AP State Syllabus AP Board 7th Class Science Solutions Chapter 14 Water – Too Little To Waste Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Science Solutions 14th Lesson Water – Too Little To Waste
7th Class Science 14th Lesson Water – Too Little To Waste Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks and give reasons.
a) Cleaning of water is a process of removing …………
b) Waste water released by houses is called …………
c) Dried ………… is used as manure.
d) Drains get blocked by ………… and …………
Answer:
a) Impurities – This is to remove the wastage to get purified water.
b) Sewage This is a liquid waste which causes harmful bacteria and other microbes.
c) Sludge – The soft wet earth or subtances which are used as manure.
d) Oil and fat The impurities stagnated in water which releases some oil and fats like fossil fuels.
![]()
Question 2.
What is sewage? Explain why it is harmful to discharge untreated sewage into rivers or seas?
Answer:
- All the waste water released by homes, industries, hospitals, offices and other users are collectively called Sewage.
- Sewage is a liquid waste.
- Most of it is water, which has dissolved and suspended impurities, disease-causing bacteria and other microbes. These impurities are called contaminants.
- If this is discharged into canals, it causes a lot of harm to animals, human beings, aquatic animals and plants if this water used.
Question 3.
Why should oils and fats not be released in the drain? Explain.
Answer:
- Oils and fats should not be released in the drain.
- If they are released they do not dissolve in water and at the same time attach themselves to the walls of the drain.
- These catch other material and finally obstruct the flow of drain water.
- This makes the drain water stagnate causing new sanitation problems.
Question 4.
Describe the steps involved in getting clarified water from wastewater.
Answer:
- Wastewater is passed through bar screens. Large objects like rags, sticks, cans, plastic packets, etc are removed by this.

- Water then goes to a grit and sand removal tank.
The speed of the incoming wastewater is decreased to allow sand, grit and pebbles to settle down. - The water is then allowed to settle in a large tank which is sloped towards the middle.

- Solids like faeces settle at the bottom a removed with a scraper. This is the sludge.
- A skimmer removes the floatable solids like grease. Water so cleared is called clarified water.
![]()
Question 5.
What is sludge? Explain how it is treated.
Answer:
Sludge:
- Waste water is passed through bar screens.
After removal of large objects, water goes to a grit and sand removal tank. Here water is allowed to settle in a large tank which is sloped towards the middle.

- Solids like faeces settle at the bottom and are removed with a scraper. This is the sludge.
- The sludge is transferred to a separate tank where it is decomposed by an aerobic bacteria.
- The biogas produced in the process can be used as fuel or can be used to produce electricity.
- Air is pumped into the clarified water to help aerobic bacteria to grow.
- Bacteria consume human waste, food waste, soaps and other unwanted matter still remaining in clarified water.
- After several hours, the suspended microbes settle at the bottom of the tank as activated sludge. The water is then removed from the top.
- The activated sludge is about 97% water. The water is removed by sand drying beds or machines.
- Dried sludge is used as manure, returning organic matter and nutrients to the soil.
Question 6.
Untreated human excreta is a health hazard. Explain.
Answer:
- If the human excreta is left untreated it reaches the canals through rain water.
- The canal water is contaminated with this.
- People who use this canal water are prone to many diseases.
- Thus it is a health hazard.
Question 7.
Name two chemical used to disinfect the water.
Answer:
- Chlorine and
- Ozone are the two chemicals used to disinfect the water.
Question 8.
Explain the function of bar screens in a waste water treatment plant.
Answer:
Large objects like rags, sticks, cans, plastic packets… etc in waste water are removed by the bar screens in a waste water treatment plant.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain the relationship between sanitation and disease.
Answer:
- Sanitation plays a major role in keeping good health for the public.
- If the sanitation is poor* both water and air becomes polluted.
- Public depend upon these two items for their healthy living. If they are contaminated public health becomes a big threat.
- Neglected sanitation leads to diseases in the people living nearby.
Question 10.
Outline your role as an active citizen in relation to sanitation.
Answer:
- I shall educated the members of my house to keep the house and surroundings clean and neat.
- I request the neighbours not to throw away their house hold wastes on roads or at any place of their choice.
- I shall suggest them to separate organic and inorganic wastes and hand over to the people who collect these waste materials.
- I propagate the importance of sanitation by mouth and also with my friends.
- I cooperate with all organisations who work in this direction.
Question 11.
What would, you do to motivate people in your street to utilise toilets?
Answer:
- I explain the people about the importance of using toilets.
- I shall emphasize how one is prone to get hookworm if goes for defecation in the open.
- Further such things lead to the contamination of air and water which causes a threat to the health of the people living nearby.
- If toilets are used the waste materials go deep into the earth and become soil in course of time without creating any problem.
- Defecation irt the open, attracts mosquitoes, house flies and other insects which inturn transmit diseases.
Question 12.
What would happen if there were no microbes that break down wastes in sewage?
Answer:
- Microbes are doing a lot of service in breaking down the complex organic compounds in waste materials to simple structured substances.
- These substances ultimately becoming a manure.
- If there were no microbes, our life will be in danger.
- All the waste organic material remain as it was and pollute air and water posing a big problem to our survival.
![]()
Question 13.
What point would you like to address in the letter for your panchayat officer about drainage system in your village/town?
Answer:
- The drainage system in our town is very poor. The drains were not cleaned regularly by the sanitary people.
- The drain walls (or pipes) in some places were broken and the drain water is not freely flowing due to obstacles
- When it rains, all the drain water along With the rain water is occupying the roads making it very unhygienic.
- We therefore request you to attend to this drainage repair work.
Question 14.
Go to a nearby railway station/bits station/ hospital/ industry. What type of sewage is released? List out where and how.
Answer:
| Place | Type of sewage | From where and how |
| Railway station | eatable items, plastic bottles tea cups etc. | People throw half of eatable items empty pet bottles, cups etc. |
| Bus station |
“ |
“ |
| Hospitals | used syringes, cotton, bandages etc., | Due to accidents and certain operations |
| Industry | ash, chemical waste water etc. | Some chemical substances are obtained in the process of preparation |
Question 15.
Fresh water is scarce. What is your contribution to make your family members aware of the need to save water?
Answer:
I shall see that my family members follow the following methods of using water.
- Pick up water that is reqired for drinking. Donot throw away the water left out in the glass.
- Water used for cleaning rice and vegetables will be sent to the garden in the backyard.
- For bath, required water is to be used.
- I suggest the members to use mild soaps as the water after bath can be sent to plants in the garden of the house.
- No spill out of water from the tap must be seen by every family member.
- ‘Think’ before you use every drop of water is the suggestion I put before the family members.
![]()
Question 16.
Prepare atleast 5 slogans on “Don’t waste water”. (OR)
Write 4 slogans on “conservation of water ”
(OR)
Write any 4 slogans on Conservation of water and wastage of water. J&JAMlIrM
Answer:
5 slogans on’Don’t waste water’.
- ’Water is our currency. Use it with care’
- ‘Water is our life. Save it’.
- ‘Water is precious. Use it but donot throw it’.
- ‘Save water. Never become a partner for its shortage’.
- ‘Water is life. Life is not water’.
Question 17.
Make a writeup for your project on preservation of rain water.
Answer:
- If villagers take up the activity of sludge removal in tanks, more: water can be stored in them. Government should take up the renovation of lakes / tanks from time to time.
- Groundwater increases if check-dams are built over rivers, streams and riverets. This water can be used for all purposes.
- The rain water which flows from roof tops cap be diverted into a pit or a big Tank in the surroundings of the house, and this water can be used for few days.
Question 18.
Is there a check dam or any other water conservation unit in your village? Write a note on it.
Answer:
We have a water tank in the middle of the village, near to the Z.P. High school.
All people of Our village get water from that tank in the morning and evening.
Question 19.
Have you got any doubt about diseases caused by untreated water? List them out.
(OR)
Ashok wants to know the effects of “drinking” contaminated water. Which questions may he ask the doctor?
Answer:
- What are the diseases caused by using untreated water?
- What are the steps to be taken to treat the untreated water?
- What are the different methods used to treat the untreated water?
![]()
Question 20.
If you see water running off from a public tap what would you do about it?
Answer:
- If I see water running off from a public tap immediately I turn off the tap and stop the run of water.
- If the control system of the tap is not there, I shall take measures to close the way out of water and report the same to the authorities.
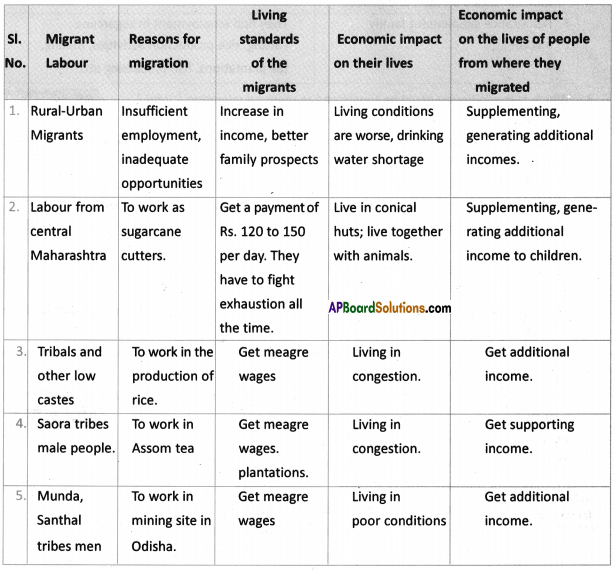
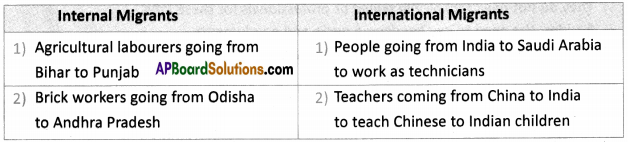
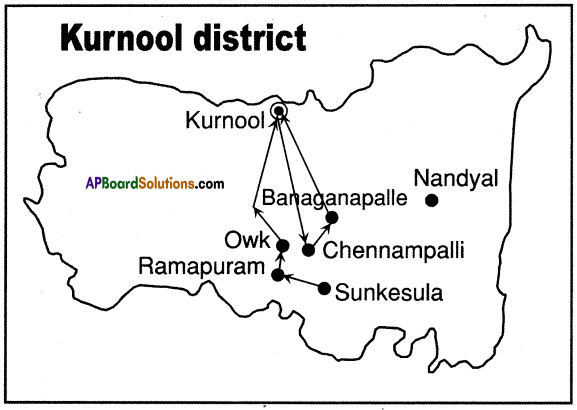
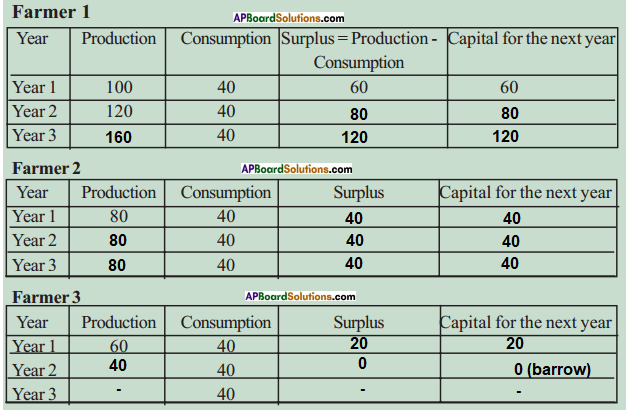
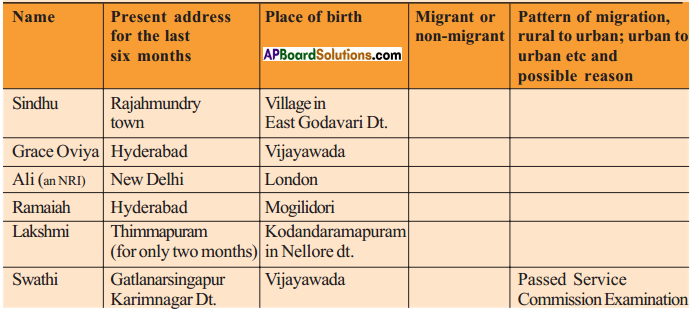 Answer:
Answer: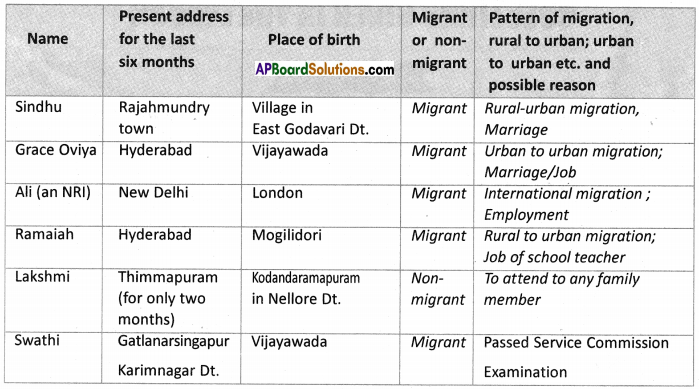
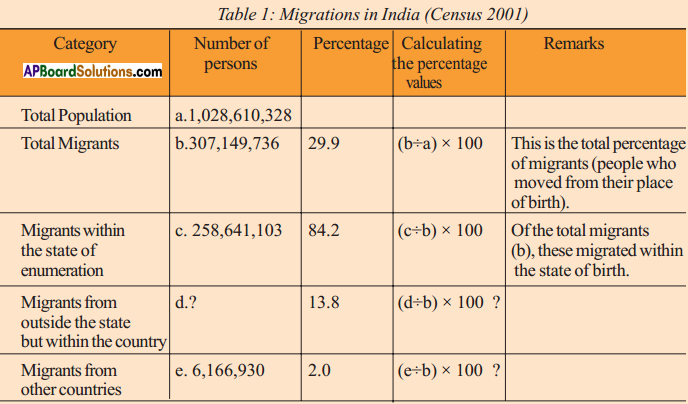 Answer:
Answer: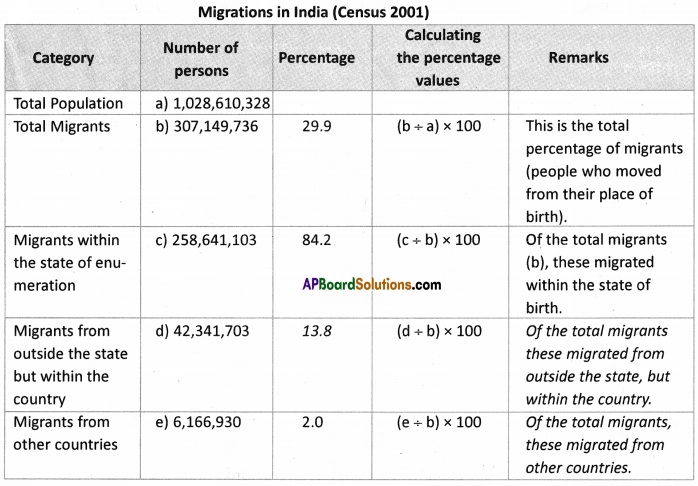
 Answer:
Answer: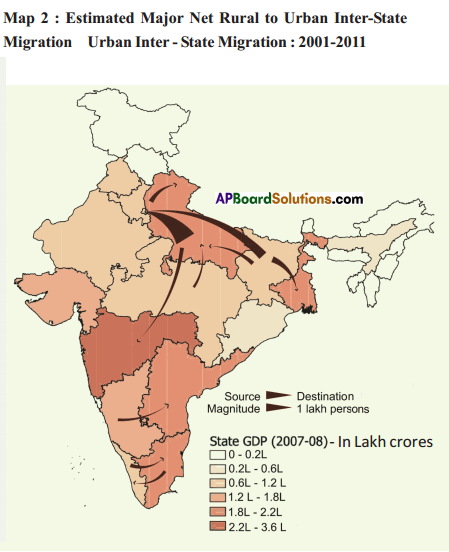 Answer:
Answer: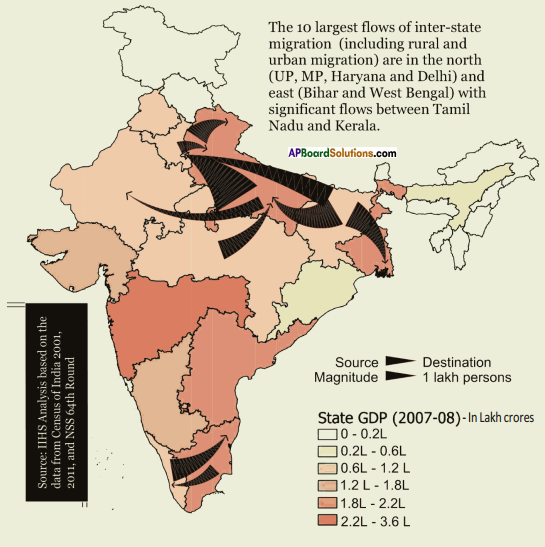 Answer:
Answer: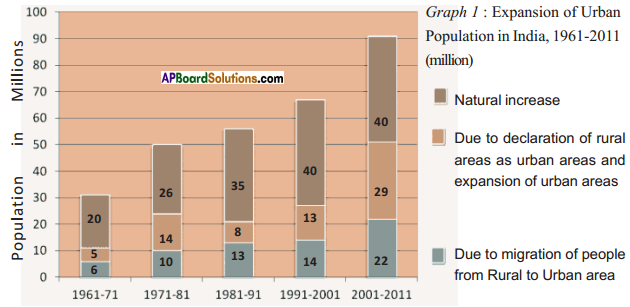 Answer:
Answer: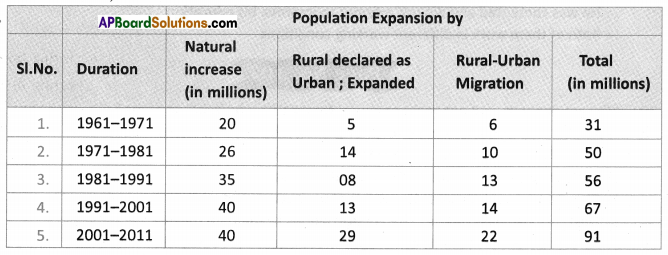
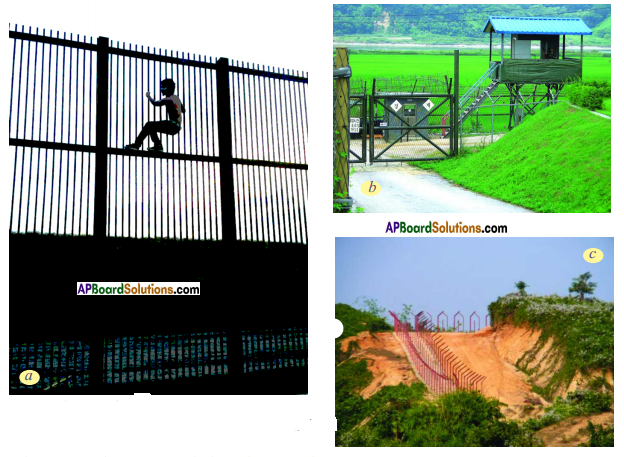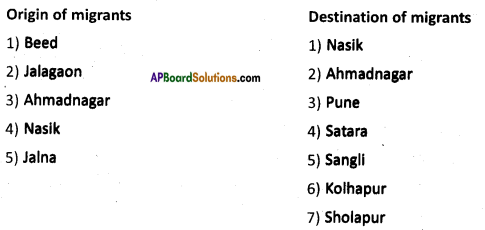
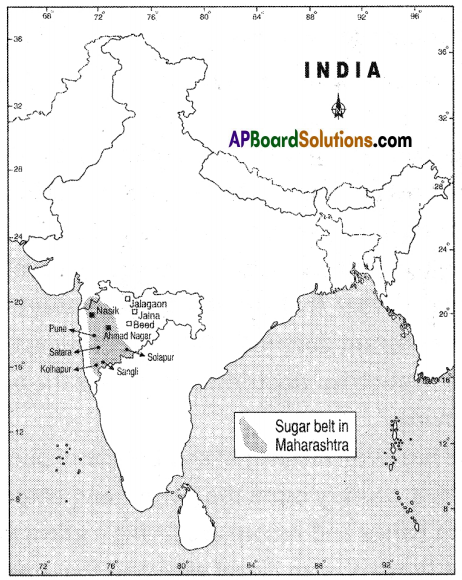
 What do you think of migrants across the border?
What do you think of migrants across the border?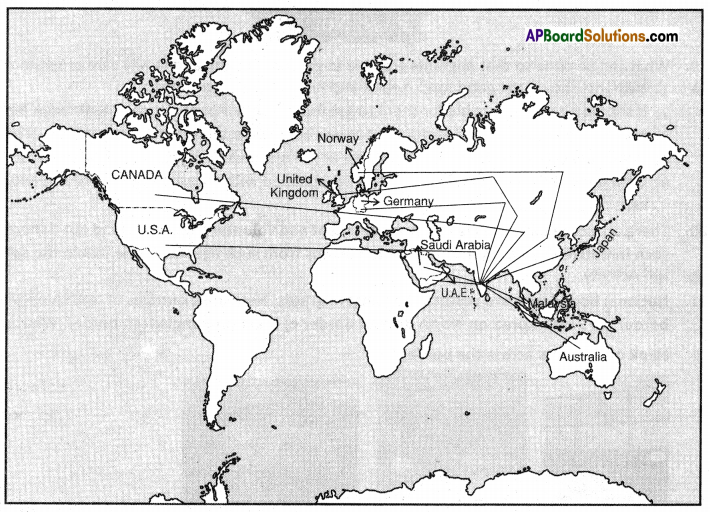

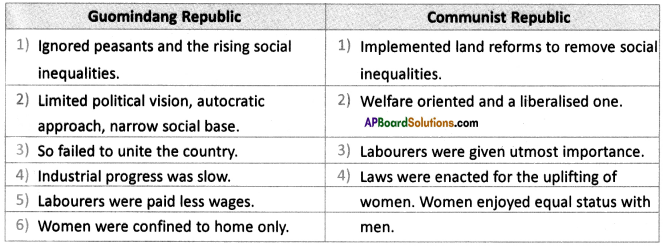
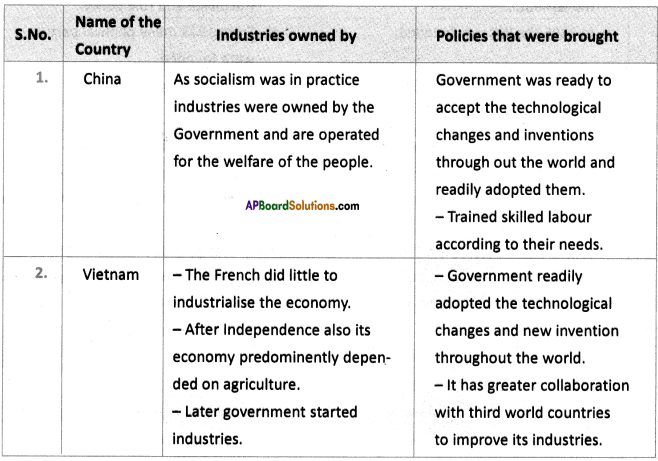
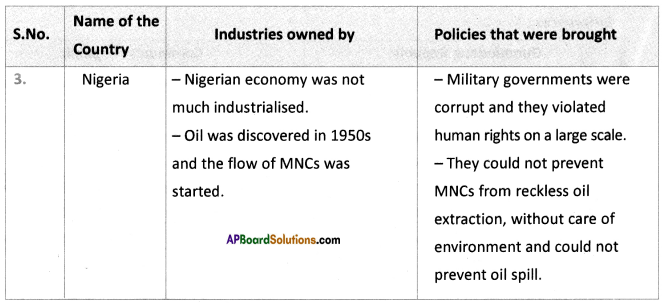
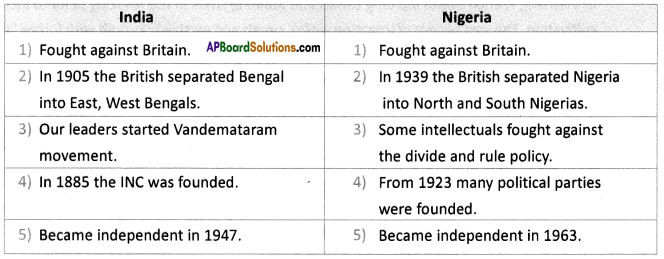













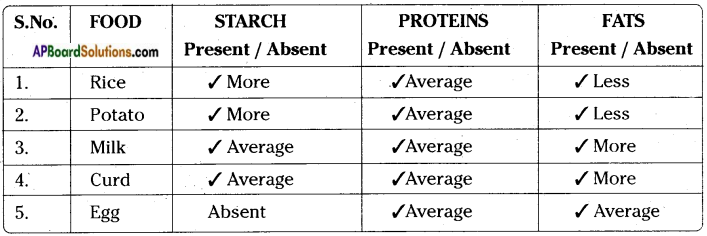
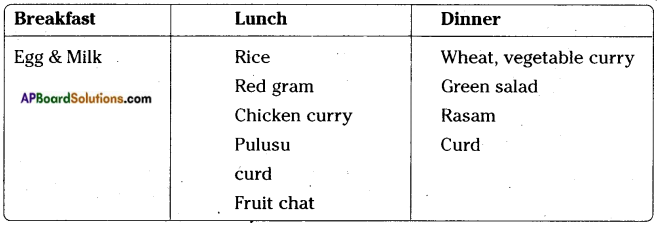





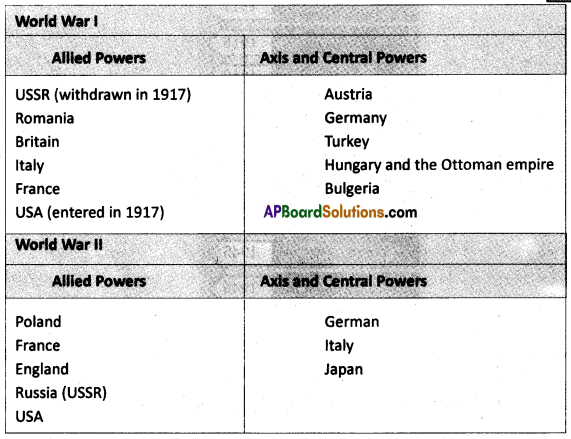
 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: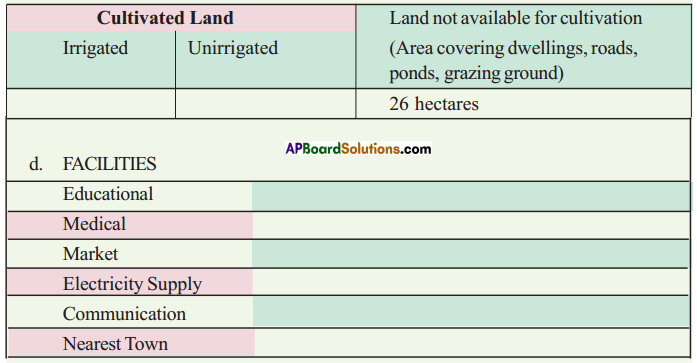
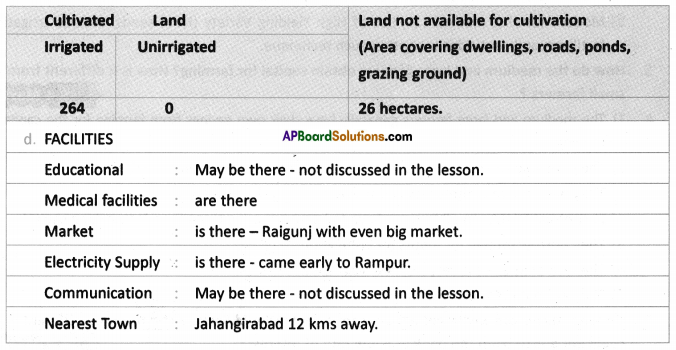
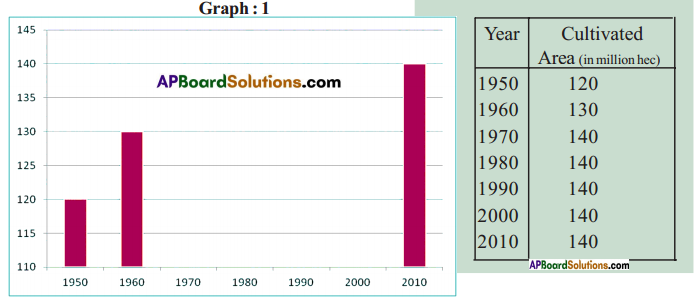
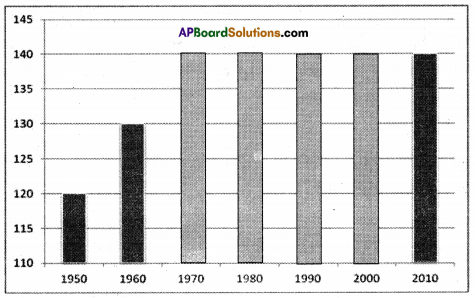
 Answer:
Answer: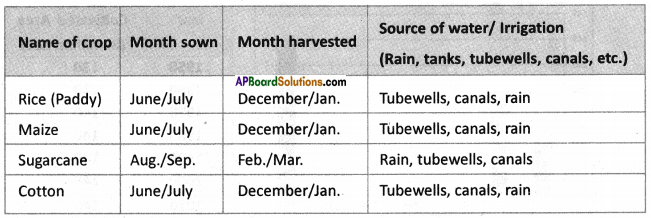
 Answer:
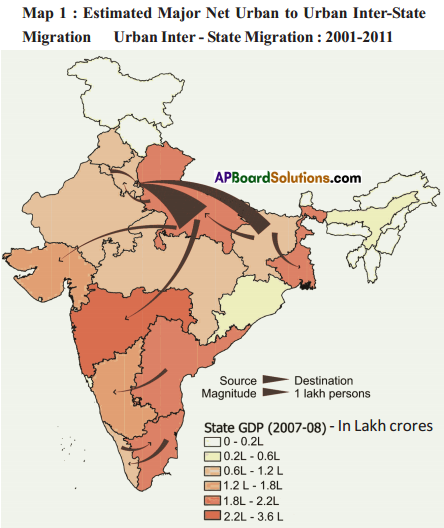
Answer: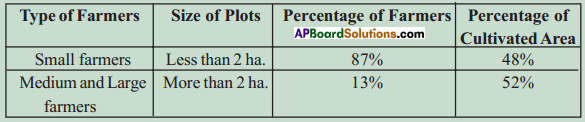 What do the arrows indicate? Would you agree that the distribution of cultivated land is unequal in India? Explain. (OR)
What do the arrows indicate? Would you agree that the distribution of cultivated land is unequal in India? Explain. (OR)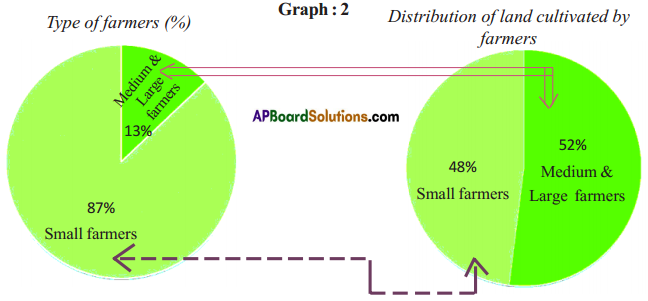 Answer:
Answer: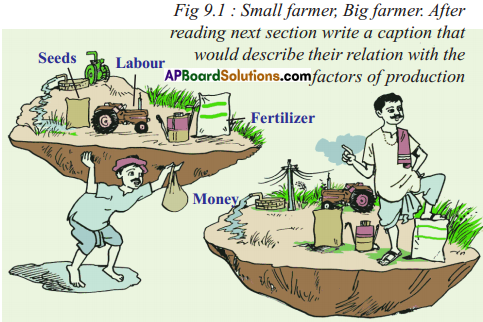 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer:
 Answer:
Answer: Answer:
Answer: