AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class English Textbook Solutions Chapter 2B What is a Player? Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class English Solutions Chapter 2B What is a Player?
9th Class English Chapter 2B What is a Player? Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What are the qualities that a true player should have?
Answer:
A true player accepts defeat with ease. He learns from his failures. He loves to share and enjoys the rival’s victory too. He knows his abilities. He continuously works for progress. He practises in all seasons and at all times. He never complains. He is not worried about past failures. He thinks of the present and plans for the future.
Question 2.
What, according to the poet, is an unacceptable crime of a player?
Answer:
Complaining about play time is an unacceptable crime.
![]()
Question 3.
Which game do you like the most? What are the qualities of a player stated in the poem? Which of them do you have?
Answer:
I like volleyball the most. The poem lists the qualities of a player. They are accepting defeat, learningfrom failures, continuous practice, knowing one’s own limitations, sharing, not complaining, not worrying about past defeats, focussing on the present, and contributing to the game. I have some of them. They are : accepting defeat, regular practice, learningfrom failures, not complaining.
Question 4.
The poet talks about certain Do’s and Don’ts for a true player. List them out in the following table. One is done for you.
| Do’s | Don ts |
| regular practice | give up at the sight of defeat |
Answer:
| Do’s | Don ts |
| 1. regular practice | give up at the sight of defeat |
| 2. learn from mistakes | give up at the sound of the buzzer |
| 3. have sensible mind | whine/complain |
| 4. contribute to the game | settle for less |
| 5. admit to be fine even when hurt | chicken out |
What is a Player? Summary in English
Jessica Taylor’s poem, “What is a Player” lists the qualities a good player possesses. An ideal player continues despite defeat and learns from failures. A good player finds pleasure in sharing and enjoys the rival’s victory too. A true sportsman never complains about his chances, for he knows it is a crime. A model player practises regularly and keeps in mind that success is not always guaranteed. The real player always aims high, works for continuous advancement, and practises day and night; in rain and shine and when healthy or not. A player is always sensible and never worries about past defeats and thinks of the present and plans for the future. A true player doesn’t do something in fear and wants to contribute to the game as long as he is there.
What is a Player? Glossary
give up (phr.v) : quit, leave
buzzer(n) : bell
whine (v) : complain
hurt (adj) : injured
sensible (adj) : reasonable, logical, sane
pondering (v + ing) : thinking
contemplating (v) : thinking; planning
chicken out (phr. v) : to decide not to do something because of fear
counts (v) : be important
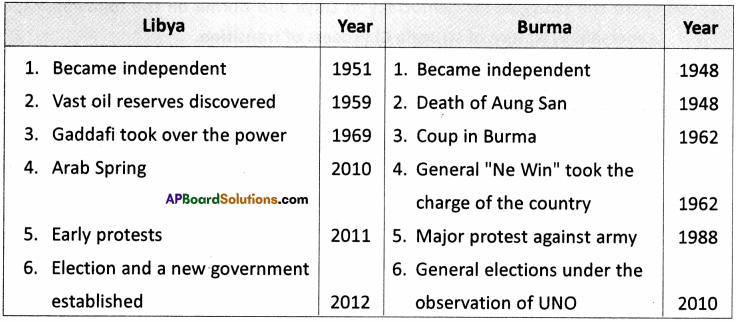


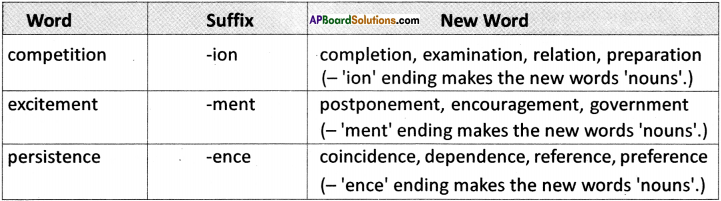
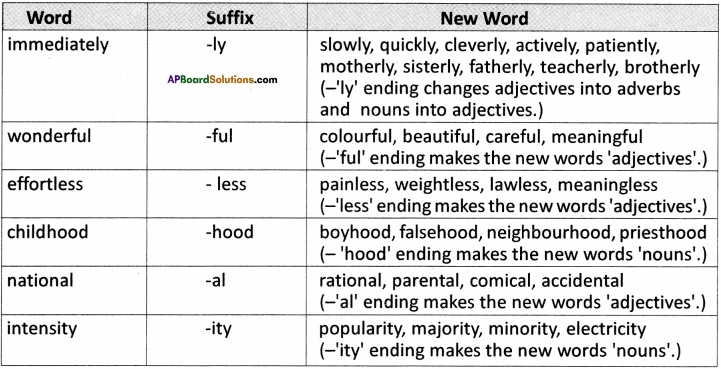

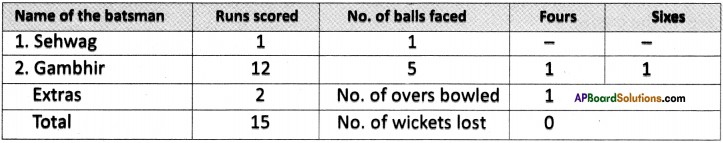





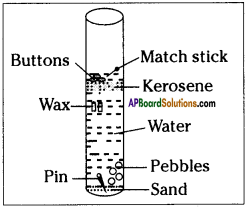
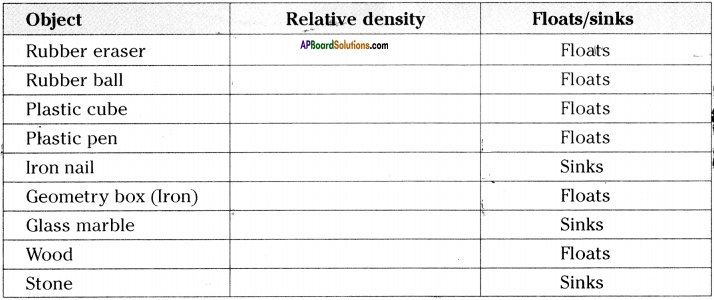
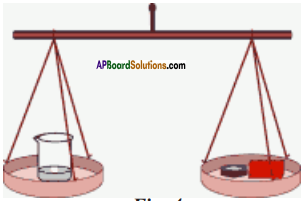


 (SA-I: 2019-20)
(SA-I: 2019-20)