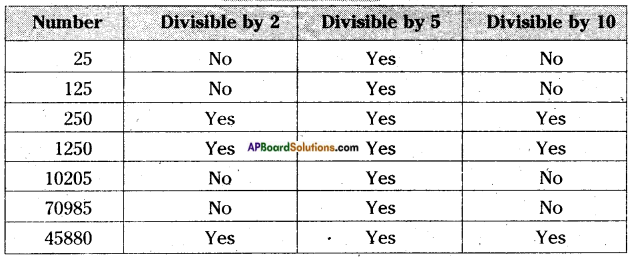
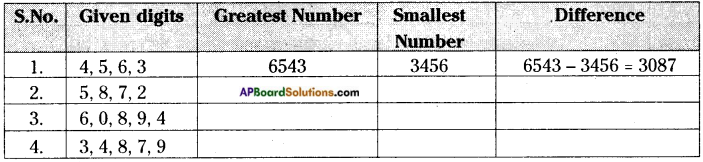
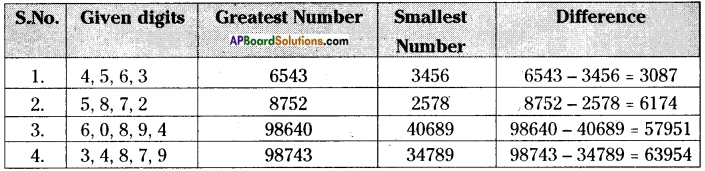
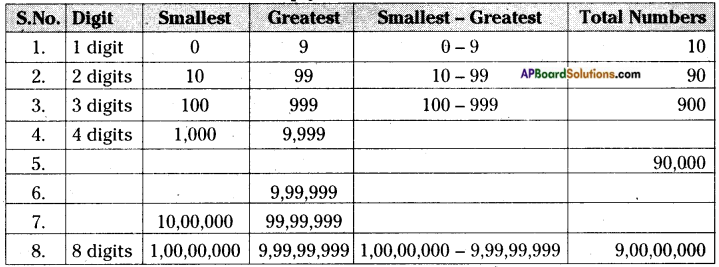
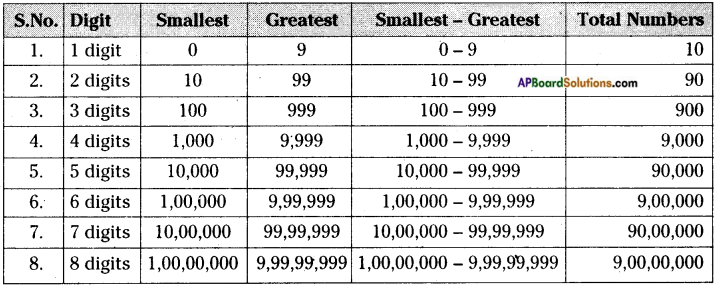
AP State Syllabus AP Board 6th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 3 HCF and LCM Ex 3.2 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Maths Solutions 3rd Lesson HCF and LCM Ex 3.2
Question 1.
Using divisibility rules, determine which of the following numbers are divisible by 11.
i) 6446
ii) 10934
iii) 7138965
iv) 726352
Answer:
i) 6446
If the difference between the sum of the digits at odd places and the sum of the digits at even places of a number is either 0 or a multiple of 11. Then the number is divisible by 11.
Sum of the digits at odd places = 6 + 4 = 10
Sum of the digits at even places = 4 + 6 = 10
Difference 10 – 10 = 0
So, 6446 is divisible by 11.
ii) 10934
Sum of the digits at odd places = 4 + 9 + 1 = 14
Sum of the digits at even places = 3 + 0 = 3
Difference = 14 – 3 = 11
is a 11 multiple by divisibility rule for 11.
So, 10934 is divisible by 11.
![]()
iii) 7138965
Sum of the digits at odd places = 5 + 9 + 3 + 7 = 24
Sum of the digits at even places = 6 + 8 + 1 = 15
Difference = 24 – 15 = 9
is not a multiple by divisibility rule for 11
So, 7138965 is not divisible by 11.
iv)726352
Sum of the digits at odd places = 2 + 3 + 2 = 7
Sum of the digits at even places = 5 + 6 + 7 = 18
Difference = 18 – 7 = 11
is a 11 multiple by divisibility rule for 11.
So, 726352 is divisible by 11.
Question 2.
Write all the possible numbers between 2000 and 2100, that are divisible by 11.
Answer:
Numbers between 2000 and 2100 are 2001, 2002, 2003, ……… , 2097, 2098, 2099.
If we divide 2000 by 11 we get remainder 9.
By adding 2 to the 2000, then we get 2002.
Check by 11 divisibility rule, 2002 is divisible by 11. (difference of sum of odd places digits and sum of even places digits is ‘0’.)
Then 11 multiples after 2002 are 2013, 2024, 2035, 2046, 2057, 2068, 2079, 2090, 2101, …… 2112.
Therefore, 2002, 2013, 2024, 2035, 2046, 2057, 2068, 2079 and 2090 are the numbers divisible by 11 in between 2000 and 2100.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the nearest number to 1234 which is divisible by 11.
Answer:
If we divide 1234 by 11 we get remainder 2.
So, 1234 – 2 = 1232 is divisible by 11
(Difference of sum of odd places digits and sum of even places digits of 1232 is ‘0’)
Therefore, the nearest number to 1234 which is divisible by 11 is 1232.