AP SCERT 8th Class Maths Textbook Solutions Chapter 14 ఉపరితల వైశాల్యము మరియు ఘనపరిమాణం (ఘనము-దీర్ఘఘనము) InText Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 14th Lesson ఉపరితల వైశాల్యము మరియు ఘనపరిమాణం InText Questions
ఇవి చేయండి
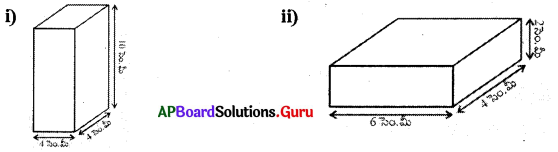
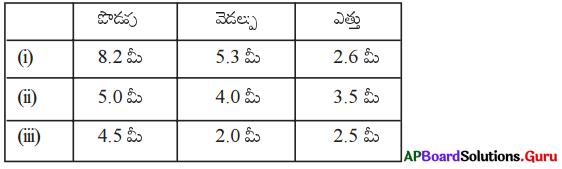
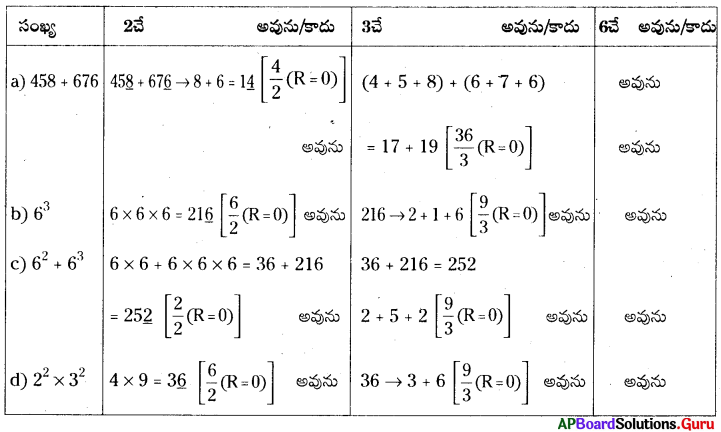
1. ఈ క్రింది దీర్ఘఘనముల యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యమును కనుగొనుము. (పేజీ నెం. 298)
సాధన.
(i) l = 4 సెం.మీ., b = 4 సెం.మీ., h = 10 సెం.మీ.
దీర్ఘఘనం యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం = 2 (lb + bh + lh)
= 2(4 × 4 + 4 × 10 + 4 × 10)
= 2(16 + 40 + 40)
= 2 × 96 = 192 చ.సెం.మీ.
(ii) l = 6 సెం.మీ., b = 4 సెం.మీ., h = 2 సెం.మీ.
దీర్ఘ ఘనం యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం = 2 (lb + bh + lh)
= 2 (6 × 4 + 4 × 2+ 6 × 2)
= 2 (24 + 8 + 12)
= 2 × 44 = 88 చ.సెం.మీ.
![]()
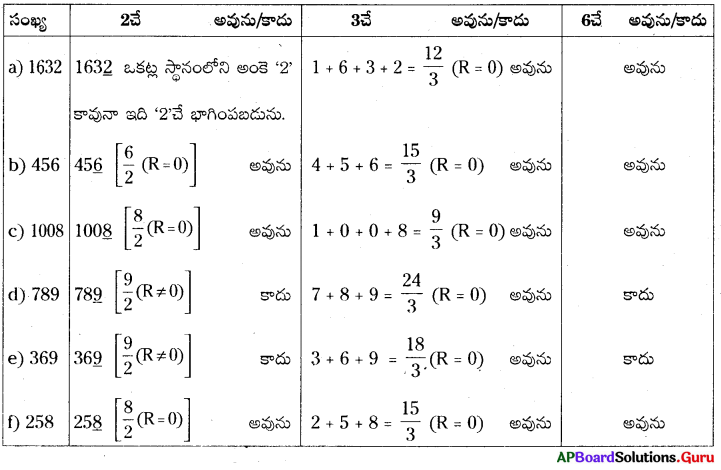
2. 6 సెం.మీ., 4 సెం.మీ. మరియు 5 సెం.మీ. కొలతలుగా గల దీర్ఘఘనము యొక్క ఘనపరిమాణమును కనుక్కోండి. (పేజీ నెం. 305)
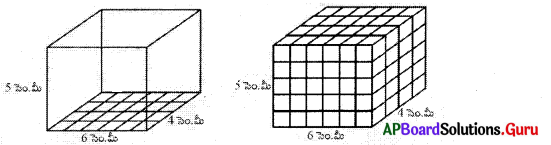
ఒక ఘనపు భుజము సెం.మీ. గా గల ప్రమాణ ఘనములను దీర్ఘఘనము పొడవు వెంబడి పేర్చుము. దీని కొరకు మనకు ఎన్ని ఘనములు అవసరము ? 6 ప్రమాణ ఘనములు అవసరము. వెడల్పు వెంబడి ఎన్ని ప్రమాణు ఘనములు పేర్చవచ్చు ? 4 ప్రమాణ ఘనములు దీనికి గల కారణము దీర్ఘ ఘనము యొక్క వెడల్పు 4 సెం.మీ. అనగా ఒక పారలో 6 × 4 ప్రమాణ ఘనములు ఉంటాయి.
దీర్ఘ ఘనములో ప్రమాణ ఘనములు అమర్చే పొరలు ఎన్ని ? 5 పొరలు అనగా దీర్ఘఘనము యొక్క ఎత్తు 5 సెం.మీ. ప్రతి పౌర 6 × 4 ఘనములు కలవు. కావున 5 పొరలలో 6 × 4 × 5 ప్రమాణ సమఘనాల దిమ్మలు ఉంటాయి. అనగా l × b × hకు సమానం.
పై చర్చ దీర్ఘఘనము యొక్క ఘనపరిమాణమునకు సూత్రము నిచ్చును.
దీర్ఘఘన ఘనపరిమాణము = పొడవు × వెడల్పు × ఎత్తు
సాధన.
6 సెం.మీ., 4 సెం.మీ. మరియు 5 సెం.మీ. కొలతలు గల దీర్ఘ ఘనం యొక్క ఘనపరిమాణం
V= lbh ⇒ V = 6 × 4 × 5 ⇒ V = 120 సెం.మీ3
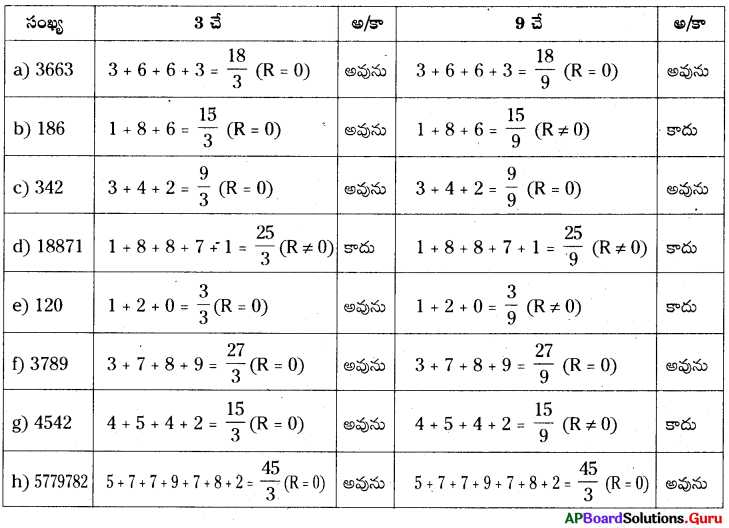
3. 64 ప్రమాణ ఘనములను ఉపయోగించి మీరు ఏర్పరచగల దీర్ఘఘనములు ఎన్ని ? ప్రతీ అమరిక యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యము కనుక్కోండి. సమాన ఘనపరిమాణము కలిగిన ఘనముల యొక్క ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యములు సమానమేనా ? (పేజీ నెం. 306)
సాధన.
64 ప్రమాణ ఘనములను ఉపయోగించి మీరు ఏర్పరచగల దీర్ఘఘనాల సంఖ్య
64 = 1 × 64 ……….. (1)
= 2 × 32 ………………… (2)
= 4 × 16 ………………….. (3)
ఈ విధంగా 3 విధాలుగా దీర్ఘఘనాలను ఏర్పర్చవచ్చు.
1. l = 64 సెం.మీ. , b = 1 సెం.మీ., h = 1 సెం.మీ.
దీర్ఘఘనం యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యము = 2 (lb+ bh + lh)
= 2(64 × 1 + 1 × 1 + 1 × 64)
= 2 (64 + 1 + 64) = 2 × 129 = 258 చ.యూ.
2. l = 32 సెం.మీ., b = 2 సెం.మీ., h = 1 సెం.మీ.
A = 2 (lb + bh + lh)
= 2 (32 × 2 + 2 × 1 + 32 × 1)
= 2 (64 + 2 + 32)
= 2 × 98 = 196 చ.యూ.
3. l = 16 సెం.మీ., b = 4 సెం.మీ., h = 1 సెం.మీ.
A = 2(lb+ bh + lh)
= 2(16 × 4 + 4 × 1 + 16 × 1)
= 2 (64 + 4 + 16)
= 2 × 84 = 168 చ.యూ.
![]()
ప్రయత్నించండి
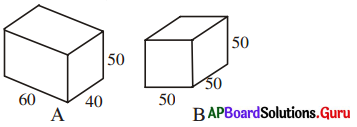
1. (i) సమ ఘనము ‘A’ యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం మరియు ‘B’ యొక్క ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యము కనుగొనండి. (పేజీ నెం. 300)
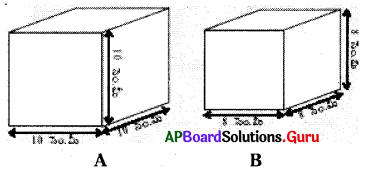
సాధన.
a = 10 సెం.మీ.
పటం A యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యము = 6a2
= 6 × (10)2
= 6 × 100 = 600 చ.సెం.మీ.
పటం B యొక్క ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యము = 4a2
= 4 × (8)2 [∵ a = 8 సెం.మీ. ]
= 4 × 64 = 256 చ.సెం.మీ.
(ii) ‘b’ భుజముగా గల రెండు సమఘనములు పటములో చూపిన విధముగా జతచేయబడి దీర్ఘఘనమును ఏర్పరిస్తే, ఆ దీర్ఘఘనము యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యము ఎంత ?
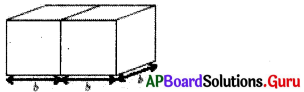
సాధన.
ప్రక్క దీర్ఘఘనం యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం = 2 (lb + bh + lh)

= 2(2b × b + b × b + 2b × b)
= 2(2b2 + b2 + 2b2)
= 2(5b2) = 10b2 చ.యూ.
![]()
(iii) సమాన భుజము పొడవు గల 12 సమఘనములు ఏ విధముగా జతచేయడము వలన అత్యల్ప సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యము కలిగిన దీర్ఘ ఘనము ఏర్పడుతుందో వివరింపుము.
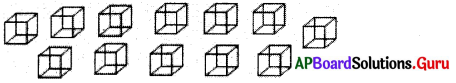
సాధన.
12 సమఘనాలను ఒకదాని ప్రక్క ఒకటి లేదా ఒకదానిపై ఒకటి అమర్చుట ద్వారా అత్యల్ప సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం సంభవించదు.
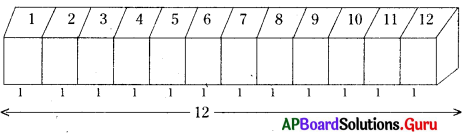
∴ A = 2(lb + bh + lh)
= 2(12 × 1 + 1 × 1 + 12 × 1)
= 2(12 + 1 + 12)
= 2 × 25 = 50 చ.యూ
కానీ, 3 సమఘనాలపై నాలుగు వరుసలుగా అమర్చుట ద్వారా అత్యల్ప సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం పొందవచ్చు.
∴ A = 2(lb+ bh + lh)
= 2(3 × 1 + 1 × 4 + 3 × 4) (∵ l = 3; b = 1; h = 4)
= 2(3 + 4 + 12) = 2 × 19 = 38 చ.యూ.
(iv) 4 × 4 × 4 కొలతలు గల ఒక సమఘనము రంగు వేయబడినది. ఆ ఘనము 64 సమఘనములుగా విభజింప బడినది. అయితే
(a) ఒక ముఖము మాత్రమే రంగు వేయబడినది. ఘనములు ఎన్ని ?
(b) రెండు ముఖములు రంగు వేయబడిన ఘనములు ఎన్ని ?
(c) మూడు ముఖములు రంగు వేయబడిన ఘనములు ఎన్ని ?
(d) ఏ ముఖము కూడ రంగు వేయబడని ఘనములు ఎన్ని ?
సాధన.
4 × 4 × 4 సమఘనం 64 సమఘనాలుగా విభజింపబడిన ఒక్కొక్క
సమఘనం యొక్క భుజం పొడవు = 1 యూ.
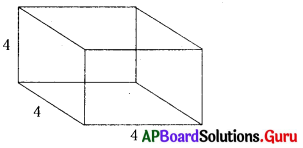
[∵ [latex]\frac{4 \times 4 \times 4}{64}[/latex] = 1]
(a) ఒక ముఖము మాత్రమే రంగు వేయబడిన (a = 4) సమఘనాల సంఖ్య = 6(a – 2)2 = 6(4 – 2)2 = 6 × 4 = 24
(b) రెండు ముఖాలు రంగు వేయబడిన సమఘనాల సంఖ్య = 12(a – 2) = 12(4 – 2) = 24
(c) మూడు ముఖాలు రంగు వేయబడిన సమఘనాల సంఖ్య 4 × a = 4 × 2 = 8
(d) ఏ ముఖం కూడా రంగు వేయబడని సమఘనాల సంఖ్య = (a – 2)3 = (4 – 2)3 = (2)3 = 8
![]()
ఆలోచించి, చర్చించి వ్రాయండి
1. దీర్ఘఘనం సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యము = ప్రకృతల వైశాల్యము + 2 × భూవైశాల్యము అని మీరు చెప్పగలరా ? (పేజీ నెం. 299)
సాధన.
దీర్ఘఘనం సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం = ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యం + 2 × భూవైశాల్యం
= 2h(l + b) + 2 × lb
= 2lh +2bh +2lb
= 2(lb + bh + lh)
∴ దీర్ఘఘనం సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం = ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యం + 2 × భూవైశాల్యం అని చెప్పగలం.
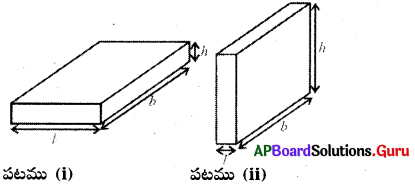
2. పటము (i)లో చూపిన దీర్ఘఘనము భంగిమను పటము (ii)లో లాగ మార్చిన వాటి ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యాలు సమానంగా ఉంటాయా ?
సాధన.
దీర్ఘఘనం యొక్క భంగిమను ఏ విధంగా మార్చినా దాని ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యములు సమానంగా ఉండవు.
![]()
3. పొడవు (i), వెడల్పు (b), ఎత్తు (h) ల కొలతలు సమానముగా గల దీర్ఘఘనపు పటమును గీచి దాని ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యము మరియు సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యములకు సూత్రము రాబట్టుము.
సాధన.
దీర్ఘఘనం యొక్క ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యం
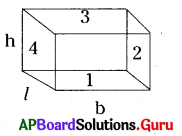
= 4 × ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యము
= 2 (l × h) + 2 × (b × h) (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 తలాలు)
= 2h (l + b) చ.యూ. (1 = 3, 4 = 2)
దీర్ఘ ఘనం యొక్క సంపూర్ణతల వైశాల్యం = 4 × ప్రక్కతల వైశాల్యం + పైన, క్రింది తలాల వైశాల్యం
= 2h (l + b) + 2(lb)
= 2lh + 2bh + 2lb
= 2(lb + bh + lh) చ.యూ.



 The process in the picture is
The process in the picture is The equipment show in the figure is
The equipment show in the figure is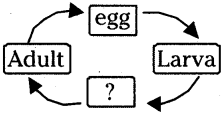
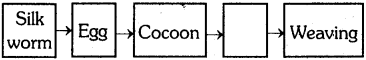
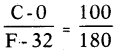
 This diagram indicates
This diagram indicates

 Indicates
Indicates