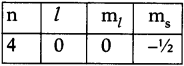
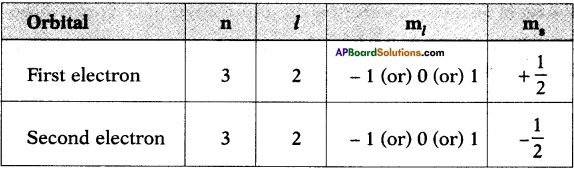
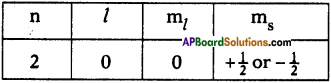
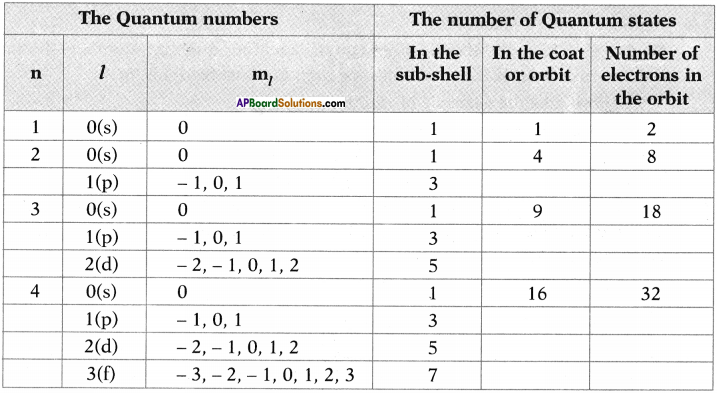
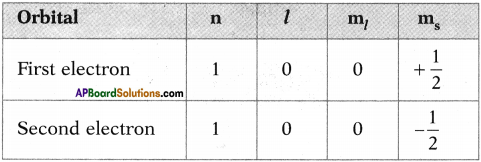
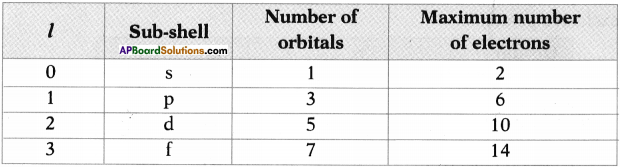
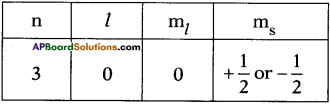
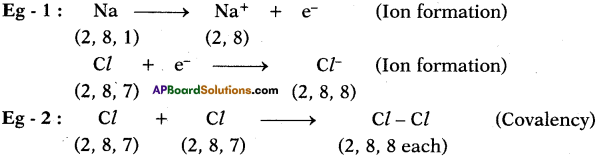
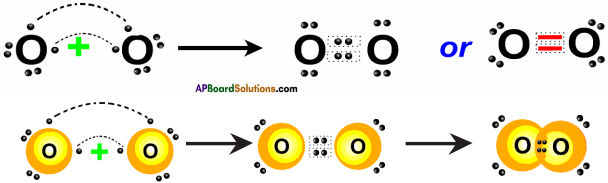
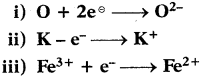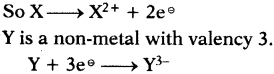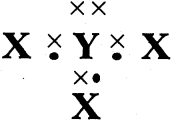AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Physical Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Principles of Metallurgy.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Chemistry Important Questions 13th Principles of Metallurgy
10th Class Chemistry 13th Lesson Principles of Metallurgy 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which method is suitable to enrich sulphide ores? (AP June 2016)
Answer:
Froth flotation method is suitable to enrich sulphide ores.
Question 2.
We use P.V.C. pipes for water supply instead of metal pipes. Why? (AP March 2017)
Answer:
PVC pipes do not rust. So they are used as water pipes instead of metal.
Question 3.
Arrange the metals Fe, Na, Ag and Zn in increasing order of their chemical reactivity. (TS March 2017)
Answer:
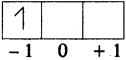
Ag < Fe < Zn < Na
(OR)
Ag, Fe, Zn, Na
![]()
Question 4.
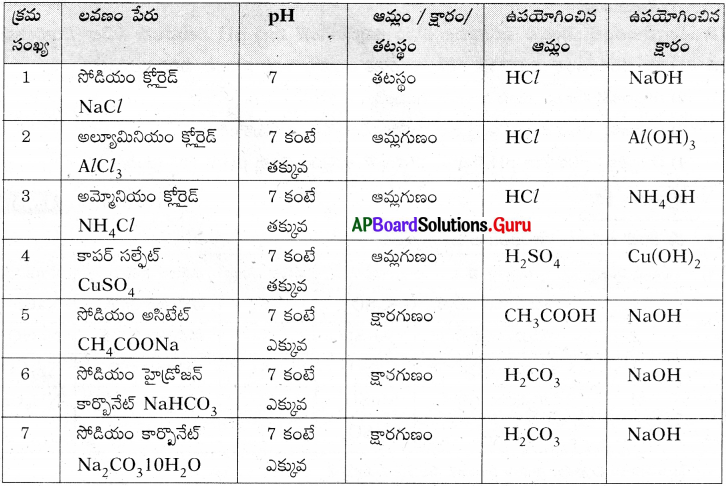
Write the deferences between Roasting and Calcination. (TS June 2018)
Answer:
1) Burning of ore in the presence of air or oxygen is called “Roasting”.
So in the roasting air is present.
2) Burning of ore in the absence of air or oxygen is called “Calcination.”
So in the calcination air is absent.
Question 5.
What are the preventive methods do you take for rusting iron materials? (TS March 2018)
Answer:
- Covering the surface of iron materials with paint or by some chemicals.
- Electroplating.
Question 6.
Mention the application of thermite process in daily life. (AP SCERT: 2019-20)
Answer:
1) Joining railing of railway tracks,
2) Joining cracked machine parts.
Question 7.
What are the essential condition that iron articles get rust? (TS June 2019)
Answer:
The essential condition that iron articles get rust is presence of water and air both.
Question 8.
What is metallurgy?
Answer:
The process of extraction of metals from their ores is called metallurgy.
Question 9.
What is the Bronze an alloy of?
Answer:
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
![]()
Question 10.
What are ores?
Answer:
The minerals from which the metals are extracted without economical loss are called ores.
Question 11.
What is the percentage of Aluminium oxide in Bauxite?
Answer:
50-70%.
Question 12.
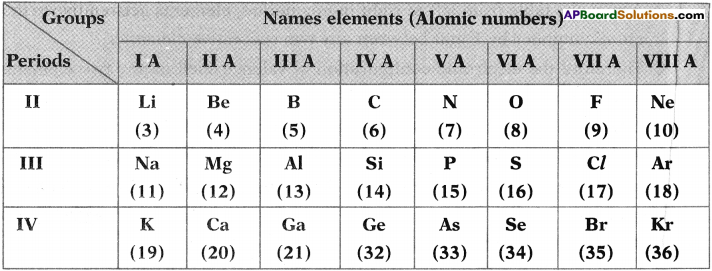
Why is 16th group called chalcogen family?
Answer:
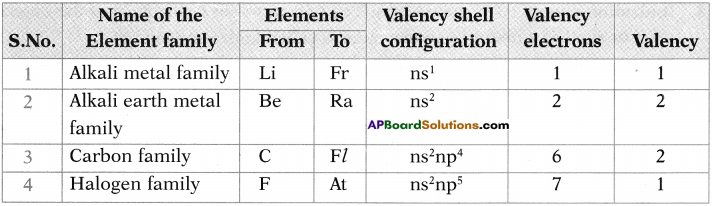
Chaleo means ore and genus means produce. We notice that the ores of many metals are oxides and sulphides. This is why oxygen-sulphur (16th group) group as chalcogen family.
Question 13.
Which metals form oxides, sulphides and carbonates?
Answer:
Moderate reactive metals.
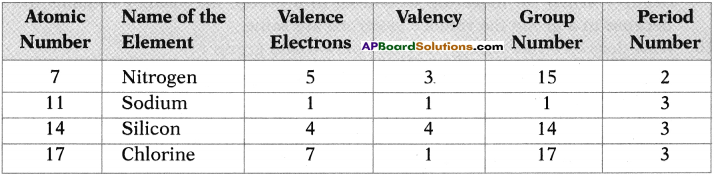
Question 14.
Based on the reactivity arrange the metals.
Answer:
Based on reactivity we can arrange metals in descending order of their reactivity as shown below:
![]()
Question 15.
What is gangue?
Answer:
The unwanted material in the ore is called gangue.
Question 16.
What is activity series?
Answer:
Arrangement of the metals in decreasing order of their reactivity is known as activity series.
Question 17.
Why do we add some impurities to ore?
Answer:
We add some suitable impurities to ore in order to decrease its melting point.
Question 18.
What is roasting?
Answer:
Roasting is a pyrochemical process in which ore is heated in the presence of oxygen or air below its melting point.
Question 19.
What is thermite process?
Answer:
The reaction of metal oxides with aluminium is called thermite process.
Question 20.
Write the chemical equations involving thermite reaction.
Answer:
2 Al + Fe2O3 → Al2O3 + 2 Fe + heat
2 Al + Cr2O3 → Al2O3 + 2 Cr + heat
Question 21.
How do you convert cinnabar into mercury?
Answer:
When cinnabar (HgS) is heated in air, it is first converted into (HgO), then reduced to mercury on further heating.
Question 22.
What is distillation of metals?
Answer:
The extracted metal in the molten state is distilled to obtain the pure metal as distillate by distillation of metals. Here the impurities are high boiling point metals.
Question 23.
What is poling?
Answer:
The molten metal is stirred with logs (poles) of greenwood and impurities are removed either as gases or they get oxidized and form slag over surface of the molten metal is called poling.
![]()
Question 24.
What is liquation?
Answer:
A low melting metal can be made to flow on a slope surface to separate it from high melting impurities is called liquation.
Question 25.
What is calcination?
Answer:
Calcination is a pyrochemical process in which the ore is heated in the absence of air.
Question 26.
What is flux?
Answer:
Flux is a substance added to the ore to remove the gangue from it by reacting with ore.
Question 27.
What are the ores of iron?
Answer:
Haematite (Fe2O3), Magnetite (Fe3O4).
Question 28.
What are the ores of zinc?
Answer:
Zinc blende (ZnS), Zincite (ZnO).
Question 29.
What is the formula of gypsum and metal present in gypsum?
Answer:
The formula of gypsum is CaSO4.2H2O. The metal present in gypsum is calcium.
Question 30.
What is a furnace?
Answer:
The furnace is one which is used to carry out pyrochemical process in metallurgy.
Question 31.
Arrange the following chlorides in ascending order of reactivity of respective metals. MgCl2, NaCl, PbCl2, HgCl2.
Answer:
The ascending order is HgCl2, PbCl2, MgCl2, NaCl.
Question 32.
What are the fuel and flux for haematite ore?
Answer:
The coke is used as fuel and limestone (CaCO3) is used as flux for haematite ore.
Question 33.
Why can copper not displace zinc from its compound?
Answer:
Copper is less reactive than zinc. So copper cannot displace zinc from its compound or salt.
Question 34.
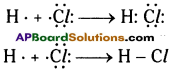
How do various metals in activity series react with chlorine on heating?
Answer:
- All the metals react with chlorine on heating to form their respective chlorides.
- But the reactivity decreases from top to bottom.
Question 35.
How do you know the reactivity of metals with chlorine decreases from top to bottom?
Answer:
We know that the reactivity of metals with chlorine decreases from top to bottom the heat evolved when the metal reacts with one mole of chlorine gas to form chloride.
![]()
Question 36.
Give some examples for corrosion.
Answer:
Examples for corrosion :
- The rusting of iron (Iron oxide)
- Tarnishing of silver (Silver sulphide)
- Development of green coating on copper (Copper carbonate) and bronze.
Question 37.
Why are potassium, sodium, calcium never found in free state?
Answer:
The metals potassium, sodium and calcium are so reactive that is why they never exist in free state.
Question 38.
How do you extract metals at the top of activity series?
Answer:
The metals at the top of activity series are extracted by electrolysis of their fused compounds.
Question 39.
What is meant by enrichment of ore?
Answer:
Some physical methods are useful in removing unwanted rocky material from ore. It is called enrichment of ore.
Question 40.
How do you extract metal from the crude metal?
Answer:
To extract metal from enriched ore it is converted into metallic oxide by reduction reaction. Then this metallic oxide is further reduced to get metal with certain impurities.
Question 41.
What are the impurities you get in the refining of copper?
Answer:
Antimony, selenium, tellurium, silver, gold and platinum.
Question 42.
What is slag?
Answer:
The substance formed due to reaction of gangue and flux,
Eg : CaSiO3, FeSiO3
Question 43.
What is meant by pyrochemical reactions?
Answer:
Pyre means heat. So the chemical reactions involving heat are called pyrochemical reactions.
Question 44.
Can you mention some articles that are made up of metals?
Answer:
Jewellery, conducting wires and utensils.
Question 45.
Why are we mixing small amount of carbon to iron?
Answer:
To make iron hard and strong.
Question 46.
What is the main difference between steel and stainless steel?
Answer:
Steel will rust whereas stainless steel will not rust.
Question 47.
Give some examples for corrosion.
Answer:
The rusting of iron, tarnishing of silver, development of green coating on copper.
![]()
Question 48.
Do metals exist in the same form as that we use in our daily life?
Answer:
No, they exist as ores and minerals and some may exist in the form of metals.
Question 49.
Do you know how metals are obtained?
Answer:
The metals are extracted from their ores.
Question 50.
Have you ever heard the words like ore, mineral and metallurgy?
Answer:
Yes, these words are related to extraction of metal.
Question 51.
Where do we carry out pyrochemical processes in metallurgy?
Answer:
Pyrochemical processes can be carried out inside the furnace.
Question 52.
Which process converts sulphide ore into oxide ore?
Answer:
Roasting is the process which converts sulphide ore into oxide ore.
Question 53.
Is silver mineral or ore? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Silver is neither mineral nor ore. It is a metal.
Question 54.
Give two examples for corrosion.
Answer:
1) Rusting of iron
2) Green coating on copper.
Question 55.
Name the form of carbon used in the blast furnace for the extraction of iron.
Answer:
Carbon is used in the form of coke to reduce iron in blast furnace.
Question 56.
Give name and formulae of sulphide ore of lead and mercury.
Answer:
a) Sulphide ore of lead is Galena. Its formula is PbS.
b) Sulphide ore of mercury is Cinnabar. Its formula is HgS.
Question 57.
What are the various pyrochemical processes used in metallurgy?
Answer:
The various pyrochemical processes used are
a) Smelting,
b) Roasting,
c) Calcination.
![]()
Question 58.
What is the gas released at anode when fused sodium chloride is electrolysed?
Answer:
When sodium chloride is electrolysed, sodium metal is formed at cathode and chlorine gas is formed at anode.
NaCl → Na+ + Cl–
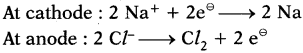
Question 59.
Which pyrochemical process is useful to convert zinc blende into oxide ore?
Answer:
Zinc blende is sulphide ore of zinc. Its formula is ZnS. So it can be converted into oxide ore by heating strongly in excess of air known as roasting.
2 ZnS + 3 O2 → 2 ZnO + 2 SO2
Question 60.
Which pyrochemical process is useful to convert Magnesite into oxide ore?
Answer:
Magnesite is carbonate ore of magnesium. Its formula is MgCO3. So it can be converted into oxide ore by heating in the absence of air.
MgCO3 → MgO + CO2
Question 61.
What is the main impurity present in iron when it is removed from the blast furnace?
Answer:
The main impurity that can be removed is slag because it is formed when gangue in the ore reacts with flux.
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
Question 62.
Name two metals normally manufactured by the electrolysis of fused compounds.
Answer:
Metals with high reactivity can be extracted by electrolysis of their fused compounds.
The examples are potassium, sodium and calcium.
Question 63.
What are the examples of corrosion?
Answer:
- Rusting of iron.
- Tarnishing of silver.
- Development of green coating on copper (CuCO3).
- Green coating on Bronze.
Question 64.
What is importance of prevention of corrosion?
Answer:
- Save the money.
- Preventing accidents such as a bridge collapse.
- Failure of a key component.
Question 65.
What is meant by galvanisation?
Answer:
Preventing the rust on metals by using layer of zinc. This phenomena is called galvanisation.
Question 66.
Write the example of electroplating in daily life.
Answer:
- Rold gold.
- Copper coating on cookware.
Question 67.
What is formula and name of iron rust?
Answer:
Iron rust is equal to hydrated ferric oxide.
Formula : Fe2O3 × H2O
Question 68.
What is importance of alloying?
Answer:
- Improving the properties of metal.
- To avoid the rust.
- To increase the hardness.
Question 69.
Which one used as flux extracting of iron from heamatite?
Answer:
Limestone or calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
Question 70.
Marne the two metals which corrode easily?
Answer:
Iron and copper.
![]()
Question 71.
Atmospheric air always contains moisture. Then, how can you protect iron articles from the affect of atmosphere?
Answer:
By painting, oiling and greasing, etc.
Question 72.
Explain the terms gangue and flux.
Answer:
The impurity present in the ore is called gangue. The substance added to the ore to remove gangue from it is called flux.
Question 73.
What are the metals are present in carnallite?
Answer:
Potassium (K) and Magnesium (Mg).
Question 74.
Write the elements are present in high reactivity series.
Answer:
Na, Mg, Al, K, Ca
(11 12 13 19 20)
Question 75.
Write the elements that are in moderate reactivity series.
Answer:
Fe, Cu, Zn, Pb.
Question 76.
Name the two metals which do not corrode easily?
Answer:
Gold and platinum.
Question 77.
Mention some important methods of refining.
a) Distillation
b) Poling
c) Liquation
d) Electrolysis
Answer:
d) Electrolysis
Question 78.
What is the role of furnace in metallurgy?
Answer:
Furnace is the one which is used to carry out pyrochemical process in metallurgy.
Question 79.
What is meant by calcination?
Answer:
It is the process of heating the concentrated ore in the absence of air.
Question 80.
Write the equation of heating of one sulphide ore in the process of roasting.
Answer:
![]()
Question 81.
Mention two methods which produce very pure metals?
Answer:
a) Electrolytic reduction.
b) Smelting.
Question 82.
What are the applications of thermite reaction in daily life?
Answer:
a) To join railings of railway tracks.
b) To join cracked machine parts.
Question 83.
Arrange the metals Ag, Mg, K in reactivity series.
Answer:
K > Mg > Ag.
Question 84.
How do you extract highly reactive metals?
Answer:
Highlyreactive metals can be extracted by electrolysis of their fused compounds.
Question 85.
What is dressing of an ore?
Answer:
The process of removal of impurities from an ore is called dressing of the ore or concentration of the ore.
Question 86.
Write the equation of example of calcination.
Answer:
![]()
Question 87.
Write the some properties of metals.
Answer:
Malleability, Ductility, Sonarity and Electrical conductivity.
Question 88.
Mention the stages involved in extraction of a metal from its ore.
Answer:
- Dressing or concentration.
- Extraction of crude metal.
- Refining or purification of the metal.
Question 89.
How do you extract moderately reactive metals?
Answer:
These metals are generally sulphides and carbonates. They are converted into oxides before reducing them to metals.
![]()
Question 90.
Give an example for reduction of metal oxide with carbon.
Answer:
The oxides are reduced by coke in a furnace which gives the metal and carbon monoxide.
![]()
Question 91.
Give an example for reduction of oxide ore with CO.
Answer:
![]()
Question 92.
What is flux?
Answer:
Flux is a substance added to the ore to remove the gangue from it by reacting with ore. If the impurity is acidic substance, basic substance is used as flux and vice – versa.
Question 93.
How do various metals in activity series react with chlorine on heating?
Answer:
- All the metals react with chlorine on heating to form their respective chlorides.
- But the reactivity decreases from top to bottom.
Question 94.
What are the substances to be added if the gangue is acidic or basic?
Answer:
If the gangue (impurity) is acidic substance like SiO2, basic substance like CaO is used as flux and if the impurity is of basic nature like FeO acidic flux like SiO2 is added to the gangue.
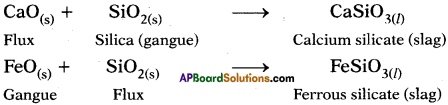
Question 95.
Why will stainless steel not rust?
Answer:
Stainless steel is prepared by mixing iron with nickel and chromium. Nickel and chromium are less reactive with oxygen. So stainless steel will not rust.
Question 96.
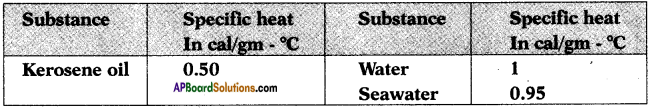
Why is sodium metal stored in kerosene?
Answer:
Sodium is highly reactive with both air (oxygen) and water. So it should be stored in kerosene.
Question 97.
Which metal gets covered with protective film of oxide when exposed to air?
Answer:
The metal is aluminium. When aluminium is exposed to air it forms a protective layer of aluminium oxide (Al2O3).
Question 98.
All ores are minerals, but all minerals need not be ores. Why?
Answer:
A mineral from which a metal can be extracted and economical loss is called ore.
Question 99.
Why is carbon not used for reducing aluminium from aluminium oxide?
Answer:
The oxide of Aluminium is very stable and can be reduced by electrolytic process.
Question 100.
Name few metals which occur in native state in nature. Why?
Answer:
Gold, Platinum, Silver are the metals which occur in native state, because of their low chemical reactivity.
Question 101.
Why do we call oxygen – sulphur group is chalcogen family?
Answer:
Chaleo means ore. We know that most of ores of many metals are oxides and sulphides. That’s why oxygen – sulphur group is called chalcogen family.
Question 102.
Aluminium occurs in combined state in nature whereas gold is in free state. Why?
Answer:
Gold has low reactivity and so occurs in free state. Aluminium is electropositive metal and high reactivity. So it is oxide or chloride.
Question 103.
What are the uses of thermite reaction?
Answer:
Thermite reaction is used to join railings of railway tracks or cracked machine parts.
10th Class Chemistry 13th Lesson Principles of Metallurgy 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
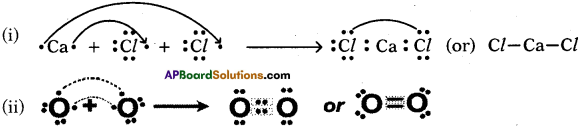
Define mineral. Mention any two ores of ‘magnesium’. (AP June 2017)
Answer:
1) Minerals :
The elements or compounds of the metals which occur in nature in the earth crust are called ‘minerals’.
2) Two ores of magnesium :
Magnesite – MgCO3
Carnalite – KCl MgCl2 6H2O
Question 2.
Potassium, Sodium, Magnesium are high reactive metals and occur as chlorides in nature. Suggest and explain the suitable method for the extraction of the above metals from their ores. (AP March 2017)
Answer:
- The suitable method to extract these metals from their chlorides is electrolysis of their fused compounds.
- It is not feasible for method of reduction, electrolysis of their aqueous solutions.
![]()
Question 3.
Predict, what happens in the field of domestic use of metals if alloys were not discovered. (TS June 2016)
Answer:
If alloys were not discovered,
- All the vessels/utensils made of single metal like iron, copper, aluminium, etc. may be used for cooking purpose.
- We may face problems like rusting of iron, tarnishing of silver and copper, etc.
- We may face the problems of corrosion of home appliances.
- We may face difficulties in cleaning of the vessels due to rusting and tarnishing.
- Cost of the utensils may be risen, because of less availability of the metals like copper.
- Using of the plastic ware may be risen for storage due to lack of steel containers.
- Brass, steel, bronze, etc. utensils are not available to use.
- Making of jewellary is also difficult.
Question 4.
Give an example with the chemical equation for the reduction of ores using more reactive metals. (TS March 2017)
Answer:
The reaction of Iron oxide with aluminium.
Fe2O3 + 2Al → 2Fe + Al2O3 + Heat
(Or)
Reaction of Titanium Chloride with Magnesium.
TiCl4 + 2Mg → Ti + 2MgCl2
(Or)
Reaction of Titanium Chloride with Sodium.
HCl4 + 4Na → Ti + 4NaCl
(Or)
Reaction of Cromium oxide with aluminium.
Cr2O3 + 2Al → 2Cr + Al2O3 + Heat
Question 5.
Write two precautions to prevent corrosion of metals in your daily life. (TS June 2018)
Answer:
Precautions to be taken to prevent corrosion of metals.
i) Painting the metals.
ii) By keeping the metals in the dry places.
iii) Cover the surface by other metals that are inert or non reactive to the atmosphere.
iv) Applying oil/grease to the metals.
v) Making of alloys.
Question 6.
| High reactivity | Moderate reactivity | Low reactivity |
| K, Na, Ca, Mg, Al | Zn, Fe, Pb, Cu | Ag, Au |
Observe the table and answer the following questions. 4jt*y (June 2019
i) Which of the above metals found even in free state in nature ?
ii) Which of the above metal’s ore are concentrated by using magnetic separation?
Answer:
i) Ag, Au.
ii) Fe.
Question 7.
Silicon is a metalloid. How do you support this?
Answer:
Silicon exhibits following properties, so I conclude that it is a metalloid.
- It is metallic lustre in nature.
- It exists in several metallic and non-metallic compounds.
- It has brittle nature.
- All metalloids usually occur in combined states both metals and non-metals.
Question 8.
Explain the reaction of various metals in activity with cold water.
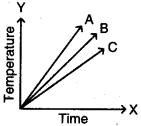
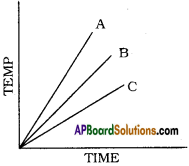
Answer:
1) From potassium to magnesium displace hydrogen from cold water with decreasing reactivity. Potassium reacts with cold water violently but reaction of Magnesium is very slow. The reactivity order is given below.
Mg < Ca < Na < K
2) From aluminium to gold do not displace hydrogen from cold water.
Question 9.
How do various metals in activity series react with steam?
Answer:
- The metals from potassium to iron displace H2 (Hydrogen gas) from steam with decreasing reactivity. That means the reaction of potassium with steam is voilent but the reaction of iron is very slow.
- The metals from lead to gold do not displace hydrogen from steam.
Question 10.
How do various metals in activity series react with dilute strong acids?
Answer:
1) The metals from potassium to lead displace hydrogen from dilute strong acids with decreasing reactivity.
a) The reaction of potassium is explosive.
b) The reaction of magnesium is vigorous.
c) The reaction of iron is steady.
d) The reaction of lead is slow.
2) The metals from copper to gold do not displace H2 from strong dilute acids.
Question 11.
What are the preventive techniques used in corrosion of metals?
Answer:
Prevention of corrosion of metals :
- Covering the surface of metal with paint or by some chemicals like bisphenol which prevent the surface of metallic object to come in contact with atmosphere.
- Covering the surface of metal by other metals like tin or zinc that are inert or react themselves with atmosphere to save the metal.
- An electrochemical method in which a sacrificial electrode of another metal like magnesium and zinc, etc. corrodes itself to save the metal.
Question 12.
What are the chemical reactions that take place inside blast furnace?
Answer:
The chemical reactions that take place inside the blast furnace.
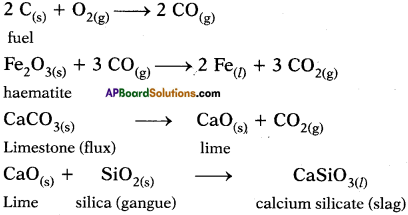
Question 13.
What are the various types of furnaces? Explain.
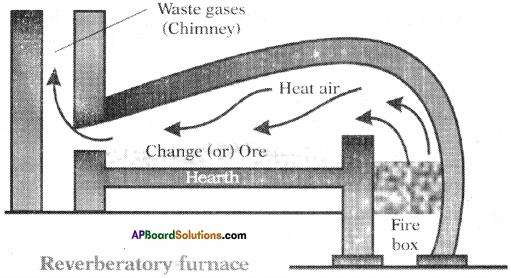
Various types of furnaces :
1) Blast furnace:
Blast furnace has both fire box and hearth combined in big chamber which accommodates both ore and fuel.
2) Reverberatory furnace :
It has both fire box and hearth separated, but the vapours (flame) obtained due to burning of the fuel touch the ore in the hearth and heat it.
3) Retort furnace :
In this furnace there is no direct contact between the hearth or fire box and even the flames do not touch the ore.
Question 14.
Why is alloying preferred for metals? Explain with examples.
Answer:
- Alloying is a method of improving properties of a metal. We can get desired properties by this method.
- For example, iron is the most widely used metal. But it is never used in its pure state.
- This is because pure iron is very soft and stretches easily when hot.
- But, if it is mixed with a small amount of carbon, it becomes hard and strong.
- When iron is mixed with nickel and chromium we get stainless steel which will not rust.
Question 15.
What is 22 carat gold? Why is it preferred for making jewellery?
Answer:
- Pure gold, known as 24 carat gold is very soft.
- So it is not suitable for making jewellery.
- It is alloyed with either silver or copper to make it hard.
- So they use 22 carat gold in which pure gold is alloyed with 2 parts of either silver or copper for making gold jewellery.
Question 16.
Write about electrolysis of NaCl.
Answer:
1) Fused NaCl is electrolysed with steel cathode and graphite anode.
2) The metal sodium (Na) will be deposited at cathode and chlorine gas liberates at the anode.
At Cathode : 2 Na+ + 2e– → 2 Na
At Anode : 2 Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Question 17.
Identify the metal present in the following ores.
i) Epsom Salt
ii) Horn Silver
iii) Cinnabar
iv) Galena
Answer:
i) Magnesium
ii) Silver
iii) Mercury
iv) Lead
![]()
Question 18.
What is meant by extraction of metals? Write the main stages of extraction of metals from its Ore.
Answer:
Separation of metals from ores is called extraction of metals. Extraction of metals involves mainly three stages.
- Concentration or dressing
- Extraction of crude metal
- Refining or purification of the metal.
Question 19.
Write differences between roasting and calcination.
Answer:
| Roasting | Calcination |
| 1. Ore is heated in the presence of oxygen or air. | 1 Ore is heated in the absence of air. |
| 2. Sulphide ore is converted into oxide ore. | 2. Carbonate ore is converted into oxide ore. |
Question 20.
What are the differences between minerals and ores?
Answer:
| Minerals | Ores |
| 1) Minerals contain a low percentage of metal. | 1) Ores contain a large percent of metal. |
| 2) Metals cannot be extracted from minerals. | 2) Ores can be used for the extraction of metals. |
| 3) All minerals cannot be called ores. | 3) All ores are minerals. |
Question 21.
What are the different types of reduction?
Answer:
The different types of reduction are
a) Chemical reduction,
b)Auto reduction,
c) Electrolytic reduction.
Question 22.
How do potassium and sodium react with oxygen?
Answer:
a) Potassium and sodium form oxides of type M2O in limited supply of oxygen.
4 K + O2 → 2 K2O
4 Na + O2 → 2 Na2O
b) In excess of oxygen they form peroxides of type M2O2.
2 Na + O2 → Na2O2
2 K + O2 → K2O2
Question 23.
How does reactivity of chlorine vary in the reactivity series?
Answer:
- All metals react with chlorine on heating to form their respective chlorides but with decreasing reactivity in the reactivity series.
- This is understood from the heat evolved when metal reacts with one mole of chlorine gas to form chloride.
Question 24.
Name two ores of calcium and give their formulae.
Answer:
The ores of calcium are
- Gypsum (CaSO4 • 2H2O)
- Limestone (CaCO3)
Question 25.
Which method is useful to separate sand from iron? Explain.
Answer:
- Sand can be separated from iron by using magnetic separation method.
- This can be done by using electromagnet. Iron being a magnetic material is attracted by electromagnet whereas sand is not attracted by electromagnet.
- So these materials are separated.
Question 26.
Which metals do not displace hydrogen from dilute strong acids?
Answer:
- Copper, mercury, silver, platinum, gold do not displace hydrogen from dilute strong acids like HCl, H2SO4, etc.
- The reactivity of these metals are less than hydrogen. So, they are unable to displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Question 27.
Which metals are not found in free state? Why?
Answer:
- The metals like potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and aluminium are never found in free state in nature.
- The reason is that these metals have high reactivity. So, they exist as compounds.
Question 28.
Why do silver and gold exist even in free state?
Answer:
- Silver and gold are least reactivity metals. So, they are also called noble metals.
- Due to least reactivity they are unable to react with other elements.
![]()
Question 29.
How do moderately reactive metals occur in nature?
Answer:
- The metals like zinc, iron, lead are moderately reactive.
- They are found in the earth’s crust mainly as oxides, sulphides and carbonates.
Question 30.
Mention the most important metals and non-metals from the following products.
a) Annapurna salt
b) Liquid used in thermometer
c) Lead of the pencil
d) Chlorophyll
e) Filament in electric bulb
f) Enamel layer on teeth
Answer:
a) Annapurna salt : Iodine, chlorine – Non-metals
b) Liquid used in thermometer : Mercury – Metal
c) Lead of the pencil : Graphite – Non-metal
d) Chlorophyll : Magnesium – Metal
e) Filament in electric bulb : Tungsten – Metal
f) Enamel layer on teeth : Calcium phosphate – Non-metal
Question 31.
What is a furnace? Explain various parts of furnace.
Answer:
Furnace :
Furnace is the one which is used to cany out pyrochemical processes in metallurgy.
Furnace has mainly three parts :
1) Hearth :
Hearth is the place inside the furnace where the ore is kept for heating.
2) Chimney:
Chimney is the outlet through which flue (waste) gases go out of the furnace.
3) Fire box :
Fire box is the part of the furnace where the fuel is kept for burning.
10th Class Chemistry 13th Lesson Principles of Metallurgy 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
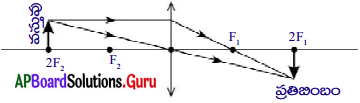
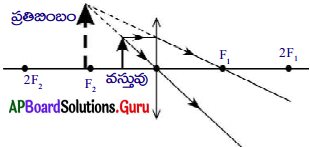
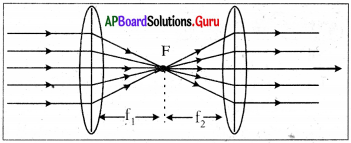
What is a furnace? Draw Reverberatory furnace and label it parts. (AP March 2018)
Answer:
1) Furnace :
Furnace is the one which is used to carry out pyrochemical processes in metallurgy.
2) Diagram of Reverberatory furnace.
Question 2.
What are the various techniques used in purification of the crude metals? Explain.
(OR)
State the methods used for the purification of crude metals. Explain in which context these methods are used. (TS June 2015)
Answer:
1) The process of obtaining the pure metal from the impure metal is called refining of the metal.
2) Some of the processes of refining are
i) Distillation
ii) Poling
iii) Liquation
iv) Electrolytic refining.
3) The process that has to be adopted for purification of a given metal depends on the nature of the metal and its impurities.
Various methods adopted in purification of metals :
1) Distillation :
This method is very useful for purification of low boiling metals like zinc and mercury containing high boiling metals as impurities. The extracted metal in the molten state is distilled to obtain the pure metal as distillate.
2) Poling :
The molten metal is stirred with logs (poles) of greenwood. The impurities are removed either as gases or they get oxidized and form slag (Scum) over the surface of molten metal.
3) Liquation :
Low melting metal like tin can be made to flow on a slopey surface to separate it from high melting impurities.
4) Electrolytic refining :
- In this method, the impure metal is made to act as anode.
- A strip of the same metal in pure form is used as cathode.
- They are put in a suitable electrolytic bath containing soluble salt of the same metal.
- The required metal gets deposited on the cathode in the pure form.
- The metal constituting impurity, goes as the anode mud.
The reactions are :
At anode : M → Mn+ + ne–
At cathode : Mn+ + ne– → M. ; (M = pure metal, n = 1, 2, 3, …….)
Question 3.
Four metals A, B, C and D are in turn added to the following solutions one by one. The observations made are tabulated below. (TS March 2015)
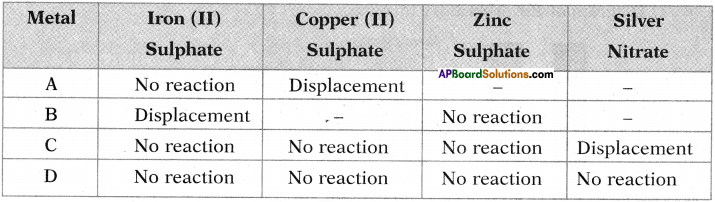
Answer the following based on the given information.
i) Which is the most reactive metal? Why?
ii) What would be observed, if ‘B’ is added to a solution of Copper (II) sulphate and why?
iii) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in order of increasing reactivity.
iv) Which one among A, B, C and D metals can be used to make containers that can be used to store any of the above solutions safely?
Answer:
i) Metal ‘B’ is more reactive.
– Metal ‘B’ is replacing iron from iron sulphate.
– Metal ‘A’ is replacing copper from copper sulphate.
– Metal ‘C’ is replacing silver from silver nitrate.
ii) Metal B displaces Cu from CuS04 solution. Because metal B is more reactive than Cu.
iii) D < C < A < B.
iv) The container made up of metal D can be used to store any solution mentioned above.
![]()
Question 4.
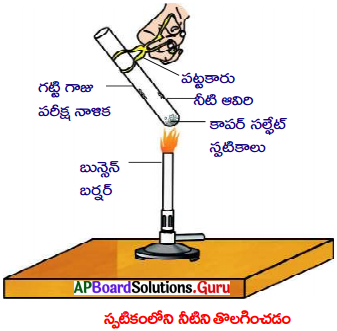
Write the physical methods used for the concentration of the ore. Explain the method used for concentration of the sulphide ore. (TS June 2017)
Answer:
Physical methods used for the concentration of the ore is,
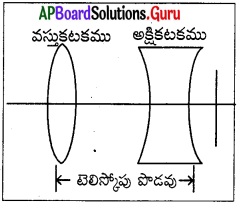
i) Hand Picking
ii) Washing
iii) Froth floatation
iv) Magnetic Separation.
Concentration of sulphide ore :
- Sulphide ore is concentrated by using froth floatation Method.
- The ore with impurities is tinely powdered and kept in water taken in a flotation cell.
- Air under pressure is blown to produce froth in water.
- Froth so produced, taken the ore particles to the surface whereas impurities settle at the buttom.
- Froth is separated and washed to get ore particles.
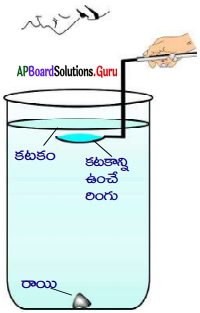
Question 5.
Draw a neat diagram of froth floatation process for the concentration of sulphide ore why we add pine oil to the mixture in this process? (AP SCERT 7201 9-20)
Answer:
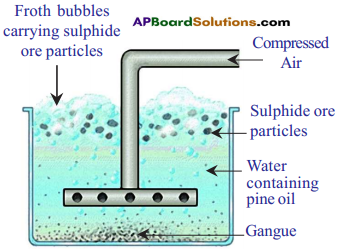
Froth floatation process for the concentration of sulphide ores
- The mineral particles in the ore are preferentially wetted by the oil and float on the top of the froath.
- The gangue particles are wetted by water and settle down.
- Thus, the minerals can be separated from the gangue by adding pine oil.
Question 6.
Describe the reaction of various metals in activity series with oxygen.
Answer:
- The metals which are at the bottom of activity series have very low reactivity and do not burn or oxidase even on surface.
Eg : Ag, Pt, Au. - The metals like Pb, Cu and Hg do not burn but only form a surface layer of oxide, i.e., PbO, CuO, HgO.
- The metals like Al, Zn, Fe react with oxygen to form respective oxides.
- The metals like Ca and Mg burn with decreasing vigorousity to form oxides.
- The metals like K, Na burn vigorously to form Na2O, K2O in limited supply of oxygen but form peroxides in excess of oxygen.
Question 7.
How do you reduce purified ore to the metal of the top of activity series? Explain.
Answer:
The reduction of ore to particular metal mainly depends on the position of metal in the activity series.
Extraction of metals at the top of activity series :
- Simple chemical reduction methods like heating C, CO, etc. to reduce the ores of the metals are not possible with metals like K, Na, Ca, Mg and Al.
- The temperature required for the reduction is too high and more expensive.
- The only method available is to extract these metals by electrolysis of their fused compounds.
Question 8.
How do you extract metals in the middle of activity series?
Answer:
Extraction of metals in the middle of the activity series :
The ores of these metals are generally present as sulphides or carbonates. Therefore prior to reduction of ores of these metals, they must be converted into metal oxides.
The metal oxides are then reduced to the corresponding metals by using the following methods :
1) Reduction of metal oxides with carbon :
The oxides are reduced by coke in closed furnace which gives the metal and carbon monoxide (CO).
![]()
2) Reduction of oxide ores with CO :
![]()
3) Auto (Self) reduction of sulphide ores:
In the extraction of copper from its sulphide ore, the ore is subjected to partial roasting in air to give its oxide.
2 Cu2S + 3O2 → 2 Cu2O + 2SO2
When the supply of air is stopped and temperature is raised, it results in the reaction of rest of the sulphide ore with oxide to form metal and S02. ‘
2 Cu2O + Cu2S → 6 Cu + SO2
4) Reduction of ores (compounds) by more reactive metals :
When highly reactive metals such as sodium, calcium, aluminium, etc. are used as reducing agents, they displace metals of low reactivity from the compound.
![]()
Question 9.
How do you extract metals at the bottom of the activity series?
Answer:
1) Metals at the bottom of the activity series are often found in free state.
2) The oxides of these metals can be reduced to metals by heat alone and sometimes by displacement from their aqueous solutions.
3) When cinnabar (HgS) is heated in air, it is converted into HgO, then reduced to mercury on further heating.
![]()
4) Displacement from aqueous solution :
When Ag2S is dissolved in KCN solution, it forms dicyanoargentate ions. When these ions are treated with Zn dust powder then Ag is precipitated.
Eg : Ag2S + 4 CN– → 2 [Ag(CN)2]– + S2-
2 [Ag(CN)2]–(aq) + Zn(s) → [Zn(CN)4]2-(aq) + 2 Ag(s)
Question 10.
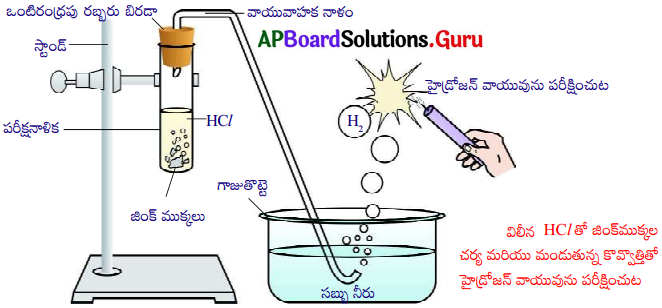
Explain the process involved in corrosion.
Answer:
1) Corrosion is an electrochemical phenomenon.
2) In corrosion, a metal is oxidised by loss of electrons generally to oxygen and results in the formation of oxides.
3) During corrosion at a particular spot on the surface of an object made of iron, oxidation takes place and that spot behaves as anode.
Anode : 2 Fe(s) → 2 Fe2+ + 4e–
4) Electrons released at this anodic spot move through the metal and go to another spot and reduce oxygen at that spot in the presence of H+.
5) This spot behaves as cathode.
Cathode : O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) + 4e– → 2H2O(l)
Net reaction : 2 Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4 H+(aq) → 2 Fe2+(aq) + 2 H2O(l)
6) The ferrous ions are further oxidised by atmospheric oxygen to ferric ions which come out as rust in the form of hydrated ferric oxide (Fe2O3 . XH2O) and with further production of hydrogen ions.
![]()
Question 11.
Explain electrolytic refining with an example.
Answer:
- The impure metal is taken as anode and pure metal is taken as cathode.
- They are put in a suitable electrolytic bath containing soluble salts of same metal.
- The required metal gets deposited on the cathode in the pure form.
- The metal constituting the impurity goes as the anode mud.
Electrode reactions :
At Anode : M → Mn+ + ne–
At Cathode : Mn+ + ne– → M (M pure metal); where n = 1, 2, 3,………….
Examples :
- In order to refine copper, impure copper is taken as anode and pure copper strips are taken as cathode.
- The electrolyte is an acidified solution of copper sulphate.
- As a result of electrolysis copper in pure form is transferred from anode to cathode.
At Anode : Cu → Cu2+ + 2e–
At Cathode : Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu - The soluble impurities go into the solution, whereas insoluble impurities from the blister copper deposited at the bottom of anode as anode mud.
Question 12.
What is activity series? Give two examples each of them.
i) Low reactivity metals
ii) Moderate reactivity metals
iii) High reactivity metals
Answer:
Arranging metals in descending order of their reactivity is called activity series,
e.g.:
i) Low reactivity : Ag (Silver), Au (Gold)
ii) Moderate reactivity : Zn (Zinc), Fe (Iron)
iii) High reactivity : K (Potassium), Na (sodium)
Question 13.
Write the balanced chemical equations, extraction of iron from haematite in the Blast furnace.
Answer:
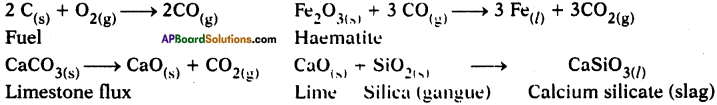
Question 14.
How do you prevent corrosion of various metals?
Answer:
Prevention of corrosion :The corrosion can be prev ented by the following methods.
1) Barrier protection :
In this method the metal surface is not allowed to come in contact with moisture, oxygen and carbon dioxide. This can be achieved by the following.
a) By coating iron with oils, paints, coal tar, grease, pitch, etc.
b) By blowing steam over red hot iron to form protective coating of Fe3O4.
c) By alloying iron with Ni, Cr, Si, etc.
2) Sacrificial protection:
Sacrificial protection means covering the iron surface with a layer of metal which is more electropositive than iron thus prevents iron from losing electrons. It is done by following methods.
a) By galvanisation (by dipping iron in a bath of molten zinc).
b) By tinning (by dipping iron in molten tin).
c) By the coating of copper.
d) Decorative coating : By using Zn, Mg and A/ powders mixed with paints.
3) Electrical protection:
In this method, the iron object to be protected from corrosion is connected to more active metal eg. magnesium, zinc or aluminium directly or through a wire. The iron object acts as cathode and the protective metal acts as anode. The anode is gradually used up to the oxidation of metal to its ions due to loss of electrons. Hydrogen ions collect at cathode and prevent rust formation.
4) Using anti-rust solution:
On applying alkyl phosphates and alkyl chromates to the iron objects corrosion can be prevented.
Question 15.
What are the salient features of the activity series?
Answer:
Salient features:
- Any metal which is placed higher up in the series can displace any metal below it in order to from the salt solution of the later metal.
- The larger the difference in the position of metals in the series, the more rapidly does the displacement take place.
- Metals which are placed above hydrogen in the series have the ability to reduce ions from dilute sulphuric acid to liberate hydrogen gas.
- Oxides of metals K, Na, Ca and Mg cannot be reduced by H2, CO or C.
- Oxides and nitrates of less reactive metals Hg, Ag and Au decompose to give metals on being strongly heated.
- Metals below copper such as mercury, silver, platinum and gold do not rust easily.
- Hydrogen though a non-metal, has been included in the series.
It occupies the position based on its formation of positive ions.
Question 16.
How do you extract metals based on activity series?
Answer:
- Highly active metals like potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium and aluminium are obtained by the electrolysis of their fused halides or oxides, that is, by electrolytic reduction because their oxides cannot be reduced by common reducing agents like carbon, carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
- Zinc is obtained only by heating its oxide with carbon.
- Iron, lead and copper are obtained by reduction of their oxides with carbon, carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
- Copper is obtained by reducing black copper oxide with carbon or by air reduction.
- Mercury and silver are obtained by heating their respective oxides to temperature above 300°C when they lose oxygen and are reduced to free metals.
- However, less active mercury can also be obtained by merely heating its sulphide in air.
- Silver and Gold are obtained by displacement from solutions containing their ions by more electropositive metal zinc.
![]()
Question 17.
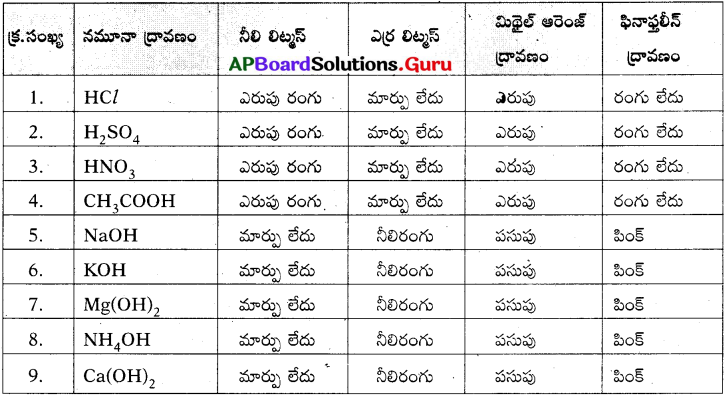
X is an element in the form of a powder. X burns in oxygen and the product is soluble in water. The solution is tested with litmus.
Write down the answers for the following questions from the above information and give reasons.
i) If X is a metal, then which colour will litmus turn ?
ii) If X is a non-metal, then which colour will litmus turn ?
iii) If X is a reactive metal, what gas will be released with dilute sulphuric acid ?
Answer:
i) If X is a metal, then the litmus turns into blue because metal reacts with oxygen and forms metallic oxide and aqueous solution of metallic oxide ore basic in nature.
ii) Mf X is a non-metal, then the litmus turns into red because non-metal reacts with oxygen and forms non-metallic oxide and aqueous solution of non-metallic oxide ore acidic in nature.
iii) If X is a reactive metal, then it releases hydrogen gas from sulphuric acid because more reactive metal displaces hydrogen from acid.
Question 18.
Complete the missing statements and give reasons.
i) Metals are ……………………….., while non-metals are poor conductors of heat.
ii) Metals are malleable, while non-metals are ……………………….. .
iii) Metals form positive ions, while non-metals form ……………………….. .
iv) Non-metals form acidic oxides, while metals form ……………………….. .
Answer:
i) Good conductors.
Reason :
Metals containing free electrons are very good conductors of electricity whereas non-metals are bad conductors of electricity because they do not have free electrons.
ii) Non-malleable.
Reason :
Metals are hard. So, they can be beaten into sheets whereas non-metals are soft, so they are non-malleable.
iii) Negative ions.
Reason :
Metals are electropositive in nature. They easily lose electrons to form positive ions, whereas non-metals are electronegative in nature. So, they gain electrons to form negative ions.
iv) Basic oxides.
Reason :
Non-metallic oxide solutions turn blue litmus into red. They are acidic in nature. So, they are called acidic oxides whereas metallic oxide solutions turn red litmus into blue. They are basic in nature. So, they are called basic oxides.
Question 19.
Answer the following questions.
a) i) Name two naturally occurring compounds of zinc other than carbonate and give their formulae.
ii) Give equations for the extraction of zinc from zinc carbonate.
b) Write equations for the action of zinc on the following.
i) dil. H2SO4
ii) Copper (II) sulphate solution.
Answer:
a) i) The ores of zinc other than carbonate ore are zinc blende (ZnS) and Zincite (ZnO).
b) i) Zn + dil. H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
Zr(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Question 20.
i) The ore zinc blende is an important source of the metal zinc. What is the name of zinc compound in zinc blende?
ii) What is the compound obtained by roasting zinc blende?
iii) What is the type of chemical reaction carried out after roasting in order to obtain zinc?
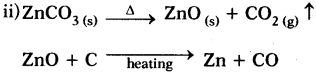
iv) What is the name of the alloy formed between zinc and copper?
Answer:
i) The zinc compound in zinc blende is ZnS (zinc sulphide).
ii) By roasting zinc blende it converts into zinc oxide.
2 ZnS + 3O2 → 2 ZnO + 2 SO2
iii) The chemical reaction carried out to convert zinc oxide to zinc metal is reduction in the presence of coke.
![]()
iv) The alloy of copper and zinc is bronze.
Question 21.
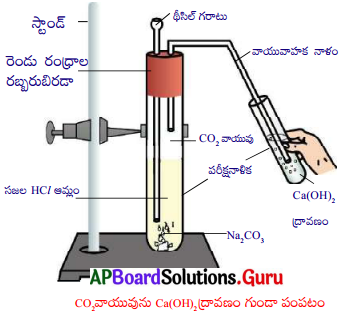
The basic material used for the production of iron in the blast furnace are limestone, coke and air in addition to iron ore.
a) Name one iron ore and write its formula.
b) Hot air is blown at the base of furnace where it reacts with coke. Give the chemical equations for the reactions that take place.
c) Higher up in the furnace the iron ore is reduced to iron by one of the gases produced in the furnace. Give the chemical equation for the reaction by which the gas is produced and give a balanced equation to show how the ore is reduced to iron.
d) Which compound produced from limestone takes part in forming the slag?
Answer:
a) The iron ore is Haematite (Fe2O3).
b) Coke bums partially to produce carbon monoxide gas.
2 C(s) +O2(g) → 2 C0(g)
c) Iron oxide reacts with carbon monoxide gas and reduces to iron.
Fe2O3 + 3 CO → 2 Fe + 3 CO2
d) Calcium carbonate (limestone) undergoes calcination to produce calcium oxide which takes part in the reaction to form slag.
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2
CaC(s) + SiO2(s) → CaSiO3(l)
![]()
Question 22.
What information do you get from metal activity series given below.
K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > [H] > Cu > Ag > Pt > Au
Answer:
- Metals below hydrogen [H] cannot displace hydrogen from acids and above hydrogen can displace hydrogen from acids.
- Metals which are higher in the series, can displace metals below it from the salt solution.
- The higher the position, the more active is the metal.
- Hydrogen has electropositive character, so it is placed among the metals.
Question 23.
The results of reactions of metals A, B, C, D, E with different solutions are given in the table below. Observe the table and write answers.
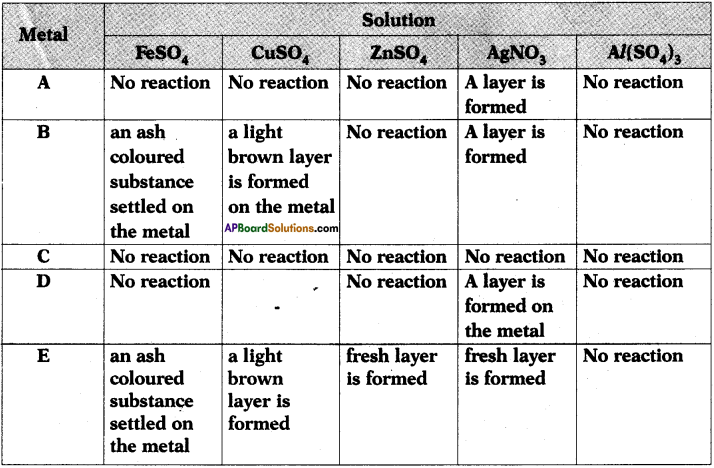
1) Which is the highly reactive metal? Why?
2) Which is the least reactive metal? Why?
3) Which metals form brown layer?
4) Arrange the metals A, B, C, D, E in the order of their reactivity?
5) Among these identify the silver, copper, iron, zinc and aluminium.
Answer:
- Metal ‘E’ is more reactive among all the metals given because it displaces all the elements from the compounds given in the table,
- Metal ‘C’ is the least reactive metal because it does not displace any other metal from the compounds given in the table.
- Metals B and E will form brown layer.
- The ascending order is as follows C < A < D < B < E.
- C is silver, A is copper, D is iron, B is zinc and E is aluminium.
Question 24.
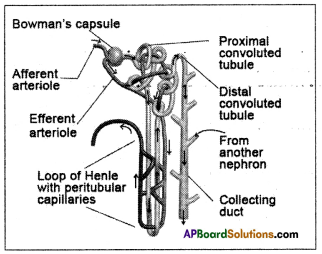
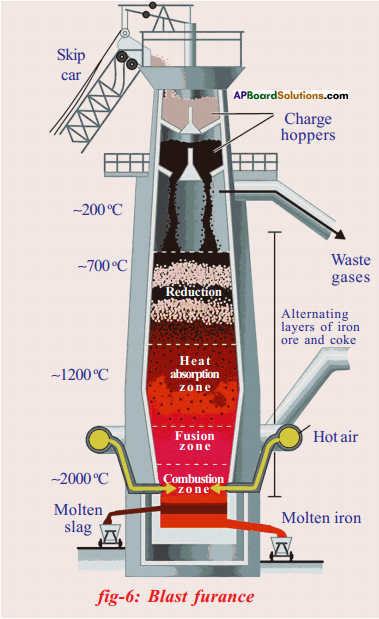
Draw the diagram of blast furnace and label its parts.
Answer:

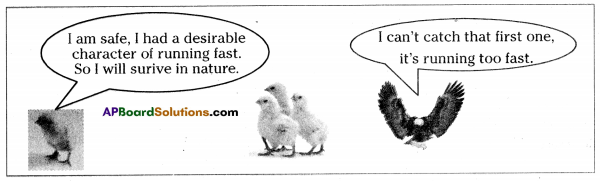

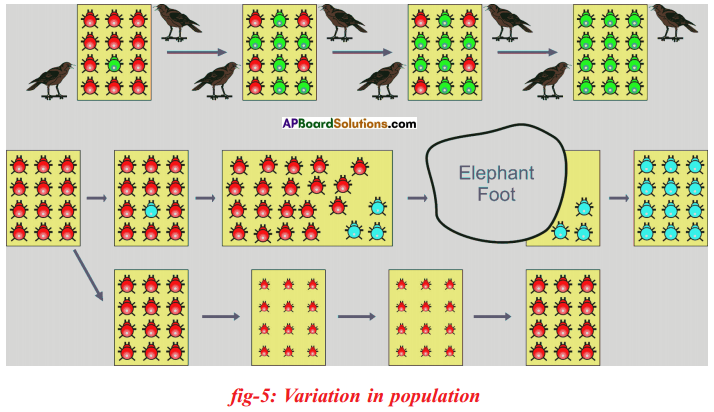 Let us consider a group of twelve beetles. They live in bushes on green leaves. Their population will grow by sexual reproduction. So they were able to generate variations in population. Let us assume crows eat these red beetles. If the crows eat more Red beetles, their population is slowly reduced. Let us discuss the above three different situations in detail.
Let us consider a group of twelve beetles. They live in bushes on green leaves. Their population will grow by sexual reproduction. So they were able to generate variations in population. Let us assume crows eat these red beetles. If the crows eat more Red beetles, their population is slowly reduced. Let us discuss the above three different situations in detail.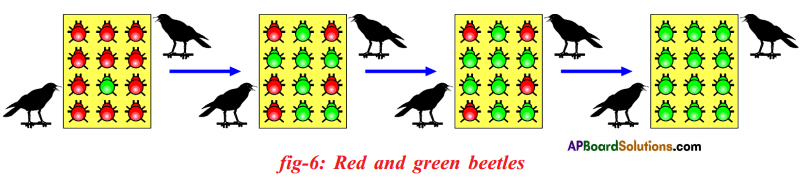 Moreover, this green coloured beetle passes its colour to Its offspring (Progeny). So that all its progeny are green. Crows cannot see the green coloured beetles on green leaves of the bushes and therefore crows cannot eat them. But crows can see the red beetles and eat them. As a result there are more and more green beetles than red ones which decrease in their number.
Moreover, this green coloured beetle passes its colour to Its offspring (Progeny). So that all its progeny are green. Crows cannot see the green coloured beetles on green leaves of the bushes and therefore crows cannot eat them. But crows can see the red beetles and eat them. As a result there are more and more green beetles than red ones which decrease in their number.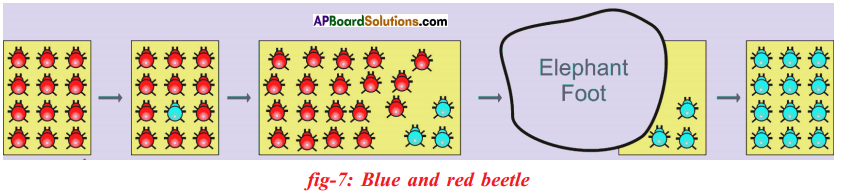 Crows can see blue coloured beetles on the green leaves of the bushes and the red ones as well. And therefore crows can eat both red and blue coloured beetles. In this case there is no survival advantage for blue coloured beetles as we have seen in case of green coloured beetles.
Crows can see blue coloured beetles on the green leaves of the bushes and the red ones as well. And therefore crows can eat both red and blue coloured beetles. In this case there is no survival advantage for blue coloured beetles as we have seen in case of green coloured beetles.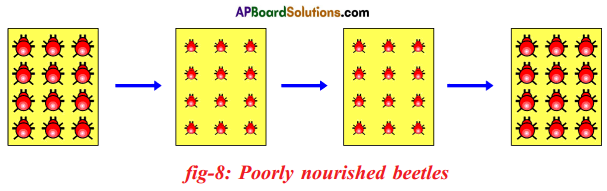 So beetles are poorly nourished. So the weight of beetles decrease but no changes take place in their genetic material (DNA). After a few years the plant disease are eliminated. Bushes are healthy with plenty of leaves.
So beetles are poorly nourished. So the weight of beetles decrease but no changes take place in their genetic material (DNA). After a few years the plant disease are eliminated. Bushes are healthy with plenty of leaves.
 Answer:
Answer: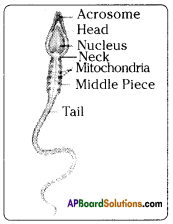
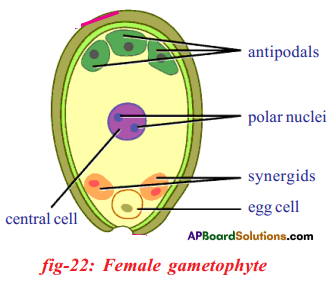
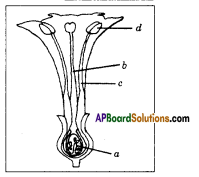
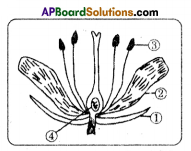 i) Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure.
i) Name male and female reproductive parts of the above figure.
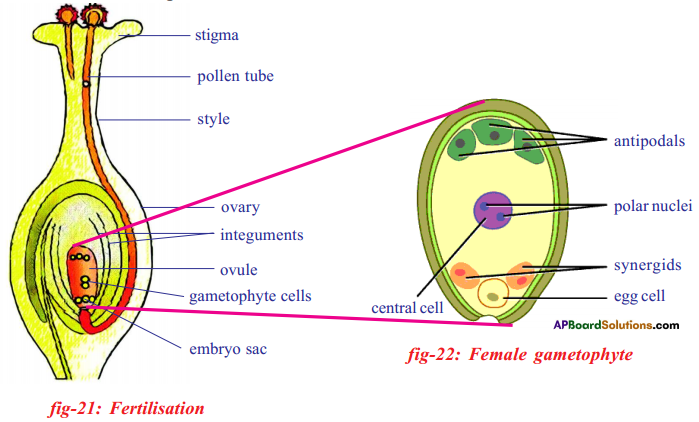
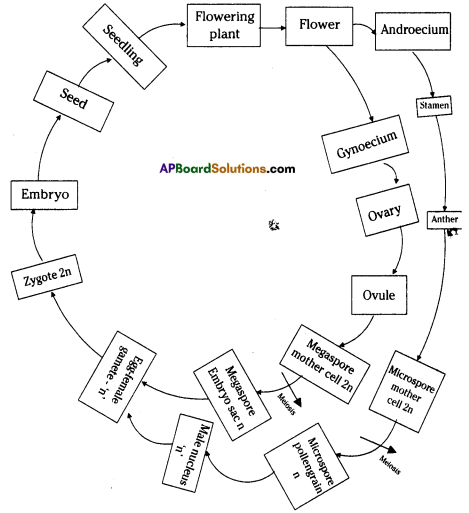
 i) What are the four main parts of a flower?
i) What are the four main parts of a flower?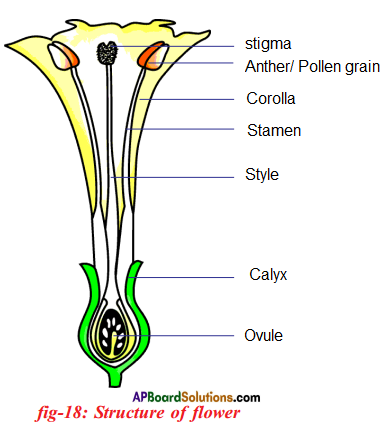 ii) A. Androecium or Stamen
ii) A. Androecium or Stamen
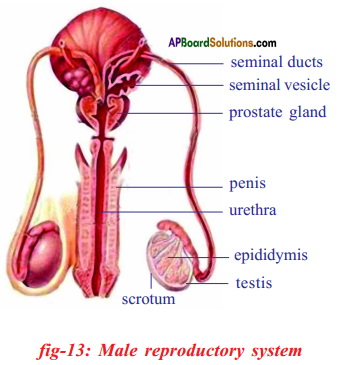 ii) The function of testosterone hormone is maintaining of secondary sexual chracters in males.
ii) The function of testosterone hormone is maintaining of secondary sexual chracters in males.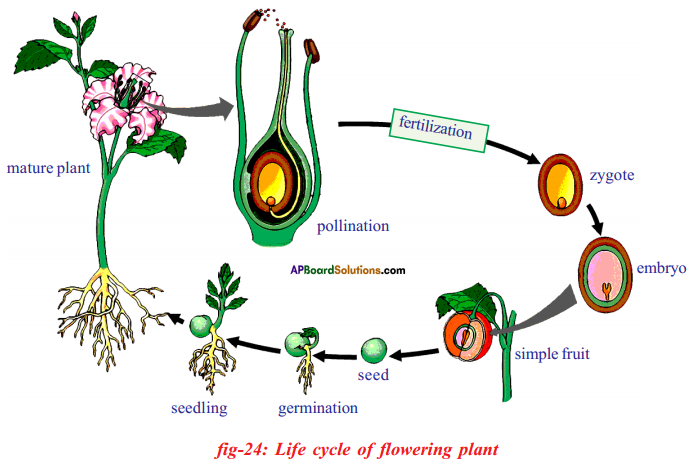
 Answer:
Answer:
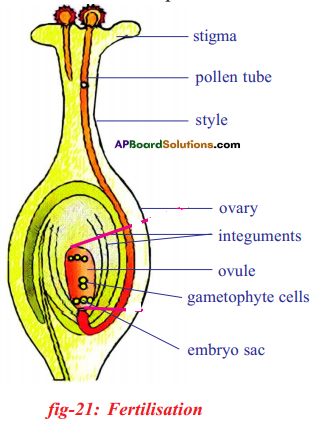
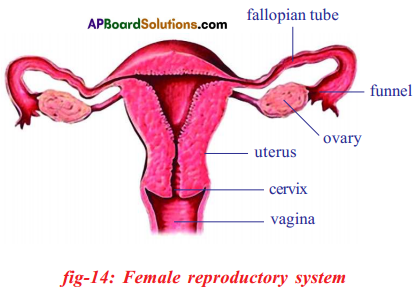 b) If fallopian tubes are closed the sperm can not reach the ova, fertilization will not happen and zygote will not form.
b) If fallopian tubes are closed the sperm can not reach the ova, fertilization will not happen and zygote will not form.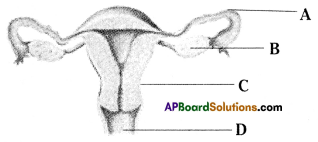
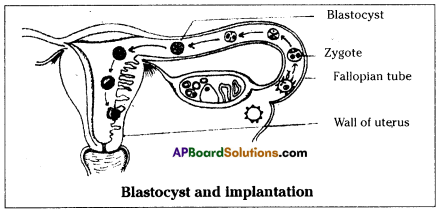
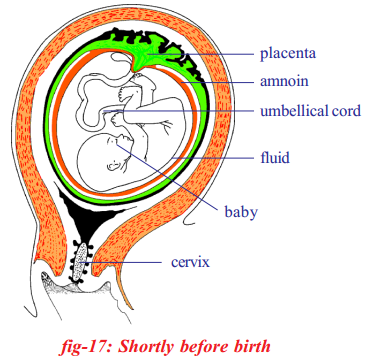




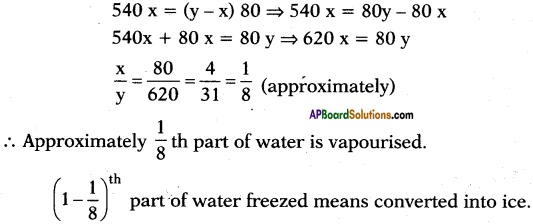
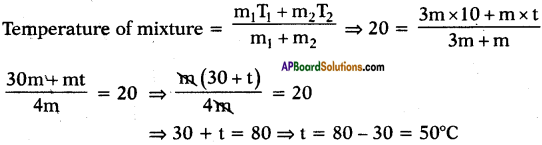
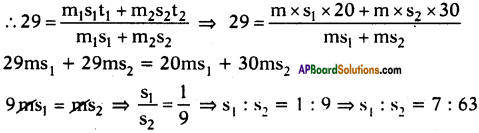

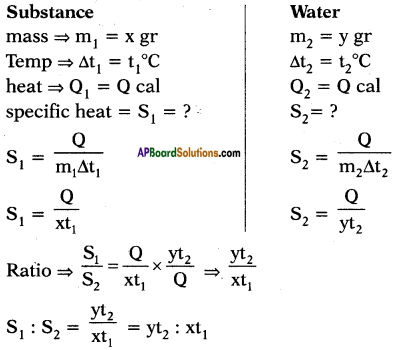





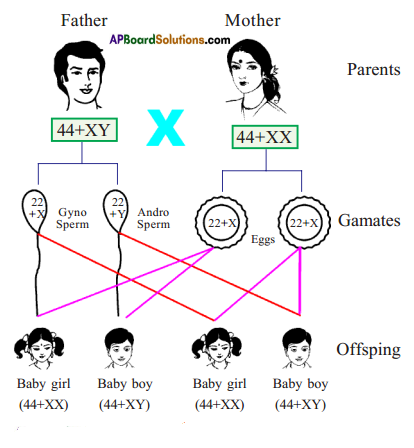
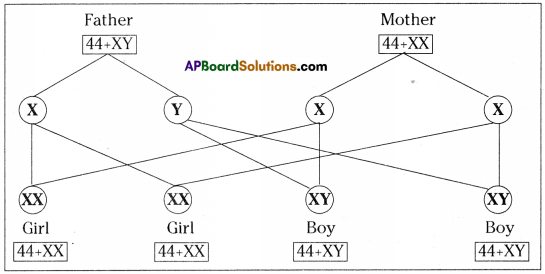
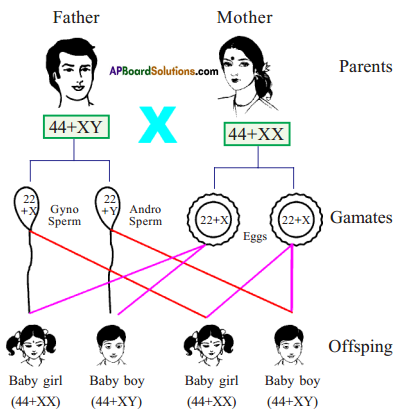
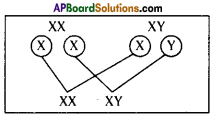 Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?
Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?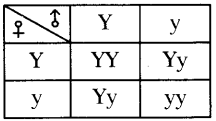 (OR)
(OR)

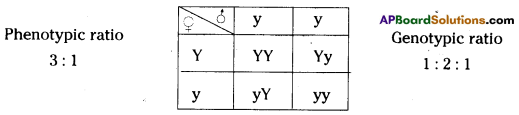
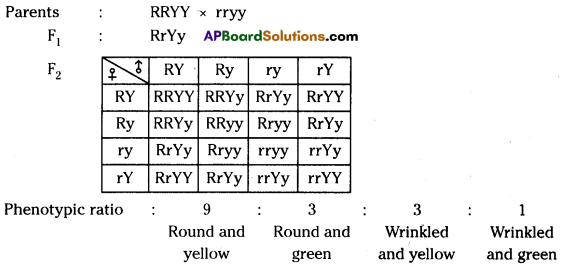
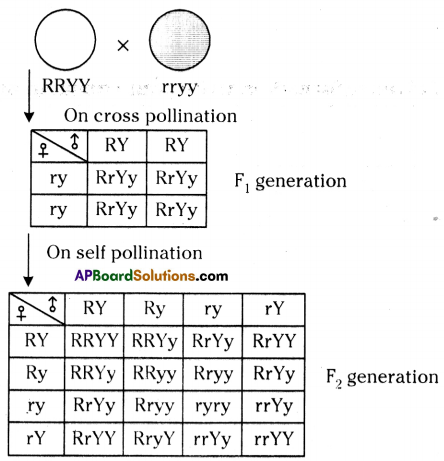
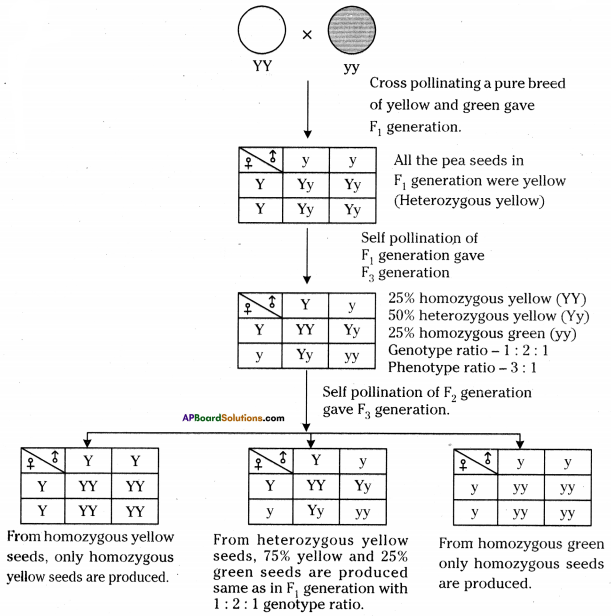
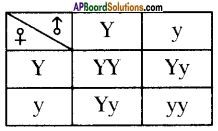 i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.
i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.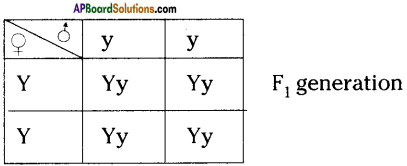 All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.
All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.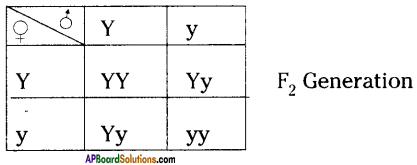 In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.
In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.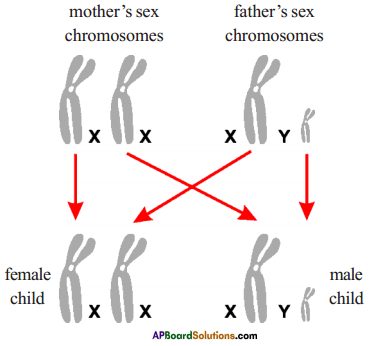 Answer:
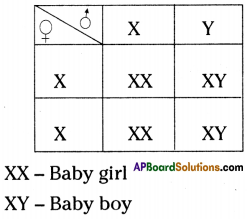
Answer: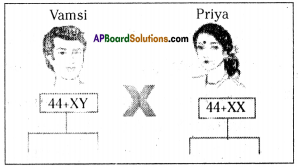 a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.
a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.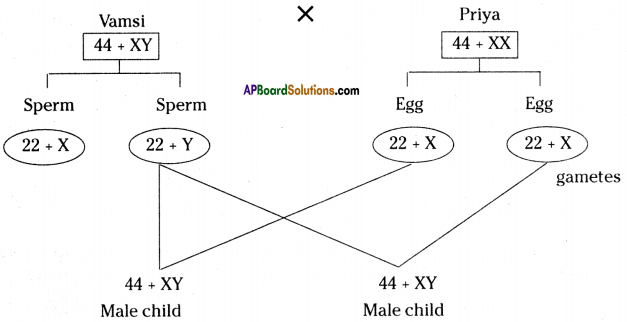 b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?
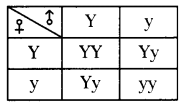
b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?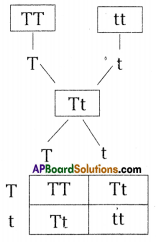 i) What does the flow – chart represent?
i) What does the flow – chart represent?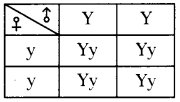
 The above is a procedure of haemodialysis in a hospital.
The above is a procedure of haemodialysis in a hospital.