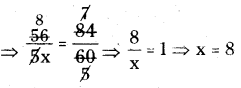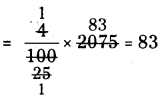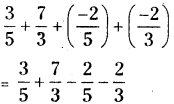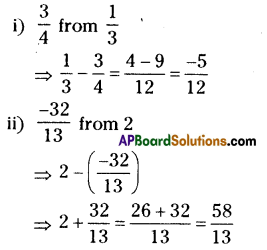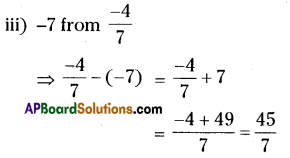AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Comparing Quantities Using Proportion Ex 5.2 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 5th Lesson Comparing Quantities Using Proportion Exercise 5.2
![]()
Question 1.
In the year 2012, it was estimated that there were 36.4 crore Internet users worldwide. In
the next ten years, that number will be increased by 125%. Estimate the number of Internet
users worldwide in 2022.
Solution:
Internet users in the year 2012
= 36.4 crores.
The number will be increased by next
10 years = 125%
∴ The no. of internet users in the year 2022
= 36.4 + 125% of 36.4
= 36.4 + [latex]\frac { 125 }{ 100 }[/latex] × 36.4
= 36.4 + 45.5
= 81.9 crores.
![]()
Question 2.
A owner increases the rent of his house by 5% at the end of each year. If currently its rent is ₹ 2500 per month, how much will be the rent after 2 years’?
Solution:
Present house rent = ₹ 2500 If the owner increases the rent by 5% on every year then the rent of the house after 2 years
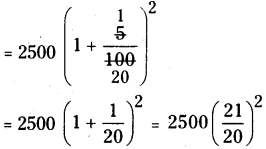
= 2500 × [latex]\frac { 21 }{ 20 }[/latex] x [latex]\frac { 21 }{ 20 }[/latex]
= ₹ 2756.25
Question 3.
On Monday, the value of a company’s shares was ₹ 7.50. The price increased by 6% on Tuesday, decreased by 1.5% on Wednesday, and decreased by 2% on Thursday. Find the value of each share when trade opened on Friday.
Solution:
The value of the share when trade opened on Friday
= ₹ 7.674

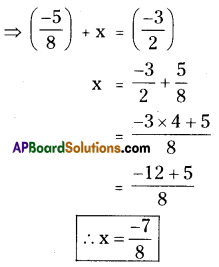
Question 4.
With most of the Xerox machines. you can reduce or enlarge your original by entering a percentage for the copy. Reshma wanted to enlarge a 2 cm by 4 cm drawing. She set the Xerox machine for 150% and copied her drawing. What will be the dimensions of the
copy of the drawing be’?
Solution:
Length of the copy = 2 cm
breadth = 4 cm
If the length is increase in 150% then its
measure = 150 % of 2 cm
= [latex]\frac { 150 }{ 100 }[/latex] × 2 = 1.5 × 2 = 3 cm
If the breadth is increase in 150% then
its measure = 150 % of 4 cm 150
= [latex]\frac { 150 }{ 100 }[/latex] × 4 = 1.5 × 4 = 6 cm
100
∴ New length = 3 cm
breadth = 6 cm
![]()
Question 5.
The printed price of a book is ₹ 150. And discount is 15%. Find the actual amount to be paid.
Solution:
The printed price of a book = ₹ 150
Discount % = 15%
∴ Discount = 15% of 150
= [latex]\frac { 15 }{ 100 }[/latex] × 150 = ₹22.5
∴ The C.P. of a book = 150 – 22.5
= ₹127.50/-
Question 6.
The marked price of an gift item is ₹ 176 and sold it for ₹ 165. Find the discount percent.
Solution:
Marked price of a gift = ₹176
S.P. = 165
Discount = 176 – 165 = ₹ 11
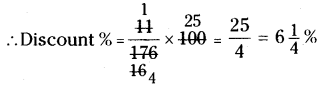
![]()
Question 7.
A shop keeper purchased 200 bulbs for ₹10 each. However 5 bulbs were fused and put
them into scrap. The remaining were sold at ₹12 each. Find the gain or loss percent.
Solution:
The C.P. of 200 bulbs at the rate of ₹10 for each = 200 × 10 = ₹ 2000
If 5 bulbs are fused then remaining are
= 200 – 5 = 195
∴ TheS.P. of 195 bulbs at the rate of ₹12 for each = 195 × 12 = ₹ 2340
∴ S.P. > C.P.
∴ Profit = S.P.-C.P.
= 2340 – 2000 = 340
Profit = [latex]\frac { Profit }{ C.P }[/latex] × 100 = [latex]\frac { 340 }{ 2000 }[/latex] × 100
Profit = 17%
Question 8.
Complete the following table with appropriate entries (Wherever possible)
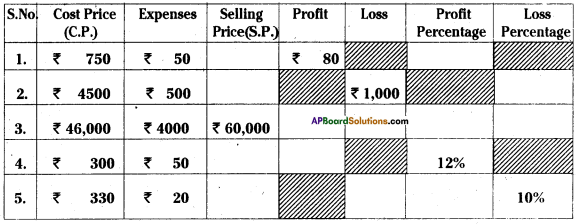
Solution:
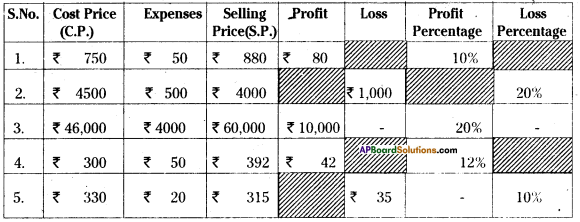
![]()
Question 9.
A table was sold for ₹2,142 at a gain of 5%. At what price should it be sold to gain 10%.
Solution:
S.P. of a table = ₹ 2142
Profit = 5%

∴ The C.P. of buyyer = ₹ 2040
Profit % = 10%
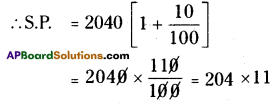
∴ S.P. = ₹2244
Question 10.
Gopi sold a watch to Ibrahim at 12% gain and Ibrahim sold it to John at a loss of 5%. If John paid ₹1,330, then find how much did Gopi sold it?
Solution:
. Let Gopi’s cost price = ₹100
Gain = 12%
∴ Gopi’s selling price to Ibrahim or Ibrahim’s cost price = ₹100 + ₹12 = ₹112
∴ Ibrahim’s loss = 5%
∴ Ibrahim’s selling price =
[latex]112\left(\frac{100-5}{100}\right)=\frac{112 \times 95}{100}[/latex] = ₹106.40
For ₹100 we get = ₹106.40
For ₹1330 how much we get ?
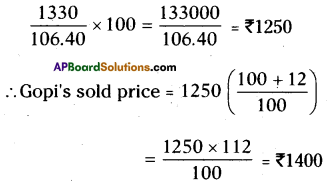
![]()
Question 11.
Madhu and Kavitha purchased a new house for ₹3,20,000. Due to some economic
problems they sold the house for ₹2,80,000. Find (a) The loss incurred (b) the loss percentage.
Solution:
C.P. of a house = ₹ 3,20,000
S.P. of a house = ₹ 2,80,000
∴ C.P. > S.P.
a) Loss
= C.P. – S.P.
= 3,20,000 – 2,80,000 = 40,000
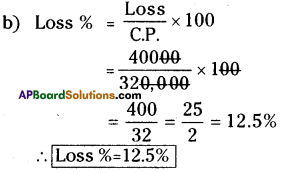
Question 12.
A pre-owned car show-room owner bought a second hand car for ₹ 1,50,000. He spent ₹20,000 on repairs and painting, then sold it for ₹ 2,00,000. Find whether he gets profit or loss. If so, what percent?
Solution:
After repair, the C.P of a car
= 1,50,000 + 20,000 = 1,70,000
S.P. of a ear = ₹ 2,00,000
∴ S.P. > C.P.
∴ Profit = S.P.-C.P.
= 2,00,000-1,70,000= 30,000
Profit = [latex]\frac { Profit }{ C.P }[/latex] × 100
[latex]\frac { 30,000 }{ 1,70,000 }[/latex] × 100 = Profit = [latex]\frac { 300 }{ 17 }[/latex]
Profit% = 17.64%
![]()
Question 13.
Lalitha took a parcel from a hotel to celebrate her birthday with her friends. It was billed with ₹ 1,450 including 5% VAT. Lalitha asked for some discount, the hotel owner gave 8% discount on the bill amount. Now find the actual amount that lalitha has to pay to the hotel owner
Solution:
After allowing 5% VAT, the total bill = ₹ 1450
If 8% discount is allowed on bill, then
Discount = 8% of 1450
[latex]\frac { 8 }{ 100}[/latex] × 1450 = ₹116
Discount = ₹116
∴ Lalitha has to pay the bill = 1450 -116
= ₹ 1334
Question 14.
If VAT is included in the price, find the original price of each of the following.
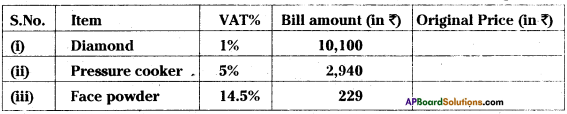
Solution:
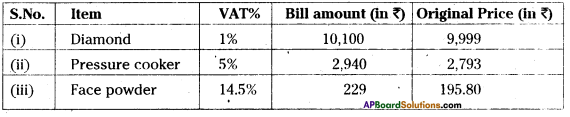
Question 15.
Find the buying price of each of the following items when a sales tax of 5% is added on them.
(1) a towel of ₹50 (ii) Two bars of soap at ₹35 each.
Solution:
Given that Sales tax = 5%
(i) Cost of a towel = ₹ 50
Sales Tax = 5% of 50
= [latex]\frac { 5 }{ 100 }[/latex] x 50 = [latex]\frac { 5 }{ 2 }[/latex] = ₹ 2.50
∴ C.P. = Net Price + Sales
Tax = 50 + 2.50 = ₹ 52.50
(ii) The cost of two soaps at the rate of
₹ 35 each = 2 × 35 = ₹ 70
Sales Tax = 5% of 70
= [latex]\frac { 5 }{ 100 }[/latex] × 70 = [latex]\frac { 7 }{ 2 }[/latex] = ₹ 3.50
∴ C.P. = Net Price + Sales
Tax = 70 + 3.50 = ₹ 73.50
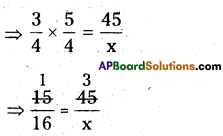
![]()
Question 16.
A Super-Bazar prices an item in rupees and paise so that when 4% sales tax is added, no rounding is necessary because the result is exactly in ‘n’ rupees, where ‘n’ is a positive integer. Find the smallest value of ’n’.
Solution:
Let the cost price = x say
∴ If x is increased 4% sales tax is added then
x + 4% of x = n
x + [latex]\frac { 4 }{ 100 }[/latex] × x = n
[latex]\frac { 140x }{ 100 }[/latex] = n
x = x = n × [latex]\frac { 100 }{ 104 }[/latex] = [latex]\frac{25 \times \mathrm{n}}{26}[/latex]
∴ n should be a least multiple of 26, then only the value of the article should be represented in only rupees.
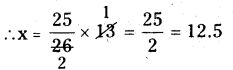
[∵n = 13, 26, 39. from them 13 should betaken]
:. Required value of the article
=12.50 + [latex]\frac { 4 }{ 100 }[/latex] × 12.5
12.50 + 0.5 = ₹13