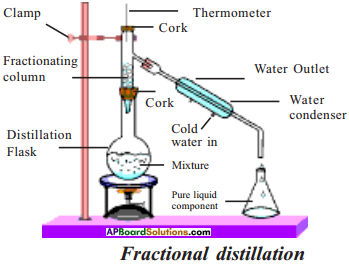
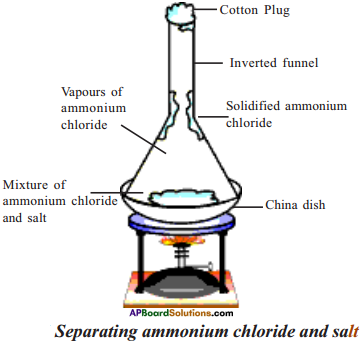
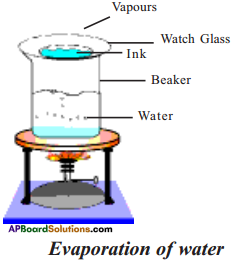
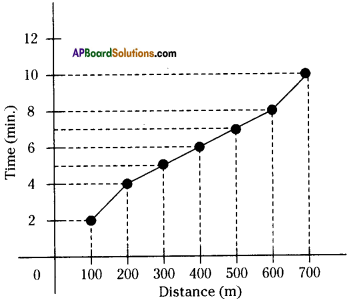
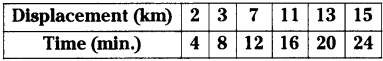
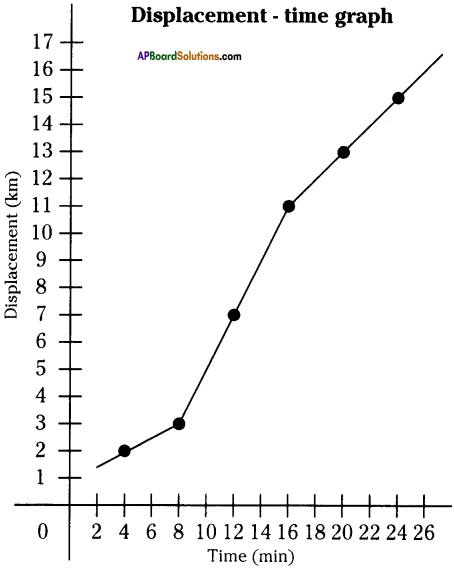
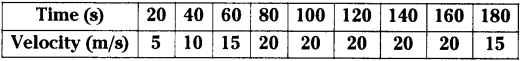
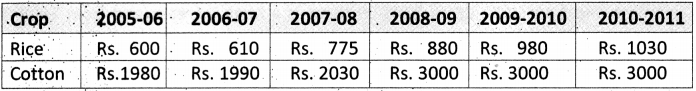
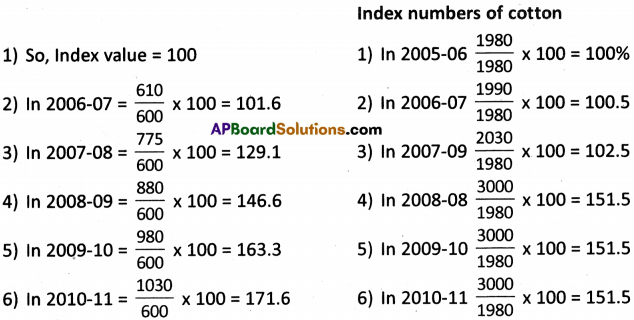
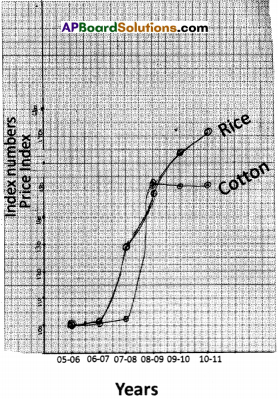
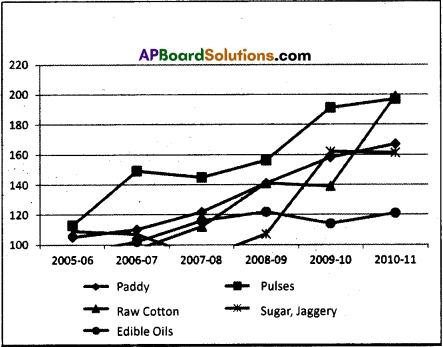
AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Physical Science Solutions Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions and Equations Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Physical Science Solutions 6th Lesson Chemical Reactions and Equations
9th Class Physical Science 6th Lesson Chemical Reactions and Equations Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Answer:
1) A chemical equation in which the number of atoms of different elements on the reactants side (left side) are same as those on product side (right side) is called a balanced chemical equation.
Ex : Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 ↑
2) All the chemical equations must balance because atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions.
3) The number of atoms of each element before and after reaction must be the same.
4) According to the law of conservation of mass, the total mass of the substances that are taking part in a chemical reaction must be the same before and after the reaction.
Question 2.
Balance the following chemical equations.
a) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
b) Hg (NO3)2 + KI → Hgl2 + KNO3
c) H2 + O2 → H2O
d) KClO3 → KCl + O2
e) C3H8 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Answer:
a) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
b) Hg (NO3)2 + 2 KI → Hgl2 + 2KNO3
c) 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
d) 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
e) C3Hg + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
![]()
Question 3.
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
a) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
b) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
c) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
d) Ammonium nitrate → Nitrous Oxide + Water
Answer:
a) Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
b) 2Al + 3CuCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3Cu
c) H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
d) NH4NO3 → N2O + 2H2O
Question 4.
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
a) Calcium hydroxide(aq) + Nitric acid(aq) → Water(l) + Calcium nitrate(aq)
b) Magnesium(sJ + Iodine → Magnesium Iodide(s)
c) Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) → Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen^
d) Zinc(s) + Calcium chloride(aq) → Zinc Chloride(aq) + Calcium(s)
Answer:
a) Ca(OH2) + HNO3 → H2O + Ca(NO3)2
This is double decomposition reaction.
b) Mg + I2 → Mgl2
This is chemical combination reaction.
c) Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 ↑
This is chemical displacement reaction.
d) Zn + CaCl2 → ZnCl2 + Ca
This is chemical displacement reaction. This reaction is not possible, because calcium is more reactive than zinc.
![]()
Question 5.
Write an equation for decomposition reaction where energy is supplied in the form of heat / light / electricity.
Answer:
Chemical decomposition reaction : A chemical reaction in which a single substance splits into two or more substances is called chemical decomposition.
For decomposition reaction energy is supplied in the form of :
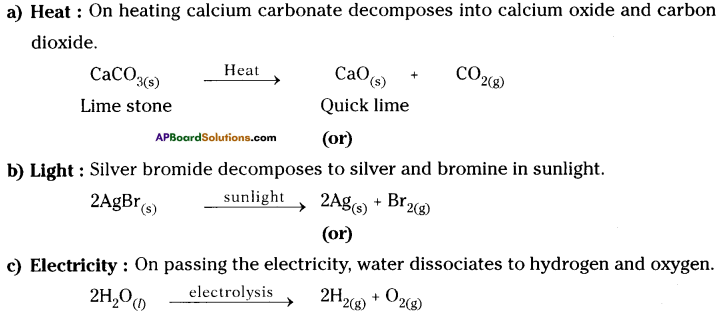
Question 6.
What do you mean by precipitation reaction?
Answer:
A reaction in which insoluble substance in water is formed as product is called precipitation reaction.
Question 7.
How does chemical displacement reactions differ from chemical decomposition reaction? Explain with an example for each.
Answer:
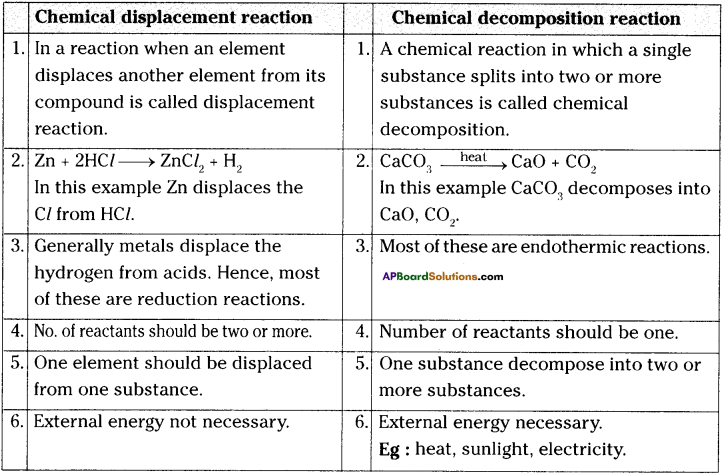
Question 8.
Name the reactions taking place in the presence of sunlight.
Answer:
1) In the presence of sunlight plants prepare their food by taking C02 from the air and H20 from the soil with their chloroplasts of the green leaves. This reaction is called photosynthesis.
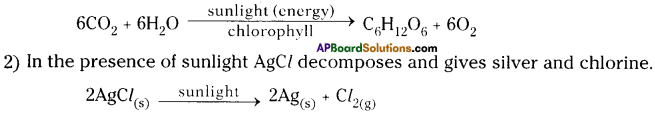
Question 9.
Why does respiration considered as an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Answer:
- We need energy to stay alive.
- We get this energy from food we eat.
- During digestion, food is broken down into simpler substances.
- For example, rice and potato contains starch.
- The starch breaks down to form glucose.
- This glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body and releases energy, which helps to do the various works.
- During this process, energy is given out. Hence this reaction can be called exothermic reaction.
- The special name of this reaction is respiration.
- So respiration is considered as exothermic reaction.
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Q (Energy)
![]()
Question 10.
What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
| Chemical displacement reaction | Chemical double displacement reaction |
| 1. In a reaction when an active element displaces less active element from its compound is called displacement reaction. | 1. If two reactants exchange their constituents chemically and form two products, then the reaction is called as double displacement reaction. |
| 2. Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 In this example Zn displaces Hydrogen from HCl. |
2. Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl In this reaction SO42- and Cl– are mutually exchanged. |
| 3. General formula to the reaction is A + BC → AC + B |
3. General formula to the reaction is AB + CD → AD + BC |
Question 11.
MnOz + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 ↑
In the above equation, name the compound which is oxidized and which is reduced.
Answer:
In the above equation, HCl compound is oxidized and MnO2 is reduced.
Question 12.
Give two examples for oxidation-reduction reaction.
Oxidation :
Oxidation is a reaction that involves the addition of oxygen or loss of hydrogen or electrons.
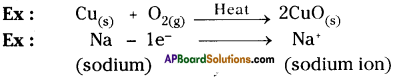
Reduction :
The process in which a substance loses oxygen or gains hydrogen or electrons is known as reduction.
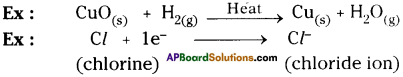
Question 13.
In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write the reaction involved.
Answer:
- Cu(s) + 2 AgNO3(aq) > Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
- This is redox reaction, copper is the reducing agent and the silver is reduced.
- Electrons from the copper metal are transferred to the silver.
- This reaction can also be called a displacement reaction because copper displaces silver as it is more reactive.
Question 14.
What do you mean by corrosion? How can you prevent it?
Answer:
- When some metals are exposed to moisture, acids, etc. they tarnish due to the formation of respective metal oxide on their surface. This process is called “corrosion”.
- Corrosion can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanizing, chrome plating or making alloys.
- Galvanizing is a method of protecting iron from rusting by coating them a thin layer of zinc.
![]()
Question 15.
Explain rancidity.
Answer:
- Oxidation reactions in food material that were left for a long period are responsible for spoiling of food. This process is called “rancidity”.
- When these processes occur in food, undesirable odours and flavours can result.
- Rancidity is an oxidation reaction.
Question 16.
Balance the following chemical equations including the physical states,
a) C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + CO2
b) Fe + O2 → Fe2O3
c) NH3 + Cl2 → N2H4 + NH4Cl
d) Na + H2O → NaOH + H2
Answer:
a) C6H12O6(s) → C2H5OH(l) + CO2(g)
b) Fe(s) + O2(g) → Fe2O3(s)
c) NH3(aq) + Cl2(g) → N2H4(l) + NH4Cl(aq)
d) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → NaOH + H2
Question 17.
Balance the chemical equation by including the physical states of the substances for the following reactions.
a) Barium chloride and Sodium sulphate aqueous solutions react to give insoluble Barium sulphate and aqueous solution of Sodium chloride.
b) Sodium hydroxide reacts with Hydrochloric acid to produce Sodium chloride and water.
c) Zinc pieces react with dilute Hydrochloric acid to liberate Hydrogen gas and forms Zinc chloride.
Answer:
a) BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s)↓ + NaCl(aq)
b) NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
c) Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
![]()
Question 18.
A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Can you predict the element ‘X’ and the black coloured substance formed? How do you support your predictions?
Answer:
The brown coloured element is copper (Cu). On heating copper reacts with oxygen
present in the atmosphere to form copper oxide which is black in colour.
The reaction is shown below.
![]()
If we pass hydrogen gas over hot copper oxide we will notice that black coating on copper turns brown because copper oxide loses oxygen to form copper.
This will support our prediction.
![]()
Question 19.
Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer:
- Ferrous reacts with oxygen in the air and form iron oxide.
2 Fe + O2 → 2 FeO - This reaction is called corrosion. It spoils the iron articles by rusting.
- Corrosion of iron articles can be prevented or minimized by shielding the metal surface from oxygen and moisture.
- It can be prevented by applying paint on the articles.
Question 20.
What is the use of keeping food in air tight containers?
Answer:
- Oxidation is defined as the interaction of oxygen molecules with all the different substances from metal to living tissue which may come into contact with it.
- When fats and oils are oxidized they become rancid. Their smell and taste change.
- Keeping food in airtight containers helps to slow down oxidation process.
- So, manufacturers of potato chips usually flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen to prevent the chips from getting oxidized.
Fill in the Blanks
1. The decomposition of vegetable into compost is an example of ……………. reaction.
2. The chemical reaction in which energy is absorbed to form a new compound is called ………….
3. The reaction 2N2O → 2N2 + O2 is an example for ………….. reaction.
4. The reaction Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2 ↑ is an example for ………….. reaction.
5. The substances that are present on left side of a chemical equation are called
6. The arrow mark between the products and reactants of a chemical equation shows of the reaction.
Answer:
- oxidation
- endothermic reaction
- decomposition
- displacement
- reactants
- direction
7. Match the following :
| 1) 2AgNO3 + Na2CrO4 → Ag2CrO4 + 2NaNO3 | a) combination reaction |
| 2) 2NH3 → N2 + 3H2 | b) decomposition reaction |
| 3) C2H4 + H2O → C2H6O | c) displacement reaction |
| 4) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2 | d) double displacement reaction |
Answer:
| 1) 2AgNO3 + Na2CrO4 → Ag2CrO4 + 2NaNO3 | d) double displacement reaction |
| 2) 2NH3 → N2 + 3H2 | b) decomposition reaction |
| 3) C2H4 + H2O → C2H6O | a) combination reaction |
| 4) Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2 | c) displacement reaction |
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of:
A) Combination reaction
B) Decomposition reaction
C) Displacement reaction
D) Double decomposition reaction
Answer:
C) Displacement reaction
![]()
2. What happens when dil. hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings? Choose the correct answer.
A) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
B) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
C) No reaction takes place.
D) Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer:
A) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
3. 2PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
Which of the following statements are correct for the above chemical reaction?
i) Lead is reduced
ii) Carbon dioxide is oxidized
iii) Carbon is oxidized
iv) Lead oxide is reduced
A) (i) and (ii)
B) (i) and (iii)
C) (i), (ii) and (iii)
D) all
Answer:
B) (i) and (iii)
4. The chemical equation
BaCl2 + Na2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl represents following type of chemical reaction.
A) displacement
B) combination
C) decomposition
D) double-displacement
Answer:
D) double-displacement
![]()
5. The reaction of formation hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine repre¬sents following type of chemical reaction i
A) decomposition
B) displacement
C) combination
D) double-displacement
Answer:
C) combination
9th Class Physical Science 6th Lesson Chemical Reactions and Equations InText Questions and Answers
9th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 90
Question 1.
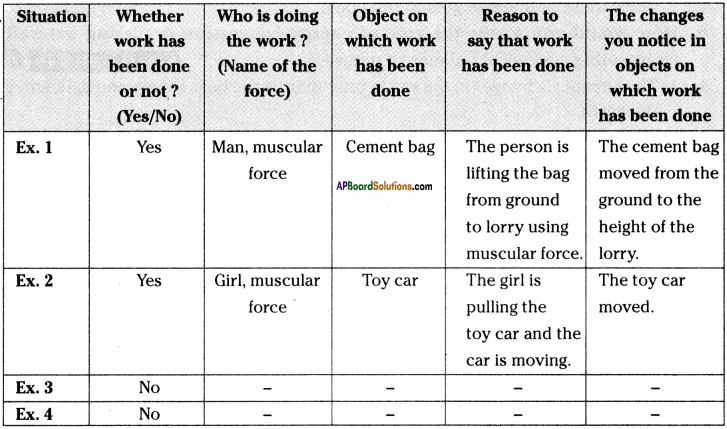
What changes do you notice generally?
Answer:
I noticed two types of changes generally. They are :
- Physical change,
- Chemical change.
Question 2.
“Coal is burnt”, “crackers are burnt” ………. changes Are they physical changes (or) chemical changes?
Answer:
They are all chemical changes.
Question 3.
Are they (coal, crackers) temporary changes or permanent changes?
Answer:
They are permanent changes.
![]()
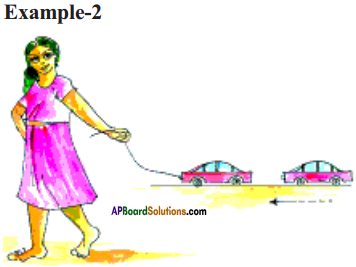
Question 4.
How do we know a chemical reaction has taken place?
Answer:
While we observe the following things, we can conclude that a chemical reaction has taken place.
- A change that changes state and colour of substance.
- A change that releases heat energy.
- A change which forms an insoluble substance as precipitate.
- A change that liberates a gas.
9th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 92
Question 5.
Do the atoms of each element on left side equal to the atoms of the element on the right side of the equation?
Answer:
Yes. The atoms of each element in left side are equal to the atoms of their corresponding element.
9th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 94
Question 6.
Are the atoms of all elements of reactants present in products?
Answer:
Yes. The atoms of all elements of reactants are present in products.
![]()
Question 7.
2 C3H8 + 10 O2 → 6 CO2 + 8 H2O.
Is it a well balanced equation as per rules ? How do you say?
Answer:
Yes, it is a balanced equation.
| L.H.S. | R.H.S. |
| Number of ‘C’ atoms = 6 | Number of ‘C’ atoms = 6 |
| Number of ‘H’ atoms = 16 | Number of ‘H’ atoms = 16 |
| Number of ‘O’ atoms = 20 | Number of ‘O’ atoms = 20 |
9th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 105
Question 8.
Did you notice the colour coating on silver and copper articles?
Answer:
Yes. I noticed. To prevent from corrosion they are colour coated like that.
9th Class Physical Science Textbook Page No. 106
Question 9.
How can we prevent the spoiling of food?
Answer:
The spoilage of food can be prevented by adding preservatives like vitamin C and vitamin E.
9th Class Physical Science 6th Lesson Chemical Reactions and Equations Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
Write an activity when calcium oxide reacts with water.
What type of reaction is this ? Write balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
- Take about 1 gm of quick lime (CaO) in a beaker.
- Add 10 ml of water to this.
- Touch the beaker with your finger.
- The beaker is hot.
- The reason is that the calcium oxide reacts with water and releases heat energy.
- Calcium oxide dissolves in water producing colourless solution [Ca(OH)2],
- Dip the red litmus paper in it.
- Red litmus paper changes into blue colour.
- We conclude that the solution obtained is a basic solution.
- It is a chemical combination reaction.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2
Activity – 2
Question 2.
What change do you observe by mixing of sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution?
(OR)
Which type of reaction is this (mixing of sodium sulphate and barium chloride solutions)?
Answer:
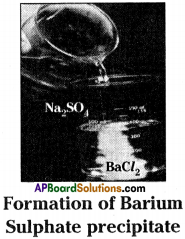
- Take about 100 ml of water in a beaker.
- Dissolve a small quantity of sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) in it.
- Take about 100 ml of water in another beaker.
- Dissolve a small quantity of barium chloride (BaCl2) in it.
- Add these (Na2SO4, BaCl2) two solutions.
- We will get a white precipitate of barium sulphate.
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4↓ + 2NaCl - It is a double displacement reaction.
Activity – 3
Question 3.
Formation of H2 gas by the action of dil. HCl and Zn pieces.
(OR)
What happens if dilute HCl is added to zinc granules. Explain the process with an experiment. What type of reaction is this? Write the balanced chemical equation for this process.
Answer:
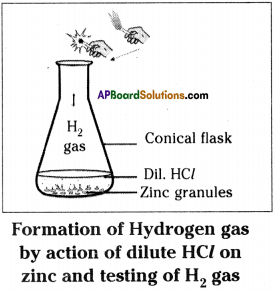
Hydrogen gas experiment:
- Take a few zinc granules in a conical flask.
- Add about 5 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid to the conical flask.
- Observe the changes in the conical flask.
- Keep a burning matchstick near the mouth of the conical flask.
- The light of burning matchstick is put off with ‘pop’ sound.
- This indicates the H2 gas has released in this reaction.
- When we touch the bottom of the conical flask with our finger, we feel hot.
- So, this reaction produces heat.
- It is a displacement reaction
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Activity – 4 Chemical Combination
Question 4.
Write an activity on burning of magnesium ribbon in the presence of air.
(OR)
Write an activity which shows burning of magnesium ribbon is a chemical combination reaction.
Answer:

1) Take about 3 cm long piece of magnesium ribbon.
2) Rub the magnesium ribbon with sand paper.
3) Hold it with a pair of tongs.
4) Burn it with a spirit lamp or burner.
5) Magnesium burns in oxygen by producing dazzling white flame and changes into white powder (magnesium oxide).
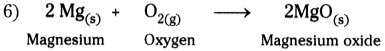
7) In this reaction magnesium and oxygen combine to form a new substance magnesium oxide.
8) A reaction in which single product is formed from two or more reactants is known as chemical combination reaction.
Activity – 5 Decomposition Reaction
Question 5.
How can you prove that CO2 is released on heating CaCO3?
(OR)
When calcium carbonate is heated it releases certain gas. What is the gas that has been released? How do you identify that gas? Write the activity of this reaction.
Answer:
- Take a pinch of Calcium Carbonate (lime stone) in a boiling tube.
- Heat the boiling tube over the flame of spirit lamp or burner.
- Now take a burning matchstick near the mouth of delivery tube.
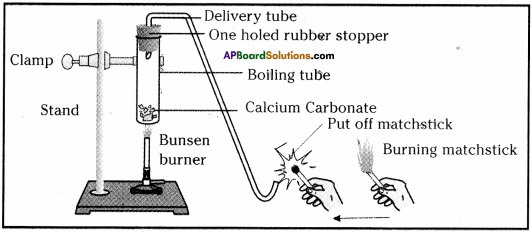
Heating of calcium carbonate and testing the gas evolved with burning matchstick
- We can observe that the matchstick kept near the mouth of the boiling tube will be put off.
- In the above activity, on heating CaC03, it decomposes to Calcium oxide (CaO) and Carbon dioxide (CO2).
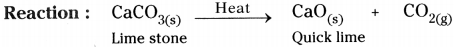
- When a decomposition reaction is carried out by heating, it is called thermal decomposition reaction.
Activity – 6
Question 6.
Write an activity to show that nitrogen dioxide (NO^ is released by heating of lead nitrate.
(OR)
Write an activity which shows thermal decomposition reaction.
Answer:
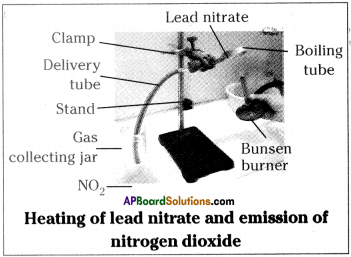
- Take about 0.5 g of lead nitrate powder in a boiling test tube.
- Hold the boiling tube with a test tube holder.
- Heat the boiling tube over a flame.
- We observe that on heating of lead nitrate brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide are released.
- On heating lead nitrate, it decomposes and gives lead oxide, oxygen and nitrogen dioxide.
6) Reaction :
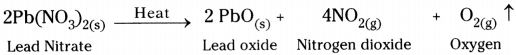
7) This is also an example for thermal decomposition reaction.
Activity – 7
Question 7.
Write an activity to show dissociate of water into hydrogen and oxygen.
(OR)
Write an activity showing decomposition of a compound in the presence of electricity.
(OR)
Draw a neat diagram representing electrolysis of water.
How do you prove that water contains hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 2 : 1?
(OR)
Explain electrolysis of water.
(OR)
What are the materials required for the experiment to show the chemical decomposition of water ? Write the procedure of the experiment. Name the products which we get in this reaction.
(OR)
Draw a neat diagram showing the electrolytic decomposition reaction of water. Write the balanced chemical equation of the above reaction.
Answer:
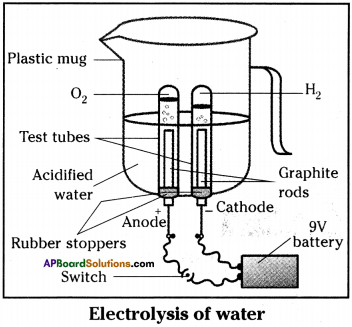
- Take a plastic mug.
- Drill two holes at its base.
- Fit two ‘one holed rubber stoppers’ in these holes.
- Insert two graphite electrodes in these rubber stoppers.
- Connect the electrodes to 9V battery.
- Fill the mug with water, so that the electrodes are immersed.
- Add few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to water.
- Take two test tubes filled with water and invert them over the two graphite electrodes.
- Switch on the current and leave the apparatus undisturbed for sometime.
- We will notice that the liberation of gas bubbles at both the electrodes.
- These bubbles displace the water in the test tubes.
- We also observe that the volume of gas collected in the both test tubes is different.
- Once the test tubes are filled with gases take them out carefully.
- Test both the gases separately by bringing a burning candle near the mouth of each test tube.
- The gas which occupies high volume makes to burn with blue flame and put off candle flame with ‘puf sound is hydrogen gas.
- The gas which occupies low volume and makes to burn candle brightly is oxygen gas.
- In the above activity on passing the electricity, water dissociates to hydrogen and oxygen gases. This is called electrolytic composition reaction.
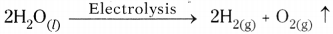
Activity – 8
Question 8.
Write an activity to observe silver bromide decomposes in the presence of sunlight.
(OR)
Write an activity for photochemical reaction.
Answer:
- Take some quantity of silver bromide on a watch glass.
- When we observe the colour of silver bromide it is light yellow in colour.
- Place the watch glass in sunlight for sometime.
- Silver bromide decomposes to silver and bromine in sunlight.
- After sometime we observe that the colour of silver bromide changes into grey colour.

- Light yellow coloured AgBr changes into Ag and Br.
- This decomposition reaction occurs in the presence of sunlight and such reactions are called photochemical reactions.
- The above decomposition reactions require some energy to convert reactants to products.
- This type of reactions are called endothermic reactions.
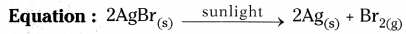
Activity – 9
Question 9.
Write an activity to show that zinc displaces hydrogen from dil. hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
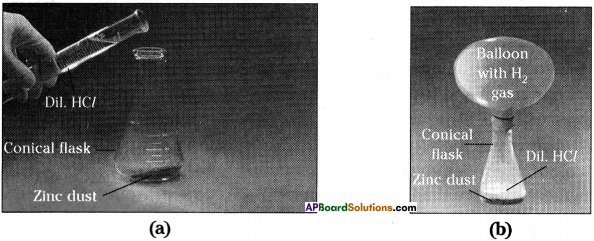
- Take a small quantity of zinc dust in a conical flask.
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid slowly.
- Now take a balloon and tie it to the mouth of the conical flask.
- We can observe that the gas bubbles coming out from the solution and the balloon bulges out.
- Zinc pieces react with dilute hydrochloric acid and liberate hydrogen gas.
- The element zinc has displaced hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid. This is one of the examples for displacement reaction.
- Equation : Zn(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) ↑
Activity – 10
Question 10.
Write an activity to show that iron displaces copper from copper sulphate.
(OR)
Write an activity about how you conduct an experiment to show that more reactive metals replace less reactive metals from their compounds. (OR)
Why is an iron nail kept in a solution brownish? Explain the activity.
Answer:

- Take two iron nails and clean them by rubbing with sand paper.
- Take two test tubes and mark them as A and B.
- Take about 10 ml of copper sulphate solution in each test tube.
- Dip one iron nail in copper sulphate solution of test tube A.
- Keep the test tube with iron nail undisturbed for 20 minutes.
- Keep the other iron nail and test tube aside. ;
- Compare the colours of the solutions in the test tubes.
- Now take out the iron nail from copper sulphate solution.
- Keep the iron nail and test tubes A and B side by side.
- Compare with the other iron nail that has been kept aside.
- We will observe that the iron nail dipped in copper sulphate solution becomes brownish.
- Blue colour of copper sulphate solution in test tube ‘A’ fades.
- Iron is more reactive than copper, so it displaces copper from copper sulphate.
- This is one of the examples for displacement reaction.
- Equation : Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Activity – 11 Double displacement reaction
Question 11.
Write an activity for the formation of lead iodide and potassium nitrate.
(OR)
Your friend has a doubt about chemical double displacement reaction. How can you clarify his/her doubt by showing an experiment? Explain.
(OR)
What happens if lead nitrate solution is added to potassium iodide solution? Explain the activity.
Answer:

It forms yellow precipitate of lead iodide.
- Take a pinch of lead nitrate and dissolve in 5.0 ml of distilled water in a test tube.
- Take a pinch of potassium iodide in another test tube and dissolve in distilled water.
- Mix lead nitrate solution with potassium iodide solution.
- We observe that a yellow coloured substance which is insoluble in water, is formed.
- This insoluble substance is known as precipitate.
- The precipitate is Lead Iodide.
- Equation : Fb(NO3)2(aq) + 2 KI(aq) → Pbl2(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
- In the above reaction, lead ion and potassium ion exchange their places each other.
- Lead ion combines with iodide ion and forms Pbl2 as precipitate and KN03 remains in the solution.
- Such reaction is double displacement reaction.
Activity – 12
Question 12.
Write an activity to show that the oxidation of copper to copper oxide.
(OR)
Write an activity for example of oxidation and reduction.
Answer:
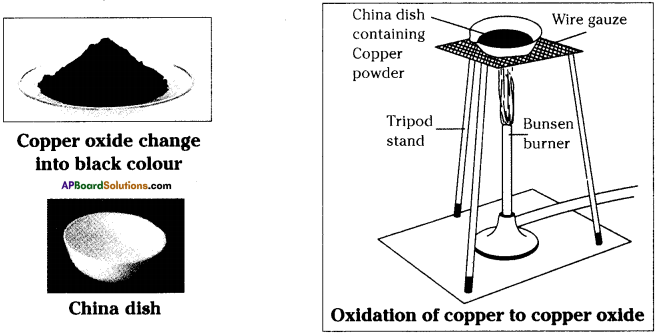
- Take about 1.0 gram of copper powder in a China dish.
- Keep the China dish on a tripod stand containing wire gauze.
- Heat it with a bunsen burner or with a spirit lamp.
- We can find that the surface layer of copper becomes black.
- On heating copper reacts with oxygen present in the atmosphere to form copper oxide.
![]()
- Here copper combines with oxygen to form copper oxide.
- Here oxygen is gained and the process is called oxidation.
- Now pass hydrogen gas over hot copper oxide.
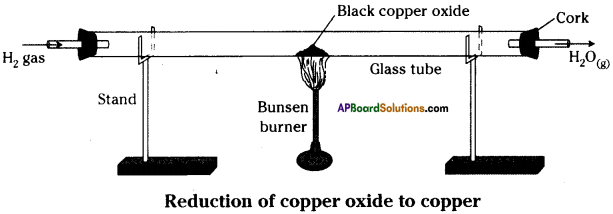
- We can observe that the black coating on copper turns brown because copper oxide loSes oxygen to form copper.
- In this process oxygen is lost and the process is called ”Reduction”.
![]()