AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 10 Soil Pollution.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology Important Questions 10th Lesson Soil Pollution
9th Class Biology 10th Lesson Soil Pollution 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What will happen if there is increase in acidic or basic nature of soil?
Answer:
- The nutrients available to plants will be greatly reduced by increase in acidic or basic nature of soil.
- This results in the decrease of plant yield.
Question 2.
What is decomposition?
Answer:
Decomposition is the process of materials being digested and broken down into simpler substances, making nutrients more available to plants.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the effects of toxic chemicals released into the soil?
Answer:
Toxic chemicals leached from oozing storage drums into the soil, underneath homes, causing an unusually large number of birth defects, cancers and respiratory, nervous and kidney diseases.
Question 4.
What is bioremediation?
Answer:
The process of using microbes to clear up the contamination in soil and water is called bioremediation.
Question 5.
What is mineralization?
Answer:
The process of converting organic elements to inorganic forms and liberating C02, ammonia, sulphate, phosphate etc…. is called mineralization.
Question 6.
What is soil erosion?
Answer:
The removal of top layer of the soil by wind, rainfall is called soil erosion.
Question 7.
What is top soil comprised of?
Answer:
Humus, living organisms and soil particles are present in the top soil.
Question 8.
What is soil profile?
Answer:
Soil profile is the vertical section of earth’s crust generally up to the depth of 1.83 metres.
![]()
Question 9.
Name the three natural resources on the earth.
Answer:
Air, water and land.
Question 10.
What is soil?
Answer:
The top most layer of the lithosphere is called soil.
Question 11.
Fertile soils have lots of humus. Why?
Answer:
Fertile soil is rich in organisms that decompose dead organic matter into humus. Humus gives minerals, absorb water and makes soil porous.
Question 12.
Why step farming is common in hills?
Answer:
Step farming is common in the hills to check soil erosion through water currents on the slopes.
Question 13.
What are the factors determining the soil type?
Answer:
The soil type depends on
a) Amounts of humus
b) Size of the soil particles
c) Microorganisms present in the soil.
9th Class Biology 10th Lesson Soil Pollution 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the components of soil?
Answer:
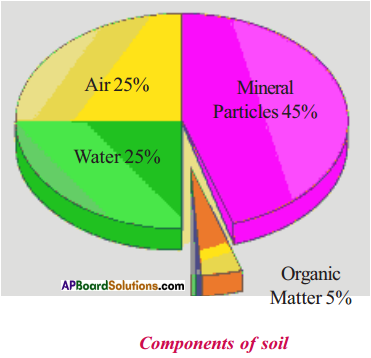
- Soil is made up of minerals and decomposed organic matter, along with air and water.
- Soil can create a habitat for fungi, bacteria and related organisms which in turn, feed and support plants life.
Question 2.
Write a short note on biodegradable waste. Give examples.
Answer:
- Substances that can be degraded by microbes into harmless and toxic substances are known as biodegradable waste.
- Agricultural and animal wastes like leaves, twigs, hay, dung etc., are examples for biodegradable wastes.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a short note on non-biodegradable waste. Give examples.
Answer:
- Substances that cannot be easily degraded are non-biodegradable substances.
- Aluminium cans, plastics, glass, DDT etc., are examples of non-biodegradable wastes.
Question 4.hat is soil erosion? What are causative factors for soil erosion?
Answer:
- Soil erosion occurs when the weathered soil particles are dislodged and carried away by wind or water.
- Deforestation, agricultural development, temperature extremes, precipitation including acid rain and human activities contribute to soil erosion.
- Humans speed up this process by construction, mining, cutting of timber, over¬cropping and overgrazing.
- It results in floods and cause soil erosion.
Question 5.
What are the problems that arise due to uncollected and decomposed solid waste in cities?
Answer:
If solid waste left uncollected and decomposed, they are a cause of several problems such as
- Clogging of drains
- Barrier to movement of water
- Foul smell
- Increased microbial activities
- Create health problems if they are solid wastes of hospital.
Question 6.
What will happen if you throw the wastes wherever you want?
Answer:
- They pollute our surroundings.
- These wastes cause land pollution.
- These wastes spread diseases.
- They show effect on the health of human beings.
Question 7.
What are the effects of soil pollution on agriculture?
Answer:
- Reduced soil fertility.
- Reduced nitrogen fixation.
- Increased erodibility.
- Larger loss of soil and nutrients.
- Deposition of silt in tanks and reservoirs.
- Reduced crop yields.
- Imbalance in soil fauna and flora.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the effects of soil pollution due to industrial waste?
Answer:
- Dangerous chemicals entering underground water.
- Ecological imbalance.
- Release of pollutant gases.
- Release of radioactive rays causing health problems.
- Increased salinity.
- Reduced vegetation.
Question 9.
What are the effects of soil pollution due to urban activities?
Answer:
- Clogging of drains
- Inundation of areas
- Public health problems
- Pollution of drinking water sources
- Foul smell and release of gases
- Waste management problems
Question 10.
What are Bio-degradable pollutants? Give examples.
Answer:
The pollutants that are degraded by natural means are called Bio-degradable pollutants.
Eg : Paper, wood, leaves, etc
Question 11.
Enlist the main causes of soil erosion.
Answer:
(a) Deforestation
(b) Urbanisation
(c) Excessive over grazing
(d) Leaving the land uncultured for a long time.
Question 12.
Fill this flow chart.
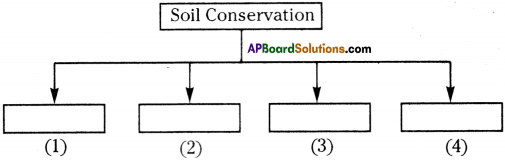
Answer:
- Contour ploughing
- Planting trees
- Crop Rotation
- Salinity Management
Question 13.
Fill this flow chart.
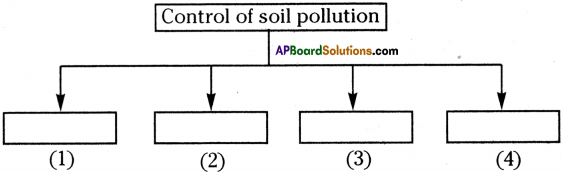
Answer:
- Reusing of materials
- Recycling and recovery of materials
- Reforesting
- Reducing chemical fertilizer and pesticides use.
Question 14.
Fill this flow chart.
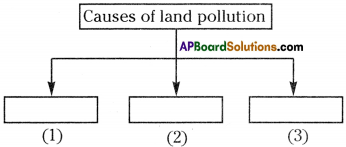
Answer:
- Agricultural soil pollution
- Soil pollution by industrial effluents and solid wastes
- Pollution due to urban activities.
9th Class Biology 10th Lesson Soil Pollution 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How soil is formed?
Answer:
- Soil formation is a long and complex process and it can take 100 to 10,000 years to create one inch of top soil.
- The factors responsible for soil formation are climate, topography, living organisms and the type of parent material.
- Parent materials come from breakdown of underlying rocks or from deposits by streams and rivers, seas and gulfs, hills, wind and glaciers or organic plant residues.
- Over time, these materials are weathered by the effect of freezing, thawing, wetting, drying, heating, cooling, erosion, plants and animals and from chemical reactions.
- Eventually, the parent material is divided into three horizontal layers, the top layer consists of mostly organic matter and biological activity.
- The middle layer is the zone of maximum material accumulation.
- The bottom layer bold is mainly the parent material, but slightly altered.
- The top soil is important since it is the foundation for the life on the earth.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the chemical properties of soil? What effects do this have on the plants?
Answer:
- The term pH is used to indicate the level of acidity or alkalinity of a soil.
- The range of pH values of a good soil lies from 5.5 to 7.5.
- Below pH 7 the soils are termed as acidic and above pH 7 alkaline.
- The pH of soil is important in determining the type of vegetation that will grow in the soil.
- Availability of plants nutrients is strongly tied to the pH in soil.
- The availability of N, K, Ca, Mg and S tends to decrease with decreasing pH.
Question 3.
What are the biological properties of soil? What effects do this have on plants?
Answer:
- Soil is the most abundant and diverse ecosystem on the earth.
- Soil organisms include both plants and animal forms ranging from submicroscopic viruses to earthworms, to large burrowing animals such as gophers (rats) and ground squirrels.
- Major microbial groups in soil are bacteria, fungi, algae and protozoa.
- These feed on plant residues burrow the soil and help in aeration and percolation of water.
- Soil microbes convert organic forms of elements to their inorganic forms and liberate carbon dioxide, ammonia, sulphate, phosphate and inorganic forms of other elements. This process is known as mineralization.
- Soil bacteria control the forms of ions in which these nutrients occurs.
Question 4.
Write the effects of insecticide DDT on environment.
Answer:
- The first widespread insecticide use began at the end of world war 11 that included DDT and gamanaxene.
- Insect soon became resistant to DDT and as the chemical did not decompose readily, it persisted in the environment.
- Since it was soluble in fat rather than water, it biomagnified up the food chain and disrupted calcium metabolism in birds, causing egg shells to be thin and fragile.
- As a result, large birds of prey such as the brown pelican, ospreys, falcons and eagles became endangered.
- DDT is now banned in most of the western countries.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the examples of pesticides. What are their effects on soil and human beings?
Answer:
- Besides DDT the most important pesticides are Benzene hexachloride (BHC), chlorinate dihydro carbons, organophosphates, aldrin, malathion, dieldrin, furodan etc., are the examples.
- The remnants of such pesticides used on pests may get absorbed by the soil particles, which then contaminate root crops grown in that soil.
- The consumption of such crops causes the pesticides remnants to enter human biological systems, affecting them adversely.
- Pesticides not only have toxic effect on human and animals but also decrease the fertility of the soil.
- Some of the pesticides are quite stable and their biodegradation may take weeks and even months.
Question 6.
Write briefly about biomagnification.
Answer:
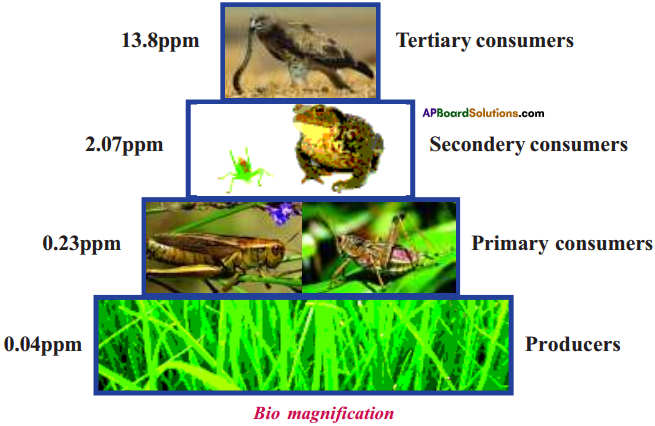
- The nutrients necessary for plant growth are found at very low concentrations in most natural waters.
- In the process of collecting nutrients, phytoplankton also collects certain human made chemicals such as some persistent pesticides.
- These may be present in the water at a very low concentrations that they cannot be measured even with a very sensitive instruments.
- The chemicals however, biologically accumulate in the organism and become concentrated at levels that are much higher in the living cells than in the open water.
- The small fish and zooplankton eat vast quantities of phytoplankton.
- In doing so, any toxic chemicals accumulated by the phytoplankton are further concentrated in the bodies of the animals that eat them.
- This is repeated at each step in the food chain.
- This process of increasing concentration through the food chain is known as bio-magnification.
Question 7.
What is solid waste? What are different types of solid waste?
Answer:
1. Solid waste may be defined as the organic and inorganic waste produced by various activities of the society which have lost their value to the first user.
2. Solid waste, on the basis of its sources of origin can be classified as
a) Municipal solid waste :
It consists of household waste, construction and demolition debris, sanitation residue.
b) Hazardous solid waste :
Industrial and” hospital waste is considered to be hazardous waste as they contain toxic substances.
c) Infectious solid waste:
Biomedical or hospital waste generated during diagnosis, treatment etc., which include sharp chemical wastes, discarded medicines and human excreta.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the different ways and methods possible for soil conservation? Briefly explain them.
Answer:
There are several ways possible for soil conservation. They are planting trees, terraces, no-till farming, contour ploughing, crop rotation, soil pH, watering the soil, salinity management, soil organisms and indigenous crops.
1. Planting trees :
a) Soil that is under a vegetative cover has hardly any chance of getting eroded as the vegetative cover acts as a wind barrier.
b) As the roots of the trees spread deep into the layers of soil they contribute to the prevention of soil erosion.
2. Terraces :
a) A terrace is a leveled section of hilly cultivated area.
b) Owing to its unique structure, it prevents the rapid surface runoff of water.
3. No-till farming : It is a way of growing crops without disturbing it through tillage.
4. Contour ploughing :
a) It is the method of ploughing across the contour lines of a slope.
b) This method helps in slowing the water runoff and prevents the soil from being washed away along the slope.
5. Crop rotation: Crop rotation helps in the improvement of soil structure and fertility.
6. Soil pH :
Maintenance of the most suitable value of pH is essential for the conservation of soil.
7. Water the soil :
Watering the soil along with the plants is a way to prevent soil erosion caused by wind.
8. Salinity management :
a) If salinity of the soil increases it results in the death of vegetation.
b) The death of vegetation is bound to cause soil erosion.
c) Hence salinity management is one of the indirect ways to conserve soil.
9. Soil organisms :
The helpful organisms of soil promote its fertility and form an element in the conservation of soil.
10. Indigenous crops :
Planting of native crops is known to be beneficial for soil conservation.
9th Class Biology 10th Lesson Soil Pollution Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write any two preventive measures for fluorosis.
Answer:
- Use river water in place of groundwater.
- Use rainwater and groundwater with less fluoride percentage.
- By using defluoridation method, fluorides can be removed from water.
Question 2.
Look at the picture and answer the questions below.
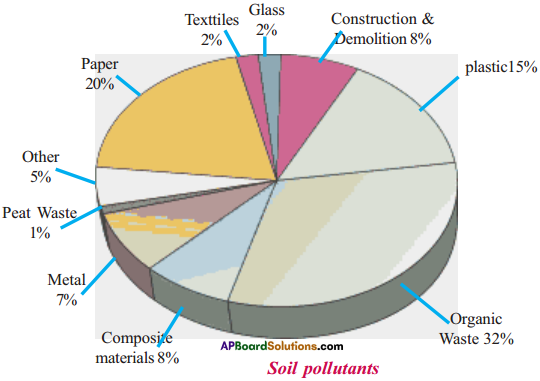
a) Which substance cause less soil pollution?
b) Which of the above pollutants can be biodegradable?
c) Give two examples of construction soil pollutants.
d) Mention any two preventive measures for soil pollution.
Answer:
1) Peat waste (1%).
2) Organic waste, peat waste, paper.
3) Construction and demolition, metals.
4) Using 4’R principle in our daily life implementing comprehensive solid waste management.
![]()
Question 3.
You know that Fluoride cause health hazards, how can you aware people of your village regarding this?
Answer:
- Using surface water sources like rivers and streams.
- Defluoridation technique is very useful in getting Fluorine free water.
- We should not consume the vegetables which are grown in high Fluoride soils.
Question 4.
Plastic is harmful to the environment. What will you do to replace it?
Answer:
We should use paper bags, jute bags and cloth bags in place of plastic bags.
Question 5.
Ravi decided not to use plastic bags. What alternative methods will you suggest?
Answer:
- Using jute covers and cloth bags in place of plastic bags.
- Using bamboo baskets in place of large plastic covers to store and carry goods.
Question 6.
There is an ecosystem, where industrial sewage occurs. Arrange the following living organisms in various trophic levels as per the persistent. (Biomagnification).
Grass, Fish, Sheep, Grass hopper, Phytoplankton, Prawn, Crow, Frog, Larval forms.
Answer:
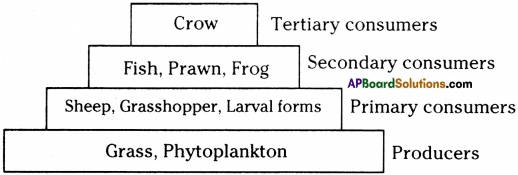
Question 7.

Observe the above diagram, answer the following questions.
i) Name the pollutant which pollutes the soil the most.
ii) Write the biodegradable materials given in the figure.
iii) What will happen if the usage of plastic increased?
iv) What metals pollute the soil, due to the excessive usage of Super Phosphate fertilisers in cultivation?
Answer:
i) Organic wastes 32%
ii) Organic wastes and paper
iii) They remain in the soil for several hundreds of years. They cause a lot of soil pollution. They damage the soil health.
iv) Nitrates and phosphates