Practice the AP 7th Class Science Bits with Answers Chapter 10 Changes Around Us on a regular basis so that you can attempt exams with utmost confidence.
AP 7th Class Science Bits Chapter 10 Changes Around Us with Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer and write its letters in the brackets.
1. Change in the shape of the balloon is done by blowing air into it. This is a……
A) manmade change
B) natural change
C) chemical change
D) periodic change.
Answer:
A) manmade change
2. Which of the following is not a man made-change?
A) preparation of bricks
B) making of paper
C) weaving of clothes
D) growing of nails
Answer:
D) growing of nails
![]()
3. Which of the following is not a fast change?
A) burning of paper
B) firing of crackers
C) making of a cake
D) spinning of a top
Answer:
C) making of a cake
4. The change happens in less time is.
A) slow change
B) fast change
C) periodic change
D) non periodic change.
Answer:
B) fast change
5. Which of the following is not reversible?
A) Weight suspended from a spring
B) Water changed to water vapour
C) Inflating of a balloon
D) Burning of a coal
Answer:
D) Burning of a coal
6. On …………… ice converts to water
A) heating
B) cooling
C) freezing
D) evaporating
Answer:
A) heating
7. some changes we cannot regain the original substance, these are.
A) manmade change
B) natural change
C) irreversible change
D) reversible change
Answer:
C) irreversible change
8. Limewater
A) Calcium Hydroxide
B) Sodium hydroxide
C) Potassium hydroxide
D) Carbonic acid
Answer:
A) Calcium Hydroxide
9. Which of the following is an irreversible change?
A) burning of wood
B) burning of Diwali crackers
C) ripening of fruits
D) all
Answer:
D) all
10. Which gas is released when lemon juice reacts with baking soda?
A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide
C) nitrogen
D)water vapour
Answer:
B) carbon dioxide
![]()
11. These changes are repeating at regular intervals of time.
A) slow change
B) fast change
C) periodic change
D) non periodic change.
Answer:
C) periodic change
12. Changes which do not occur at regular intervals of time and which cannot be predicted are called
A) slow change
B) fast change
C) periodic change
D) non periodic change
Answer:
D) non periodic change
13. Crystallization requires
A) heating
B) cooling
C) evaporating
D) A or C
Answer:
A) heating
14. In crystallization….
A) no new substances are formed.
B) new substances are formed.
C) no heating is required
D) none
Answer:
A) no new substances are formed.
15. Crystallization is
A) chemical change
B) physical change
C) periodic change
D) non periodic change
Answer:
B) physical change
16. Choose correct answer.
S: Crystallization is a Physical Change.
R: In crystallization no new substances are formed.
A) S and R are correct.
B) S and R are incorrect.
C) S is correct and R is incorrect.
D) S is incorrect and R is correct.
Answer:
A) S and R are correct.
17. Which change takes place when ice cube melts?
A) colour
B) phase
C) chemical
D) all
Answer:
B) phase
18. When a piece of gold is melted?
A) no new substances are formed.
B) new substances are formed.
C) chemical composition changes
D) none
Answer:
A) no new substances are formed.
![]()
19. When a piece of gold is melted, its chemical composition in the Solid form and also in the liquid form.
A) changes
B) varies
C) remains same
D) different
Answer:
C) remains same
20. In physical change ……….. changes.
A) shape
B) colour
C) size
D) all
Answer:
D) all
21. It is not a characteristic of a physical change…
A) No new substances are formed
B) Temporary and reversible in nature.
C) The chemical properties of a substance do not change.
D) It is a periodic change.
Answer:
D) It is a periodic change.
22. In curdling of milk is
A) a physical change
B) reversible change
C) chemical change
D) temporary change
Answer:
C) chemical change
23. When magnesium burns in the presence of oxygen, it forms magnesium oxide
A) magnesium oxide
B) magnesium chloride
C) carbon dioxide
D) none
Answer:
A) magnesium oxide
24. Magnesium Hydroxide is…..
A) an acid
B) a base
C) a neutral
D) none
Answer:
B) a base
![]()
25. Characteristic of a chemical change
A) During chemical change new substances are formed.
B) It is a permanent change and irreversible in nature.
C) Chemical composition of the substance changes.
D) All
Answer:
D) All
26. In chemical change which is not happens.
A) Heat, light may be released or absorbed.
B) A colour change may take place and sound may be produced.
C) Original substances may be formed on reversing the process
D) None
Answer:
C) Original substances may be formed on reversing the process
27. Rusting of iron requires
A) moisture
B) air
C) both
D) none
Answer:
C) both
28. Rust is…
A) iron oxide
B) calcium chloride
C) iron peroxide
D) above all
Answer:
A) iron oxide
29. Oxidization is observed in
A) iron articles
B) apples
C) brinjal
D) none
Answer:
D) none
30. Which of the following is used to prevent browning of the outer surface of the potato and brinjal?
A) cold water
B) lemon juice
C) ascorbic acid
D) above all
Answer:
D) above all
31. Which of the following is used in galvanizing?
A) zinc
B) chromium
C) A & C
D) none
Answer:
C) A & C
32. This process of deposition of a layer of zinc on iron is called
A) oxidation
B) galvanization
C) crystallization
D) none
Answer:
B) galvanization
33. Due to this process of brown layer is formed on the surface of fruits and vegetables.
A) oxidation
B) galvanization
C) crystallization
D) none
Answer:
A) oxidation
34. Which of the following is a useful change?
A) global warming
B) acid rain
C) plastic decomposition
D) fermentation
Answer:
D) fermentation
35. Which of the following occurs due to drastic increase in the emission of carbon dioxide by the burning of fossil fuels
A) global warming
B) floods
C) earth quakes
D) fermentation
Answer:
A) global warming
36. Ice converting to water, water converting to steam are ………. changes.
A) reversible
B) chemical
C) periodic
D) all
Answer:
A) reversible
37. Ripening of fruits is ………….. change.
A) reversible
B) physical
C) periodic
D) irreversible
Answer:
D) irreversible
38. The change occurs only in Size, colour and shape of the substance and no change in chemical composition are called ………….. changes
A) chemical
B) physical
C) periodic
D) irreversible
Answer:
B) physical
39. ………. change occurs with the formation of new substance in different chemical composition.
A) Reversible
B) Physical
C) Periodic
D) Chemical
Answer:
D) Chemical
![]()
40. The process of depositihg zinc on iron metals is called
A) oxidation
B) galvanization
C) rusting
D) crystallization
Answer:
B) galvanization
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. The changes which were taken place by the involvement of human beings are called ………………. change.
2. Changes which occur in ………………. duration of time are called fast changes.
3. Changes which takes longer duration of time to happen are called ………………. Change.
4. Changing of vegetable to curry : slow reaction:: changing of acid into vapour ………………. .
5. On ………………. water converts to ice.
6. The changes in which the formed substance can be converted into their ………………. are called reversible changes.
7. ………………. changes Limewater into milky white.
8. Vinegar + Baking Soda → Sodium acetate + ………………. + water
9. ………………. + Lime water → Calcium carbonate + water
10. Changes in which we cannot get the original substance by reversing the experimental conditions are called ………………. Changes.
11. ………………. changes are repeating at regular intervals of time .
12. The process of separating a soluble solid from the solution by heating or evaporating is called ………………. .
13. A ………………. is usually temporary and reversible in nature.
14. The substances which undergo change in colour or state or size or shape are ………………. .
15. When a Magnesium ribbon burns it gives ………………. light leaving a powdery substance behind.
16. ………………. + Water → Magnesium Hydroxide
17. Changes that occur with the formation of new substance with different chemical composition or transformation of a substance into another substance with the evolution or absorption of heat or light energy are termed as ………………. .
18. Iron + Oxygen (from air) + Water → ……………….
19. Apply a coat of paint or grease on iron articles. Prevents ………………. .
20. To prevent iron articles from coming contact with oxygen in air and water, a layer of another metal like ………………. is coated on them.
21. The process of deposition of a layer of zinc on iron is called ………………. .
22. Browning is not only observed on iron articles but also on cut fruits and ………………. .
23. Rubbing of the surface of cut fruits with ………………. to avoid from browning.
24. The process of reaction with ………………. is called oxidation.
25. ………………. waste is a widely recognized source of pollution.
26. ………………. gases are produced when fossil fuels such as coal and oil are burned in power station, factories and homes.
27. Oil spills occur when ………………. is released into the environment.
28. Formation of day and night, occurrence of seasons are ………………. changes.
29. Curding of milk : useful changes :: ………………. : harmful change.
Answer:
- 1. man-made
- short
- slow
- fast reaction
- cooling
- original substance
- Carbon dioxide
- carbon dioxide
- Carbon dioxide
- irreversible
- periodic changes
- crystallization
- physical change
- physical changes
- brilliant white dazzling
- Magnesium Oxide
- chemical change
- rust (Iron oxide)
- rusting of iron
- chromium or zinc
- Galvanization
- vegetables
- juices of citrus fruits
- oxygen
- Plastic
- Acidic
- liquid petroleum
- periodic
- global warming
III. Match the following.
1.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Ripening of fruit | a) physical change |
| 2) Burning of a dry leaf | b) chemical change |
| 3) Melting of ice | c) periodic change |
| 4) Day and nights | d) fast change |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Ripening of fruit | b) chemical change |
| 2) Burning of a dry leaf | d) fast change |
| 3) Melting of ice | a) physical change |
| 4) Day and nights | c) periodic change |
2.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Carbon dioxide | a) galvanizing |
| 2) Oxygen | b) crystallization |
| 3) Zinc | c) global warming |
| 4) sugar | d) oxidation |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Carbon dioxide | c) global warming |
| 2) Oxygen | d) oxidation |
| 3) Zinc | a) galvanizing |
| 4) sugar | b) crystallization |
3.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) browning of vegetables | a) vinegar |
| 2) browning of iron | b) dazzling light |
| 3) formation of crystal | c) galvanization |
| 4) burning of magnesium | d) crystallization |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) browning of vegetables | a) vinegar |
| 2) browning of iron | c) galvanization |
| 3) formation of crystal | d) crystallization |
| 4) burning of magnesium | b) dazzling light |
4.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) more time | a) physical change |
| 2) less time | b) chemical change |
| 3) time period | c) periodic change |
| 4) reversible | d) fast change |
| 5) new substances | e) slow change |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) more time | e) slow change |
| 2) less time | d) fast change |
| 3) time period | b) chemical change |
| 4) reversible | c) periodic change |
| 5) new substances | a) physical change |
5.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Zinc | a) Chemical changes |
| 2) Formation of Magnesium oxide | b) Natural changes |
| 3) Belum Caves | c) Periodic changes |
| 4) Changes in seasons | d) Oxidation |
| 5) Photosynthesis | e) Galvanisation |
| f) Crystallization |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Zinc | e) Galvanisation |
| 2) Formation of Magnesium oxide | d) Oxidation |
| 3) Belum Caves | b) Natural changes |
| 4) Changes in seasons | c) Periodic changes |
| 5) Photosynthesis | a) Chemical changes |
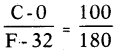
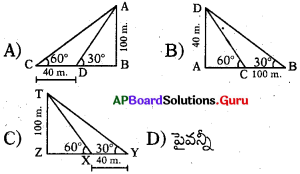
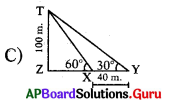
 This diagram indicates
This diagram indicates

 Indicates
Indicates