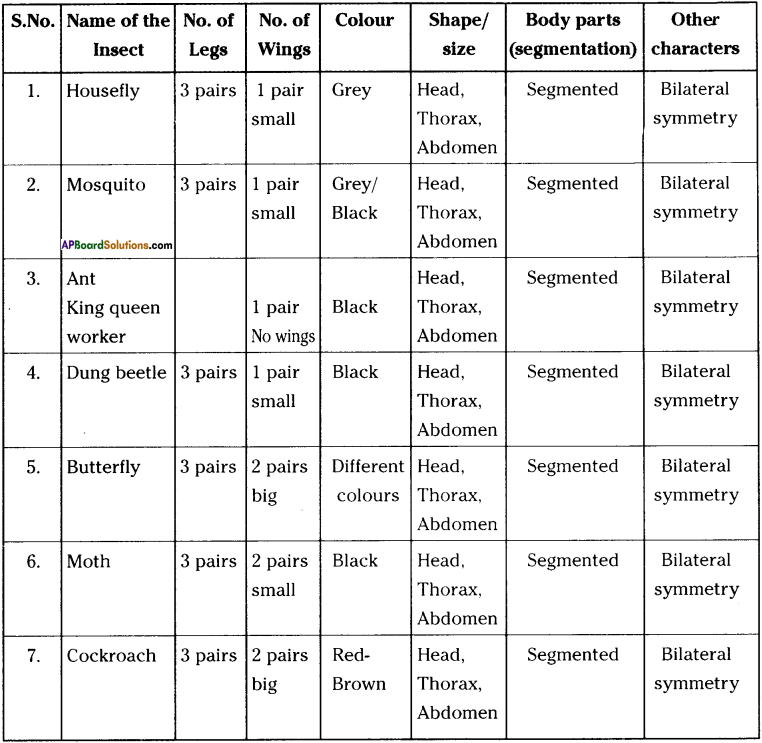
AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 3 Animal Tissues.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology Important Questions 3rd Lesson Animal Tissues
9th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Animal Tissues 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
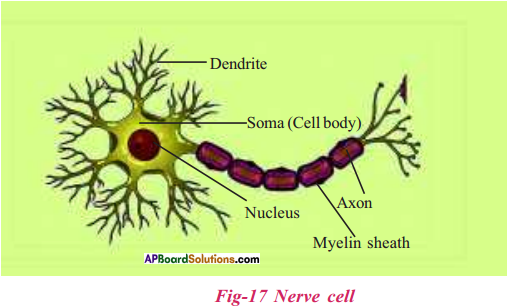
What are the parts of a nerve cell?
Answer:
We can identify 3 distinct parts in nerve cell. They are :
- Cell body or cyton
- Axon
- Dendrites
Question 2.
How the bone is made up of?
Answer:
- Bone is made up of calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate.
- These salts are secreted by osteocytes.
- Osteocytes are present in the bone marrow.
![]()
Question 3.
What is granular epithelium?
Answer:
Sometimes a portion of epithelial tissue folds inward and formed a multicellular gland. Hence, it is called as granular epithelium.
Question 4.
Where do we found columnar epithelium?
Answer:
Columnar epithelium present where absorption and secretion occurs.
Eg : Intestine.
Question 5.
Why the ‘AB’ group human beings are called as universal recipients?
Answer:
- ‘AB’group human beings can receive the blood from any other groups.
- Hence, they are called as universal recipients.
Question 6.
Why the ‘O’ group people are called as universal donors?
Answer:
- ‘0’group human beings can donate the blood to any other group.
- So, these people are known as universal donors.
![]()
Question 7.
Name some modified epithelial cells.
Answer:
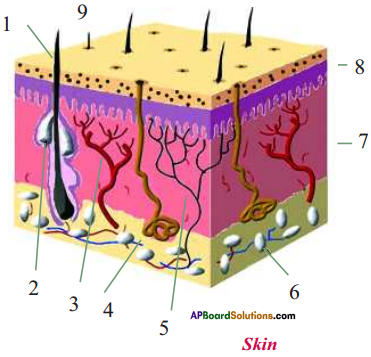
- Skin is a kind of epithelial tissue.
- Nails and hair grow from it.
- The scales of fishes and reptiles and feathers of birds etc., are the modified epithe-lial cells.
Question 8.
What is tendon? What is its use?
Answer:
- Tendon is a type of connective tissue, which is also made of fibres.
- The tendon joins the muscle to the bone. It is also made of collagen.
Question 9.
Where do we found cuboidal epithelium? Why?
Answer:
Cuboidal epithelium can be found in the lining of kidney tubules, the ducts of salivary glands. They provide mechanical support.
Question 10.
What is the main function of WBC?
Answer:
WBC provides immunity to the body by providing the body against infections.
Question 11.
Give two examples of cartilage.
Answer:
Tip of the nose and external ear are two examples of cartilage.
![]()
Question 12.
Name the muscle tissue that connects muscle to a bone.
Answer:
Tendon
Question 13.
What is the yellow fibres that are connecting bones known as?
Answer:
Ligament.
Question 14.
What are the involuntary muscles?
Answer:
The muscles whose contraction is not under the control of will power.
Eg : Cardiac muscles.
Question 15.
Write the functions of cartilage.
Answer:
- Provides flexibility and support to the body parts.
- It smoothens the surface at the joints.
Question 16.
Name the tissue that is present in the hump of a camel or blubber of whale.
Answer:
Adipose tissue
![]()
Question 17.
Name the fat storage tissue and state its location in our body.
Answer:
Adipose tissue stores fat in our body. It is present just below the skin and between internal organs.
Question 18.
Name the types of Rh factors of human body.
Answer:
Positive and Negative (A+, A-)
Question 19.
Name the tissue that is present in brain.
Answer:
Nervous tissue formed with neurons is present in the brain.
Question 20.
What is called action potential?
Answer:
Whenever a nerve is stimulated, it produces a small electrical current (0.055V) called action potential.
Question 21.
What is the other name for Areolar tissue?
Answer:
Fibroblasts.
Question 22.
Name the tissue that acts as insulator.
Answer:
Adipose tissue
Question 23.
What is bone made of?
Answer:
Bone is made of calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate.
Question 24.
Where do you find Osteocytes?
Answer:
In the central hollow portion of the bone called bone marrow.
Question 25.
Where you can see Haversian canal?
Answer:’
In Osteocytes (or Bone cells)
![]()
Question 26.
Name the tissue that is present in embryos of several vertebrae.
Answer:
Cartilage
Question 27.
Where do you find contractile proteins?
Answer:
In muscle fibres.
Question 28.
What are the 3 major portions of a nerve cell?
Answer:
1) Cell body
2) Axon
3) Dendrite (or) cyton
Question 29.
Name the only cells in our body, which do not have the ability of regenaration.
Answer:
Nerve cells.
Question 30.
Where do you see Nissl’s granules?
A. Nerve cells
Question 31.
Which nodes present at regular intervals on the nerve cells?
Answer:
Ranvier Nodes.
Question 32.
What is a nerve?
Answer:
Axons of several nerve cells form bundles called nerve.
Question 33.
Nerve tissue has neurons and supporting cells. Name the supporting cells of the nerve tissue.
Answer:
Glial cells.
![]()
Question 34.
How do Monocytes destroy the foreign materials?
Answer:
Monocytes move like amoeba and along with granulocytes they attack the foreign materials and engulf them. The foreign materials are destroyed inside these cells.
Question 35.
What are corpuscles?
Answer:
Cells present in blood are called corpuscles.
Question 36.
What is the “grave yard of RBC”?
Answer:
Spleen
Question 37.
What are granulocytes?
Answer:
Neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils
Question 38.
What are agranulocytes?
Answer:
Lymphocytes and monocytes
Question 39.
How many RBC are present in 1 ml of blood?
Answer:
5 million of RBC 1 ml of blood (in human adults).
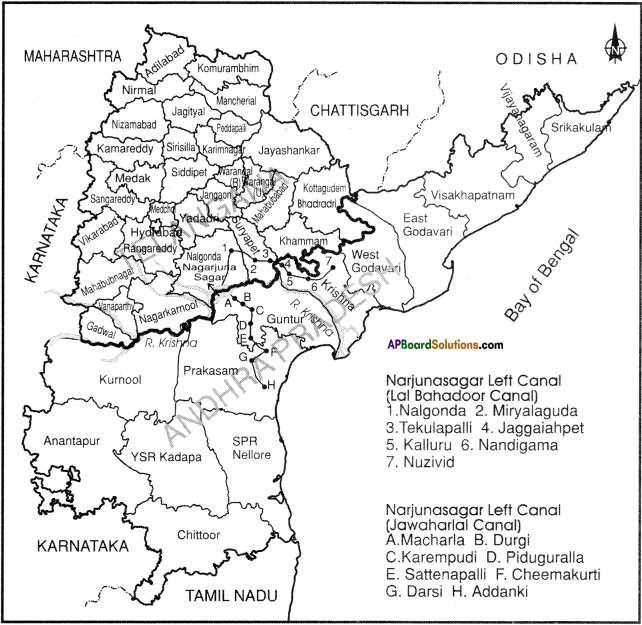
9th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Animal Tissues 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Do you find any difference between skin cells and muscle cells?
Answer:
- There is a difference between skin cells and muscle cells.
- Skin cells are arranged in the form of layers. This is called stratified squamous epithelium.
- Muscle cells are elongated ones and responsible for movement in the body.
Question 2.
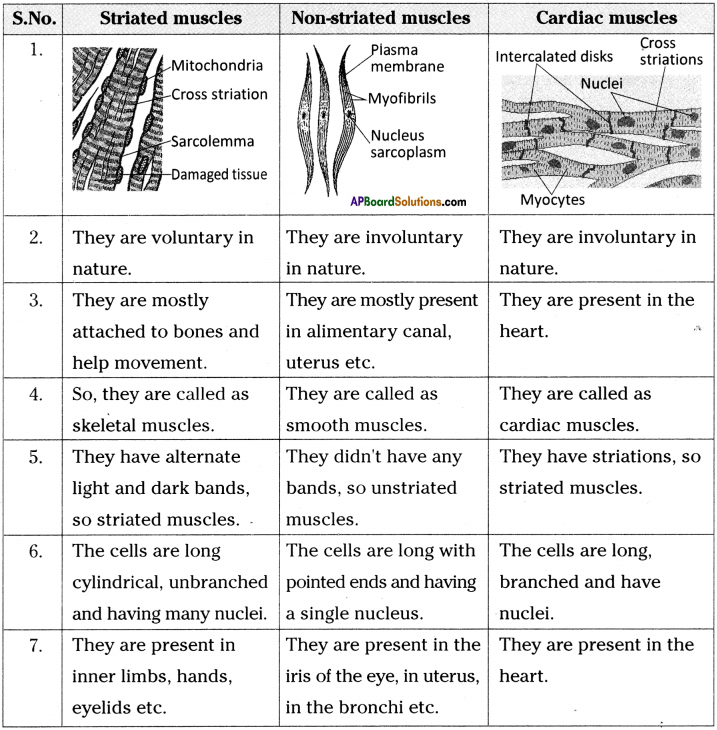
Why the involuntary muscles are also called as unstriated muscles?
Answer:
- Unstriated muscles are also called as smooth muscles.
- They have no striations or alternate light and dark bands.
- The cells are long with pointed ends.
- So, they are called as unstriated muscles.
![]()
Question 3.
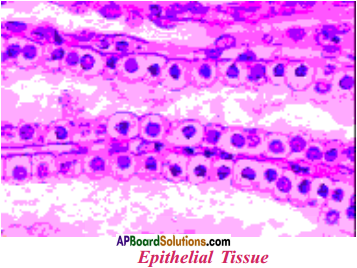
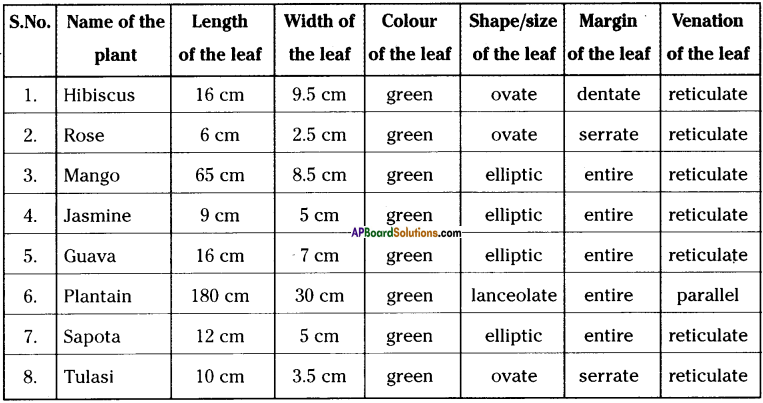
What is epithelial tissue ? How many types are there?
Answer:
- Epi means outer, thelium means tissue.
- The epithelial tissue, extremely thin and flat, form a delicate lining.
- Three types of epithelial tissues are identified. They are :
a) Squamous epithelium
b) Cuboidal epithelium
c) Columnar epithelium
d) Granular epithelium
Question 4.
What is squamous epithelium? Where it is found?
Answer:
- The epithelial tissue, extremely thin and flat, form a delicate lining is called squamous epithelium.
- It is found in oesophagus, lining of mouth, lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli etc.
- The epithelial cells in skin are arranged in the form of layers, called stratified squa¬mous epithelium.
Question 5.
What is involuntary movement?
Answer:
- We cannot start or stop the movement of muscles by wanting to do so.
- The movement is called involuntary, the muscles caused for it are called involun-tary muscles.
Eg : Movements in the alimentary canal, blood vessels etc.
Question 6.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of squamous epithelium. A.
Answer:
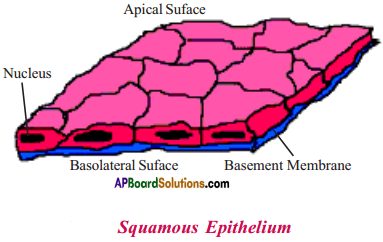
Question 7.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of areolar tissue.
Answer:
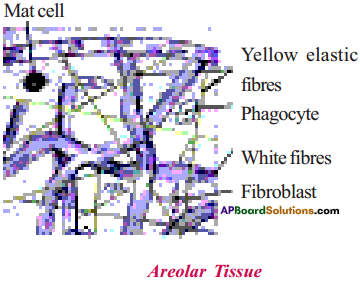
Question 8.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of osteocyte.
Answer:
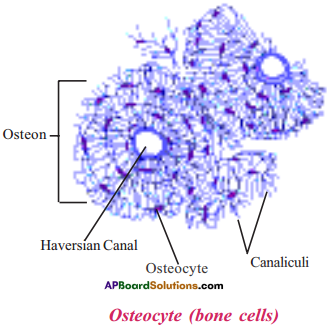
Question 9.
Why the pus formed in our body?
Answer:
1. Some white blood cells sacrify their life to fight against external enemy, i.e., micro-organisms.
2. These dead WBC come out of wound.
3. This is generally called pus.
4. The body excretes the dead cells in that manner.
Question 10.
Write the muscles that are present in the body parts.
Answer:
| Body part | Muscle present |
| 1. Oesophagus | Smooth muscles |
| 2. Heart | Cardiac muscles |
| 3. Face | Involuntary muscles |
| 4. Lungs | Smooth muscles |
| 6. Hands | Involuntary muscles |
Question 11.
How are proteins present in blood helpful to our body?
Answer:
Blood contains Haemoglobin, which contains Iron in its molecule. It transports Oxygen and carbon dioxide in our body.
Question 12.
Why ‘AB’ blood group is called Universal acceptor?
Answer:
‘AB’ blood group is called universal acceptor. A person with AB’ blood group can take all types of human blood, if Rh factor matches.
![]()
Question 13.
What is muscular tissue? What is its function?
Answer:
Muscular tissue consists of elongated cells called muscular fibres. This tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
Question 14.
What is the unique feature of cells of nervous tissue as compared to other body cells?
Answer:
All cells possess the ability to respond to stimuli. However, the cells of nervous tissue are highly specialised for being stimulated and then transmitting the stimulus very rapidly from one place to another within the body. The brain spinal cord and nerves are all composed of nervous tissue.
Question 15.
Give four differences between bone and cartilage.
Answer:
| Bone | Cartilage |
| 1. Porous. | 1. Non – Porous. |
| 2. Blood vessels present. | 2. Blood vessels absent. |
| 3. Hard and flexible. | 3. Flexible, not very hard. |
| 4. Matrix made up of protein and mineral salts. | 4. Matrix made up of proteins. |
Question 16.
Raghu wants to know more about blood. What questions Raghu will ask the teacher?
Answer:
Raghu might ask the following questions.
- What would happen if blood possesses compact tissue?
- Do all the organisms are having red coloured blood in their bodies?
- What will happen if blood platelets are decreased in the blood?
- What will happen if the percentage of Haemoglobin is decreased in the blood?
Question 17.
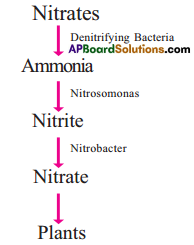
Complete the following flow chart.
Answer:
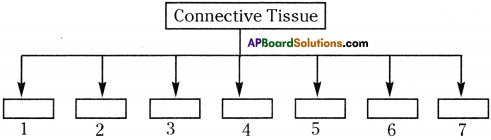
- Areolar tissue
- Cartilage
- Bone
- Ligament
- Tendon
- Adipose Tissue
- Blood
Question 18.
What are the constituents of pl& ma?
Answer:
Mainly water and several nutrients such as glucose, amino acids, proteins, vitamins and hormones, etc. required for the body and excretory products such as lactic acid, urea, salts etc…. plasma also contains factors responsible for blood clotting.
Question 19.
Draw a diagram showing blood cells.
Answer:
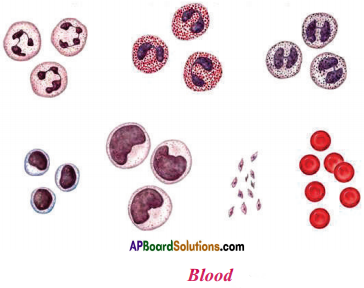
Question 20.
Draw a diagram showing cartilage.
Answer:
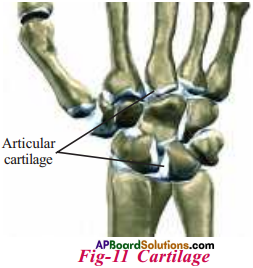
9th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Animal Tissues 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write a note on areolar tissue.
Answer:
- Areolar tissue is one type of connective tissue which joins different tissues.
- It helps in packing and helps to keep the organs in place.
- These cells are called fibroblasts.
- These are the major components of areolar tissue.
- These cells secrets fibrous material which holds the other tissue in position.
- They also help in repair of the tissue when they are injured.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a note on WBC.
Answer:
- White blood cells or WBC are one type of blood cells.
- They do not have haemoglobin, hence they are colourless.
- They are also called as leucocytes.
- They are less in number when compared to the RBC.
- They are two types :
1. Granulocytes,
2. Agranulocytes. - Granulocytes are three types. They are neutrophils, basophils and esinophils.
- Granulocytes attack and destroy the microorganisms that enter the blood.
- Agranulocytes are two types. They are lymphocytes and monocytes.
- Lymphocytes secret anti-bodies to guard against foreign material, that enter into blood.
- So, lymphocytes are also called as microscopic policemen.
- Monocytes attack the foreign materials and destroyed them.
- So, they are called “scavengers”.
Question 3.
What are the functions of connective tissue?
Answer:
Connective tissue connects the organs and muscles. It performs so many functions.
- Helps in binding the other tissues and organs together.
- Provides a frame work and support to various organs in the body.
- Plays a major role in the transport of material from one tissue to another.
- Helps in the body defence.
- Helps in the body repairs.
- Helps in the storage of fat.
Question 4.
Write a note on a nerve cell or neuron with the help of a neat diagram.
Answer:
Nervous tissue is made up of neurons.
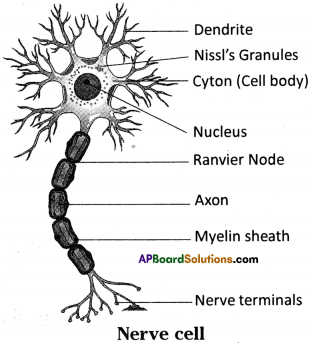
It has 3 parts :
- Cell body or cyton
- Axon
- Dendrites.
Cell body or Cyton :
- It has a large nucleus and cytoplasm.
- The cytoplasm contains Nissl’s granules.
Dendrites:
- Projections arising from cell body are called dendrites.
- They are sharp, branched and more in number.
- The dendrite connected to another nerve cell’s axon.
Axon :
- One projection of the cyton is long, called as axon.
- In some nerve cells, axon covered with myelin sheath.
- Nodes on axon are called Ranvier Nodes.
- Axon of a nerve cell is connected with dendrites of another cell to frame a web like structure throughout body.
Question 5.
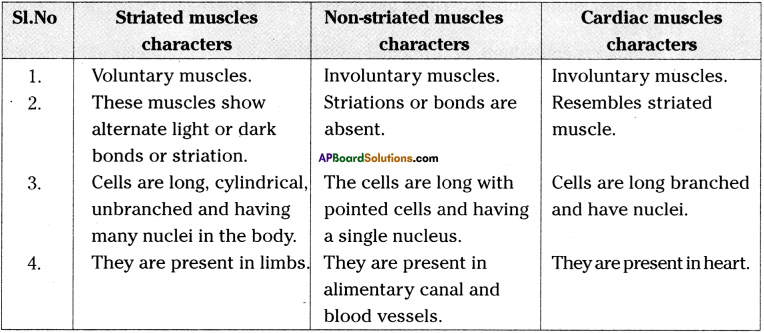
Read the table and answer the following questions.
1) Where do you find unstriated muscles in our body?
2) Name the muscles which are present in heart.
Answer:
1) Wall of alimentary canal, Iris of the eye, uterus, bronchi of lungs.
2) Cardiac Muscles.
Question 6.
Draw a neat diagram showing different muscles and lable their parts.
Answer:
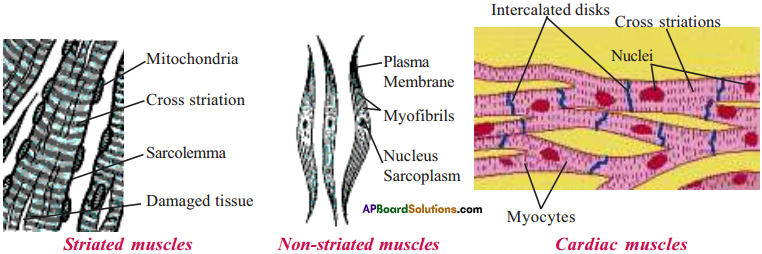
9th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Animal Tissues Important Questions and Answers
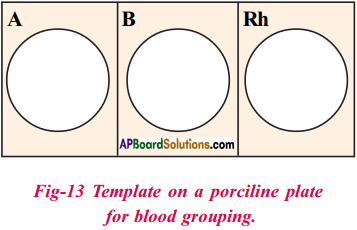
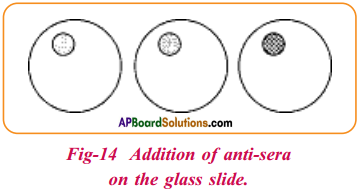
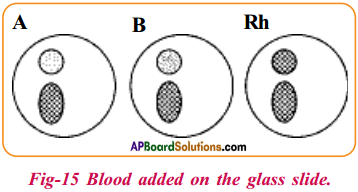
Question 1.
Rajiv used a blood group identification kit to test his blood group. Explain what will he observe if his blood is Rh factor positive.
Answer:
Rajiv observes for
i) Agglutinations in the circles where Anti D serum was tested,
ii) Agglutination in Anti Rh – D circle. „
Question 2.
Kamalakar teacher conducts an experiment to show blood cells under microscope to his students. Name the materials used by the teacher for the experiment.
Answer:
Microscope, slide, blood sample, syringe, needle.
![]()
Question 3.
Briefly explain epithelial tissue with examples.
Answer:
1) Epithelial tissue is one of the most important tissue of animal tissues.
2) Epithelial tissue is present in the skin, lining of mouth, lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli and kidney tubules. There are three types of epithelial tissue in our body.
They are
- Squamous epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelium and
- Columnar epithelium
1) Squamous epithelium :

a) This epithelium is extremely thin and flat, form a delicate lining.
b) We can observe this tissue, in oesophagus, lining of mouth, lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli where transportation of substances selectively occurs through permeable membrane.
c) As this epithelial cells in skin are arranged in the form of layers. This is called as “stratified squamous epithelium”.
2) Cuboidal epithelium :
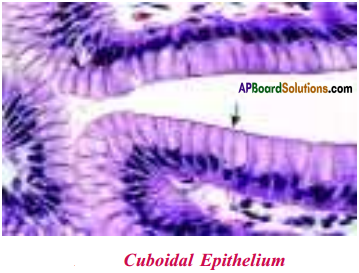
a) This tissue forms the lining of organs or tubules or other parts.
b) It provides mechanical support.
3) Columnar epithelium :
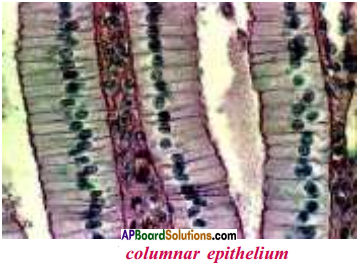
a) This is present where absorption and secretion occurs.
b) The scales of fishes, feathers of birds our skin, nails and hairs are also modified epithelial cells.
Question 4.
Read the following paragraph and answer the given questions.
| Connective tissues help in binding the other tissues and organs together and provide a frame work and support to various organs in the body. Areolar tissue is a type of connective tissue that helps in packing and also help to keep organs in place. Fat stor¬ing adipose tissue is found below skin and between internal organs. Bone and cartilage form skeletal system, which gives support to the body. Ligament connects bone with bone whereas tendon connects muscle with bone. |
i) Which connective tissue is called packing tissue?
ii) Which connective tissue joins muscle with bone?
iii) What are the main components of skeletal system?
iv) Where do you find adipose tissue in the body?
Answer:
i) Areolar tissue
ii) Tendon
iii) Cartilage
iv) Adipose tissue is found below the skin and between internal organs.
Question 5.
Draw the structure of neuron. Label parts. What is the function of myelin sheath?
Answer:

Function of myelin sheath :
- Myelin is an insulating layer that forms around nerves. It is made up of proteins and fatty substances.
- This myelin sheath allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efficiently along the nerve cells.
Question 6.
Write the names of the following.
a) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
b) Tissue that transports food in animals.
Answer:
a) Adipose tissue
b) Blood
![]()
Question 7.
Doctor examine Kshitija’s blood report and said, that she did not have the required levels of haemoglobin. What questions will you put the doctor to know about the effects of low level Haemoglobin?
Answer:
- What changes can we observe in a person who has low percentage of haemoglobin?
- What are the reasons for the low haemoglobin levels?
- Which type of food should we require to improve haemoglobin levels?
- Name the disease that occurs when we have less haemoglobin in our blood.
Question 8.
Observe the given diagram :
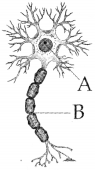
a) Identify the name of the diagram.
b) Write the names of the parts A & B.
c) Name the granular structure in the cytoplasm.
Answer:
a) The given diagram is nerve cell.
b) A – Cyton (cell body)
B – Axon
c) Nissl’s granules
![]()
Question 9.
A lab technician added a few drops of “Antigen-D” to a blood sample. What is the aim of him by doing so?
Answer:
If agglutination occurs in Anti RhD serum the Rh factor is positive and if it does not the Rh factor is negative.