Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material 13th Lesson Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material 13th Lesson Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds and classify them into primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
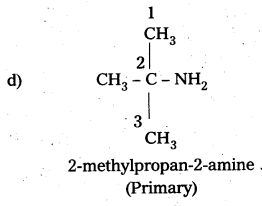
i) (CH3)3CHNH2
ii) CH3 (CH2)2 NH2
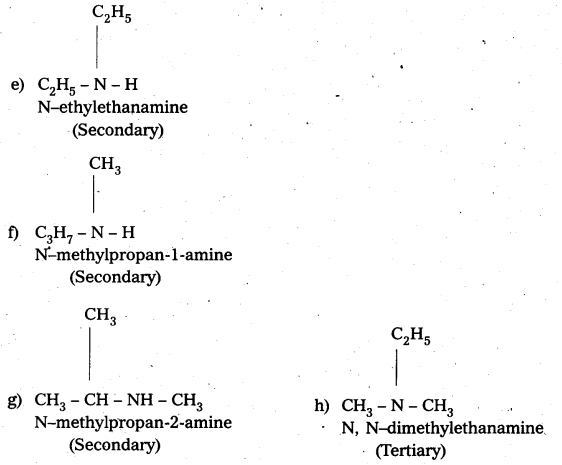
iii) (CH3CH2)2 NCH3
Answer:
i) (CH3)3CHNH2 :
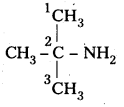
IUPAC name : 2 – methyl 2 – propananine ^ – NH
It is a 1° – amine
ii) CH3 (CH2)2 NH2:
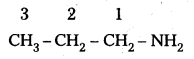
IUPAC name : 1 – Propananine
It is a 1° – amine
iii) (CH3CH2)2 NCH3
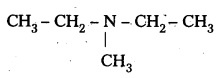
IUPAC name : N – Elthyl N – Methyl Ethanamine
It is a 3° – amine
![]()
Question 2.
Explain why ethylamine is more soluble in water, whereas aniline is not soluble.
Answer:
Elthyl amine is more soluble in water due to the presence of hydrogen bonding. Where are in case of aniline due to presence of bulky hydrocarbon part, the extent of hydrogen bonding is less and it is not soluble in water.
Question 3.
Why aniline does not undergo Friedel – Crafts reaction ?
Answer:
Aniline is a lewis base and AlCl3 is a Lewis acid. In Friedal Craft’s reaction both of these combined to form a complex
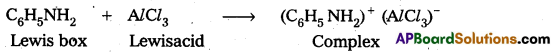
Lewis box Lewisacid Due to formation of complex the electrophilic substitution tendency decreases in aniline and it does not undergo these reaction.
Question 4.
Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis exclusively forms primary amines only. Explain.
Answer:
Gabriel Phthalinide synthesis exclusively forms primary amines only.
Reason : In this reaction primary amines are formed without the traces of 2° (or) 3° amines.
Question 5.
Arrange the following bases in decreasing order of pKb values. C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, (C2H5)2 NH and C6H5NH2.
Answer:
The decreasing order of pKb values.of gives amines is
C6H5NH2 > C6H5NHCH3 > C2H5NH2 > (C2H5)2NH
![]()
Question 6.
Arrange the following bases in increasing order their basic strength. Aniline. P – nitroaniline and P – toluidine.
Answer:
The increasing order of basic strength of given compounds is
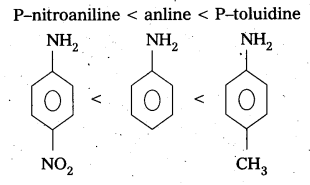
Question 7.
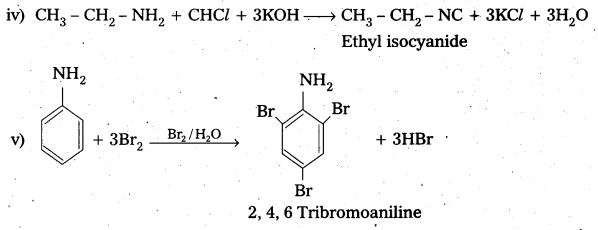
Write equations for carbylamine reaction of any one aliphatic amine. [A.P.& T.S. Mar. 16]
Answer:
When Ethyl amine (1° – amine) reacts with chloro form in presence of alkali to form ethyl isocyanide.
CH3 – CH2 – NH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOH ![]() CH3 – CH2 – NC + 3KCl + 3H2O
CH3 – CH2 – NC + 3KCl + 3H2O
Question 8.
Give structures of A, B and C in the following reactions.
![]()
Answer:
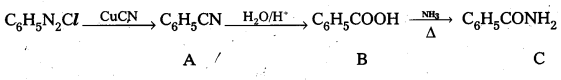
A – Phenyl Cyanide B – Benzoic acid C – Benzamide
Question 9.
Accomplish the following conversions. [Mar. 14]
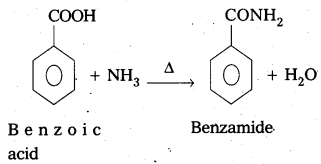
i) Benzoic acid to benzamide
ii) Aniline to P – bromoaniline.
Answer:
Conversion of benzoic acid to benzamide
ii) Conversion of Aniline to P – bromo aniline
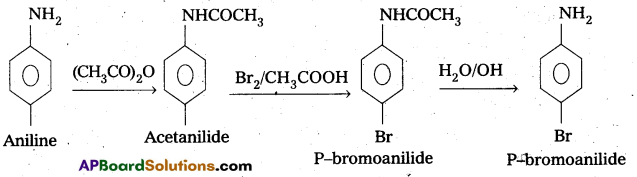
Question 10.
Why cannot aromatic primary amines be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
Answer:
Aromatic 1° – amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalinide synthesis beczause aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with the an ion formed by phthalinide.
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
i) CH3CH2NHCH2CH2CH3
ii) PhCH2CN
Answer:
i) CH3CH2NHCH2CH2CH3
N – Ethyl 1 – Propanamine
ii) PhCH2CN
Phenyl Ethane nitrile (Benzyl cyanide)

Question 2.
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds.
i) Methylamine and dimethylamine
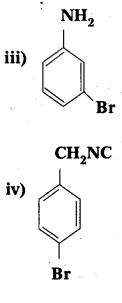
ii) Aniline and N.Methylaniline .
iii) Ethylamine and aniline
Answer:
i) Methyl amine (1° – amine) and dimethyl amine (2° – amine) are distinguished by iso cyanide test (or) Carbylamine (est. Methyl amine responds to carbylamine reaction to produce methyl isocyanide where as dimethyl amine does not respond to the iso cyanide test
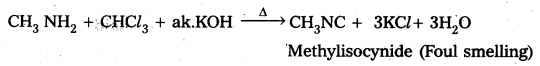
ii) Aniline (1° – amine) and N.methyl (2° – amine) aniline are distinguished, by carbylamine test (or) isocyanide test. Aniline responds to carbyl amine test to give foul smelling phenyl iso cyanide where as N – methyl aniline does not responds to carbyl amine Test.
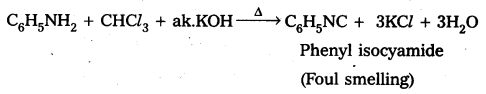
iii) Ethyl amine (1° – aliphafic amine) and aniline (1° – aromatic amine) are distinguished by Diazotisation reaction. Aniline under go diazotisation reaction to form benzene diazonium salt where as ethyl amine form highly unstable alkyl diazonium salt
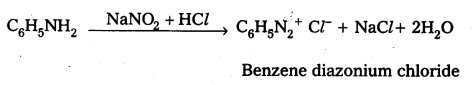
![]()
Question 3.
Account for the following :
- pKb of aniline is more then of methylamine.
- Reduction of alkylcyanide forms primary amine whereas alkyl isocyanide forms secondary amine.
Answer:
- In aniline there exist conjugation between the electron pair on nitrogen and benzene ring and is less available for protonation than in nethyl amine.
∴ pKb value of aniline is more than that of methylamine and aniline is less basic. - The reduction of alkyl cyanides forms 1°- amines. In alkyl cyanides alkyl group is attached to carbon atom of cyanide, Where as in alkyl iso cyanides alkyl group is attached to nitrogen atom of isocyanide. So reduction of alkyl isocyanide forms 2°- amines.
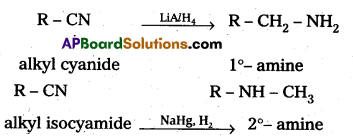
Question 4.
How do you prepare the following ?
i) N, N-Dimethyl proponamine from ammonia
ii) Propanamine from chloroethane
Answer:
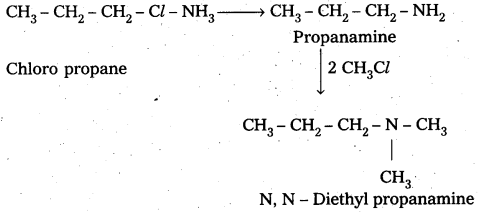
i) Preparation of N, N – Di nethyl propanamine from ammonia : Chloro propane reacts with ammonia followed by the reaction of methylchloride to form N, N – Di methyl propananine.
ii) Preparation of propanamine from chloroethane : Chloro ethane reacts with KCN followed by the reduction forms propanamine
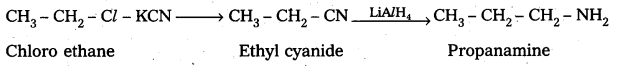
Question 5.
Compare the basicity of the following in gaseous and in a queous state and arrange them in increasing order of basicity.
Answer:
Givein compounds CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N and NH3.
In the above compounds methly substituted ammonium ion gets stabilised due to dispersal of the positive charge by the +1 effect of the methyl group. Hence methyl amines are stronger bases than ammonia. Basic nature of amines increase with increase of methyl groups. This trend is followed in gaseous phase.
(CH3)3 N > (CH3)2 NH > CH3 NH2 > NH3
In the aqueous phase the substituted ammonium cations get stabilised not only by electron releasing effect of the alkyl group but also by solvation with water molecules. Due to steric hinderance the basic strength of methyl amines in the aqueous state changed as follows
(CH3)2 NH > CH3 NH2 > (CH3)3 N > NH3
![]()
Question 6.
How do you carryout the following conversions?
i) N – Ethylamine to N, N – Diethyl propanamine
ii) Aniline to Benzene suiphonamide
Answer:
Conversion of
i) N – Ethyl amine to N, N – Diethyl propanamine Ethyl amine reacts with ethyl chloride and propyl chloride to from N N – Di ethyl propanamine.
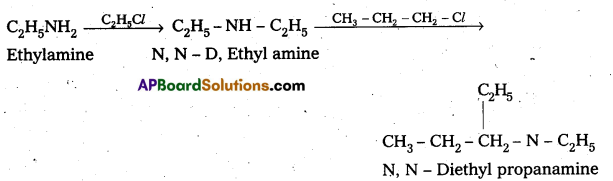
ii) Conversion of Aniline to Benzene sulphonamide : Aniline reacts with benzene sulphonyl chloride to form N – Phenyl benzene suiphonamide.
C6H5NH2 + C6H5SO2Cl → C6H5NHSO2 C6H5 + HCl Phenyl benzene sulphonamide
Question 7.
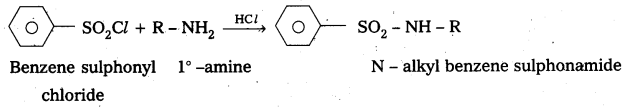
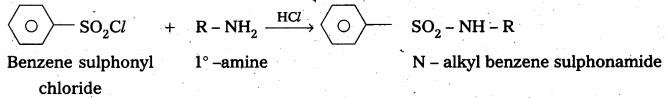
Explain with a suitable example how benzene sulphonylchioride can distinguish primary secondary and tertiary amines.
Answer:
Benzene suiphonyl chloride is called Hinsbergs reagent. This is used to distinguish the 1°, 2°,. 3° – amines.
— with le – amine: Benzene suiphonyl chloride reacts with 1° amine and produce N – Alkyl benzene sulphonamide which is soluble in alkali.
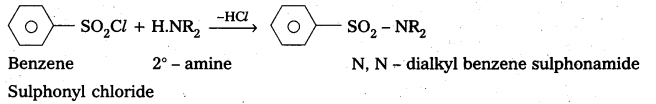
—, with 2° – amine: Benzene suiphonyl chloride reacts with 2° – amine and produce N, N – DiaLkyl benzene sulphonamide which is insoluble in alkali
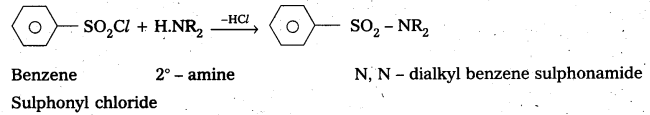
—, with 3° – amine : Benzene sulphonyl chloride does not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride.
Question 8.
Write the reactions of
i) aromatic and
ii) aliphatic primaiy amines with nitrous acid.
Answer:
i) Reaction of aromatic 1° – amine with nitrous acid : Aromatic 1° – amine react with , nitrous acid at low temperature (0 – 5°C) to form diazonium salts.
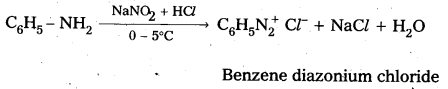
ii) Reaction of Aliphatic 1° – amine with nitrous acid : Aliphatic 1° – amine react with nitrous acid to form highly unstable diazonium salts which gives nitrogen gas and alcohols after decomposition.
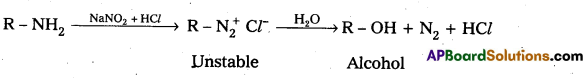
Question 9.
Explain why amines are less acidic than alcohols of comaparable molecular masses.
Answer:
Amines are less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular massey
Explaination : In alcohols the O – H bond is more polar than N – H bond of amines. Hence Amines releates H+ ion with more difficulty as compared to alcohol.
![]()
Question 10.
How do you prepare Ethyl cyanide and Ethyl isocyanide from a common alkylhalide ?
Answer:
Preparation of ethyl cyanide : Ethyl chloride reacts with aq. Ethanolic KCN to form Ethyl cyanide as a major product
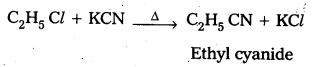
Preparation of Ethyl isocyanide : Ethyl chloride reacts with aq. Ethanolic AgCN to form Ethyl iso cyanide as a major product
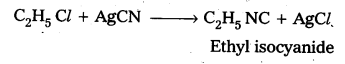
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
An aromatic compound A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound B which on heating with Br2 and KQH forms compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B and C.
Answer:
Given that an aromatic compound A on treatment with aq. NH3 and heating forms compound ‘B’. Which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N.
1. From the above information ‘B is amide and ‘C’ is amine
2. Molecular formula of ‘C’ is C6H7N, So ‘C’ is Amiine (C6H5NH2)
3. Compound A on treatment with aq. NH3 forms B.
So ‘A’ is Benzoic acid (C6H5 – COOH)
and B’ is Benzamide (C6H5 – CONH2)
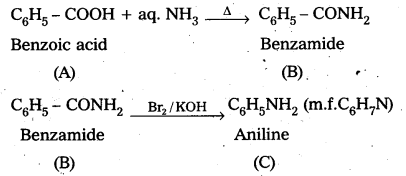
Question 2.
Complete the following conversions.
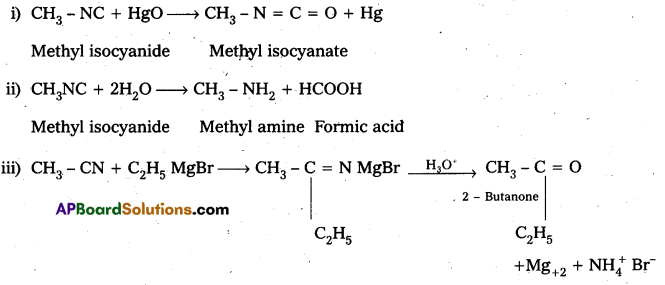
i) CH3NC + HgO → ?
ii) ? 2H2O → CH3NH2 + HCOOH
Answer:
Question 3.
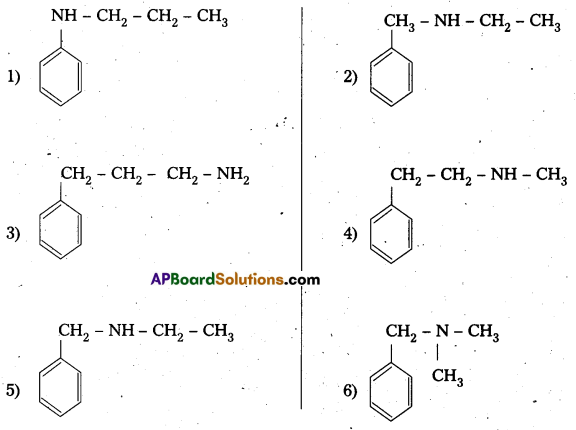
i) Write the structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula C9H13N.
ii) What reducing agents can bring out reduction of nitrobenzene?
iii) Write the product formed when benzyl chloride is reacted with ammonia followed by treatment with methyl and ethyl chlorides. Write the product
Answer:
i) Given compound molecular formula C9H13N
The structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the above formula C9H13N
ii) The reducing agents that bring out the reduction of nitro benzene are :
- H2/Pd (or) Pt (or) Ni [Ethanol]
- Sn + HCl (or) Fe + HCl
- Li AlH4
- Zn + alc.KOH
- Zn + NH4Cl
![]()
iii) a) Benzyl chloride reacts with ammonia to form benzyl amine followed by the reaction with methyl chloride forms N, N – Dimethyl phenyl methanamine
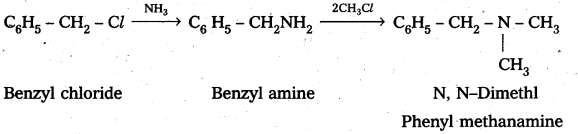
b) Benzyl chloride reacts with ammonia to form benzyl amine followed by the reaction with Ethyl chloride form
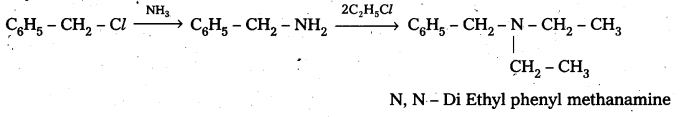
Question 4.
i) Identify the amide and cyanide which on reduction with appropriate reducing agent gives n – butylamlne.
ii) Write the mechanism of Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Answer:
i) a) Propyl cyanide on reduction gives n – Butylamine
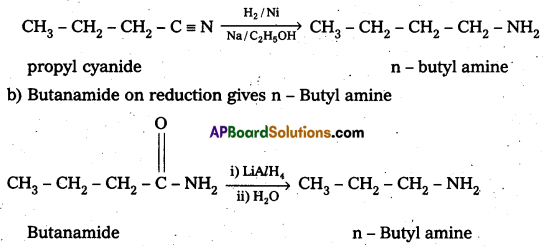
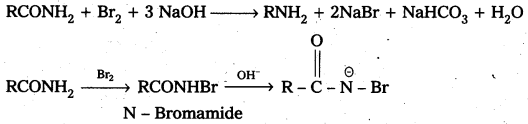
ii) Hoffmann bromamide reaction : It is a simple way of converting an amide to an amine having one carbon atom less than the starting amide. The reaction is a rearrangement which is brought about by bromide in presence of alkali. It is believed to proceed through the steps shown below.

Question 5.
How do you make the following convertions ?
i) Chlorophenylmethane to phenylacetic acid
ii) Chlorophenylmethane to 2 – phenylethanamine.
Answer:
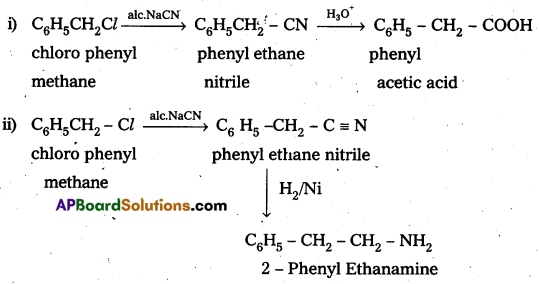
![]()
Question 6.
Identify the starting amide which gives p – methyl aniline on reaction with bromine and sodium hydroxide and write all the steps involved in the reaction. .
Answer:
P – methyl Acetanilide reacts with bromine and sodium hydroxide to form P – methyl aniline.
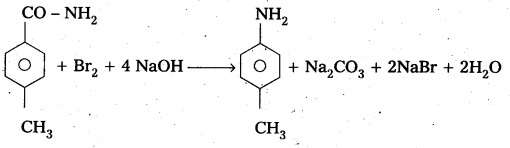
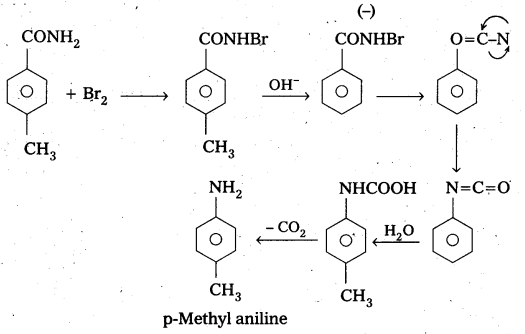
Question 7.
Explain why the order of basicity for methyl amine, N, N – dimethyl amine and N, N, N – tnmethyl amine changes in gasous and a aqueous medium.
Answer:
Given compounds
CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N and NH3
In the above compounds methyl substituted, ammonium ion gets stabilised due to dispersal of the positive charge by the + 1 effect of the methyl group. Hence methyl amines are stronger bases than ammonia. Basic nature of amines increase with in increase of methyl groups. This trend is followed in gaseous phase.
(CH3)3 N> (CH3)2 NH > CH3NH2 > NH3.
In the aqueous phase the substituted ammonium cations get stabilised not only by electron releasing effect of the alkyl group but; also by solvation with water molecules. Due to sterichindrance the basic strength of methyl amines in the aqueous state changed as follows
(CH3)2 NH > CH3 NH2> (CH3)3 N > NH3
![]()
Question 8.
Write the equations involved in the reaction of Nitrous acid with Ethylamine and aniline.
Answer:
Reaction of Ethylamine with nitrous acid : Ethyl amine reacts with nitrous acid to form highly unstable diazonium salt which gives nitrogeñ gas and Ethyl alcohol after decomposition.
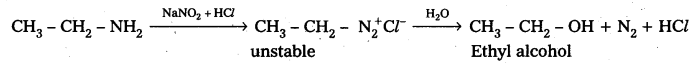
Reaction of Aniline with nitrous acid : Aniline reacts with nitrous acid at low temperatures (0- 5°C) to form diazomum salts. (Benzene diazonium salt)
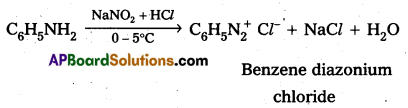
Question 9.
Explain with equations how methylamine, N, N – dimethylamine and N, N, N – trimethylamine react with benzenesulphonyl chloride and how this reaction Is useful to separate these amines.
Answer:
Benzene suiphonyl chloride is called Hinsbergs reagent. This is used to distinguish the 1°, 2°, 3° – amines.
-. with 1°- amine : Benzene sulphonyl chloride reacts with 1°-. amine and produce N – Alkyl benzene sulphonamide which is soluble in alkali.
.- with 2° – amine: Benzene sulphonyl chloride reacts with 2° – amine and produce N, N – Dialkyl benzene sulphonamide which is insoluble in alkali
—, with 3° – amine: Benzene sulphonyl chloride does not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride.
Question 10.
Explain why aniline In strong acidic medium gives a mixture of Nitro anilines and what steps need to be taken to prepare selectively p – nitro aniline.
Answer:
In strong acidic medium anime under go nitration to form mixture of nitro animes. In strongly acidic medium aniline is protonated to form the anilinium ion which is metadirecting. So besides the ortho and para derivatives meta derivative also formed.
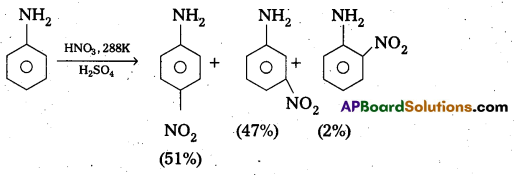
By protecting – NH2 group by acetylation reaction with acetic an hydride the nitration reaction can be controlled and the – P – nitro derivative can be formed as major product.
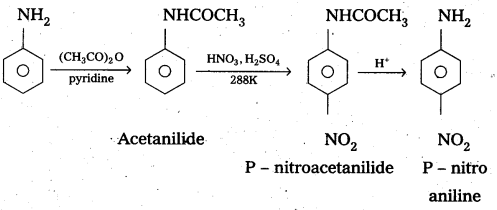
Question 11.
i) Account for the stability of aromatic diazoniun ions when compared to aliphatic diazonium ions.
ii) Write the equations showing the conversion of aniline diazoniumchloride to
a) chlorobenzene, b) Iodobenzene and c) Bromobenzene
Answer:
i) —> Aliphatic diazonium salts which are formed from 1° – aliphatic amines are highly unstable and liberate nitrogen gas and alcohols.
—> Aromatic diazonium salts formed from 1° – aromatic amines are stable for a short time in solution at low temperatures (0 – 5°C). The stability of arene diazonium ion is explained on the basis of resonance.
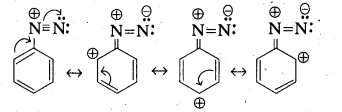
ii) a) Conversion of aniline diazonium chloride to chloro benzene
C6H5N2+ ![]() C6H5Cl + N2
C6H5Cl + N2
b) Conversion of aniline diazonium chloride to Iodo benzene
C6H5N2+Cl– + KI → C6H5I + N2 + KCl
c) Conversion of aniline diazonium chloride to Bromo benzene
C6H5N2+Cl– ![]() C6H5Br + N2
C6H5Br + N2
![]()
Question 12.
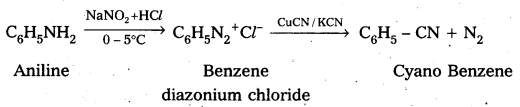
Complete the following conversions : Aniline to
i) Fluorobenzene
ii) Cyanobenzene
iii) Benzene and
iv) Phenol
Answer:
i) Aniline to Fluorobenzene
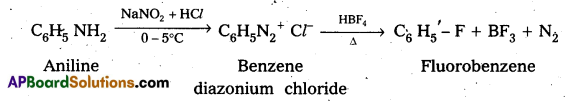
ii) Aniline to cyano benzene
iii) Aniline to Benzene
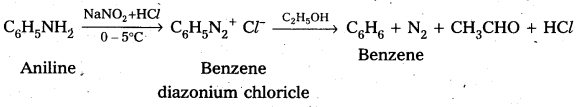
iv) Aniline to phenol
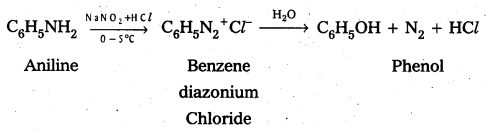
Question 13.
Explain the following name reactions: [A.P. Mar. 18]
i) Sandmeyer reaction
ii) Gatterman reaction
Answer:
i) Sandmeyer reaction: Formation of chioro benzene, Brono benzene (or) cyano benzene from benzene diazonium salts with reagents Cu2Cl2/HCl, Cu2Br2/HBr, CuCN/KCN is called sandmayers reaction.
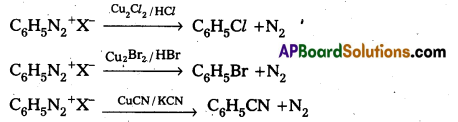
ii) Gatterman reaction : Formation of chloro benzene, Bromobenzene from benzene diazonium salts with reagents Cu/HCl, Cu/HBr is referred as gatterman reaction.
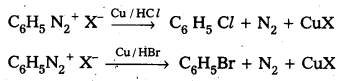
Question 14.
Write the steps involved in the coupling of Benzene diazoniumchloride with aniline and phenol.
Answer:
Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in which the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with the diazonium salt to form P-hydroxyazobenzene. This type of reactionsis known as coupling reactions. Similarly the reaction of diazonium salt with aniline yields P – amino azobenzene.
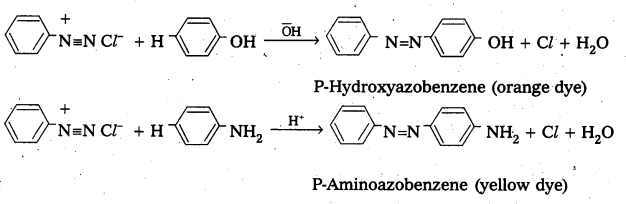
Question 15.
Write the equations involved in the conversion of acetamide and propanaldehydeoxime to methyl cyanide and ethyl cyanide respectively.
Answer:
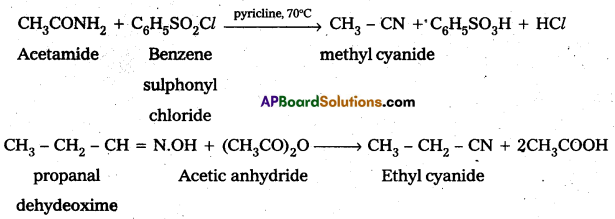
Textual Examples
Question 1.
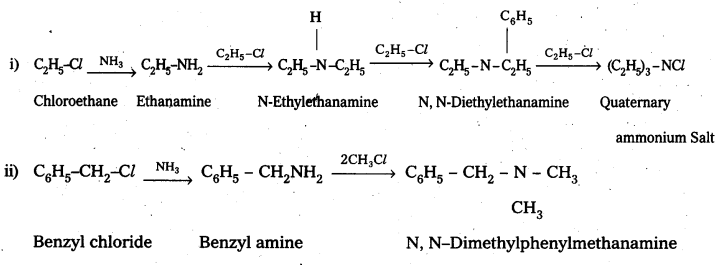
Write chemical equations for the following reactions:
i) Reaction of ethanolic NH3 with C2H5Cl.
ii) Ammonolysis of benzyl chloride and reaction of amine so formed with two moles of CH2Cl.
Solution:
Question 2.
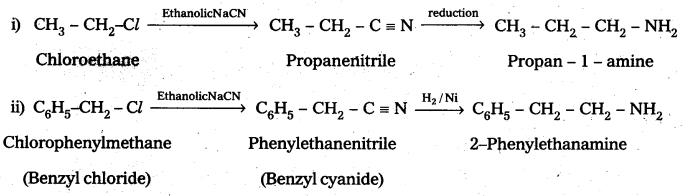
Write chemical equations for the following Conversions:
i) CH3 – CH2 – Cl into CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – NH2
ii) C6H5 – CH2 – Cl into C6H5 – CH2 – CH2 – NH2
Solution:
![]()
Question 3.
Write structures and IUPAC names of
i) the amide which gives propanamine by Hoffmann bromarnide reaction.
ii) the amine produced by the Hoffmann degradation of benzamide.
Solution:
i) Propanamine contains three carbons. Hence, the amide molecule must contain four carbon atoms. Structure and IUPAC name of the starting amide with four carbon atoms are given below:
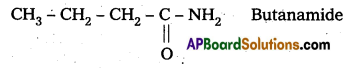
ii) Benzamide is an aromatic amide containing seven carbon atoms. Hence, the amine formed from benzamide is aromatic primary amine containing six carbon atoms.

Question 4.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their basic strength:
C6H5NH2, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2 NH, NH3. [T.S. Mar.’19]
Solution:
The decreasing order of basic strength of the above amines and ammonia follows the following order:
(C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2 > NH3 C6H5NH2
Amines also react with benzoyl chloride (C6H5COCl). This reaction is known as benzoylation.
CH3NH2 + C6H5COCl → CH3NHCOC6H5 + HCl
Methanamine Benzoyl chloride N – Methylbenzamide
What do you think is the product of the reaction of amines with carboxylic acids ? They form salts with amines at room temperature.
![]()
Question 5.
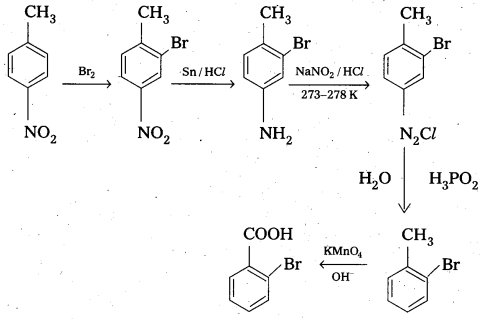
How will you convert 4 nitrotoluene to 2 – bromobenzoic acid?
Solution:
Intext Questions
Question 1.
Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary.
iii) (C2H5)2CHNH2
iv) (C2H5)2NH
Solution:
i) Primary
ii) Tertiary
iii) Primary
iv) Secondary.
Question 2.
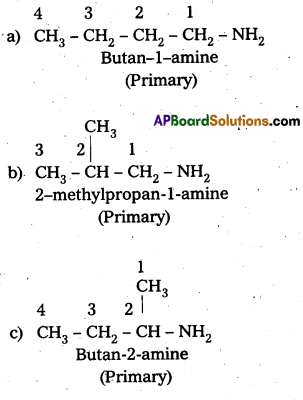
i) Write the structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular – formula, C4H11N.
ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines ?
Solution:
i) and ii) Eight isomers of C4H11N are :
![]()
iii) Isomerism exhibited by different amines are:
a) Chain isomers : i.e., have different carbon chains (a) and (b), (c) and (d).
b) Position isomers : i.e., functional group occupy different positions, (b) and (c), (b) and (d), (a) and (d).
e) Metamers: i.e., different alkyl groups are attached to the same functional group, (e) and (0, (g) and (e).
d) Functional isomers : i.e., have different functional groups. All the three categories (1°, 2° and 3°) of amines are the functional isomers of each other.
Question 3.
How will you convert
i) benzene into aniline ?
ii) benzene into N, N-dimethylaniline ?
iii) Cl-(CH2)4-Cl into hexan-1, 6-diamine ?
Solution:
i) Benzene into aniline:
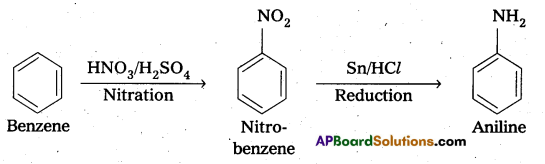
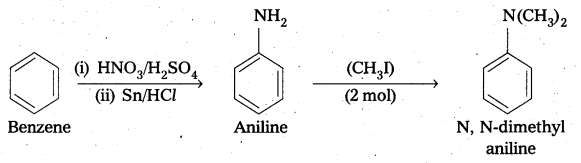
ii) benzene into N, N-dimethylaniline
iii) Cl-(CH2)4-Cl into hexan-1, 6-diamine
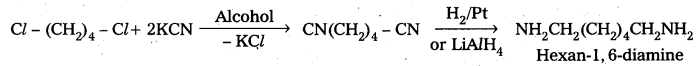
Question 4.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength.
i) C2H5NH2, C6H5NH2, NH3, C6H5CH2NH2 and (C2H5)2NH
ii) C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, (C2H5)3N, C6H5NH2
iii) CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N, C6H5NH2, C6H5CH2NH2
Solution:
i) C2H5NH2 < NH3 < C6H5CH2NH2 < C6H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH
ii) C6H5NH2 < C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)3N < (C2H5)2NH
iii) C6H5NH2 < C6H5CH2NH2 < (CH3)3N< CH3NH2 < (CH3)2NH
![]()
Question 5.
Complete the following acid-base reactions and name the products.
i) CH3CH2CH2NH2 + HCl →
ii) (C2H5)3N + HCl →
Solution:
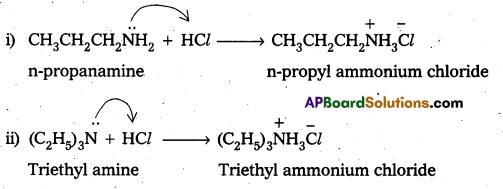
Question 6.
Write reactions of the final alkylation product of aniline with excess of methyl iodide in the presence of sodium carbonate solution.
Solution:
Hofmann’s ammonolysis reaction: In the presence of excess methyl iodide, aniline (primary amine) forms quartemary ammonium salt.
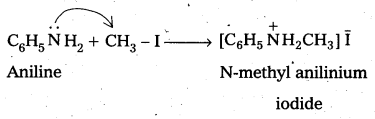
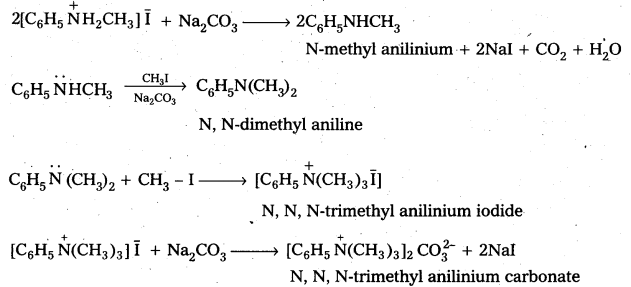
Question 7.
Write the chemical reaction of aniline with benzoyl chloride and write the name of the product obtained.
Solution:
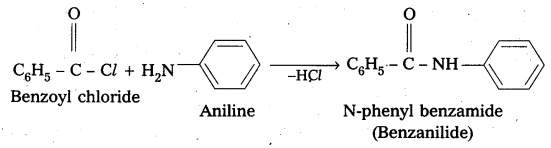
![]()
Question 8.
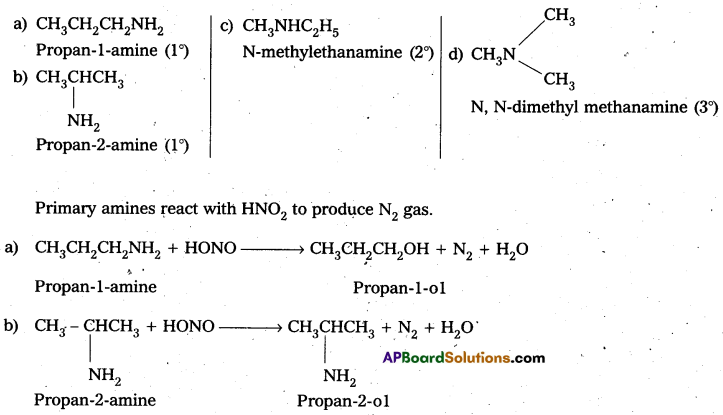
Write the structures of different isomers corresponding to the molecular formula C3H9N. ‘ Write IUPAC names of the isomers which will liberate nitrogen gas on treatment with nitrous acid.
Solution:
C3H9N has four isomers :
Question 9.
Convert :
(i) 3-methyl aniline into 3-nitrotoluene.
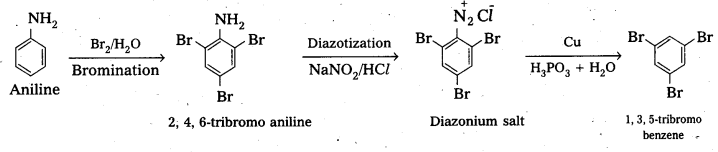
(ii) anline into 1, 3, 5-tribromobenzene.
Solution:
i) 3-methyl aniline into 3-nitrotoluene.
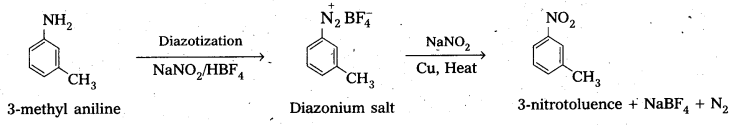
(ii) Anline into 1, 3, 5-tribromobenzene.