SCERT AP Board 9th Class Social Solutions 9th Lesson Credit in the Financial System Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Solutions 9th Lesson Credit in the Financial System
9th Class Social Studies 9th Lesson Credit in the Financial System Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
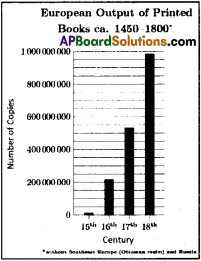
Most of the credit needs of the poor households are met from informal sources. The dependence of richer households on informal credit is less. Do you agree? Use the data given in page 114 to support your answer.
Answer”
- Yes. Most of the credit needs of the poor households are met from informal sources. And the dependence of richer households on informal credit is less. The following statistical data proves that.
- As per All-India Debt and Investment Survey 2003,
a) 85% of the credit needs of the poor households are met from informal sources.
b) Whereas only 10% of the rich households loans are from informal source.
![]()
Question 2.
How are the high interest rates on loans harmful?
Answer:
- Getting loans at high interest rates means a larger part of the earning of the borrowers is used to repay the loans.
- So the borrowers will have less income left for themselves.
- In certain cases, the high interest rate of borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower.
- The debt will be increasing day by day.
- High interest rates and increasing debt sometimes make the farmers depressed and in some cases force them to commit suicides.
Question 3.
What is the basic idea behind the SHGs for the poor? Explain in your own words.
Answer:
- The idea behind selfhelp groups is to organize rural poor, especially women into small groups and pool their savings.
- To help the poor households to get loans at cheaper rates and without difficulty.
- To create self-employment opportunities for the members e.g.: For buying seeds, fertilizers, raw materials, for acquiring assets like sewing machines, hand-looms, cattle, etc.
- These groups are meant to make women financially self-reliant.
- These groups aim to save rural poor section from the traps of moneylenders who charge high interest rates.
Question 4.
Talk to a banker and find out what are the purposes for which people in urban areas generally take loans?
Answer:
Generally, urban people take loans for the following purposes. There is a huge demand for loans for various economic activities.
- To construct a house or to buy a flat.
- To conduct family functions like marriages, deliveries of sisters, etc.
- To purchase household appliances like, fridges, TV, washing machines, furnitures, air conditioners etc.
- To buy vehicles like scooters and cars etc.
- Sometimes they want to establish a business or dream to start a small scale industry for which they may go for a loan.
- Sometimes they take loans to meet the medical expenses of the family members and dependents.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the difference between the bank loans and through SHG?
Answer:
| Loans through the banks | Loans through the SHGs |
| 1. Bank loans require proper documents and collateral. | 1. Collateral usually kept by banks is not necessary. |
| 2. Banks sanction loans to all sections of people. | 2. SHGs generally sanction loans to rural poor, especially women. |
| 3. Loans are generally sanctioned in the name of the individuals. | 3. SHGs sanction loans in the name of the group. |
| 4. Bank loans are generally for many purposes. | 4. These loans are meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members. |
| 5. Recovery of the loan is difficult in case if the individual fails to repay the loan. | 5. All the group members are jointly responsible for the repayment of the loan. Hence recovery of the loan is easy. |
Question 6.
Read the paragraph 3rd under the heading of ‘Self Help Group for the Poor’ and answer the question. How are SHGs working in your area?
| In recent years, government and Non Government Organisations (NGOs) have tried out some newer ways of providing loans to the poor. The idea is to organise rural poor, in particular women, into small Self Help Groups (SHGs) and pool (collect) their savings. A typical SHG has 15-20 members, usually belonging to one neighbourhood, who meet and save regularly. Saving per member varies from Rs. 25 to Rs. 100 or more, depending on the ability of the people to save. Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs. The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the moneylender charges. |
(OR)
“Self Help, Groups play a vital role in the women empowerment. They not only provide economic support but also help in eradicating poverty”. Explain the work of a self help group in your village.
Answer:
The working of SHGs in our area :
- There are 10 to 11 SHGs in our village.
- All are registered. They voluntarily coming together to save regular small savings of money, mutually agreeing to contribute to a common fund and to meet their emergency needs on the basis of mutual help.
- They pool their resources to become financially stable, taking loans from the money collected by that group and by making everybody in that group self-employed.
- They borrow loans from banks and repay it back regularly.
- An economically poor individual gains strength as a part of a group.
Question 7.
What are the services rendered by the banks in fulfilling the needs of farmers?
Answer:
- Short-term loans to farmers for raising crops, i.e. crop loans.
- Medium and long term loans to farmers for agriculture and allied activities.
- Loans to farmers for pre-harvest and post-harvest activities.
- Loans to farmers upto 25 lakh against pledge/hypothication of agriculture produce.
- Export credit to corporates, partnership figures, and institutions engaged in agriculture.
- Loans for purchase of agricultures land.
- Loans to distressed farmers indebted to non-institutional lenders.
- Bank loans to PACS, FSS, LAMPS, etc.
- Loans to farmers under Kisan credit card scheme.
- Export credit to farmers for exporting their own farm produce.
- Loans to allied activities to agriculture.
![]()
Question 8.
Is there any incident of farmers committing suicide in your area? If so, find out reasons and make a report, discuss in the classroom by adding a few newspaper clippings related to this issue.
Answer:
Yes. Recently an incident happened at Atmakur village in Anantapur district. There was a 53-year-old farmer in the village. He was a well-respected farmer. He cultivated cotton. He expanded the small plot he owned by leasing adjoining land. The money was never abundant, but he managed to arrange matches and festive wedding ceremonies for his two sisters, and then his daughters. His sons were sent to school.
And then, his crop failed – heavy rains washed it out two years ago, drought withered his fields the next. He was defeated not just by insurmountable loans but by the humiliation he felt about the unpaid debt. So he committed suicide.
Farmers work from early morning till late night. They wait an entire year to harvest a crop, despite all uncertainty. Most of the farmers are not getting MSP (Minimum Support Price). They are tied to the traders and middlemen who are dealing in agricultural inputs. This depresses the price that farmers are to get for their output. It is time the government implemented the schemes for the welfare of the farmers.
9th Class Social Studies 9th Lesson Credit in the Financial System InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending? (Text Book Page No. 109)
Answer:
- Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns and uses this as a guarantee to a lender.
- It is a security or guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid.
- If the borrower fails to repay the ioan, the lender has the right ot sell the asset or collateral to obtain payment.
Question 2.
How does the demand for collateral affect poor person’s capacity to borrow? (Text Book Page No. 109)
Answer:
- Bank loans require collateral.
- Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevent the poor from getting bank loans.
- In such cases, they approach the moneylenders.
- However, the moneylenders charge high interest rates.
- Finally the poor may be pushed into a situation from which recovery is very difficult.
- Hence the demand for collateral against loans may force the poor to approach informal sources.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the differences between formal and informal sources of credit? (Text Book Page No. 114)
Answer:
| Formal Sources of Credit | Informal Sources of Credit |
| 1. Banks and cooperatives are the formal sources of credit. | 1. Moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives and friends, etc. are the informal sources of credit. |
| 2. The formal credit providers follow certain rules and regulations framed by government and in particular, the RBI. | 2. The informal money lenders do not follow such government rules. They evolve their own procedure. |
| 3. The formal credit providers have to follow certain expectation of government. | 3. These people will not have to reach to the expectations of the government. |
| 4. Rate of interest in the formal source of credit is generally low or reasonable. | 4. Whereas most of the informal lenders charge exorbitant rates, i.e. high interest rates. |
| 5. Banks and cooperatives demand collateral against loans. | 5. Collateral against loans is not necessary for most of the loans. |
| 6. Formal credit providers cannot use any illegal ways to collect the loan amount. | 6. Informal providers use many coercive and illegal ways to collect the loan amount. |
Question 4.
Why should credit at reasonable rates be available for all? (Text Book Page No. 114)
Answer:
- Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
- In such cases, the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower.
- This could lead to increasing debt.
- High interest rates are hurdles for those who want to establish an enterprise.
- For these reasons, banks and cooperative societies need to lend more at reasonable rates.
Question 5.
Why are demand deposits considered as money? (Text Book Page No. 105)
Answer:
- The demand deposits can be withdrawn on demand.
- The demand deposits possess the essential characteristics of money that is a medium of exchange.
- Since demand deposits are accepted widely as a means of payment, along with currency, they constitute money in the modern economy.
![]()
Question 6.
The deposits kept at the bank are also insured by the government? Find out the details. (Text Book Page No. 1o5)
Answer:
- All the commercial banks pay premium to insure the deposits.
- The deposits of the individuals, only to an extent of one lakh, will be issued by the banks.
Question 7.
Do you think fixed deposits that people keep with banks will easily work like money? Discuss. (Text Book Page No. 105)
Answer:
Since one can withdraw money in cash or make payments by cheque it makes these deposits work like any other form of money such as currency notes.
Question 8.
Tick the correct option(s): (Text Book Page No. 110)
(a) Over the years, Rama’s debt
- will rise, (✓)
- will remain constant.
- will decline.
(b) Arun is one of the few persons to take a bank loan. One reason for this is
- He is an educated person.
- Banks demand collateral which everyone cannot provide, (✓)
- Interest rate on bank loans is same as the interest rate charged by the traders.
- There is no documentation work required for getting bank loan.
![]()
Question 9.
Talk to some people to find out the credit arrangements that exist in your area. Record your conversation. Are there any differences in the terms of credit? (Text Book Page No. 111)
Answer:
Credit arrangements in our area :
- Banks
- Gold loans by Gold shop
- Moneylenders
- Finance organizations, etc.
All the terms of credit are one and the same in all the sources except banks. In Banks, getting a loan is tough. But the interest rate, repayment mode, etc. are flexible.
Question 10.
Some SHG groups charge very high interest rates for loans to its members? Is this fair? Discuss. (Text Book Page No. 115)
Answer:
No, it is not fair. The SHGs are formed to help the poor. If it charges high interest rates, the same problem of access to credit arises. So it is not fair. The interest rate should be reasonable as bank’s.
Question 11.
Read the two different credit scenarios of Alisha and Swapna and fill in the following table. (Text Book Page No. 108)
Answer:
| Alisha | Swapna | |
| Why did they need credit? | He is a shoe manufacturer. To complete the production of 3000 pairs of shoes, he needed a loan. | She takes a loan from the moneylender to meet the expenses of cultivation. |
| What was the risk? | Risk is very low. | Risk is high as agriculture is a gambling on monsoons. |
| What was the outcome? | Completed the production on time and made good profits. | The failure of the crop made loan repayment impossible. She has fallen in debt-trap. |
Question 12.
Supposing, Alisha continues to get orders from traders. What would be his position after 6 years? (Text Book Page No. 108)
Answer:
- Financially he may come to a position.
- For next order, he may not borrow loan.
- There is a possibility of establishing small scale industry.
- There is a possibility of employment for others also.
![]()
Question 13.
What are the reasons that make Swapna’s situation so risky? Discuss the following factors: role of moneylenders and climate. (Text Book Page No. 108)
Answer:
1. Pesticides :
Due to low quality of pesticides, the farmers undergo losses. They are deceived many times in this matter.
2. Role of Moneylenders :
Moneylenders lend loans on high rate of interest and there will be a restriction to the farmers to sell the crop production for low price to them only. And they will sell production on higher rates. So moneylenders are benefited from both sides.
3. Climate :
Indian farmers depend on monsoon type of climate. They gamble on monsoon. If sufficient rainfall occurs, farmer will go for better situation. And in case of insufficient rainfall – drought may occur. This leads to worst situation.
So, we can guess that pesticides, role of moneylenders, and climate make Swapna’s situation so risky.
Question 14.
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct option from the brackets : (Text Book Page No. 109)
While taking a loan, borrowers look for easy terms of credit. This means ________ (1) (low/high) interest rate, ________ (2) (easy / tough) conditions for repayment, ________ (3) (less/more) collateral and documentation requirements.
Answer:
- low
- easy
- less
Question 15.
Fill the following details for Sivakami, Arun, Rama, and Vasu. (Text Book Page No. 111)
Answer:
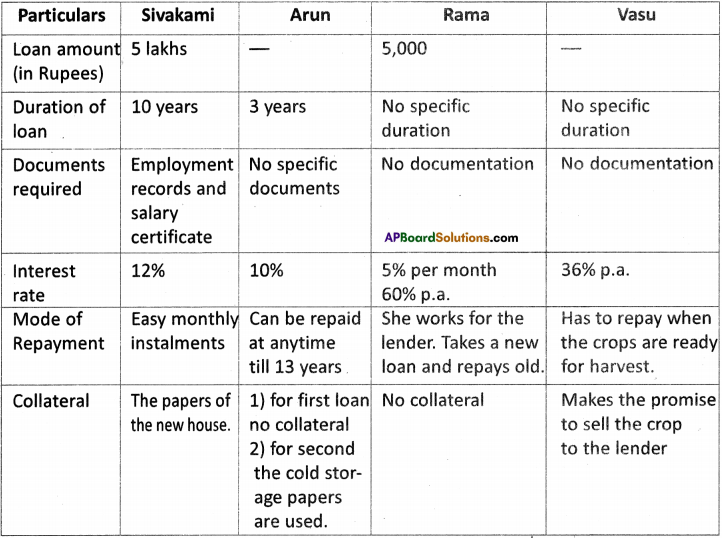
Question 16.
List the different sources of credit in the above examples. (Text Book Page No. 110)
Answer:
- Bank loans
- Cooperative loans
- Moneylenders
- Relatives
- Traders
- The land owners
- The employers, etc.
Question 17.
Underline the various uses of credit in the above passage. (Text Book Page No. 110)
Answer:
- Loan for the construction of a house.
- Loan for completing the production of any kind.
- To meet the expenses of cultivation.
- To meet the expenses on sudden illnesses or functions in the family.
- Sometimes to meet the daily expenses.
Question 18.
How is a loan to an SHG member different from an individual ioan by a bank? (Text Book Page No. 115)
Answer:
SHG loans are group loans and individual loans are personal loans.
![]()
Question 19.
Talk to someone who has taken a bank ioan. What was the purpose and how did she approach the bank? (Text Book Page No. 107)
Answer:
I have conducted an interview with Miss B.P.P.S. Lalitha. She has borrowed an education loan from the SBI, Ongole.
1. She has approached nearest branch of ……………… bank.
2. She has submitted previous education records, father’s income certificate, admission details for the ……………. course, details about the course and job opportunity after the completion.
3. With the above details, she approached Education loan officer. After verifying all the papers he sanctioned the loan. She has to repay the loan amount after completion of her education (immediately after 6 months).
Question 20.
Interview a bank manager. What are the loans that they have given? Are there any activities for which they would not give loans? (Text Book Page No. 107)
Answer:
I have interviewed the bank manager of Andhra Bank, Sai Nagar, Nellore.
The loans they gave are :
- Personal loans!’
- Housing loans
- Education loans
- Vehicle loans
- Mortgage loans
- Gold loans
- SHG loans and
- Business loans, etc.
Other activities:
- Maintains relations with the customers.
- Helping the small entrepreneurs by giving suggestions.
- Acquiring deposits
- Promoting and marketing the branch and its products.
- Meeting with customers and resolving any problems or complaints.
- Ensuring there is a high level of customer service.
- Monitoring sales targets and
- Reporting to head office.
![]()
Question 21.
People also require credit for consumption and to manage many socio-cultural aspects. Marriages require a huge expenditure on both bride and groom which compel families to borrow. Do you think there are other reasons for people borrowinjnTionevinvour area? Find out from your parents and teachers and discuss in the class. (Text Book Page No. 109)
Answer:
Reasons for people borrowing :
1) Life cycle needs :
Such as wedding, funerals child birth, education, house building, widowhood, and old age.
2) Personal emergencies:
Such as sickness, injury, unemployment, theft, harassment of dwellings.
3) Disasters:
Such as fires, floods, cyclones, and man-made events like war or bulldozing of dwellings.
4) Investment opportunities:
Expanding a business, buying land or equipment, improving housing, securing a job (which often requires paying a large bribe), etc.
Question 22.
The following table shows how urban families borrow from two sources in 2003 (in percentage). Read the table carefully and fill in the blanks in the passage given. (Text Book Page No. 113)
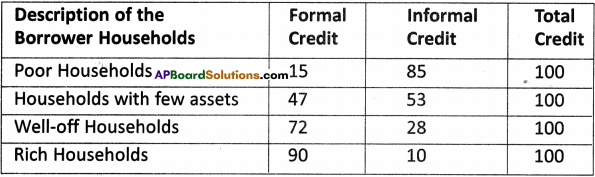
Source : India’s Debit and Investment Survey – 2003 by N.S.S. conducted R.E.P. 501, December 2005.
The table above Shows the share of formal and informal sources for people living in urban areas. The people include both rich and poor households. You can see that ….(1)….per cent of the credit needs of the poor households are met from informal sources. Formal sources of credit account for only ..(2)…per cent. Compare this with the rich households. What do you find? Only ..(3)….percent of their loans are from informal sources, while ..(4)…per cent is from formal sources. You would find a similar pattern in rural areas.
Answer:
- 85%
- 15%
- 10%
- 90%
Question 23.
Find out: What is the role of a federation of SHG groups? (Text Book Page No. 115)
Answer:
i) Federations have been providing a number of services to SHGs and individual members.
ii) These could be grouped into 4 categories.
- Institutional development
- Financial intermediation
- Livelihood enhancement or business development services and
- Social intermediation
Question 24.
What would happen if all the depositors went to ask for their money at the same time? (Text Book Page No. 1o7)
Answer:
- All commercial banks deposit certain percent of their deposits with the Reserve Bank of India.
- Next, advances loans to customers.
- Keeps only 15% of their deposits as cash.
- If all the depositors want their money back, there will not be any liquid cash with the bank.
- When banks are unable to pay cash, then immediately people’s trust on the bank is lost.
![]()
Question 25.
Apart from banks people keep deposits in other institutions such as housing societies, companies, post office schemes, etc. Discuss how is that different from bank deposits? (Text Book Page No. 1o7)
Answer:
- In bank deposits, there will be security for the cash as the banks work under the norms of the RBI. Post office also offers good security. Other than post office and banks, the security for deposits is less.
- There will not be any locking period for the banks. Whereas in societies and other companies, there will be locking period.
- Premature cancellation is possible with the bank deposits which is not possible for other deposits.
Question 26.
Should there be a supervisor such as the Reserve Bank of India that looks into the loan activities of informal lenders? Why would its task be quite difficult? (Text Book Page No. 114)
Answer:
- Due to vast geographical conditions and diversified cultures the Reserve Bank of India cannot check or supervise informal credit.
- Most of the transactions are on oral agreement between the borrower and the lender.
- There will not be any registered transaction. Most of the cases a lot of black money is involved.
Hence it is difficult for the RBI to supervise informal credit.
Question 27.
Can everyone get credit at a cheap rate? Who can get? (Text Book Page No. 11o)
Answer:
- No, everyone cannot get loan at cheap rates.
- Only priority sector, like agriculture, animal husbandary, poultry, etc. gets loan at cheaper rates.
- Banks have to extend 40% of their loans to priority sector.
![]()
Question 28.
Do you think that the low share of formal sector credit for poorer households has been one of the factors for farmer distress in Andhra Pradesh? Discuss. (Text Book Page No. 114)
Answer:
- Absence of collateral is one of the major reason which prevents the poor from getting formal loans.
- Informal lenders know the borrowers personally. Hence they give loans but charge very high interest rates.
- High interest rates charged by informal loans and crop failures, etc. are the reasons for distress of farmers in Andhra Pradesh.