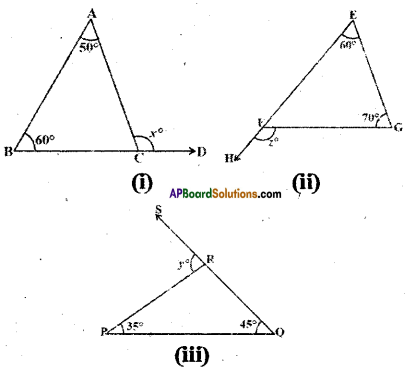
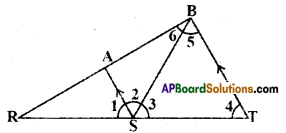
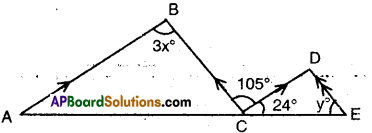
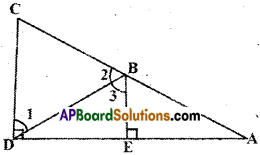
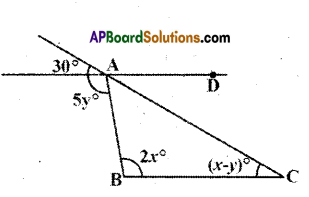
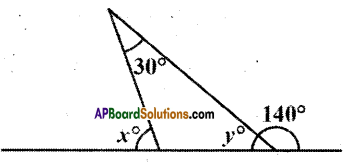
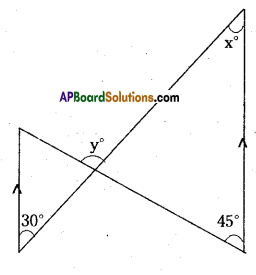
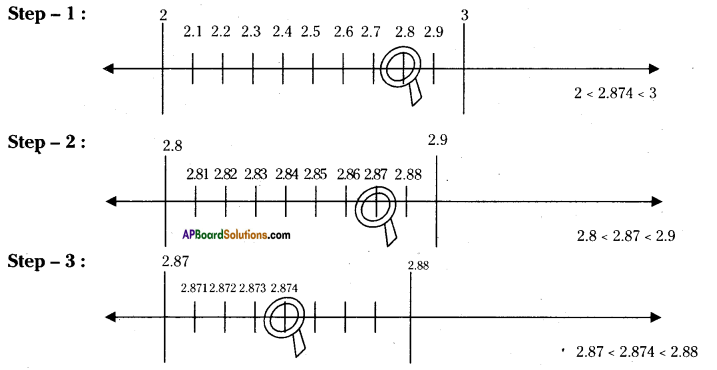
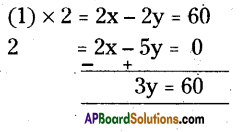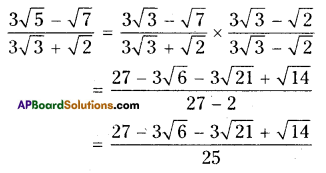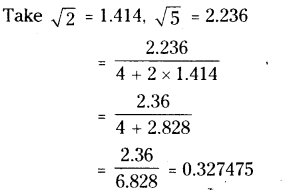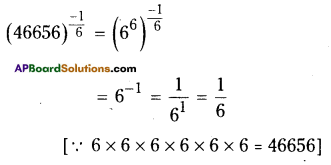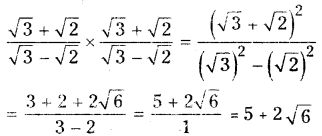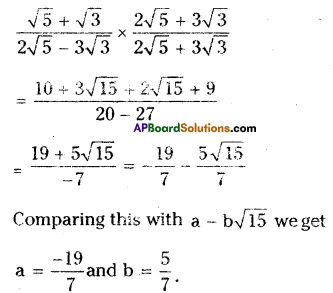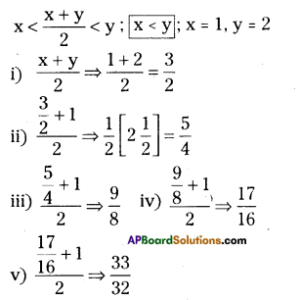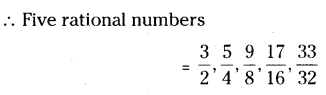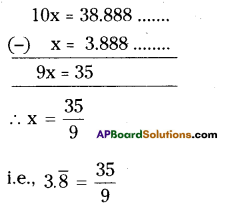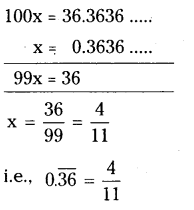AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Co-Ordinate Geometry Ex 5.1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Maths Solutions 5th Lesson Co-Ordinate Geometry Exercise 5.1
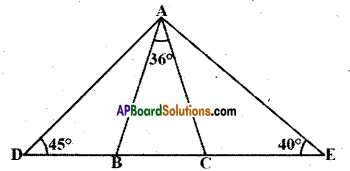
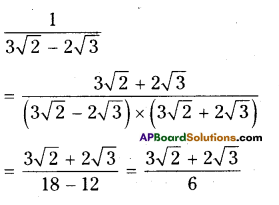
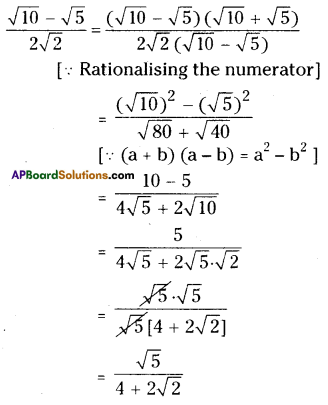
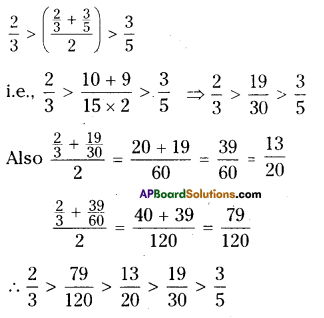
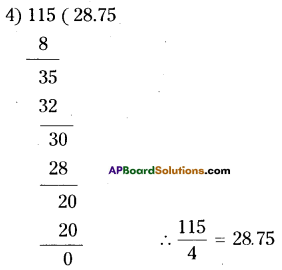
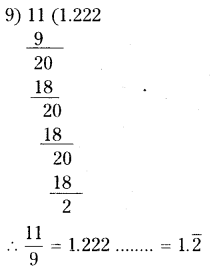
Question 1.
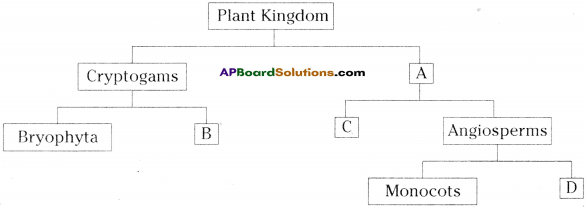
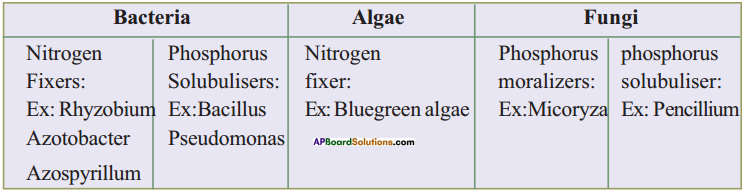
In a locality, there is a main road along North – South direction. The map is given below. With the help of the picture answer the following questions.
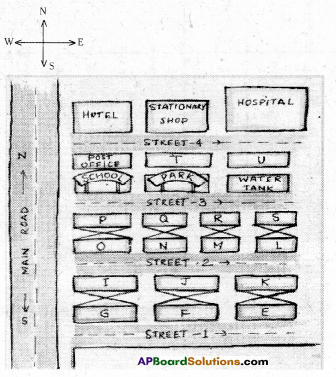
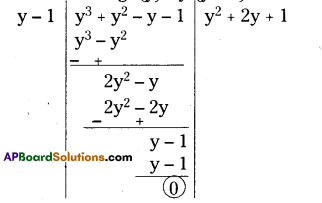
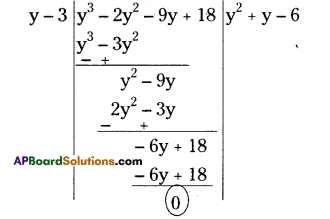
i) What is the 3rd object on the left side in street no. 3 while going in east direction ?
ii) Find the name of the 2nd house which is on right side of street 2 while going in east direction.
iii) Locate the position of Mr. K’s house.
iv) How do you describe the position of the post office ?
v) How do you describe the location of the hospital ?
Solution:
i) Water tank
ii) Mr. J’s house
iii) In street No. 2, 3rd house on right side.
iv) In street No. 4, the first house on right side.
v) In street No. 4, the last house on left side.