AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Maths Solutions 6th Lesson Progressions InText Questions
AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Maths Textbook Solutions Chapter 6 Progressions InText Questions and Answers.
10th Class Maths 6th Lesson Progressions InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write three examples for finite A.P and three for infinite A.P. (Page No. 130)
Answer:
Examples for finite A.P
i) 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 where a = 3; d = 2.
ii) x, x + a, x + 2a, x + 3a, x + 4a, x + 5a where a = x; d = a.
iii) \(\frac{1}{9}\), \(\frac{2}{9}\), \(\frac{3}{9}\), \(\frac{4}{9}\), \(\frac{5}{9}\), \(\frac{6}{9}\), \(\frac{7}{9}\), ….
where a = \(\frac{1}{9}\); d = \(\frac{1}{9}\).
Examples for infinite A.P
i) 10, 20, 30, 40, ……
where a = 10, d = 10.
ii) 5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8, 9.9,……
where a = 5.5; d = 1.1.
iii) -100, -95, -90, -85,…..
where a = – 100, d = 5.
Do these
![]()
Question 1.
Write three examples for finite A.P and three for infinite A.P. (Page No. 130)
Answer:
Examples for finite A.P
i) 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 where a = 3; d = 2.
ii) x, x + a, x + 2a, x + 3a, x + 4a, x + 5a where a = x; d = a.
iii) \(\frac{1}{9}\), \(\frac{2}{9}\), \(\frac{3}{9}\), \(\frac{4}{9}\), \(\frac{5}{9}\), \(\frac{6}{9}\), \(\frac{7}{9}\), ….
where a = \(\frac{1}{9}\); d = \(\frac{1}{9}\).
Examples for infinite A.P
i) 10, 20, 30, 40, ……
where a = 10, d = 10.
ii) 5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8, 9.9,……
where a = 5.5; d = 1.1.
iii) -100, -95, -90, -85,…..
where a = – 100, d = 5.
(Page Nos. 131, 132)
Question 2.
Take any Arithmetic Progression.
Answer:
4, 7, 10, 13, 16, ……
Question 3.
Add a fixed number to each and every tetm of A.P. Write the resulting numbers as a list.
Answer:
4, 7, 10, 13, 16, …….
Adding ‘5’ to each term of the above A.P. we get
4 + 5, 7 + 5, 10 + 5, 13 + 5, 16 + 5,…
9, 12, 15, 18, 21, ……
In the list obtained the first term
a1 = 9; a2 = 12, a3 = 15, a4 = 18,
Also a2 – a1 = 12 – 9 = 3
a3 – a2 = 15 – 12 = 3
a4 – a3 = 18 – 15 = 3
……………………………………
i.e.,
d = a2 – a1 = a3 – a2 = a4 – a3 = …. = 3
∴ The resulting list forms an A.P.
![]()
Question 4.
Similarly subtract’a fixed number from each and every term of A.P. Write the resulting numbers as a list.
Answer:
4, 7, 10, 13, 16, ……
Subtracting ‘2’ from the each term of A.P in given series, we get
4 – 2, 7 – 2, 10- 2, 13 – 2, 16 – 2, ……
2, 5, 8, 11, 14, ……
In the list obtained, the first term
a1 = 2 , a2 = 5, a3 = 8, a4 = 11,
Also a2 – a1 = 5 – 2 = 3
a3 – a2 = 8 – 5 = 3
a4 – a3 = 11 – 8 = 3
……………………………………
i.e., d = a2 – a1 = a3 – a2 = a4 – a3 = 3
∴ The resulting list forms an A.P.
Question 5.
Multiply and divide each term of A.P by a fixed number and write the resulting numbers as a list.
Answer:
4, 7, 10, 13, 16, ……
Multiplying each term by 3, we get
4 × 3, 7 × 3, 10 × 3, 13 × 3, 16 × 3, ……
12, 21, 30, 39, 48, …….
In the list obtained the first term a1 = 12 and a2 = 21, a3 = 30, ….
Also a2 – a1 = a3 – a2 = …… = 9
∴ The resulting list also forms an A.P.
Now divide every term by 7, we get
\(\frac{4}{7}\), \(\frac{7}{7}\), \(\frac{10}{7}\), \(\frac{13}{7}\), \(\frac{16}{7}\), …… is the resulting list.
Question 6.
Check whether the resulting lists are AP in each case.
Answer:
The first term
∴ d = a2 – a1 = a3 – a2 = a4 – a3 = ….. = \(\frac{3}{7}\)
and the above list forms an A.P.
Question 7.
What is your conclusion?
Answer:
If a1, a2, a3, …… are in A.P, then

i.e., “If each term of an A.P is added/ multiplied / divided by a fixed number, the resulting terms also form an A.P” and fixed term is subtracted from each term of an A.P, then the resulting terms also form an A.P.
![]()
Try these
Question 1.
i) Which of these are arithmetic progressions and why? (Page No. 128)
a) 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 15, ……
Answer:
2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 15, …… is not an A.P.
∵ a2 – a1 = 3 – 2 = 1
a3 – a2 = 5 – 3 = 2
a4 – a3 = 7 – 5 = 2
i.e., The difference between any two successive terms is not same throughout the series.
(or)
Every number is not formed by adding a fixed number to its preceding term.
b) 2, 5, 7, 10, 12, 15 ……
Answer: The given list does not form an A.P, since each term is not obtained by adding a fixed number to its preceding term.
c) -1,-3,-5,-7, ……
Answer: -1,-3,-5,-7,….. is an A.P.
a2 – a1 = – 3 – (- 1) = -3 + 1 = -2
a3 – a2 = – 5 – (-3) = -5 + 3 = -2
a4 – a3 = – 7 – (- 5) = -7 + 5 = -2
Every number is formed by adding a fixed number to its preceding term,
ii) Write 3 more Arithmetic Progressions.
Answer:
a) a = -7;d = -3 and
A.P. is-7, – 10, – 13, – 16, …….
b) a = 15; d = 4 and
A.P. is 15, 19, 23, 27, 31, …….
c) a = 100; d = 50 and
A.P. is 100, 150, 200, 250, ……..
![]()
Think & Discuss
(Page No. 129)
Question 1.
Think how each of the list given above form an A.P. Discuss with your friends.
a) Heights (in cm) of some students of a school standing in a queue in the morning assembly are 147,148, 149,…, 157.
Answer:
The given list forms an A.P, since each term starting from the second is obtained by adding a fixed number + 1 to its preceding term.
b) Minimum temperatures (in degree ‘ Celsius) recorded for a week, in the month of January in a city, arranged in ascending order are -3.1, -3.0, -2.9, -2.8, -2.7, -2.6, -2.5, …….
Answer:
The given list forms an A.P, since every term starting from the second is obtained by adding a fixed number +0.1 to its preceding term.
c) The balance money (in Rs.) after paying 5% of the total loan of Rs. 1000 every month is 950, 900, 850, 800, …, 50.
Answer:
The given list forms an A.P, since each term starting from the second is obtained by adding a fixed number (-50) to its preceding term.
d) Cash prizes (in Rs.) given by a school to the toppers of Classes I to XII are 200, 250, 300, 350, ….., 750 respectively.
Answer:
The given list forms an A.P, since each term starting from the second is obtained by adding a fixed number 50 to its preceding term.
e) Total savings (in Rs.) after every month for 10 months when Rs. 50 are saved each mouth are 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 450, 500.
Answer:
The given list forms an A.P, since every term starting from the second term is obtained by adding a fixed number 50 to its preceding term.
![]()
Question 2.
Find the common difference of each of the above lists. Think when is it positive?
Answer:
Common difference d = a2 – a1
a) 148 – 147 = 1
b) -3.0 – (-3.1) = 0.1
c) 900 – 950 = -50
d) 250 – 200 = 50
e) 100 – 50 = 50
Common difference is positive when a2 > a1
Question 3.
Make a positive Arithmetic Progression in which the common difference is a small positive quantity.
Answer:
a = 50 ; d = 0.5 then A.P is 50, 50.5, 51, 51.5, 52, ……
Question 4.
Make an A.P in which the common difference is big (large) positive quantity.
Answer:
a = 100; d = 1000 then A.P. is 100, 1100, 2100, 3100, 4100, ……
Question 5.
Make an A.P in which the common difference is negative.
Answer:
a = 80, d = -7
then A.P. is 80, 73, 66, 59, 52, ……
![]()
Do these
(Page No. 143)
Find the sum of indicated number of terms in each of the following A.Ps.
i) 16, 11, 6, …..; 23 terms.
Answer:
Given: 16, 11, 6, …..; S23
t1 = a = 16; t2 = 11; t3 = 6,
d = t2 – t1 = 11 – 16 = -5
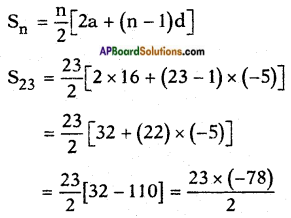
= -23 × 39 = -897
ii) -0.5, -1.0, -1.5,…..; 10 terms.
Answer:
Given : -0.5, -1.0, -1.5, …. S10
a = – 0.5
d = t2 – t1 = (-1.0) – (-0.5)
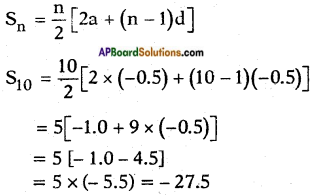
![]()
iii) -1, \(\frac{1}{4}\), \(\frac{3}{2}\), …… ;10 terms.
Answer:
Given: -1, \(\frac{1}{4}\), \(\frac{3}{2}\), …… ;S10.
a = – 1
d = t2 – t1 = \(\frac{1}{4}\) – (-1) = 1 + \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\)
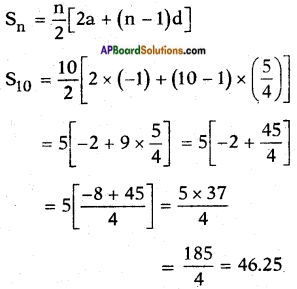
Do these
(Page No. 149)
Find which of the following are not G.P.
Question 1.
6, 12, 24, 48, ……
Answer:
Given: 6, 12, 24, 48, ……
a1 = a = 6; a2 = 12; a3 = 24, a4 = 48,…
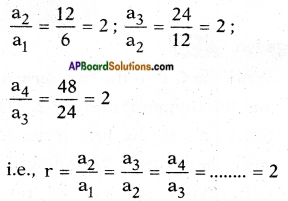
The given list is of the form
a, ar, ar2, ar3,
∴ The given numbers are in G.P.
![]()
Question 2.
1, 4, 9, 16, ……
Answer:
Given: 1, 4, 9, 16, …..
a1 = a = 1
a2 = 4; a3 = 9, a4 = 16

∴ The given numbers do not form a G.P.
Question 3.
1, -1, 1, -1, …..
Answer:
Given: 1, -1, 1, -1, …….
a1 = a = 1
a2 = -1; a3 = 1, a4 = -1, …..

∴ The given list forms a G.P.
Question 4.
-4, -20, -100, -500, ……
Answer:
Given: -4, -20, – 100, -500, ……
a1 = a = -4, a2 = -20, a3 = -100, a4 = -500,

∴ The given list forms a G.P.
![]()
Think & Discuss
(Page No. 149)
Question 1.
Explain why each of the lists above is a G.P.
i) 1, 4, 16, 64, 256, …….
Answer:
Here
a = 1 = a1; a2 = 4; a3 = 16; a4 = 64,….
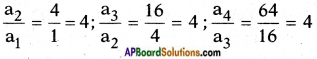
i.e., Common ratio r = 4.
ii) 550, 605, 665.5, ……..
Answer:
The given series is in G.P. Since every term can be obtained by multiplying its preceding term by a fixed number ‘1.1’.

iii) 256, 128, 64, 32,…….
Answer:
The given series forms a G.P.
Since every term, starting from the second can be obtained by multiplying its preceding term by a fixed number \(\frac{1}{2}\).
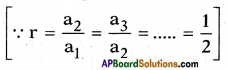
iv) 18, 16.2, 14.58, 13.122, …….
Answer:
The given list forms a G.P.
Since each term, starting from the second can be obtained by multiplying its preceding term by a fixed number 0.9.
here 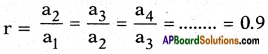
![]()
Question 2.
To know about a G.P. what is minimum information that we need?
Answer:
To know whether a number pattern forms a G.P or not, we should check that the ratio between the successive terms is equal or not.