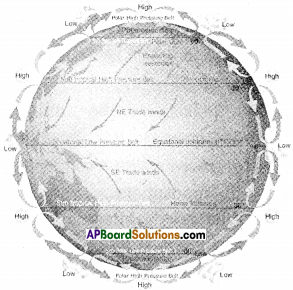
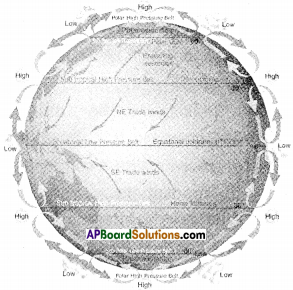
AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Social Studies Important Questions Chapter 2 The Natural Realms.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Social Studies Important Questions 2nd Lesson The Natural Realms
9th Class Social 2nd Lesson The Natural Realms 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write any two landforms which are formed by work of water? (SA-II : 2016 – 17)
Answer:
V-shaped valley. Deltas etc.
Question 2.
Give any one reason for the following. (SA-I : 2019 – 20)
Answer:
The majority of Earth’s volcanoes and earthquakes take place along the pacific basin. A. Plate boundaries are found all the way around the pacific basin.
9th Class Social 2nd Lesson The Natural Realms 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the effects of movements of tectonic plates. (SA-III : 2015 – 16)
Answer:
- The movement of these plates have changed the position and size of the continents over millions of years.
- These movements influenced the evaluation of the present land form features of India.
- The movement of plates form a chain of mountains.
- This process causes earthquakes etc.
![]()
Question 2.
Arrange the following concept in a correct manner in the given table. (SA-II : 2017 – 18)
Concept: Mushroom rock, Sea arches, plunge pool, U shaped valley.
| Factors | Land forms |
| 1. Work of water | |
| 2. Work of glaciers | |
| 3. Work of winds | |
| 4. Work of waves . |
Answer:
| Factors | Land forms |
| 1. Work of water | Plunge pool |
| 2. Work of glaciers | U Shaped valley |
| 3. Work of winds | Mushroom rock. |
| 4. Work of waves . | Sea arches |
Question 3.
With reference to the Third Order Landforms, answer the following questions : (SA-I : 2019 – 20)
a) What are ‘Third Order Landforms’?
Answer:
The shaping of the landforms by wind and water are called ‘Third Order Landforms’.
b) What are the factors that cause their formation?
Answer:
Water, wind, glaciers and waves.
9th Class Social 2nd Lesson The Natural Realms 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain how air and water transform the surface of the Earth? (SA-II : 2018 – 19)
Answer:
The Air and water transform the surface of the earth by the four activities.
These are:
Weathering :
Water and moisture in the air also help this process. Water reacts with the chemicals of the rocks and further weakens the rock. These processes by which the rocks are weakened and broken are called “Weathering”.
Erosion :
Flowing water and wind have great power and can slowly wear away or cut away the rocks and soil cover in higher places. Water acts in many ways, as rain, river, flowing ground water, sea waves, glaciers etc. Wind too takes many forms like storms, gusts etc.
The active wearing away of the earth’s surface by these moving agents is called erosion.
Transportation :
The eroded material in the form of small rocks, gravel, mud fine soil etc. carried by winds and water is called transportation.
Deposition :
When the rivers and winds slow down, they do not have the force to carry the material any more and they dump them. This dumped debris help to form plains and river basins.
9th Class Social 2nd Lesson The Natural Realms Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the natural realms of the Earth? Describe them.
Answer:
There are four natural realms of the earth. They are
- Lithosphere
- Hydrosphere
- Atmosphere
- Biosphere.
1. Lithosphere:
The hard top part of the earth, the solid crust, which is made up of rocks and minerals and covered with a thick layer of soil. Soil is called lithosphere. It has high mountains, plateaus, plains, deep valleys and oceans. We and most other living beings live on this realm.
2. Hydrosphere :
The realm of water is called hydrosphere. It comprises various sources of water and different types of water bodies like rivers, lakes, seas, oceans, etc. and in the atmosphere in the form of water vapour and clouds. Life on earth is not possible without water.
3. Atmosphere :
The thin layer of air that surrounds the earth is atmosphere. It consists of a large number of gases including oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, water vapour, etc. and also dust particles. This cover of air is held around the earth by its gravitational force and rotates around the sun with the Earth.
4. Biosphere :
The realm of life including bacteria which live high on atmosphere or in deep oceans constitutes the biosphere. Life needs the presence of all the three realms, land, water and air. So life resides in the intersection of the three natural realms. Life also actively changes the three other realms.
![]()
Question 2.
What are called plates? How many plates are there on the earth?
Answer:
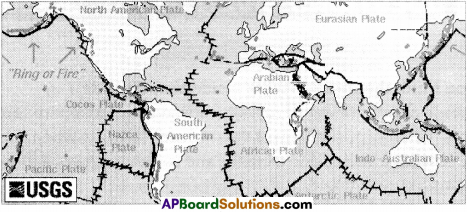
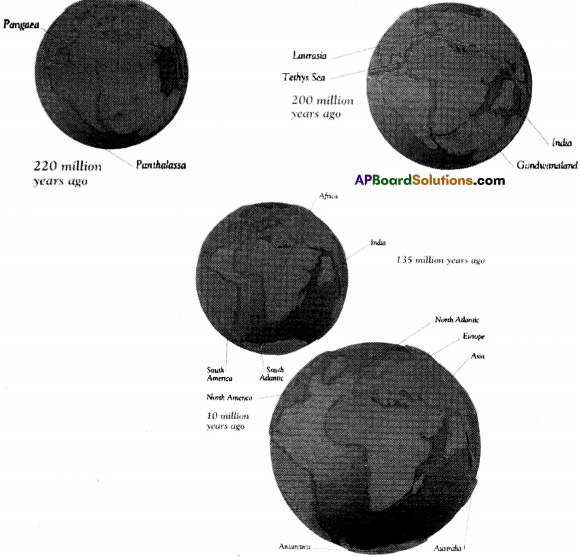
The massive base of rocks on which all the continents and even the oceans are actually situated are called plates. There are six major plates and several minor ones on the Earth. The African, North American, South American, Indo-Australian, Antarctic, Eurasian, and Pacific are the major plates. Nazca and Arabian are some among the minor plates.
Question 3.
What are plate tectonics? How are they caused?
Answer:
- The plates actually float on the mantle.
- They are constantly being pushed and therefore keep moving slowly.
- As a result of this movement, one plate pushes another neighbouring plate.
- One plate is pushed under into the mantle while the other plate is pushed up to form a chain of mountains.
- This movement of plates is called plate tectonics.
- Plate tectonics cause earthquakes.
Question 4.
What is called sea-floor spreading? How does it occur?
Answer:
The eruptions on the mid-ocean ridge create new ocean floor made of basalt rocks, which then spread literally from the ridge and this newest crust slowly pushes the plate away from the ridge, which is called ‘sea-floor spreading’.
Question 5.
How is the river deposition useful to man?
Answer:
- As water in a river flows down a slope, it plucks sediment from the land. Other streams join it forming a broad river basin.
- The water carries soil, sand and sediments down stream.
- As the river reaches flatter ground, it slows down and drops the sediments there. This is called deposition.
- The sediments build up a flood plain.
- At the river’s mouth, the water loses its force, drops all its sediments and thus deltas are formed.
- Flood plains and deltas make fertile farm land.
- The sediments deposited in flood plains and deltas are called silt.
- Silt is rich in nutrients.
- Many ancient civilisations flourished in flood plains and deltas.
Thus the deposition of rivers are useful to man.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the landforms originated by the wind action?
Answer:
Strong winds carry sand and fine soil which strike the hard rocks. These too act as abrasive sand paper and erode the hard rocks. The wind action creates a number of interesting erosional and depositional features in the desert.
1. Sand Dunes :
Due to weathering and persistent wind action there is a large accumulation of fine sand in many deserts. These form ‘sand dunes’.
2. Mushroom Rock :
Winds erode the lower section of the rocks more than the upper part. Therefore such rocks have narrower bottom and wider top like mushrooms. So they are called mushroom rocks.
3. Inselberg:
The isolated residual hills rising abruptly from the ground are called inselberg or Island Mountain. They are characterized by their very steep slopes and rather rounded tops.
4. Loess Plains :
a) The fine dust, which is fertile and yellow in colour, is blown beyond the deserts and is deposited on neighbouring land. This soil is called Loess. Loess are in fact fine loam, rich in lime and extremely porous.
b) The plains formed by deposition of loess are called Loess Plains.
Question 7.
Name the landforms due to the Glacier action.
Answer:
1. Slow moving of mass of ice (a river of ice) is called Glacier.
2. A Glacier erodes through a process called “Plucking” in which it lifts pieces of rock and transports them.
3. The landforms created due to Glacier’s action are :
a) U shaped Valley:
Through the dual process of plucking and abrasion, glaciers create a “U shaped Valley”.
b) Moraines :
Pebbles, cobbles, sand etc., may be deposited at various parts of the
glaciers. The deposition of this till is called moraines. –
c) Huge rugged boulders:
The huge rocks, which cannot be carried by, are left behind in the form of huge rugged boulders.
d) Ozone :
Ozone is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula 03. It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. Ozone’s 03 formula was determined in 1865.
![]()
Question 8.
Prepare a table showing depositional and erosional features separately.
Answer:
| Features of deposition | Features of erosion |
| 1. When the rivers and winds slow down they do not have the force to carry the materials any more and they dump them. | 1. Flowing water and wind have great power. They can slowly wear away or cut away the rocks and soil cover in higher places. |
| 2. This dumped debris helps to form plains and river basins. | 2. Water as rain, river, flowing ground water, sea waves, glaciers is responsible for erosional activities. |
| 3. Much of the debris is actually transported by rivers to the sea. Layer after layer these deposits accumulate in the bottom and overtime get transformed to sedimentary rocks. | 3. The active weathering away of the earth’s surface by these moving agents is called erosion. |
| 4. The landforms formed because of deposition are 1. plains 2. deltas 3. meanders 4. ox-bow lakes and 5. sand dunes and beaches. | 4. The landforms formed because of erosion are 1. V-shaped valleys 2. Gorges 3. Canyons 4. Plunge pools 5. U-shaped valleys 6. Inselberg 7. Mushroom rock, etc. |
Question 9.
What are the natural realms of the Earth?
Answer:
There are four natural realms of the earth. They are
- Lithosphere
- Hydrosphere
- Atmosphere and
- Biosphere.
Question 10.
What are called plates?
Answer:
The massive base of rocks on which all the continents and even the oceans are actually situated are called plates.
Question 11.
What is called sea-floor spreading?
Answer:
The eruptions on the mid-ocean ridge create new ocean floor made of basalt rocks, which then spread literally from the ridge and this newest crust slowly pushes the plate away from the ridge, which is called ‘sea-floor spreading’.
Question 12.
What is Lithosphere?
Answer:
Lithosphere is the solid crust or the hard top part of the Earth. It is made up of rocks and minerals. It is covered with a thick layer of soil.
![]()
Question 13.
How many major plates are there on the earth? What are they?
Answer:
There are six major plates on the earth. They are African, North American, South American, Indo Australian, Antarctic, Eurasian and Pacific plates.
Question 14.
What is meant by intrusive landforms?
Answer:
Intrusive landforms :
Some part of the lava may not reach the surface and may cool under the surface and become rocks; These are called ‘intrusive landforms’.
Question 15.
Which are called ‘Third order landforms?
Answer:
The shaping of the landforms by wind and water is called ‘Third order landforms’ by geographers.
Question 16.
How is lithosphere useful to mankind?
Answer:
- Lithosphere is the solid crust or the hard top part of the earth.
- When it heats due to sunrays or cools down, it influences air and water too.
- We and most other living beings live on this realm.
- We use the rocks and soils and other things found in this hard crust in many ways.
Question 17.
What is the impact of vegetation on lithosphere?
Answer:
- Trees, plants and grass constitute vegetation.
- Vegetation contribute to the weathering of rocks by driving roots into fine cracks or holes in the rocks.
- They also enable water and moisture to enter into rocks which further enable weathering.
- On the other hand plant or grass cover on soils prevent easy denudation or transportation of soil by wind or water.
![]()
Question 18.
Which processes cause the formation of ‘Third Order landforms’?
Answer:
- The shaping of landforms by wind and water are called ‘third order landforms’.
- They include carved mountains, valleys, deltas, sand dunes, etc.
- Processes like weathering, erosion, transportation, and deposition are largely responsible for these landforms.
Question 19.
What do you mean by geomorphic cycle?
Answer:
- Landforms continuously keep on changing due to denudation activities.
- But these changes occur very slowly.
- The structure of mountains, plateaus and plains keep on changing through process known as ‘erosion cycle’ or ‘geomorphic cycle’.
Question 20.
How are gorges formed?
Answer:
- A gorge is almost equal in width at its top as well as its bottom.
- The Byson gorge in Andhra Pradesh on the Godavari, Indus gorge in Kashmir etc., are examples.
- Where the rocks are very hard, the river cuts a narrow valley, the sides are so steep that these ‘gorges’ are formed.
Question 21.
What is a canyon?
Answer:
- A canyon is characterised by steep like side slopes and may be as deep as a gorge.
- A canyon is wider at its top than bottom.
Question 22.
How ocean rocks or crust are formed?
Answer:
These are formed by lava rising up from the mantle. The eruptions on the ridges create new ocean floor made of basalt rocks, which then spreads laterally from the ridge. The first order landforms such as oceans and continents are formed at the time when the hot earth was cooling. While the earth’s interior continued to cool, it contracted and the outer crust wrinkled forming ridges i.e., mountains and basins i.e., oceans.
The second order landforms such as plains, plateaus and mountains are formed as a result of the internal processes of the earth. The third order landforms such as carved mountains, valleys, deltas, sand dunes are formed as a result of the shaping of the land forms by wind, water.
![]()
Question 23.
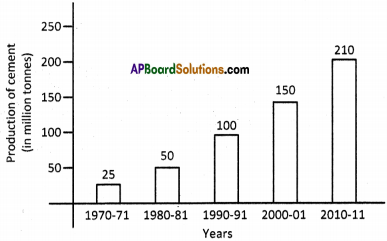
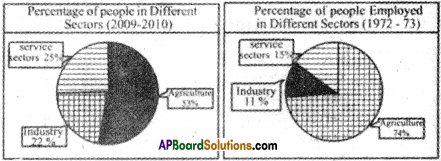
What are the four main “realms” of the earth? Explain how a cement factory world impact the various “realms”.
Answer:
- Realms are areas which have some common features.
- There are four major natural realms on the earth.
- They are :
1. Lithosphere,
2. Hydrosphere,
3. Atmosphere and
4. Biosphere. - Cement factory is a mineral based industry.
- Unscientific way of mining may lead to earthquakes.
- Excessive emission of gases and dust may lead to air pollution.
- Heating of limestone and clay may emit mercury which may damage the brains of the children.
Question 24.
Write about “Plate tectonics”.
(OR)
What is plate tectonics?
Answer:
- The region where the two plates meet and push each other, a lot of pressure is exerted.
- One plate is pushed under into the mantle while the other plate is pushed up, to form a chain of mountains.
- This movement of plates is called ‘Plate tectonics’.
Question 25.
What are the two kinds of changes happening in the Lithosphere?
Answer:
- There are two kinds of changes taking place in the lithosphere.
- They are :
a. The slow movement
b. The sudden movement.
3) The slow movement leads to the formation of the crust.
4) The sudden movements (eruption of volcanoes and earthquakes) can be destructive and cause much damage.
Question 26.
How are Igneous rocks formed?
Answer:
- When volcano erupts, the molten material (also accompanied by steam, smoke and various gases) comes out from the depths of the earth.
- The molten materials cool on the earth and form hard rocks called “Igneous rocks”.
Question 27.
Write about “Intrusive landforms” and “Extrusive landforms”.
Answer:
- When volcano erupts, some part of the lava may not reach the surface and may cool under the surface and become rocks which are called “intrusive landforms”.
- A part of the lava which pours on the surface of the earth forms the “extrusive landforms”.
![]()
Question 28.
List out landforms originated due to the work of waves.
Answer:
- The erosion and deposition by the sea waves give rise to coastal landforms.
- “Sea Arches”, “Sea Cliff’, Cape, Bay and beaches are formed due to the work of the waves.
Question 29.
From which Greek word is the word Hydrosphere derived?
Answer:
It comes from the Greek word ‘hudor’ meaning water.
Question 30.
Write about the word Atmosphere.
Answer:
“Atmosphere” is derived from two greek words “atmos” means vapour and “sphaira” means sphere or ball.
Question 31.
Name few volcanoes that are situated in India.
Answer:
The Barren islands, and Narcondam are volcanoes situated in India.
Question 32.
What is weathering?
Answer:
The gradual disintegration of rocks by atmospheric forces or weather forces is called weathering.
![]()
Question 33.
What is erosion?
Answer:
The active wearing away of the earth’s surface, by different agents, is called erosion.
Question 34.
“The Earth is a deeply interconnected system” – Interpret the statement.
Answer:
The Earth consists of four major realms.
- Lithosphere,
- Hydrosphere,
- Atmosphere and
- Biosphere.
All these four are interrelated. All these four spheres together help the birth, existence, and continuance of life on Earth. Life needs the presence of all the other three realms land, water, and air. Life resides in the intersection of the three natural spheres. Life also actively changes the three other realms.
We cannot think of one realm without the crucial role of others. We cannot tamper with one aspect of it without affecting everything around us including ourselves. Thus we can say that the Earth is a deeply inter connected system.
Question 35.
“One day in very distant future the land you are standing upon will go under the Himalayas” – Interpret the above statement.
Answer:
At the margins of the plates where one plate meets another often the incoming plate dips under the stable plate. In fact the incoming plate actually goes into the mantle of the earth and becomes molten due to the heat of the mantle.
The plate thus going under into the mantle actually pulls the rest of the plate with it. For example, the Indian plate pushes the Eurasian plate and goes under if where the Himalayan mountains are.
Thus one day in very distant future the land we are standing upon will go under the Himalayas and join the mantle.
![]()
Question 36.
“The low lands what we see today were once mountains and plateaus” – Explain.
Answer:
External forces like water and air work vigorously to wear away the surface and the interaction of these constructive and destructive forces gives rise to the great diversity of present day landforms. These external processes on one hand wear away the surface of the rocks and mountains then they transport the wornout particles and deposit them in low lands and basins.
The processes of wearing away and deposition cause a general leveling of the surface. Processes like weathering, erosion, transportation and deposition are largely responsible for these landforms. It is known as denudation process.
Denudation is a continuous process. The landforms continuously keep on changing due to denudation activities. But these changes occur very slowly. Thus the low lands what we see today were once mountains and plateaus.
Question 37.
Read the paragraph and answer the following questions.
In some cases, where the rocks are very hard, the river cuts a very narrow valley, the sides are so steep that ‘Gorges’ are formed. The Byson gorge in A.P. on the Godavari, Indus Gorge in Kashmir are examples of this. Another important erosion form is Canyon. A Canyon is characterized by steep side slopes and may be as deep as a gorge. A gorge is almost equal in width at its top as well as its bottom.
1) Write any two similarities between gorges and canyons?
Answer:
a) It is as deep as gorge.
b) Both are formed with work of water.
2) Write any two differences between gorges and canyons?
Answer:
a) Canyon has a steep like side slope whereas gorge is too steep without side slope.
b) Canyon is wider at the top than at the bottom. Whereas Gorge is almost equal in width at its top as well as at its bottom.
3) Give an example of canyon.
Answer:
The Grand canyon on river Colorado.
4) How are gorges useful ?
Answer:
Gorges are suitable for construction of dams.
![]()
Question 38.
Last year (2015) Nepal witnessed a devastating earthquake. Learn about it.
Answer:
- Earthquake occured on 25th April 2015 and after shocks were felt on 12 May, 26th April, and 25th November of 2015.
- With a magnitude ranging from 7.8 to 8.1 on Richter scale, it caused a huge damage of about $ 5 billion.
- Nepal suffered 8,857 deaths and 21,952 persons were injured along with India, China, and Bangladesh.
- It’s hypocenter was at a depth of 8.21 cm and with epicenter was at east of district of hamjung.
- UNESCO world heritage sites in Khatmandu valleys and temples were damaged.
- It also triggered avalanche on Mount Everest causing as many as 200 deaths.
- It was believed to be the worst earthquake. Nepal suffered after 1934 Nepal-Bihar earthquake.
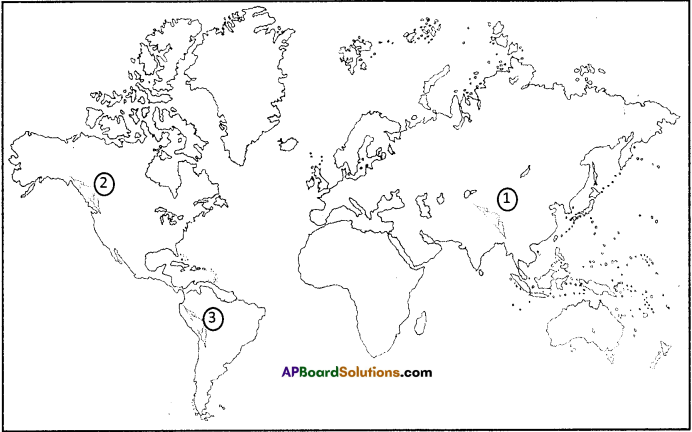
Question 39.
1. Locate different continents and oceans on the given world map.
Answer:
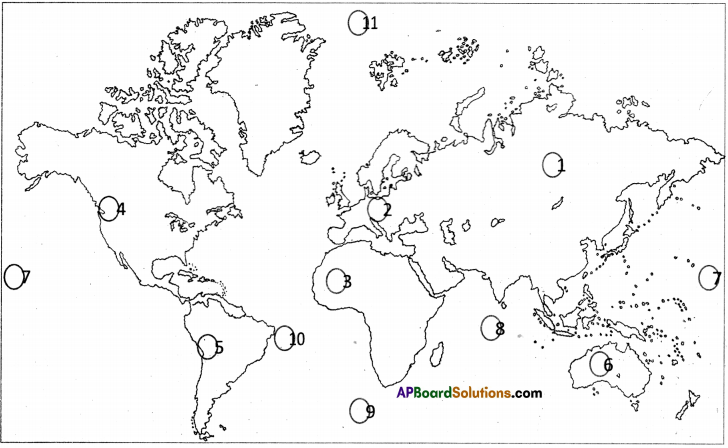
- Asia
- Europe
- Africa
- North America
- South America
- Australia
- Pacific Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- Antarctic Ocean
- Atlantic Ocean
- Arctic Ocean
Question 40.
Observe the map and answer the following questions.

Which parts of India lie near plate margins?
Answer:
- The states of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Jammu and Kashmir lie near plate margins.
- So these areas are earthquake prone areas.
Question 41.
Label the patrs to the given diagram.
Answer:
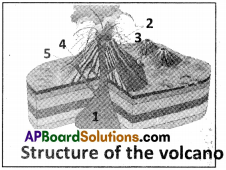
- Magma chamber
- Lava
- Central vent
- Layers of lava and ash from past eruptions
- Side vent
Question 42.
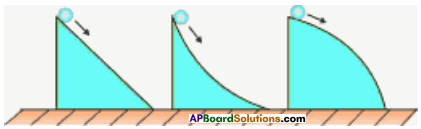
Why do you think glaciers make U-shaped valleys while rivers make V-shaped valleys?
Answer:
The shape of the trail left by the glacier is a function of the ice’s pressure on the ground. So if you look at the cross-section of a glacier is the laziest pattern the glacier can make, i. e. U. So the glaciers make U-shaped valleys.
In the high mountains, the flow of a river is very swift as it descends the steep slopes and it exerts a great force in cutting the mountain vertically. As a result a deep valley develops, narrow at the bottom and wide at the top. Thus V-shaped valleys are formed.
![]()
Question 43.
Appreciate the benefit with the eruption of a volcano?
Answer:
- There are various benefits with the eruption of volcano.
- Fertile soils are formed, like ones in deccan plateau.
- Valuable minerals from interior of the earth were brought to the surface or nearer to it.
- The soils formed like this are proved to be most populous areas, like in Java island.