uses the resources of the society and depends on the society for its functioning. This creates an obligation on the part of business to look after the welfare of society. Therefore, all the activities of the business should be such that they will not harm, rather they will protect and contribute to the interests of the society.
Social responsibility of business refers to all such duties and obligations of business directed towards the welfare of society. So, every business must contribute in some way or the other for their benefit. E.g. : Every business must ensure a satisfactory rate of return to investors, provide good salary, security and proper working condition to its employees, make available quality products at reasonable price to its consumers, maintain the environment properly, etc. Social responsibility implies that a business should not do anything harmful to the society in course of business activities of a businessman.
Social Responsibility Towards Different Interest Groups :
The business generally interacts with owners, investors, employees, suppliers, customers, competitors, gov-ernment and society. They are called interest groups. Such interest groups are given below.
Social responsibility towards different interest groups
- Responsibility towards owners
- Responsibility towards employees
- Responsibility towards suppliers
- Responsibility towards customers
- Responsibility towards government
- Responsibility towards society
1) Responsibility towards owners :
Owners are the persons who own the business. They contribute capital and bear the business risks. The primary responsibilities of business towards its owners are to :
- Run the business efficiently.
- Proper utilisation of capital and other resources.
- Growth and appreciation of capital.
- Regular and fair return on capital invested by way of dividends.
2) Responsibility towards employees :
Business needs employees or workers to work for it. These employees put their best effort for the benefit of the business. The responsibility of business towards its employees include:
- Timely and regular payment of wages and salaries.
- Proper working conditions and welfare amenities.
- Opportunity for better career prospects.
- Job security as well as social security like facilities of provident fund, group insurance, pension, retirement benefits, etc.
3) Responsibility towards suppliers :
Suppliers are businessmen who supply raw materials and other items required by manufacturers and traders. Certain suppliers, called distributors, supply finished products to the customers. The responsibilities of business towards these suppliers are :
- Giving qualitative goods at reasonable prices.
- Dealing on fair terms and conditions.
- Availing reasonable credit period.
- Timely payment of dues.
4) Responsibility towards customers :
No business can survive without customers. As a part of the responsibility of business towards them the business should provide the following facilities.
- Products and services must be qualitative
- Giving delivery of goods within stipulated time
- Reasonable price
- There must be proper after-sales services.
- Complaints and grievances of the customers, if any, must be settled quickly.
- Unfair means like underweighing the product, adulteration, etc. must be avoided.
5) Responsibility towards government:
Business activities are governed by the rules and regulations framed by the government. The various social responsibilities of the government are:
- Setting up units as per guidelines of the government.
- Payment of fees, duties and taxes regularly as well as honestly.
- Conforming to pollution control norms set up by government.
- Not to indulge in corruption through bribing and other unlawful activities.
6) Responsibility towards society :
A society consists of individuals, groups, organizations, families, etc. They all are the members of the society. Thus, it has certain responsibilities towards society, which may be as follows :
- to help the weaker and backward sections of the society
- to preserve and promote social and cultural values
- to generate employment
- to protect the environment
- to conserve natural resources and wildlife
- to promote sports and culture
![]()
Question 4.
Classify and describe each type of Economic activities.
Answer:
All the activities in which the people participate from morning till night are called human activities. Every individual is engaged in some activities to fulfil his/her set of needs and wants. All these activities are intended to satisfy human needs.
All the activities of human beings can be classified into two types. They are :
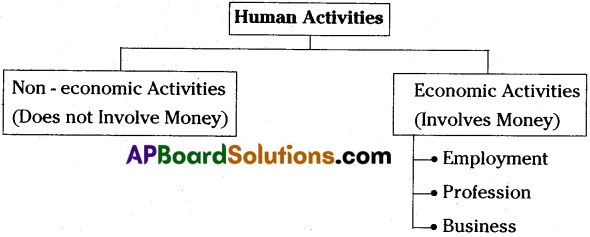
Non – economic Activities :
Those human activities do not involve money or money’s worth, such activities are termed as non-economic activities. Human beings engage themselves in non-economic activities due to love, affection, patriotism, charity, sympathy, and other such sentiments.
E.g. : A mother looks after her children, young man helps a blind man to cross the road, etc.
Economic Activities:
Human beings undertake certain economic activities for earning money or livelihood. Working as a teacher in a school, a doctor in a hospital, a worker in a factory, a farmer in a field, an emloyee in an office, a merchant selling goods, etc.
In other words, an human being involves in any activity together with money or money’s worth, such activities are termed as human economic activities. Such human economic activities are classified into three types. They are given below ;
- Profession
- Employment
- Business
1) Profession:
An activity which involves the rendering of personalized services of a specialized nature based on professional knowledge, education and training is called a profes¬sion. Services rendered by doctors, lawyers, chartered accountants, engineers, etc. come under this category.
2) Employment:
An employment is a contract of service. A person who works under the contract for a salary is called an employee and the person who has given the job to the employee is called employer. An employee works under an agreement as per the rules of service and performs tasks assigned to him by the employer. The relationship between the employer and the employee is that of a ‘Master’ and ‘Servant’.
3) Business:
Business is one of the human economic activities. Business is an economic activity involving production, exchange, distribution and sale of goods and services with an objective of making profits.
Short Answer Questions
Quelition 1.
Business objectives.
Answer:
Objectives of business mean the purposes for which business is established and carried on. Proper selection of objectives is essential for the success of a business. Objectives serve as the guidelines for the future direction and management of business. Therefore, every businessman must select and define his business objectives carefully and clearly.
Objectives of business may be classified into four broad categories. They are :
- Economic objectives
- Social objectives
- Human objectives
- National objectives
Every businessman seeks to earn profits by satisfying the wants of people. It is the hope of earning profits which induce people to enter into business. No business can survive without making adequate profits. Thus profit is the fundamental economic objective of business.
If profit maximization is regarded as the sole objective of business, it is likely to result in unfair practices such as hoarding, black marketing, etc. The profit making and social service objectives are not contradictory to each other.
Business must discharge social responsibilities in addition to earning profits. It should aim at servicing the community.
![]()
Quelition 2.
Social objectives.
Answer:
Business does not exist in a vacuum. It is a part of society. It cannot survive and grow without the support of society. Business must therefore discharge social responsibilities in addition to earning profits.
Social objectives – Definition :
“The primary aim of business should be service and subsidiary aim should be earning of profit.” – Henry Ford
Some important social objectives are given below :
- Business is expected to supply the goods and services required by the society. Goods and services should be of good quality and these should be supplied at reasonable prices.
- Employees must be given fair compensation for their work. In addition to wages and salary a reasonable part of profits should be distributed among employees by way of bonus. Such sharing of profits will help to increase the motivation and efficiency of employees. So, fair remuneration to employees is an important social objective.
- Business should provide job opportunities to the members of the society. In a country like India unemployment has become a serious problem and no government can offer jobs to all. So, employment generation is also one of the social objectives.
- Business should provide support to social, cultural and religious organisations. Business enterprises can build schools, colleges, libraries, hospitals, etc.
- Every business enterprise should pay tax dues to the government honestly and at the right time. These direct and indirect taxes provide revenue to the government for spending on public welfare. So, payment of government dues is also one of the important social objectives.
Quelition 3.
Role of profit in business.
Answer:
A business enterprise is established for earning some income. It is the hope of earning profits that inspires people to start business. Profit is essential for the survival of every business unit. Just as a person cannot live without food, a business firm cannot survive without profit. Profits enable a businessman to stay in business by maintaining intact the wealth producing capacity of its resources.
Profit is also necessary for the expansion and growth of business. Profits ensure continuous flow of capital for the modernisation and extension of business operations in future. Profit also serves as the barometer of stability, efficiency and progress of a business enterprise.
Quelition 4.
Brief explaination of economic activities.
Answer:
The term business refers to “the state of being busy”. Every business individual is engaged in some activities to fulfil his/her set of needs and wants. All these activities are intended to satisfy human needs. E.g.: A farmer engages himself in agricultural activities and an employee works in the office, a teacher teaches in the classroom, etc. for satisfying his needs, comforts and luxuries.
All the activities of human being can be divided into two types. They are :
- Economic Activities
- Non-economic Activities
Economic activities :
Those human activities that are involved in money, such activities are termed as economic activities. Human beings undertake certain economic activities for earning money or livelihood. Working as a teacher in a school, a doctor in a hospital, a worker in a factory, a merchant selling goods or an industrialist manufacturing goods, all these are economic activities. These economic activities are concerned with production, exchange and distribution of goods and services.
Very Short Answer Questions
Quelition 1.
Define Business. [Mar. 2018, 17 ; May 17 – A.P.]
Answer:
A business is an economic institution. It is concerned with production and distribution of goods and rendering of service in order to earn profits and acquire wealth. Business may be defined as “a human activity directed towards producing or acquiring wealth through buying and selling of goods”. – L.H. Haney
Profits are consideration of Business.
![]()
Quelition 2.
What is a Profession?
Answer:
Profession is one of the human economic activities. An activity which involves the rendering of personalised services of a specialized nature based on professional knowledge, education and training is called a profession. E.g. : Doctors, Lawyers, Chartered Accountants, Engineers, etc.
Remuneration is consideration of Profession.
Quelition 3.
What is Employment?
Answer:
Employment is also one of human economic activities. Any activity assigned to a person by the employer under an agreement or rules of services comes under the category of employment.
A person who undertakes such activity is called employee.
Salary is consideration of Employment.