AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Social Studies Important Questions Chapter 12 Sustainable Development with Equity.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Social Studies Important Questions 12th Lesson Sustainable Development with Equity
10th Class Social 12th Lesson Sustainable Development with Equity 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
1. How does the Green Revolution lead to an increase in food grains?
Answer:
- Use of high yielding varieties.
- Improvement of irrigational facilities.
- Use of new methods of cultivation.
- Use of pesticides and fertilisers.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the main theme of Rachel Carson’s book ‘Silent Spring’?
Answer:
The impact on birds and human beings of spraying DDT for mosquito control.
Question 3.
What is the aim of Chipko movement?
Answer:
The main aim of Chipko Movement is to protect forests.
Question 4.
Write any two slogans on the environmental protection.
Answer:
- Save the environment, save life.
- Save the nature to save the future.
- Go green and eliminate the global warming.
Question 5.
Write one main characteristic of organic farming.
Answer:
In organic farming the farmers use local resources including on-farm biological processes. Pest predators available them. Micro-organisms which make nutrients more accessible to the plants. Chemical fertilizers and pesticides are not used only for animal manure.
Question 6.
What is HDI as a measure of development?
Answer:
As a measure of development, HDI is an improvement over GDP and per capita income.
![]()
Question 7.
Which expands the meaning of development?
Answer:
HDI expands the meaning of development to include social indicators of education and health.
Question 8.
Which are central to the production process?
Answer:
Many naturally existing substances like land, water, minerals and ores, products from trees and animals are central to the production
process.
Question 9.
What does the overuse of ground water imply?
Answer:
Over use of ground water implies that the stock of groundwater is being depleted. Very rapidly the ground water has been falling to lower and lower levels.
Question 10.
Which are central to modern development?
Answer:
Irrigation and power have been produced and both are central to modern development.
Question 11.
What is called NBA?
A. The resistance to Sardar Sarovar and other
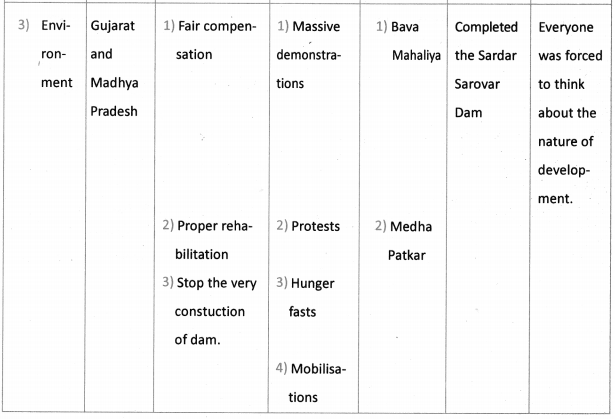
dams with similar consequences in the Narmada valley has taken the form of a social movement. It is called Narmada Bachao Andolan (NBA).
Question 12.
“It is unjust to ask the poor people”
What is it?
Answer:
We have several thousands of communities living off the environment. To destroy the environment means to destroy these communities. It is unjust to ask poor people to bear the cost of development.
Question 13.
Which governments banned chemical fertilizers and pesticides?
Answer:
The Sikkim government and Uttarakhand government.
![]()
Question 14.
When did the Chipko movement start and where?
Answer:
The Chipko movement started in the early 1970s in the Garhwal Himalayas of Uttarakhand.
Question 15.
Expand HDI.
Answer:
Human Development Index.
Question 16.
What is meant by “Water Recharge”?
Answer:
Water Recharge means the percolation of water into the ground to be extracted.
Question 17.
Write about Chipko Andolan?
Answer:
Chipko means embrace the villagers hugged the trees saving them interposing their bodies between them and the contractor’s axes.
Question 18.
What are the natural resources to use in production?
Answer:
Natural resources used in production are land, water, and minerals, forests, etc.
Question 19.
What is meant by sustainable development?
Answer:
Sustainable development is a development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
![]()
Question 20.
What are the activities to take up through an alternative Public Distribution System?
Answer:
Alternate PDS advocates the practice of millets, establishment of community grain bank, issue of cards and ensuring food security in the village.
10th Class Social 12th Lesson Sustainable Development with Equity 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Observe the table which shows the growth in the extraction of some key-minerals in India.
Answer:
Extraction of minerals in a thousand Tonnes
| Minerals | 1997-1998 | 2008-2009 |
| Bauxite | 6,108 | 15,250 |
| Coal | 2,97,000 | 4,93,000 |
| Iron ore | 75,723 | 2,25,544 |
| Chromite | 1,515 | 3,976 |
After your observation, what do you think about the environmental loss of such rapid growth of mining.
- Ground water pollution would increase.
- Temperatures would increase.
- Air pollution would increase near the mining areas.
- Water storage capacity would decrease due to soil erosion.
- Extreme burning of coal leads to ozone depletion.
- Accidents may occur due to heavy mining.
- People may face natural calamities like earthquakes.
Question 2.
What is meant by sustainable development?
Answer:
Sustainable development is a development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In other words, a better quality of life for everyone – now and for generations to come.
![]()
Question 3.
How does organic farming promote bio-diversity?
Answer:
- Chemical fertilizers and pesticides are not used in organic farming.
- Only echo friendly farming techniques are used.
- Methods like crop rotation, using compost and use of Local resources are used.
- Number of crops are produced in farms instead of one or two crops.
Question 4.
Write two slogans on enlightening people regarding “environment protection”.
Answer:
Slogans on Environment Protection.
- Grow plants – Get oxygen
- Avoid plastic bags – Promote cotton bags.
Question 5.
What are the aspects taken as indicators to measure Human Development?
Answer:
Indicators of development:
- Per capita income
- Literacy rate
- Average years of schooling
- Expected years of schooling
- Life expectancy at birth
- Health status
- Employment status
- Equal distribution
Question 6.
Create two slogans to prevent Global warming.
Answer:
- All be nice – Save the ice
- Global warming – Not charming
- Protect Mother Earth – It protects all
Question 7.
Identify the importance of the environment in the development of a nation.
Answer:
The development has to be achieved at any cost. Growth in GDP and modern industrial development are necessary, it is argued, for raising the living standards of people and reducing poverty. Since modern industrial and agricultural development are intensive in use of natural resources including energy, depletion of resources and pollution of the environment is to be expected. It is a sacrifice that has to be borne for higher growth. Once high economic growth and prosperity is achieved, pollution and environmental degradation can be handled. One can spend money and clean up the air and rivers, drink bottled water and build cars that are fuel efficient. After all this is the route the developed countries have taken.
![]()
Question 8.
Prepare a pamphlet on the importance of ‘Sustainable Development’.
Answer:
Importance of Sustainable Development
The development which meets the needs of the present people without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs is called sustainable development. Better quality of life is necessary not only for us but for the next coming generations also. The present concept of development is not like this.
The present scenario is quite adversary. There is no such feeling of future generations and their needs. All generations have the right on utilizing the natural resources like water, air and soil and so on. If we do not consider this, how the next generations survive that everyone should think of.
To what extent the natural resources we need to that extent only we should use. This concept is to be spread among the people.
Government should take up awareness programmes on this issue. Stringent actions should be initiated against who violate the eco laws and acts. In some areas multinational companies have taken up the lands and pumping out the water and selling them. How does the government give permission to such companies which lead to fall down of ground water level? Government should think about this and take action to make sustainable development a real concept.
Question 9.
Why is it necessary to focus on sustainable development now a days?
Answer:
Focus on sustainable development nowadays is compulsory to meet the needs of the present as well as future generations. We have to provide better quality of life for everyone. Conservation of fertility of soil is also essential for future crops. Factory emissions are to be prevented to make the air and water pure.
Question 10.
Differentiate between the environment’s ‘Source function’ and ‘Sink function’.
Answer:
Differences between the Environment’s source function and Sink function.
| Source function | Sink function |
| 1. The sectors of the economy are dependent on natural resources in various degrees. | 1. It is (environment) to absorb and render harmless the waste and pollution from various activities. |
| 2. The potential of an environment to provide these resources is referred to as an environment’s source function. | 2. Unwanted byproducts of production and consumption say exhaust gases from combustion, water used to clean products, discarded packaging and goods no longer wanted are absorbed by the environment. |
Question 11.
How is environmental protection linked with our lifestyle?
Answer:
Our life style is linked with environment protection. We should be habituated to use organic productions. We should avoid plastic. Use renewable energy sources. Reducing quarrying and deforestation to zero. Industrial waste should be disposed in a proper manner. Public transport with compressed Natural Gas is to be encouraged. Radiating devices are to be minimized.
![]()
Question 12.
On what does the primary sector depend?
Answer:
In primary sector activities – agriculture, mining, quarrying – and in the manufacturing and energy sector, production is hugely dependent on natural resources. The other sectors of the economy too are dependent on natural resources in various degrees.
Question 13.
What is environment’s source function?
Answer:
The potential of an environment to provide these resources is referred to as an “environment’s source function”. This function is depleted as resources are consumed or pollution contaminates the resources.
Question 14.
What is another function that the environment provides?
Answer:
There is another function that the environment provides. It is to absorb and render harmless the waste and pollution from various activities. Unwanted by-products of production and consumption say exhaust gases from combustion, water used to clean products, discarded packaging and goods no longer wanted are absorbed by the environment. This is as important as the source function.
Question 15.
What does the ‘sink function’ describe?
Answer:
The “sink function” describes an environment’s ability to absorb and render harmless waste and pollution. When waste output exceeds the limit of the sink function, long-term damage to the environment occurs.
Question 16.
What happened in the past fifty years?
Answer:
In the past fifty years of economic development, both these functions of the environment have been overused. This has been said to affect the carrying capacity of the environment, i.e., the capacity of the environment to support economic production and consumption in the future.
Question 17.
What is modern development for people who have been displaced? Why?
Answer:
For people who have been displaced modern development has been unjust and destructive. Because they have lost access to their greater resource, the local environment. Without the local environment, their lives would be reduced to nothing.
![]()
Question 18.
How are environmental movements?
Answer:
While each of these movements has slightly different contexts, they are essentially demanding the rights of the local communities over the environment. Chipko movement acted to prevent the cutting of trees and reclaim their traditional forest rights that were threatened by contractors. Narmada Bachao Andolan has stood for the rights of the people over land, forests and river.
Question 19.
What is the impact on the environment that the use of pesticides and chemicals?
Answer:
- The excessive use of pesticides and chemical fertilizer exhibit a negative impact on society.
- Environment cannot absorb harmful substances than a limit.
- When waste output exceeds the limit the sink function limit, danger occurs to the environment.
- It pressures on environment’s ability to provide different resources for production.
Question 20.
Is it correct to take HDI (Human Development Index) as a measure of development?
Answer:
- As a measure of development HDI is an improvement over GDP and per capita income.
- The idea of development hardly limited to production of goods and services.
- Rapid expansion of production and income coexist with malnutrition and lack of education and health.
- HDI expands the meaning of development to include social indicators of health and education.
Question 21.
A high % workforce in low-paid employment, an increase in GDP and the enormous variety of goods and services being produced can benefit only a select groups. Read this and interpretate?
Answer:
- In India 90% of workforce is in the unorganized sector, where the conditions of working are not encouraging at all.
- Incomes of both self employed and wage workers in unorganized sectors are generally low and at times pitiably so.
- With, such a high percentage of the workforce is low paid employment, an increase in GDP and the enormous variety of goods and services being produced can benefit only to select groups.
![]()
Question 22.
Construction of big dams “leads to environmental problems”. Read this and interpretate.
Answer:
- They disrupt the lives and livelihoods of lakhs of people.
- Many people lose their access to local environment.
- Many people drop from a state of self – sufficiency to scarcity.
- They were at times made to depend on external forces.
- Many lose their needs without access to the environment.
- Rich biodiversity and treasure of knowledge is lost which comes traditionally.
10th Class Social 12th Lesson Sustainable Development with Equity 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How does the lifestyle of people influence the environment? What are your suggestions to protect the environment ?
Answer:
Influence:
- There is a strong bondage between the lifestyle of human kingdom and environment.
- Environment fulfills many of our needs.
- There are various ways in which our lifestyles of people influence the environment.
- The people of a region lives according to their environment. Their traditions, cultures, festivals, etc. are based on their environment.
My Suggestions:
- Natural resources should be used limitedly.
- Forests should not be cut down. We should take care of them.
- Industrial wastes should be recycled.
- The establishment of industries which release more pollution should be restricted.
- People should be enriched with the knowledge of environment.
Question 2.
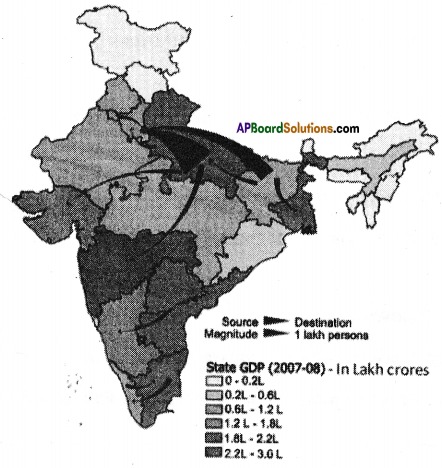
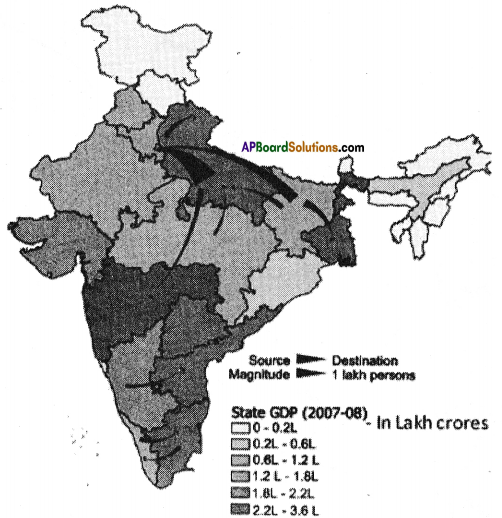
Observe the following Graph diagram.
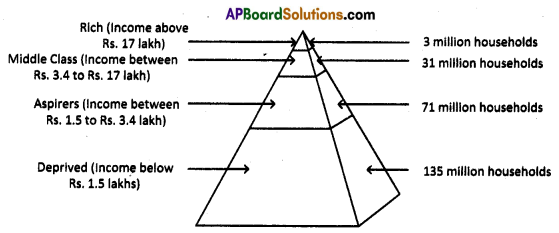 Write a brief note on the inequality in India based on the graph.
Write a brief note on the inequality in India based on the graph.
Answer:
- 3 million households with annual income above Rs. 17 lakh are classified as rich.
- 31 million households with annual income between Rs. 3.4 to Rs. 17 lakh are classified as middle class.
- 71 million households income is between Rs. 1.5 to Rs. 3.4 lakh classified as aspirers.
- 135 million lakhs classified as deprived.
- In our country, more than 90% of the people are in unorganised sector.
- It clearly says that the rich are becoming more rich, whereas the poor remain poor.
- There is inequality in holding wealth as well as opportunities.
- Wide inequalities in incomes and opportunities across people cannot be the basis for a just society.
![]()
Question 3.
Read the text given below and write your opinion.
It is also important to realize that not only do people lose out as they are removed from their local environments, equally, the environment is denuded of Its rich biodlverslty as the traditional knowledge is lost along with the people.
Answer:
The largest of the dams constructed is the Sardar Sarovar, which floods more than 37,000 hectares of forest and agricultural land, displacing more than half a million people and destroying some of India’s most fertile land. The project has devastated human lives and bio-diversity by inundating thousands of acres of forest and agricultural land. A disproportionate number of those being displaced are Adivasi’s and Dalits.
Access to the environment serves a large number of their needs which otherwise they would have to pay for.
As they lose access to environment either because of displacement, or because the environment is destroyed and polluted, the poor are the greatest sufferers. The question of environment and sustainability is intimately connected to the issue of equity.
Question 4.
Write a letter to your district collector on the problems of environment in your area.
Answer:
Anandnagar Colony,
Visakhapatnam,
Date: xxxxxxxxx.
To,
The District Collector,
Visakhapatnam District,
Visakhapatnam.
Respected Sir,
I am Srinivasa Rao, the resident of Gajuwaka. I would like to bring a few lines to your notice about problems of environment in our local area.
In our locality the migrant number is increasing. They are coming to city because of their needs and problems but it leads to new problems here. Water supply, sewage and other waste disposal, transportation and pollution problems are arising. There are plastic covers on the roads everywhere. Many animals on the roads eat those covers and die. As the garbage is increasing and it is not properly cleaned, unbearable stench is spread. There may be a scope for different diseases.
I request you to take proper effective measures wherever polluted industries are there and they should be shut down and minimise polluted plying vehicles and reduce the release of greenhouse gases.
Yours faithfully,
…………………………
…………………………
Question 5.
Study the table given below and answer the questions.
Growth in Extraction of Some Key Minerals in India (in thousand tonnes)
a) What do the particulars of above table tell about?
Answer:
Growth in extraction of some key minerals in India
b) In comparison to other minerals, which one is not being extracted more than double in 2008-09?
Answer:
Coal is not being extracted more than double in 2008 – 09.
c) What might be the reasons for increase in mining?
Answer:
- Number of industries increased.
- Using machinery in mining.
- Consumption of minerals increase.
- Greed of human beings.
d) What do you think would be the environmental and human costs of such rapid growth in mining?
Answer:
- Sustainability of minerals
- Diversion in the direction of river flow
- Causes for floods.
- Extinction of forest cover.
![]()
Question 6.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion on it.
We are already experiencing the negative consequences of rapid economic growth on several fronts – the problem of groundwater and pesticides being two stark examples. We have several thousands of communities living off the environment. To destroy the environment means to destroy these communities.
- The idea of development has been contested through problems of environment.
- The groundwater levels fell rapidly and groundwater recharge is also not to the expected level.
- Fertilizers made the soil less fertile and ever increasing costs to farmers.
- Industrialisation has resulted in a world where natural resources are threatened.
My Opinion: Always we should be able to integrate enviromental concerns with the idea of progress, along with issues of equity and justice. We have to find an environmentally sustainable pathway out of poverty.
Question 7.
Read the paragraph, understand and write your opinion on it.
While industrialisation has brought a lot of material comforts, at least to some, it has resulted in a world where natural resources are threatened and now even the climate is being disrupted. This pattern of growth clearly cannot continue.
Answer:
Opinion on Paragraph :
- Industrialisation in the world has brought a lot of material comforts for humans to lead a happy life.
- Man has invented from small pin to big plane with these metals obtained by mining.
- But at the same time the minerals are reducing in their quantity because man’s short sighted ness.
- As a result of man’s greediness the natural resources such as metals and fossil fuels are declin-ing and threatening our planet to fell in danger.
- Because of over use of these resources, climatic changes are going on with the depletion of ozone layer damage and environment degradation.
I conclude that this type of growth does not create sustainable development to the planet and further it becomes unjustifiable in degrading our environment.
![]()
Question 8.
How would the rapid extraction of natural resources effect the future development prospects?
Explain.
Answer:
- Yes, I agree with this statement.
- We are extracting minerals and natural resources rapidly.
- Modern industrial development and agricultural development are intensive in use of minerals and natural resources.
- If this extraction goes on like this, the mineral deposits and natural resources will be depleted.
- The extent of our current use of minerals and natural resources is such that the chances of future generations to have access to their fair share of scarce resources are endangered.
- Moreover, the consequences in terms of impacts on the environment may induce serious damages that go beyond the carrying capacity of the environment.
Question 9.
Read the following paragraph and interpret in your own words.
Recent data on the status of groundwater resources in India suggests that the groundwater is under serious threat of overuse in many parts of the country. Nearly one-third of the country is pumping out more groundwater than what goes in as recharge. About 300 districts have reported a water level decline of over 4 meters during the past 20 years, which points to an alarming rate of extraction.
Answer:
- According to this paragraph the groundwater resources are decreasing as we are overusing it.
- Maximum of water is pumped out from deep layers.
- Recharging is less and pumping is more.
- In future it will become a major problem to all people.
- The rate of extraction of water is dangerous for our existence.
- Extraction of groundwater doesn’t affect the particular area where the extraction is going on but it affects all surrounding areas also.
- The depth of the bore wells is increasing day by day.
- There should be a change in the human attitude.
- Our behavior should be environment friendly.
- We should not over use ground water.
- Deep wells should be discouraged.
- Plastic usage should be prohibited.
- The government should take stringent action against the people who do not follow these conditions.
Question 10.
Read the following paragraph and interpret in your own words.
This pattern of development is in direct contrast to what sustainable development stands for Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In other words, a better quality of life for everyone-now and for generations to come.
Answer:
- According to the paragraph given, the development which meets the needs of the present people without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs is called sustainable development.
- Better quality of life is necessary not only for us but for the next coming generations also. The present concept of development is not like this.
- The present scenario is quite adversary to the paragraph. There is no such feeling of future
generations and their needs. - All generations have the right on utilizing the natural resources like water, air and soil and so on.
- The government should take up awareness programmes on this issue.
- Stringent actions should be initiated against who violate the eco laws and acts.
- The government should think about this take action to make sustainable development a real concept.
![]()
Question 11.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion.
For most rural communities, the link between the environment and the lives of the people is very strong. Access to the environment serves a large number of their needs (like food, firewood, fodder, economically valuable articles, etc.) which otherwise they would have to pay for. As they lose this access to environment either because of displacement, or the environment is destroyed and polluted, the poor are the greatest losers. The question of environment and sustainability is intimately connected to the issue of equity.
Answer:
- According to the paragraph given here, the rural people are attached with environment for their food and other commodities.
- When there is a displacement they don’t have this facility of getting commodities.
- These poor people suffer a lot when the environment is destroyed and polluted.
- My opinion on this paragraph is that many a time it is happening in many places.
- When displacement takes place, the forest dwellers have to face many problems.
- They don’t have sufficient food and land for cultivation.
- They don’t get loans as they are new to the money lenders of that place.
- The government should think about the troubles of these people when they are asked to move from their living places.
- I am not opposing to construct dams and projects but the displacement should not lead to troubles.
- Alternate arrangements should be made keeping their problems in mind.
Question 12.
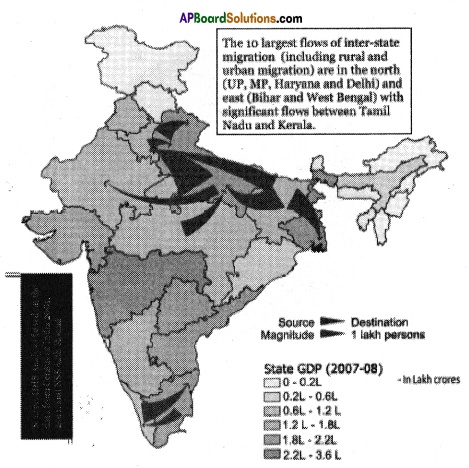
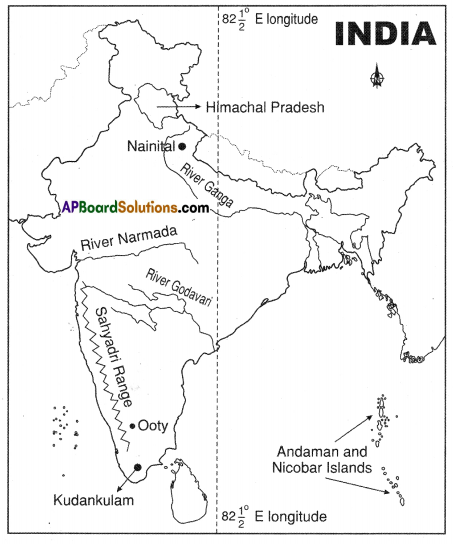
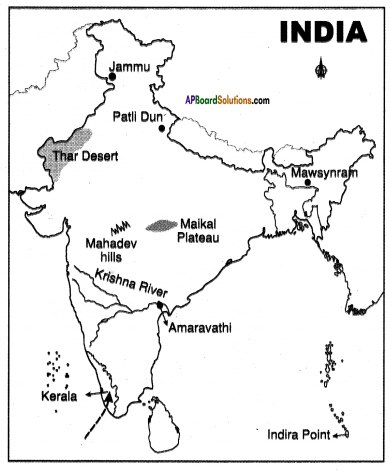
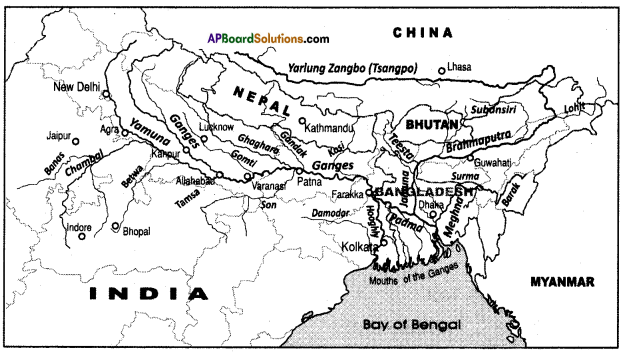
Locate the following points in the Indian map provided.
- Mumbai
- Hyderabad
- Madhya Pradesh
- Gujarat
- Tamil Nadu
- Kerala
- Punjab
- Uttar Pradesh
- River Narmada
- Sardar Sarovar Project
- Andhra Pradesh
- Delhi.
Answer:
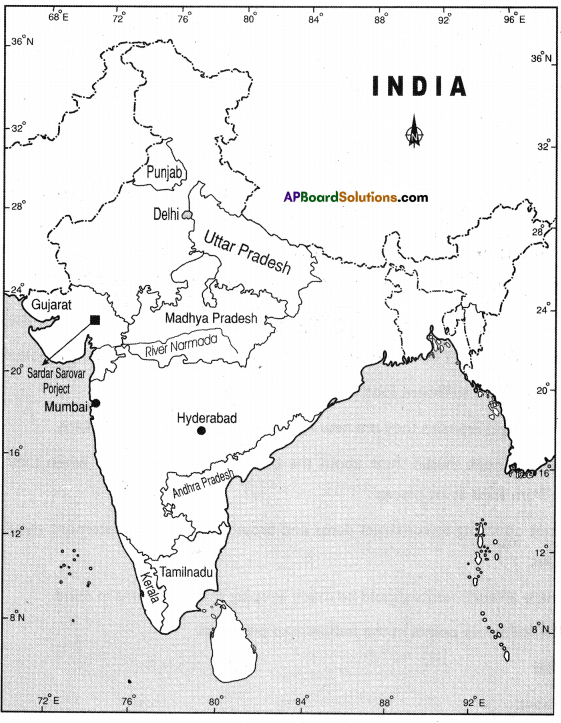
![]()
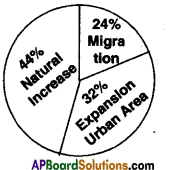
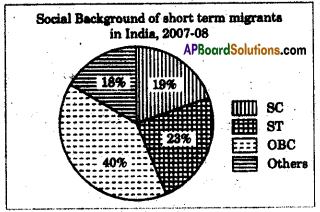 Answer:
Answer: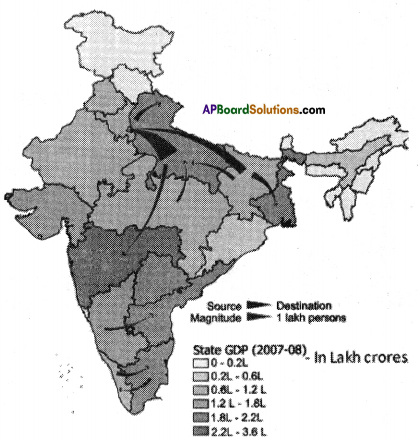
 Answer:
Answer:
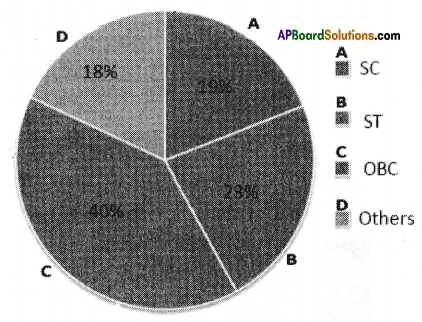
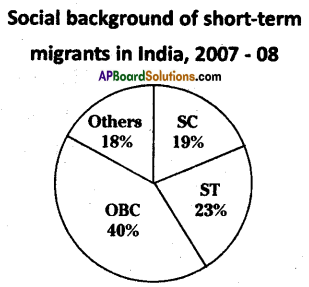 Write a paragraph analyzing it.
Write a paragraph analyzing it.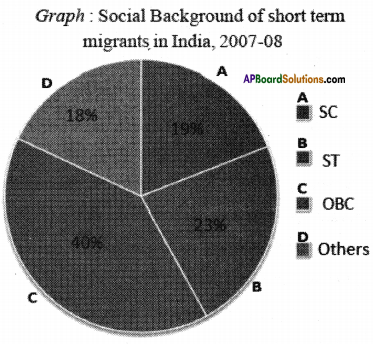

 Observation:
Observation:
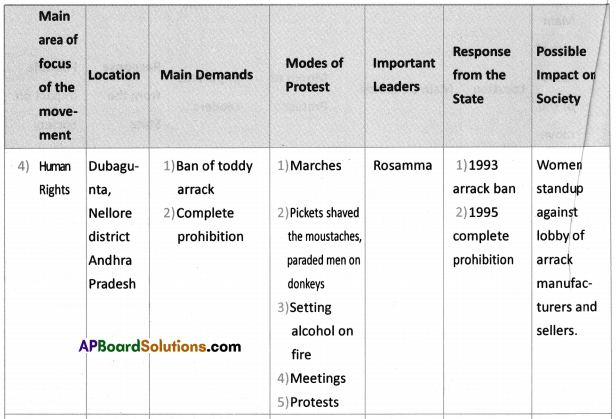
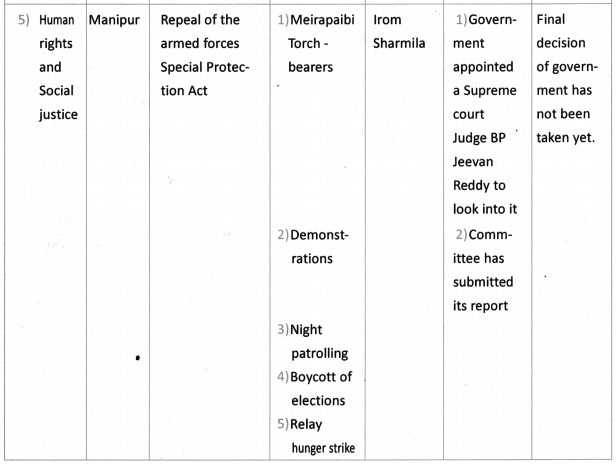
 Answer:
Answer: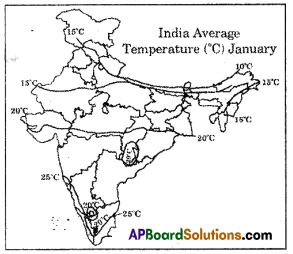
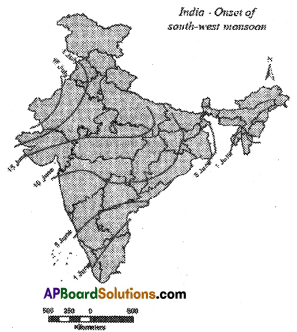 a) When do monsoons reach Maharashtra?
a) When do monsoons reach Maharashtra?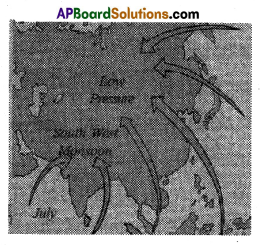 a) Why do winds always blow towards low-pressure regions?
a) Why do winds always blow towards low-pressure regions?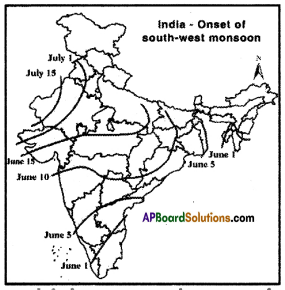 a) In which state, the south-west monsoon enter first?
a) In which state, the south-west monsoon enter first?
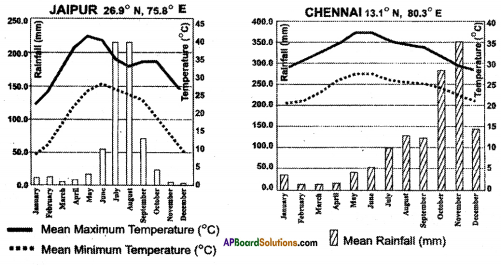 a) Why is there a difference between the rainy season of Chennai and Jaipur?
a) Why is there a difference between the rainy season of Chennai and Jaipur?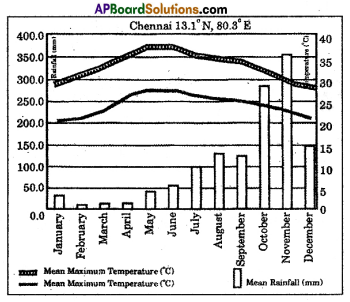 Answer:
Answer: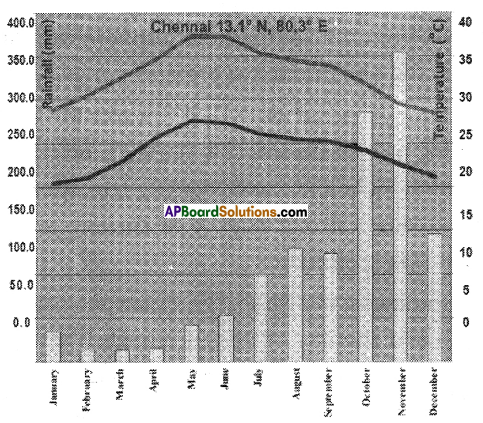 a) In which longitude does Chennai lie?
a) In which longitude does Chennai lie?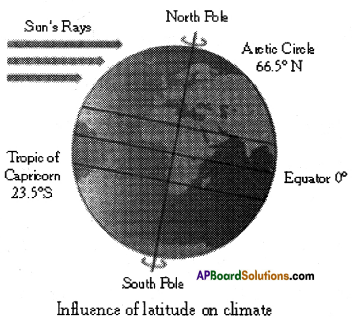
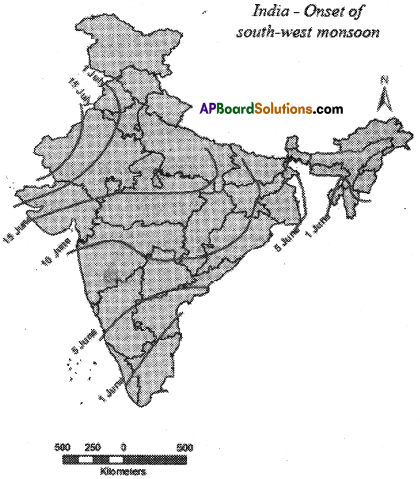 a) In which state south-west monsoons enter first in India?
a) In which state south-west monsoons enter first in India?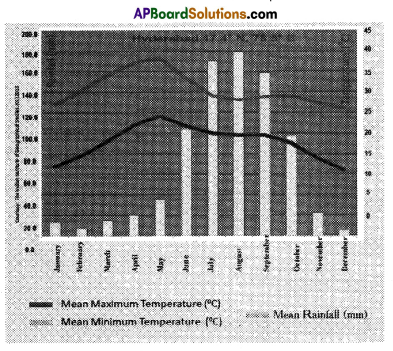 a) Where is Hyderabad located?
a) Where is Hyderabad located?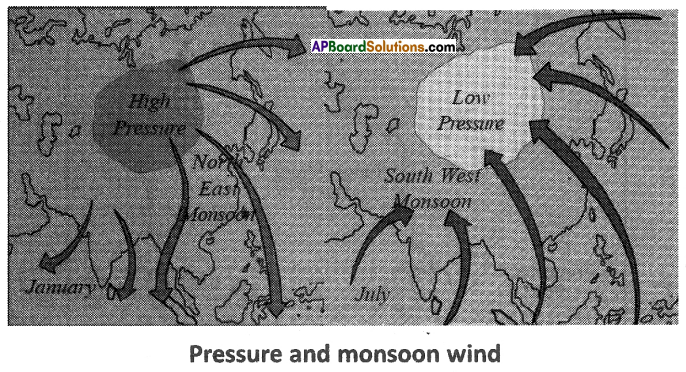 a) In which direction are the winds blowing?
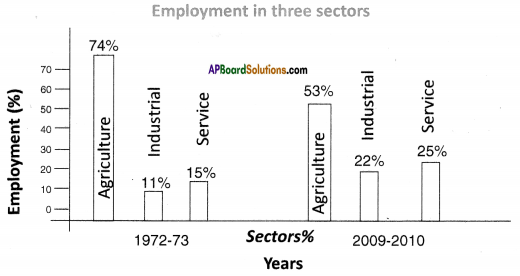
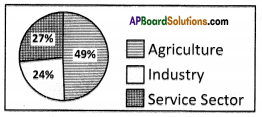
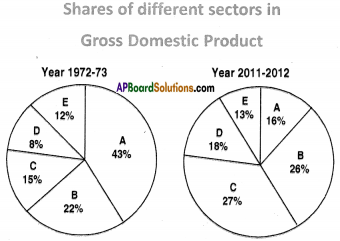
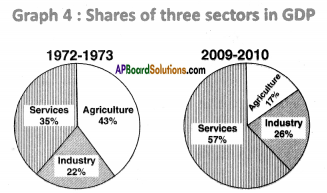
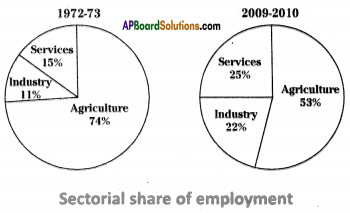
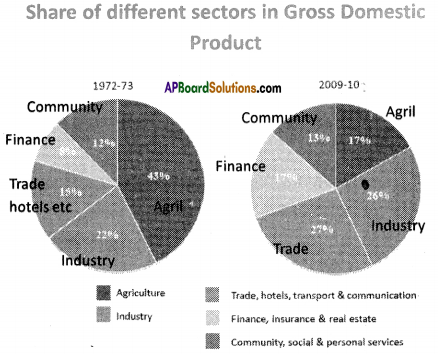
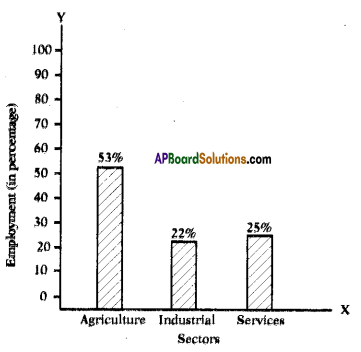
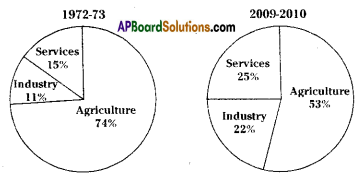
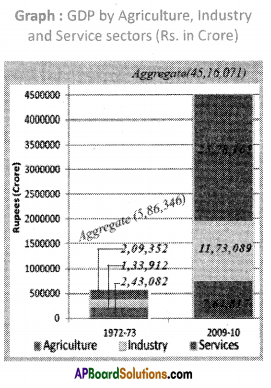
a) In which direction are the winds blowing?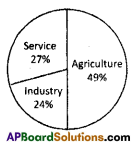 (a) Which sector provides less employment?
(a) Which sector provides less employment?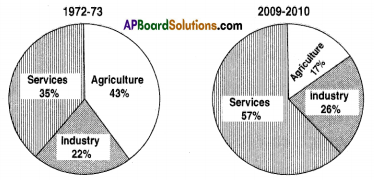
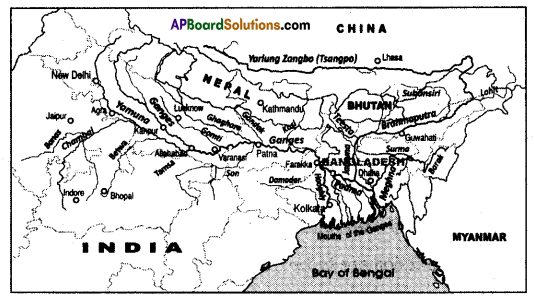 a) What is the River Ganga called in Bangladesh?
a) What is the River Ganga called in Bangladesh?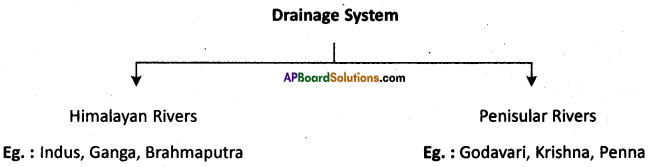

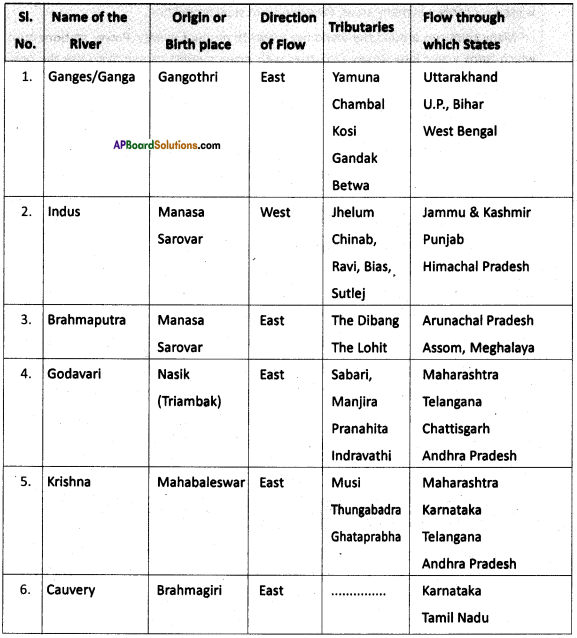
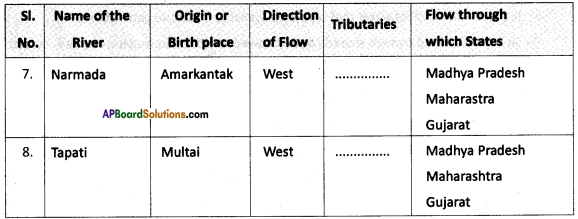
 a) Mention any two tributaries of river Ganga.
a) Mention any two tributaries of river Ganga.