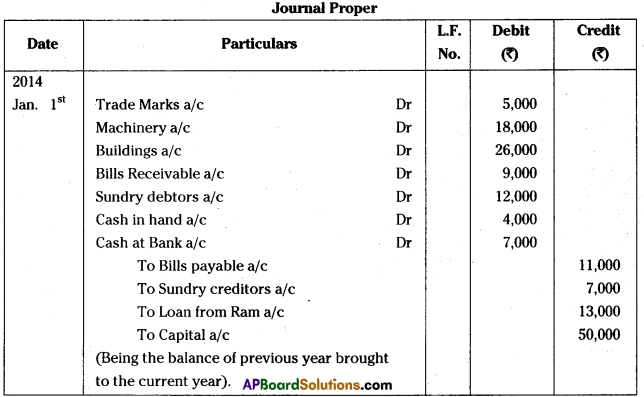
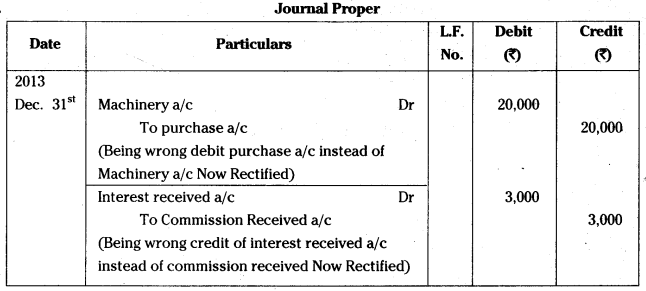
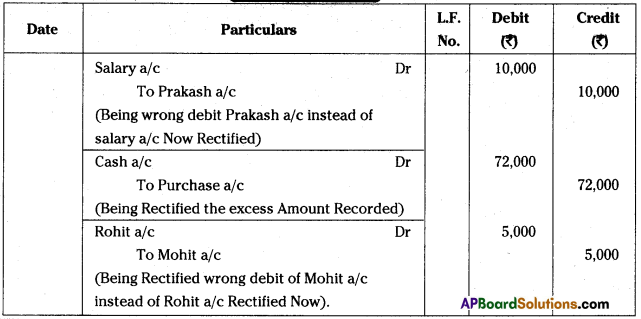
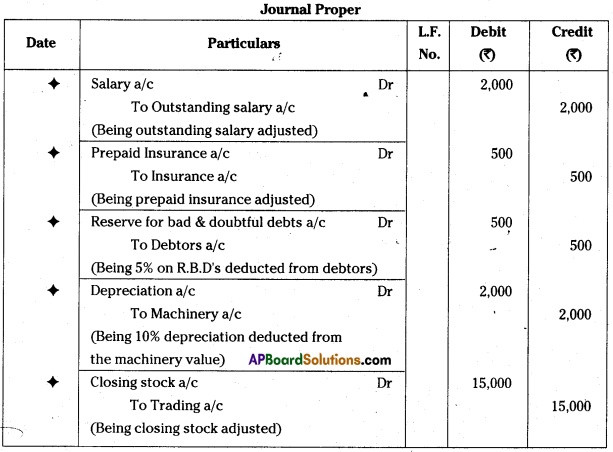
Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 3rd Lesson Forms of Business Organization Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 3rd Lesson Forms of Business Organization
Essay Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Sole Proprietorship and discuss its merits and demerits. [Mar. 17 ; May 17- A.P.]
Answer:
A business unit is commenced with a single person i.e. owned by a single person it is called “Sole proprietorship concern”. The person who does the business is called sole trader. The individual may run the business on his own or may obtain the assistance of employees.
Sole proprietorship concern is also known as individual entrepreneurship, it is easiest to form and is also the simplest in organisation. In the sole trading concerns the sole trader contributes capital and runs the business. There are no legal formalities to be followed except those required for a particular type of business.
A sole proprietor contributes and organises the resources in a systematic way and controls the activities with objective of earning profit.
Sole proprietorship – Definitions:
“A type of business unit where one person is solely responsible for providing the capital and bearing the risk of the enterprise, and for the management of the business.” – J.L. Hanson
“Sole proprietorship is a form of business where the individual proprietor is the supreme judge of all matters pertaining to his business.” – Kimball and Kimball
Merits:
The following are the merits of sole proprietorship concern.
- Easy to form
- Quick decision and prompt action
- Direct contact with customers
- Flexibility in operation
- Maintence of business secrets
- Motivation
- Self employment
1) Easy to form :
It is very and simple to form a sole proprietorship form of business organisation. Less legal formalities are required to be observed. Naturally, the business can be wound up any time if the proprietor so decides.
2) Quick decision and prompt action :
Since he is the sole organizer, he can take quick decisions. He can act promptly according to the changes in the market. Because, nobody interferes in the affairs of the sole proprietory organisation.
3) Direct contact with customers :
He is the owner and manager of the concern. He will be in a position to study the tastes and needs of customers personally since he establishes good contacts with them.
4) Flexibility in operation :
It is very easy to initiate and implement charges as per the requirements of the business. The expansion or curtailment of Forms of Business Organization does not require many formalities as in the case of other forms of business organisation.
5) Maintenance of business secrets :
The business secrets are known only to the proprietor. He is not required to disclose any information to others unless and until he himself so decides. He is also not bound to publish his business accounts.
6) Motivation:
In this organisation the entire profit of the business goes to the owner. This motivates the proprietor to work hard and run the business effectively and efficiently.
7) Self-employment:
Small scale units can be easily started. Nationalised banks are also helping in this direction.
Demerits:
The following are the demerits.
- Limited resources
- Lack of continuity
- Unlimited liability
- Limited managerial skills
1) Limited resources :
The resources of a sole proprietor are always limited. Being the single owner, it is not always possible to arrange sufficient funds from his own sources. So, the proprietor has a limited capacity to raise funds for his business.
2) Lack of continuity :
The continuity of the business is linked with the life of the proprietor. Illness, death or insolvency of the proprietor can lead to closure of the business. Thus, the continuity of business is uncertain.
3) Unlimited liability :
As per law, the proprietor and business are one and same. So personal proprietors of the owner can also be used to meet the business obligations and debts.
4) Limited managerial skills :
As there is only one man the managerial ability is limited. The sole trader has limited financial sources, administration, sale and marketing skills. However, all skills required to take decisions may not be present in a single person alone.
![]()
Question 2.
“One man management is best in the world provided one man is big enough to take care of everything.” Discuss.
Answer:
Business organisation is an organised entity having group of people working together to achieve or common goal. In order to achieve the desired goal, try to organisations mobilise capital or finance, employ labour or man power and other resources like land and building, plant and machinery, furniture and fitting, etc. Finally, all these resources are put together in a useful manner to achieve the end results.
Sole proprietorship concern is one of the business organisations. When a business organisation is owned by a single person, it is called sole trade in concern. It is also known as “one man’s business”. The person who does the business is called the sole trader or sole proprietor. The sole trader carries on business by himself and for himself. He is the proprietor, manager and controller of business. He enjoys all profits and bears all losses.
According to James Stephenson, a sole trader is a person who carries on business exclusively by and for himself. The leading feature of this kind of concern is that the individual assumes full responsibility for all risks connected with conduct of business. He is not only the owner of the capital of the undertaking, but is usually the organizer and manager and takes all the profits or responsibility for losses.
Sole proprietorship has several advantages but proves to be inadequate as the business expands. One man control is ideal if the man is competent enough to manage everything. But in reality, one man cannot look after every aspect of business. Therefore, sole proprietorship is suitable for small scale business.
In spite of all the limitations, a sole trading concern is a popular form of organisation in all parts of the world. Thus, we can say that it has its own place in the field of business even today. Its future is bright. In the words of William R. Basset, “One man control is the best in the world, if that one man is big enough to manage everything. But a business must be small, indeed to permit one man actually to know and to supervise everything. The danger is always present that he thinks he knows, when really he does not know. If the one man is away or ill, the business stops and when he dies, business vanishes or has to be rebuilt”. Thus, one man control is strictly limited to small business only.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is sole proprietorship?
Answer:
A sole proprietor contributes and organises the resources in a systematic way and controls the activities with the objective of earning profit.
The sole proprietorship is that form of business ownership which is owned and controlled by a single individual. He receives all the profits and bears risks of his property in the success of failure of the ent.erprises^It is the first stage in the evolution of the forms of organisation and is thus, the oldest among them,
Sole proprietorship also known as individual entrepreneurship, it is the easiest to form and is also the simplest in organisation. All that is required is that the individual concerned should decide to carry on some particular business and find the necessary capital. For this purpose, he may depend mostly on his own savings, or else, he may borrow part or whole from his friends or relatives. There are no legal formalities to be followed except those required for a particular type of business.
Question 2.
Explain the features of sole proprietor.
Answer:
“Sole proprietorship is a form of business where the individual proprietor is the supreme judge of all matters pertaining to his business.” – Kimball and %imball
The important features of sole proprietorship :
- The business is owned by only one person.
- The business is controlled by a single individual.
- The risk is borne by a single person only i.e. sole trader.
- The liability of the sole trader is unlimited.
- The business concern has no separate legal entity, i.e. as per law the sole trader and firm both are same.
- To commencement of business, legal formalities are very less. So it is easiest form.
- Decisions are made by sole trader only.
Thus, a sole proprietor or trader is a person who sets up his business with his own resources. He is the owner, entreprenuer, financier, manager, controller of Lie business and sole responsible for the results of its operations.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the limitations of sole trader.
Answer:
The following are the limitations of sole trading concern.
- Limited resources
- Lack of continuity
- Unlimited liability
- No suitable for large scale operations
- Limited managerial skills
1) Limited resources :
The resources of a sole proprietor are always limited. Being the single owner, it is not always possible to arrange sufficient funds from his own sources. So, the proprietor has a limited capacity to raise funds for his business.
2) Lack of continuity :
The continuity of the business is linked with the life of the proprietor. Illness, death or insolvency of the proprietor can lead to closure of the business. Thus, the continuity of business is uncertain.
3) Unlimited liability :
As per law, the proprietor and business are one and same. So personal proprietors of the owner can also be used to meet the business obligations and debts.
4) Not suitable for large scale operations :
Since the resources and the managerial ability is limited, sole proprietorship form of business organisation is not suitable for large scale business.
5) Limited managerial skills :
As there is only one man the managerial ability is limited. The sole trader has limited financial sources, administration, sale, and marketing skills. However, all skills required to take decisions may not be present in a single person alone.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
No separate entity
Answer:
The sole proprietorship unit does not have an entity separate from the owner. The businessman and its enterprise are one and the same, and the businessman is responsible for everything that happens in his business firm.
Question 2.
Unlimited liability
Answer:
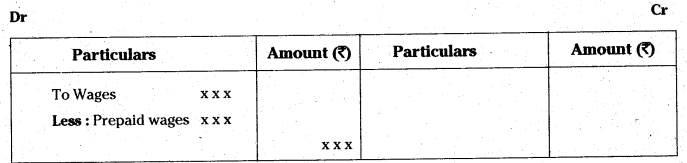
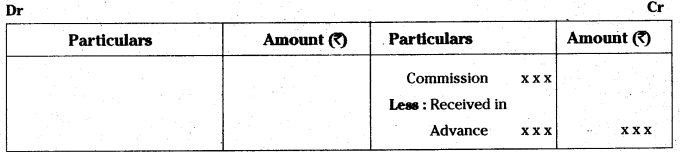
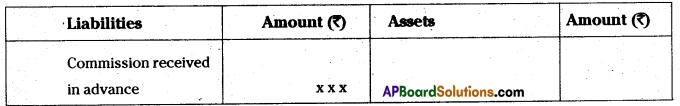
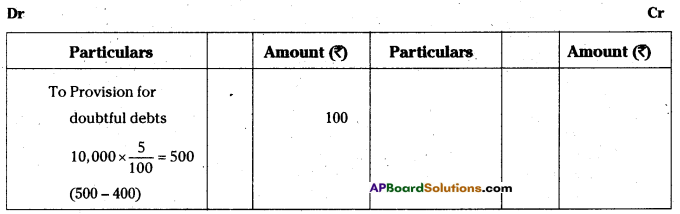
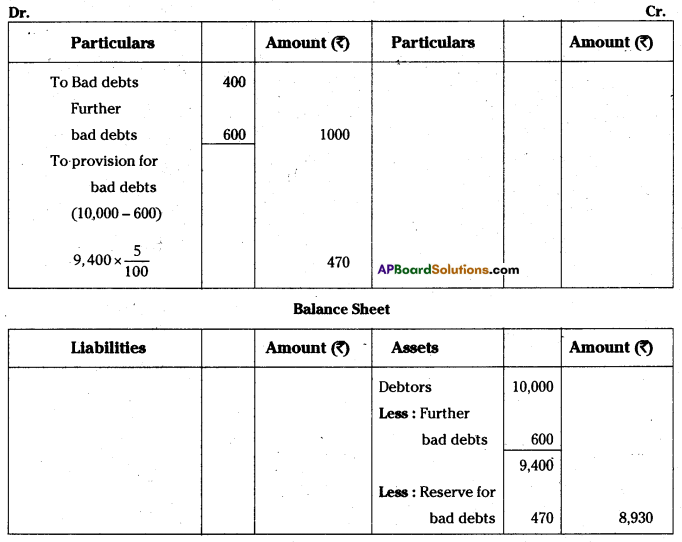
The liability of the sole proprietor is unlimited. In case of loss, if his business assets are not enough to make the payment of business liabilities, his personal property can also be utilised to pay off the liabilities of the business.
![]()
Question 3.
Forms of business organisation
Answer:
Arrangement of ownership and management of business organisations is termed as “Form of business organisation”. Business organisations may be owned and managed by a single individual (sole proprietorship) or a group of individuals (partnership) or in the form of a company (joint stock company).