AP State Syllabus AP Board 6th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Maths Solutions 10th Lesson Practical Geometry Ex 10.1
![]()
Question 1.
Construct a line segment of length 6.9 cms using ruler and compass.

Solution:
Steps of construction:
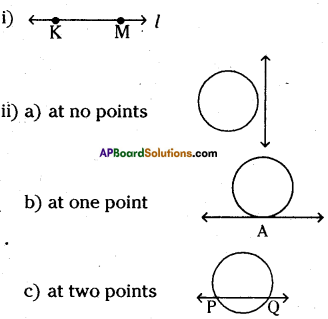
- Draw a line l. Mark a point A on the line l.
- Place the metal pointer of the compass on the zero mark of the ruler. Open the compass, so that pencil point touches the 6.9 cm mark on the ruler.
- Place the pointer at A on the line l and draw an arc to cut the line. Mark the point where the arc cuts the line as B
- On the line l, we got the line segment AB of required length.
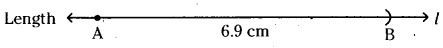
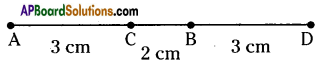
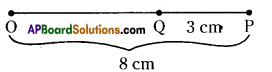
Question 2.
Construct a line segment of length 4.3 cms using ruler.
Solution:
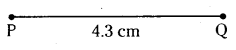
Steps of construction:
- Place the ruler on paper and hold it firmly.
- Mark a point with a sharp edged pencil against 0 cm mark on the ruler. Name the point as P.
- Mark another point against 3 small divisions just after the 4 cm mark. Name this point as Q.
- Join points P and Q along the edge of the ruler.
Therefore, PQ is the required line segment of length 4.3 cm.
![]()
Question 3.
Construct a circle with centre M and radius 4 cm.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
- Mark a point M on the paper.
- By using compasses take 4 cm as the radius on with the scale.
- Place the metal point on M and draw a circle from M.
Hence required circle is constructed with center M and radius 4 cm.
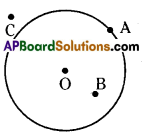
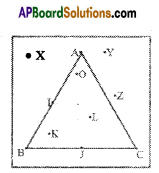
Question 4.
Draw any circle and mark three points A, B and C such that
(i) A is on the circle
(ii) B is in the interior of the circle
(iii) C is in
Solution: