Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Study Material 9th Lesson Economy of Andhra Pradesh Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Study Material 9th Lesson Economy of Andhra Pradesh
Essay Questions
Question 1.
Write an essay on the economy of Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh is one of the largest states in India in terms of area and population. It is the eighth largest state in terms of geographical area, accounting for 4.96% of the area of the country. The state has a total geographical area of 160.21 lakh hectares. In terms of population, it is the 10th largest state with 4.96 crores i.e., 4.10% of the country’s population.
State Gross Domestic Product (SGDP) : The SGDP may also be called as state income. SGDP is defined as the total value of the finished goods and services produced within the boundaries of the state during a year.
The three sectors in A.P Economy area as follows.
- Primary sector: Agriculture, Animal husbandry, Forests etc.
- Industrial sector : Industries, Electricity, Irrigation.
- Tertiary sector: Trade, Hotels, Transport, Communication etc.
The SGDP A.P an increase trend from 2005 – 06 ₹ 1,41,977 crore to 2013 – 2014 it was ₹ 2,50,282 crores. The growth rate of SGDP of A.P 6.08% in 2013 – 14.
Per capita income : The per capita income gives a better idea of the standard of the people. A.P per capita income was ₹ 85,797 in 2013-14.
Agriculture: Agriculture and allied actives remained the main source of livelihood of the state population. During 2013-14 food crops are grown in 54.92 lakh hectors.
Industry: The industrial development in A.P in going on the same lines of the industrial development of India. The industrial sector contribution in GSDP undergoes slight changes. It shares decreased from 23.7 during 2007-08 to 20.7% by 2013-14.
Tertiary Sector: The share of tertiary sector in the SGDP has shown a tremendous increase from ₹ 64,411 crore to ₹ 1,40,054 crore in 2013-14.
![]()
Question 2.
What is SGDP ? Explain the trends in SGDP of Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
The State Gross Domestic Product may also be called as the State Income.
The State Gross Domestic Product is defined as the total value of the final/finished goods and services produced within the geographical boundaries of the state during a year.
The directorate of economics and statistics estimates the SGDP in Andhra Pradesh. The directorate makes use of the product and income methods for estimation of SGDP”. The three sectors in Andhra Pradesh Economy are as follows :
- Primary Sector : Agriculture, Animal husbandly, Forests, Mines and Quarries.
- Industrial Sector : Industries, Electricity/Gas, Irrigation, Construction.
- Tertiary Sector : Trade, Hostels, Transport, Communication, Real Estate, General Administration, Social Services.
The railway, insurance, banking and communication services are called supra regional sectors. The income generated in these sectors are estimated by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO) and the centre allots the share to the states proportionately.
Andhra Pradesh makes use of the product method for estimating the SGDP in Agriculture sector, Forests, Animal husbandry, Industries, Mines and Quarries and the Income Method in Irrigation, Transport, Power Supply of Gas, Insurance, Banking and Communication sectors.
Trends of SGDP in Andhra Pradesh: The following table explains the trends in SGDP of Andhra Pradesh.
GSDP of A.P at Constant (2004 – 05) prices
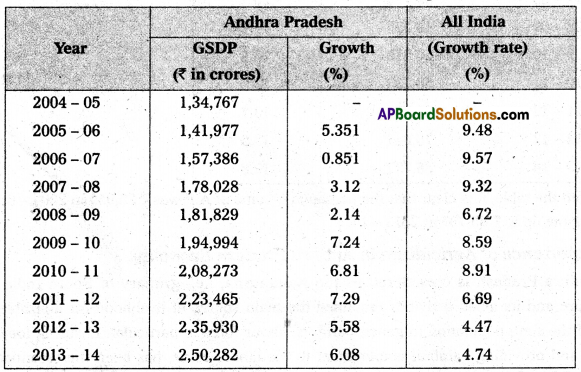
GSDP of AP in about 4.36% of Indian G.D.P. It is notical that the growth rates of both A.P and India are not showing a steady trend but are fluctuating.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the trends in population and percapita income growth in Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
With 13 districts, A.P occupies tenth place among all states of India with 4.96 crores of population according to 2011 census, The population of A.P is 4.96 crores and that of India is 121.06 crores. So the percentage of A.P population is 4 in the total Indian population. The decadal growth rate of population of A.P is always lower than the Indian growth rate. By 2011 the population growth rate of A.P(9.21) is almost half of the national average 17.69.
The density of population in Andhra Pradesh has gone up. During 2011, the density of population per sq. km is 304 persons for the state, as against 382 persons for the country. Among the districts, the Krishna district having high density with 518 persons followed by West godavari district 470 persons per sq.km. The lowest density area is Y.S.R Kadapa with 188 persons.
The fertility rate in A.P is also showing downward trend in the recent decade.
The percapita income gives a better idea of the standard of living of people. The following table reveals the changes in percapita income of Andhra Pradesh from 2004-05 to 2013-14.
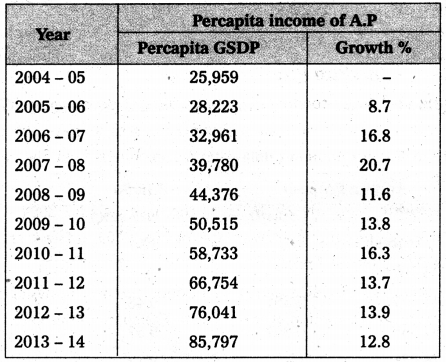
From the table, it is clear that the percapita income of A.P. was ₹ 25,959 in 2004 – 05 and has gone up to ₹ 85,797 at 2013 – 14.
Question 4.
Importance of Agriculture in Andhra Pradesh Economy.
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh is considered as the Annapurna, i.e., granary of South India. Agriculture and its allied activities remained the main source of livelihood for a sizable chunk of the state population in general and its labour force in particular. Ensuring food security and providing gainfaul employment to the labour force, has been the essential premise of the policy makers. Raising form incomes through crop diversification and encouraging alternative methods of forming perhaps help to improve the standards of the farmers in the state.
With regard to foodgrain production in India, Uttar Pradesh stands in the 1st place, Punjab in the second and A.P in the third. The table provides information on the food grain production in Andhra Pradesh.
Area under Food & Non Food Crops in the State
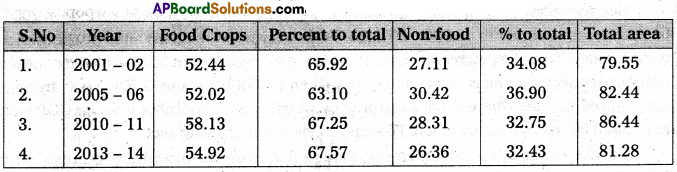
From the above table we can come to the conclusion that food crops are dominating with around 65% of are put for their production and the trend is continuing over the year. During 2013 – 14 food crops are grown in 54.92 lakh hectares which is 67.57% of total area in that year.
According to 2013 – 14 provisional estimates, 11,698 thousand tonnes of food grains are produced in which 10,618 thousand tonnes are cereals and millets and 1,080 thousand tonnes pulses. 2,242 thousand tonnes of oil also produced from various parts of the state.
![]()
Question 5.
Importance of Industry in Andhra Pradesh Economy.
Answer:
The role of industrial sector in any economy decides its pace of development. The state of Andhra Pradesh is endowed with wide varieties of natural resources, longest coastline in South India. Infrastructure, communication system, experts in technical field and wide market opportunities.
The contribution of this sector was only 29,124 cr. in the base year ie., 2004 – 05 increased to 51,838 crores in 2013 – 14 continuously except for 2008 – 09. Infact it share decreased from 23.7 during 2007 – 08 to 20.7 percent by 2013 -14.
The share of industrial sector in providing employment opportunities to the labour force remained same in both state and the nation over the years. The share of this sector is increasing very sluggishly.
The value of industrial exports from the state is continuously increasing. It is ₹ 1,29,001 crore in 2012 – ’13. In the total silk units of the country, A.P’s sick units are 10.2 percent and state stood in fourth place. There are 44 State Level Public Enterprises (SLPEs) functioning in the combined state with the capital of ₹ 69,125 crore. Among them, APCPDCL, A.P. GENCO, APSPDCL, Housing Board etc., are top level SLPEs. Andhra Pradesh Industrial Infrastructure Corporation (APIIC) is the nodal agency for special economic zones in the state, A.P. is the first state in the country to announce an exclusive SEZ policy. As on March 2014, there were 32 number of SEZs in the state in which 10 were IT related, 6 multiproduct, 4 pharmaceuticals, 2 biotech and 10 sector specific SEZs. Recently, State Finalized Visakapatnam SEZ in an area of 3,500 acres.
Question 6.
Importance of tertiary sector in Andhra Pradesh economy.
Answer:
A service sector is the fastest growing sector in Andhra Pradesh as it is in total India. It is expanding as of agriculture is losing, the industrial sector being constant.
Service sector is the major contributor to the state GSDP with 48.54 percent in 2004- OS and increase further to 55.96 by 2013-14. ₹ 64.411 crore were contributed by the service during 2004 – 05 which increases enormously to 1,40,054 crore in 2013 – 14. This means only service sector alone is contributing more than half of the states GSDP. Same trend is also noticed in India where service sector is the single largest contributor to the GDP with more than 50 percent contribution. IT sector is the faster growing sector.
Service sector is the second largest among the three sectors with provides nearly 1/4th of the employment opportunities in the state. It is providing livelihood to nearly 25 percent of labour force, which is, on par with the national average (25.4 percent).
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the Irrigation facilities in Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
Irrigation : Andhra Pradesh is blessed with many major rivers. The most important being Godavari, Krishna, Thungabhadra, Penna and Vamsadhara. The State, share of dependable flows from all the rivers and streams is estimated at 2.746 TMC, and only 1.753 TMC has been utilized so far. Apart from rivers the state consists of many artificial lakes and reservoirs for irrigation and drinking water.
Irrigation development as well as management is of utmost importance in the State. Andhra Pradesh is rightly called “A River State” as it is blessed with major river systems like the Godavari, Krishna, Thungabhadra, Vamsadhara and other rivulets. Presently, 54 major, medium and other projects are being considered under Jalayagnam, with a hope to irrigate 52 lakh acres.
Polavaram project is a multi – purpose irrigation project witch has been accorded ’National Project Status’ by Central Government. This dam across the Godavari river is under construction located in West and East Godavari District in Andhra Pradesh and its reservoir spreads in parts of Chhattisgarh and Orissa States also. The project is expected to enabling irrigation of23,20,000 in Krishna, West Godavari, East Godavari, Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram and Srikakulam districts of Andhra Pradesh.
The Pattiseema Project is crucial as it will lift 80 tmft of surplus Godavari water from Pattiseema to Krishna Basin and divert it through Srisailam to the parched Rayalaseema till Polavaram project is completed. Government also announced that Pattiseema project would not go aganist the interest of farmers of twin Godavari districts, but would meet drinking and irrigation water need of Rayalaseema.
Government of Andhra Pradesh is also encouraging drip irrigation system, in the State. It is supplying drip irrigation equipment on subsidized rates to the farmer. A.R ranks 1st in Micro irrigation system in the country and so far covers 5.63 lakh hectors.
Question 8.
Explain about the transport facilities in Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
The transport facilities available in Andhra Pradesh can be classified into four categories.
They are :
- Railways
- Roadways
- Airways
- Waterways.
1) Railways : They have played a significant role in boosting the economy of the State alongside developing the industrial and the tourism sectors. Andhra Pradesh mainly served by three major railway zones viz., South Central Railway, Southern Railway and East Coast Railway. State has total 444 railway stations and having 3,355 km of rail network. State Government proposals are with Ministry of Railways to set a new Railway Zone in newly formed Andhra Pradesh.
One of the highest broad gauge tracks in the world is in Eastern Ghats route that runs from Visakhapatnam to Anantagiri. Vijayawada railway station is the highest grosser in the SCR zone and one of biggest railway junctions in India.
2) Roadways : Roads are one of the basic modes of transportation system and also an important priority sector of infrastructure. Systematic development of road is one of the important pre-requisites for development and acceleration of growth in the economy. Among the different modes of domestic transportation systems, road transport carries more than 80 percent of the goods and passenger traffic.
Andhra Pradesh has an extensive road network of 1,46,954 km with 42,511 km of State Highways, 3,144 km of National Highways and 101,484 km of District Roads. Andhra Pradesh Road Development Corporation (APRDC), established 1998 is responsible for Maintenance and Management of roads.
National highways and State highways connect to every village and town within the State, as well as to major cities of neighbouring States. National Highway 5, with a highway network of around 1,000 km runs from Srikakulam district to Nellore district.
The Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (APSRTQ operates public bus services in the state owned by the State Government. Pandit Nehru Bus Station in Vijayawada is the largest bus terminus in the State.
3) Civil Aviation (or) Airways : Government has entered into Memorandum of understanding with Airports Authority of India (AAI) For up – gradation / modernization of non – metro airports at Vijayawada, Tirupati, Kadapa and Rajahmundry airports. The Airport Authority of India (AAI) has proposed to upgrade the Tirupati airport to International standards. AAI proposed Master plan for development of Rajahmundry airport.
4) Seaports (or) Waterways : Andhra Pradesh has the second longest coastline of 972 km after Gujarat in India. Ports provide development and growth of maritime activities such as international trade of exports and imports, ship repairs, tourism, fishing and water sports.
Ports are a gateway to trade and commerce. Visakhapatnam, the largest port in the State is also one of the largest ports in terms of handling cargo in the country.
![]()
Question 9.
Role of Information Technology (I.T) in the economic development of Andhra Pradesh. .
Answer:
The combined State of A.P had taken a leadership position in E-Govemance and IT. However, the new state of A.P formed on 2nd June 2014, accounts for only 2 percent of the IT export Turnover of the combined State and about 1.8 percent of employment Significant, consistent and planned efforts have to be made if these figures have to attain respectability over the next 5 years.
A.P is called as Hi-tech Capital and Cilican Valley of India. But after bifurcation, Government announced that Vizag city having all potential to be developed as IT center. IT parks would be developed in all district headquarters across the State in a phased manner said minister for IT, P. Raghunatha Reddy. Following important points can be drawn from AP’s IT sector.
- Vizag may be the IT Capital of the State.
- Every district headquarter will have IT park.
- IT sector contributes 38.22 percent of total exports from A.P (United Andhra)
- IT sector provides employment opportunities to around 3 lakh employees by 2013.
- This sector export value was nearly 36 thousand crore by 2013.
- Out of 3 IT professionals working in USA, one is from India and out of 3 Indians, one is represented from A.P.
- State having highest number of IT Special Economic Zones (SEZs) in India – 10 out of 56.
- IT export expected to go up from current level of ₹ 36,000 crore to about ₹ 150,000 crore by 2017.
- Direct employment from existing 3 lakh to 7 lakh.
- State Government is looking forward to integrate IT and BT. It says Information Technology and Biotechnology need to come together to streamline manufacturing processes.
Latest IT policy of A.P – 2014 : To face the challenges in IT sector development after the bifurcation of the State, the Government of Andhra Pradesh has developed a blueprint “Re-imagining Andhra Pradesh – role of E-Govemance, Electronics and IT “for development of ICT Industry in the State.
Government shall endeavor to establish state-of-the-art infrastructure of international standards suiting to the requirements of the IT/ITESC Industry. Visakhapatnam will be developed as a Mega IT Hub, through an initial effort of developing an IT township with a built – up space of 5 million square feet. A signature tower of 1 million square feet shall form the nucleus of the Mega IT Hub. IT Hubs shall also be developed at Vijayawada, Kakinada, Tirupati and Anantapur. Fiscal and non – fiscal incentives are announced in the policy to attract investment in the field.
![]()
Question 10.
Briefly give an account of the Welfare schemes of Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
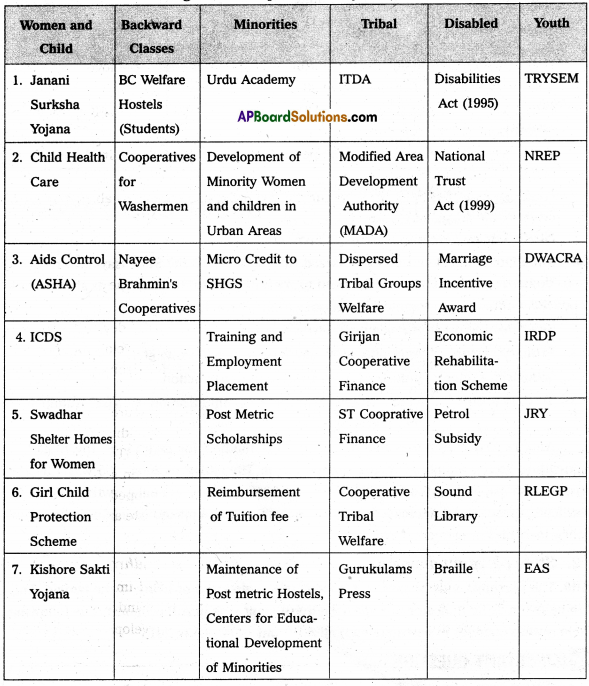
The foremost objective of any welfare state is to sustain and improve the living standards of people. Although since a long time, agriculture and industry have been recognized as prime drivers of economic growth; social sector development is gaining ground especially in the context of human development. The concept of human development invariably highlights the importance of bringing improvement in the social infrastructure like education, health care, nutrition, water supply, housing, social security etc. Further, public investment on these social overheads ensures social justice and equality in the society.! Government of A.P has been implementing various welfare programmes schemes. Some of the important welfare programmes. The following table shows section wise – welfare programmes by A.P Government.
Section-wise Welfare Programmes Implemented by Government of Andhra Pradesh
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
State Gross Domestic Product (SGDP).
Answer:
The State Gross Domestic Product may also be called as the State Income. The State gross domestic product is defined as the total value of the final/finished goods and services produced within the geographical boundaries of the State during a year.
The three sectors in A.P economy are as follows.
- Primary sector : Agriculture, Animal husbandary, Forests etc.
- Industrial sector : Industries, Gas, Irrigation, Construction.
- Tertiary sector : Trade, Hotels, Transport, Communication, General Administration Social Services.
Andhra Pradesh makes use of the product method for estimating the SGDP in Agriculture sector, industrial sector, service sector. The GSDP in 2004 – 05 was 1,34,767 crores and it has incrosed to ₹ 2,50,282 crores in 2013 – 14. The annual growth in 2005 – 06 was 5.35 percent and it decreased to 2.14% in 2008 – 09 and picked up again and reached 7.29% in 2011-12.
![]()
Question 2.
State percapitaincome.
Answer:
The percapita income gives better idea of the standard of living of the people. This can be taken as an indicator of improving living standards in A.P economy. The following table reveals changes in percapita income A.P from 2004 – 05 to 2013 – 14.
Percapita Income of A.P and All India at Current Prices
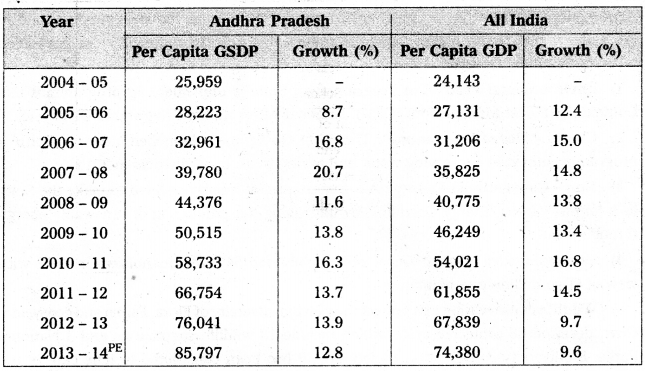
The state PCI is always higher than the national average. For 2013-14 the gap between State and National percapita incomes is ₹ 11,417. Among the districts Viaskhapatnam with a percapita income ₹ 1,13,860 stands tall, while Srikakulam remains at the bottom with almost half of the PCI Visakhapatnam.
Question 3.
Occupational distribution of labour in A.P. [A.P. Mar- 18]
Answer:
Occupational distribution pattern in any country decides the level of economic growth. Any economy can be divided into
- Agriculture sector
- Industrial sector
- Service sector
Dividing the total population according to their occupation or work is known as occupational distribution of population or labour.
According to the statistical abstract of A.P 2014, prepared on the basis of the 2011 census, the total number of workers is A.P is 2,30,80,964. Among them, the total number of workers in industry sector in A.P is 33,40,133 which is 14.47% of total work force. Total number of workers related to primary sector is 1,43,92,736. i.e., 62.36% and 34.77% of total work force based on service sector.
The number of people depending on agriculture sector is still very high. Tertiary sector is in the second place and providing livelihood to the larger percent of population after agriculture sector. In A.P secondary sector’s contribution is steady and constant.
![]()
Question 4.
Environmental protection activities in the state. [A.P. Mar. 17]
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh having good environmental conditions. Its coastline is second in India and first in South Indian states. To protect this rich environment, steps have been taken by the State Government.
1) Environmental Protection Programmes : State is implementing programmes like Community Forest Management (CFM), National Afforestation Programme (NAP) etc.
2) Chettu – Neeru Programme : The State Government launched ‘neeru – chettu’ a programme aimed at conserving water and saving trees, in all districts in 2015.
3) Non – Conventional Energy : A.P Department of Energy decided to make the State as a largest “Green Energy Corridor”, by increasing the production of renewable energy through solar.
4) Vanamahotsava : Forest Department celebrated 64th Vanamahotsava in 2013 with view of ‘Two million tree plantation”.
5) Wildlife conservation: To protect the rich bio-diversity of Flora, Fauna and ecosystem Govt, declared 66 protected areas which include 13 wildlife sanctuaries and 3 National Parks. Biodiversity conservation society of A.P has been constituted to take care of the conservation measures of wild life sanctuaries. The Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve has been notified and made functional.
Question 5.
Importance of Tourism in A.P. [A.P. Mar. 18, 16]
Answer:
Andhra Paradesh Tourism Development corporation is state government agency which promotes tourism in A.P. The state government is making efforts to bring the world to A.P and take A.P to the world. A new tourism policy was announced in 2010 and steps are initializing to make Andhra Pradesh as a tourist – friendly destination. The important types of tourism in A.P are as follows.
- Pilgrim Tourism
- Health Tourism
- Buddhist Tourism
- Beach Tourism
- Farm Tourism
- ECO Tourism
- Leisure Tourism
The tourist spots in A.P are attracting both domestic and foreign tourists.
The state is also famous for pilgrim tourism. All these attractions are increasing the inflow of foreign and domestic tourists in A.P.
Tourism is now becoming a revenue source for the state’s treasury along with IT sector.
![]()
Question 6.
Population characteristics of Andhra Pradesh. A.P. Mar. 16]
Answer:
The demographic characteristics of newly formed State of Andhra Pradesh with 13 districts (Coastal Andhra & Rayalaseema). The population of 4.96 crore which accounts for 4.1% of the country’s population makes it the 10th most popular state in the Country of this male are 2,48,30,513. A female population is 2,47,46,950 in 2011 census. Sex ratio for every 1000 male is 997 and female is 943 in 2011. Where the rural population is 349.67 in 2011, in total population the density of population goes up 304 per sq.km in 2011 census. The fertility rate in A.P is also showing a downward trend in the recent years. The literacy rate is 67.35 in 2011 for A.P in which male literacy is 74.77 and that of female is 59.96. State has 5.64% less literates when compare to the Nation.
Question 7.
Welfare schemes related to different sections in Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
The foremost objective of any welfare state is to sustain and improve the living standards of people. Government of A:P has been implementing various welfare progra-mmes/schemes some of the important programmes implemented by the government of Andhra Pradesh.
Welfare programmes of women and child they are Janani Suraksh Yojana, Child Health Care services, Kishore Sakti Yojana, Widow Pension Scheme, Pavala Vaddi Scheme, Abhaya Hastham Ready to eat etc. some of the youth welfare programmes are TRYSEM, DWACRA, Rajeev Udyoga Sree etc., some of minorities programmes are Urdu Academy, Micro credit to SHGS, Post Metrict Scholarships, Reimbursement of tution fee etc.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
SGDP [A.P. Mar. 18]
Answer:
The state gross domestic product is defined as the total value of the final goods and services produced with in the geographical boundaries of the state during a year.
![]()
Question 2.
Density of population in A.P.
Answer:
The density of population determines the magnitude of the burden that State is being called upon to carry and to determine the future potential of growth.
Density of population = Total population in the area/total area in square k.m
In A.P the density of population is 304 per square km in 2011 census.
Question 3.
Literacy rate in A.P.
Answer:
Literacy is the reading and writing skill of the people. The literacy rate is 67.35 in 2011 for A.P. in which male literacy is 74.77 and that of female is 59.96. State has 5.64% less literates when compare to the Nation, West godavari stood in 1st place. Vizianagaram having lowest literacy rate.
Question 4.
Project Tiger. [A.P. Mar. 18, 16]
Answer:
This programme is being implemented with the objective of increase the number of our National animal tiger. The Nagarjuna Sagar, Srisailam Tiger Reserve Spreads over the districts of Kurnool, Prakasam, Guntur which is the home to over 50 tigers and able to support even more.
Question 5.
Sarva Siksha Abhiyan.
Answer:
This was introduced during 2001 – 2002 with an aim to provide universal elementary education for all children in the 6 to 14 age group by 2014 SSA has how been renamed as ‘Rajiv Vidya Mission’ in A.P.
![]()
Question 6.
Any Welfare Programme.
Answer:
Government of A.P has been implemention various welfare programmes/schemes. Some of the welfare programmes are Pavala Vaddi scheme, Abhaya Hastam Ready to eat, Metric Scholarships, Micro credit to self help groups etc.
Question 7.
Eco – Tourism [A.P. Mar. 17]
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh vision – 2020 envisaged East Godavari tourism as a growth engine. It is one of the important type of tourism in A.P. Maredumilli, Nelapattu (Nellore) Mamandur, Talakona (Chittoor), Balapalli (Kadapa), Ethipothala (Guntur), Kambala Konda (Visakhapatnam) are the famous eco – tourism centres in A.P
Question 8.
Civil aviation in A.P
Answer:
Government has entered into memorandum of understanding with Airports Authority of India (AAI) for up – gradation / modernization of non metro airports at Vijayawada, Tirupati, Kadapa and Rajahmundary. AAI has proposed to upgrade the Tirupati airport International standards.
Question 9.
Roadways in A.P
Answer:
Roads are one of the basic modes of the transportation system and also an important priority sector of infrastructure. Road transport carries more than 80% of the goods and passenger traffic. A.P has extensive road network of 1,46,954 km with 42,511 km of State Highways 3,144 k.m of National Highway and 1,01,484 km of District Roads.
![]()
Question 10.
Sea – ports in A.P [A.P. Mar. 17, 16]
Answer:
Ports are a gateway to trade and commerce. A.P has the second longest coastline of 972 km after Gujarat in India. Ports provide development and growth of maritime activities. Visakha is the largest port in the State and also one of the largest port in terms of handling cargo in Country.