Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material 11th Lesson Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material 11th Lesson Haloalkanes And Haloarenes
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the structures of the following compounds.
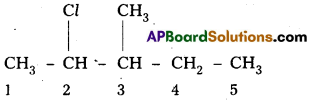
i) 2-chloro-3-methylpentane,
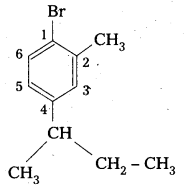
ii) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene.
Answer:
i) 2-chloro-3-methylpentane
Structure :
ii) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene.
Structure :
![]()
Question 2.
Which one of the following has highest dipole moment ?
i) CH2Cl2
ii) CHCl3
iii) CCl4
Answer:
CH2Cl2 has high dipole moment (μ = 1.62 D) among the three alkyl halides.
Reason: The total of two C – Cl dipole moments is reinforced by the total of two C-H bonds.
CCl4 has zero dipole pioment. CHCl3 has 1.03 D dipole moment due to presence of C-H bond.
Question 3.
What are ambident nucleophiles ?
Answer:
Ambident nucleophiles: The nucleophiles which are able to attack at two (or) more different sites are called ambident nucleophiles.
Eg.: Alkyl halides react with AgCN to form alkyl cyanide and isocyanides.
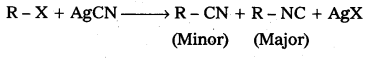
Question 4.
Write the isomers of the compound having molecular formula C4H9Br.
Answer:
Compound having molecular formula C4H9Br has five isomers.
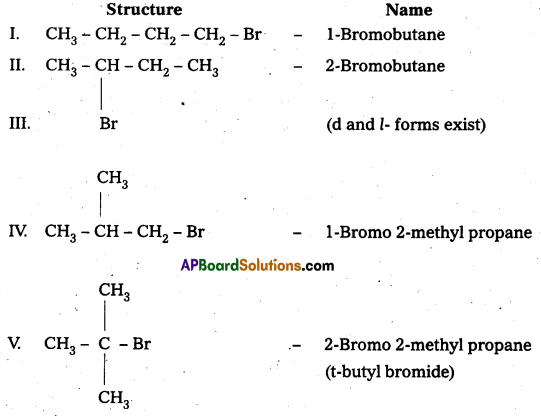
![]()
Question 5.
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with -OH?
(i) CH3Br or CH3I
(ii) (CH3)3CCl or CH3Cl
Answer:
i) CH3 – I reacts faster in SN2 – reaction with OH than CH3 – Br.
Reason: The bond dissociation enthalpy of C -1 bond (234 KJ/mole) is less than that of (-Br bond (293 KJ/mole).
ii) CH3 – Cl reacts faster in SN2-reaction with -OH than-(CH3)3C-Cl.
Reason: The order of reactivity of alkyl halides in SN2-reactions is l°-alkyl halide > 2°- alkyl halide > 3°-alkyl halide.
Due to high steric hindrance in 3°-alkyl halide i.e., (CH3C – Cl. It is less reactive towards SN2-reaction, whereas in case of CH3-Cl (1°-alkyl halide) less steric hindrance observed. So, it is high reactive towards SN2-reactions.
Question 6.
Explain why the alkyl halides though polar are immiscible with water.
Answer:
Alkyl halides are polar but these do not dissolve in water i.e., immiscible in water.
Reason : Among water molecules strong inter molecular hydrogen bonding is present. This hydrogen bond is difficult to be broken by alkyl halides.
Question 7.
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed aqueous KOH ?
Answer:
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5 the 2nd one i.e., C6H5CHClC6H5 gets hydrolysed more easily than C6H5CHCl.
This can be explained by considering SNI reaction mechanism. In case of SNI reactions reactivity depends upon the stability of carbo cations.
C6H5CHClC6H5 forms more stable carbo cation than C6H5CH2Cl.
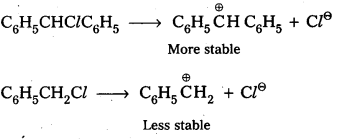
![]()
Question 8.
Treatment of alkyl halides with aq.KOH leads to the formation of alcohols, while in presence of alc.KOH what products are formed ?
Answer:
- Treatment of alkyl halides with aq. KOH leads to the formation of alcohols. Here Nucleo- phillic substitution reaction takes place.
Eg.: C2H5Cl + aq.KOH → C2H5OH + KCl - Treatment of alkyl halides with alc.KOH leads to the formation of alkenes. Here elimination reaction takes place.
E.g.: C2H5Cl + alc. KOH → C2H4 + KCl + H2O
Question 9.
What is the stereochemical result of SN1 and SN2 reactions ? [T.S. Mar. 17]
Answer:
- The stereochemical result of SN1 reaction is reacemisation product.
- The stereochemical result of N2 reaction is inversion product.
Question 10.
What type of isomerism is exhibited by O, m and p-chlorobenzenes ?
Answer:
o, m and p-chloro benzenes exhibits position isomerism.
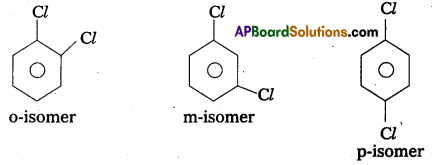
These are positional isomers.
![]()
Question 11.
What are Enantiomers? [T.S. Mar. 19]
Answer:
Enantiomers : The stereo isomers relatëd to each other as non-superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers.
- These have identical physical properties like melting point, boiling points refractive index etc.
- They differ in rotation of plane polarised right.
Short Answer Questions
Questions 1.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
i) CH3CH(Cl)CH(I)CH3
ii) ClCH2CH = CHCH2Br
iii) (CCl3)3CCl
iv) CH3C(p-Cl-C6H4)2CH(Br)CH3
Answer:
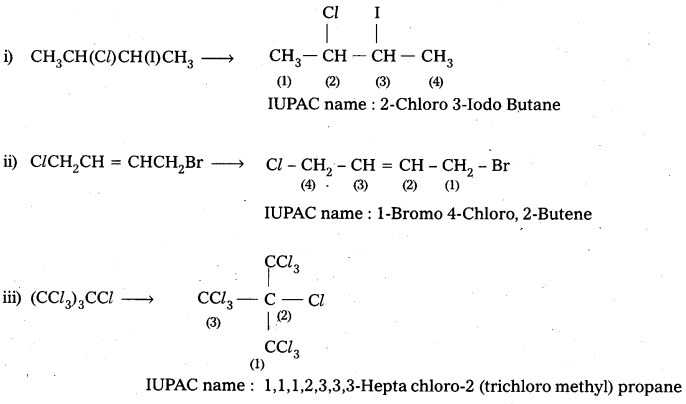
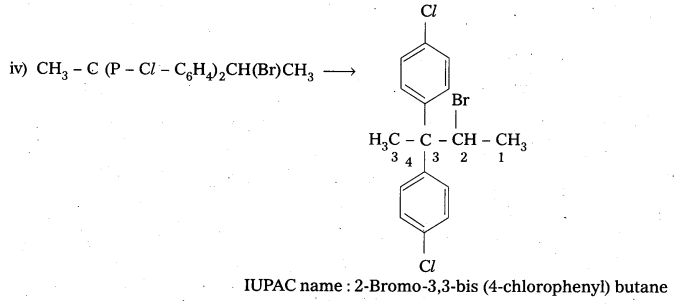
![]()
Question 2.
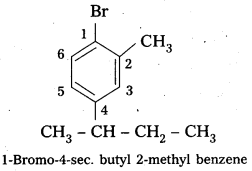
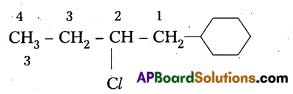
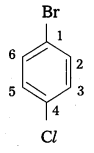
Write the structures of the following organic halides.
i) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene,
ii) 2-Chioro- 1 -phenylbutane
iii) p-bromochlorobenzene l
iv) 4-t-butyl-3-iodoheptane.
Answer:
i) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene.
Structure:
ii) 2-chloro- 1-phenylbutane.
Structure:
iii) p-bromo chlorobenzene Br
Structure:
iv) 4-t-butyl-3-iodoheptane
Structure:
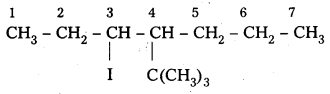
Question 3.
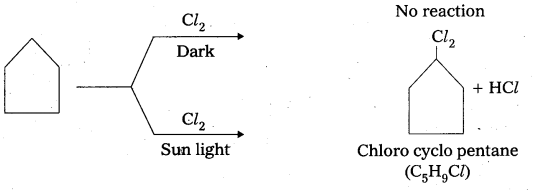
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro- compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. Identitfy the hydrocarbon.
Answer:
- The given compound molecular formula C5H10. It represents general formula CnH2n. It may be an alkene (or) cyclo alkane.
- Given that the alkene does not react with Cl2 in dark condition it is not an alkene, so it is a cyclo alkene.
Question 4.
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in. SN2 reaction with -OH ? [A.P. Mar. 19]
i) CH3Br or CH3I
ii) (CH3)3CO or CH3Cl .
Answer:
- Among CH3Br and CH3I, CH3 – I reacts faster in SN2 reaction with OH⊗ because bond dissociation energy of C – I is less than the bond dissociation energy of C – Br.
- Among CH3Cl and (CH3)3CCl, CH3 – Cl reacts faster in SN2 reaction with OH⊗ because (CH3)3CCl has high steric hindrance than CH3Cl.
![]()
Question 5.
Predict the alkenes that would be formed in the following reactions and identify the major alkene.

Answer:
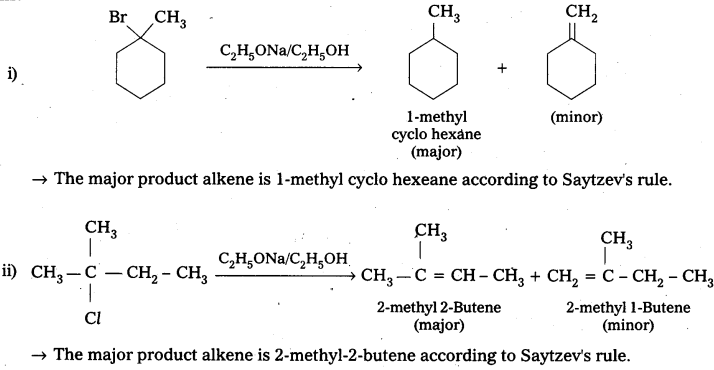
Question 6.
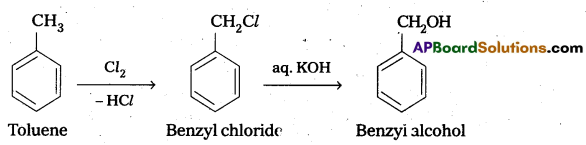
How will you carry out the following conversions ?
i) Ethane to bromomethene
ii) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
Answer:
i) Conversion of Ethane to Bromo Ethane.
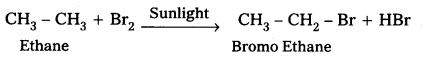
ii) Conversion of toluene to benzyl alcohol:
Question 7.
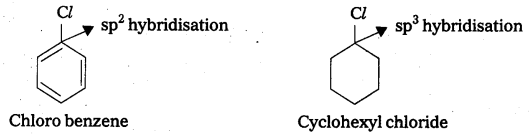
Explain why the dipole moment of chlorobenzene Is lower than that of cyclohexyichloride.
Answer:
The dipole moment of chloro benzene is lower than that of cylo hexyl chloride.
Explanation:
- The polarity of C – Cl bond in chiorobenzene is less than the polarity of C — Cl bond in cyclo hexyl chloride.
- The above fact is due to the sp2 hybridisation of ‘C’ atom in chiorobenzene where as in cyclo hexyl chloride ‘C’ atoms hybridisation is sp3 – hybridisation.
![]()
Question 8.
Write the mechanism of the following reaction.
![]()
Answer:
Given reaction is
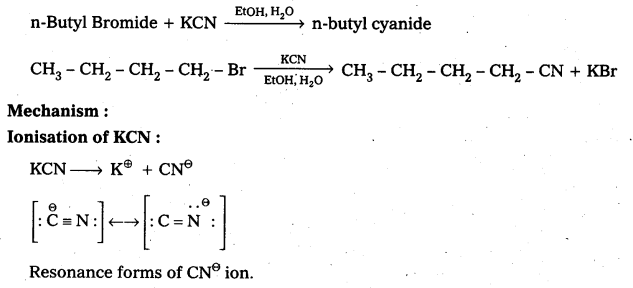
CN⊖ ion is an ambident nucleophile. It has the tendency to attack through C-atom (or) through N-atom. Attack through C-atom results cyanide product and attack through N- atom results isocyanide. But in presence of polar solvent KCN ionises and forms cyanide as major product.
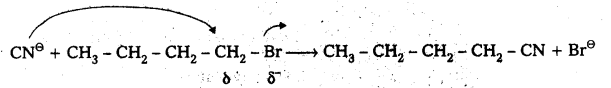
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as primary, secondary, tertiary, vinyl or aryl halides,
i) CH3CH(CH3)CH(Br)CH3
ii) CH3C(Cl)(C3H5)CH2CH3
iii) m-ClCH2C6H4CH2C(CH3)3
iv) O-Br-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3
Answer:
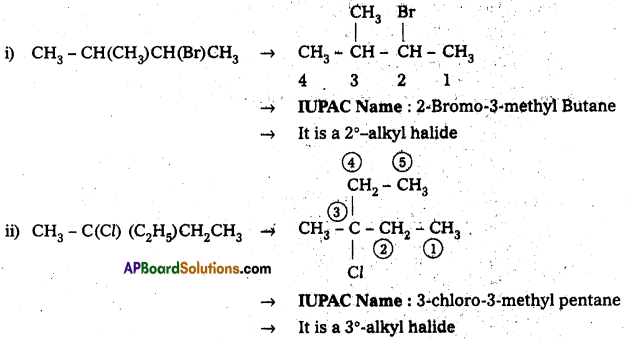
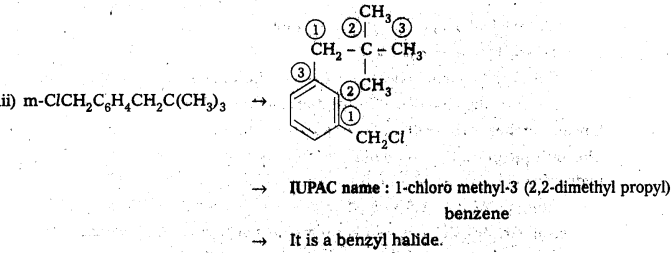
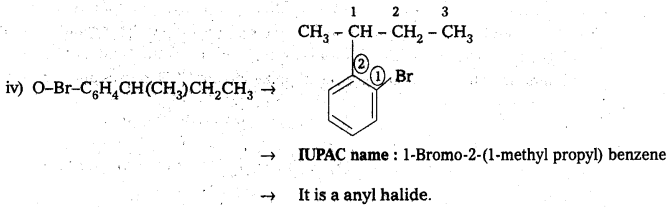
![]()
Question 2.
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds.
i) 2-Bromo-3-methylhexane
ii) 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-iodooctane
iii) 4-tertiary-butyl-3-iodo benzene
iv) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene.
Ans:
i) 2-Bromo-3-methyl hexane
Structure:
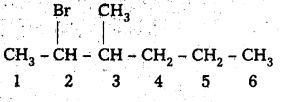
ii) 2-(2-chloro phenyl) 1-iodo octane
Structure:
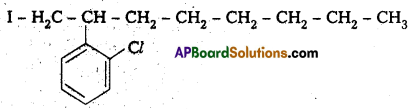
iii) 4-tertiary-butyl-3-iodo benzene
Structure:
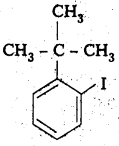
iv) 1 -Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2 -methyl benzene
Structure:
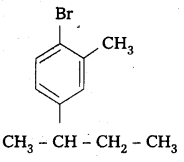
Question 3.
Discuss the physical properties of haloalkanes.
Answer:
Physical properties of halo alkanes:
- Pure alkyl halides are colourless, Bromides and iodides exhibits colour when exposed to light.
- Most of volatile halogen compounds have sweet smell.
- Lower members of alkyl halides are gases and higher members are liquids (or) solids.
- The boiling points of chlorides, bromides and iodides are higher than those of hydrocarbons.
- The boiling points of alkyl halides decrease as follows RI > RBr > RCl > RF.
- In case of isomeric halo alkanes boiling points decrease with increase in branching.
- The density of halo alkane, increase with increase in no. of carbon atoms, halogen atoms and atomic mass of the halogen atoms.
- Halo alkanes, have theTendency to dissolve in organic solvents and are very slightly soluble in water.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the mechanism of Nucleophilic bimolecular substitution (SN2) reaction with one example. [T.S. Mar. 16] [Mar. 14]
Answer:
Nucleophilic Bimolecular substitution Reaction SN2:
- The nucleophilic substitution reaction in which rate depends upon concentration of both reactants is called SN2 reaction.
- It follows 2nd order kinetics. So it is called bimolecular reaction.
Eg.: Methyl chloride reacts with hydroxide ion and forms methanol and chloride ion. - Here the rate of reaction depends upon the concentration of two reactants.
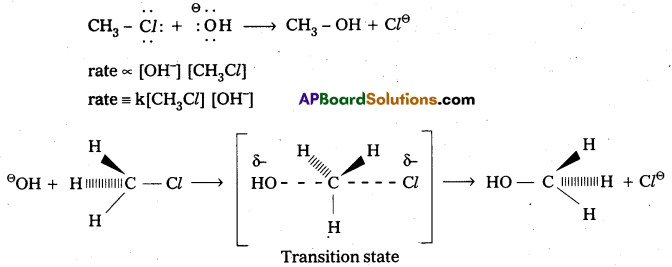
- In the above mechanism the configuration of carbon atom under attack inverts in much the same way as an umbrella is turned inside out when caught in a strong wind. This process is called inversion of configuration.
- In transition state the carbon atom is simultaneously bonded to the incoming nucleophile and out going group. It is very unstable.
- The order of reactivity for SN2 reactions follows : 1°-alkyl halides > 2°-alkyl halides > 3°-alkyl halides.
Question 5.
Explain why allylic and benzylic halides are more reactive towards SN1 substitution while 1-halo and 2-halobutanes preferentially undergoes SN2 substitution.
Answer:
1) Allylic and benzylic halides show high reactivity towards the SN1 reaction.
Reason: The carbocation thus formed gets stabilised through resonance phenomenon as shown below.
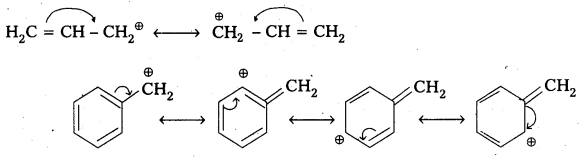
2) 1-halo and 2-halo butanes preferentially under goes SN2 substitute.
Reason : SN2 reactions involve transition state formation. Higher the steric hindrance lesser the stability of transition state. The given 1-halo and 2-halo butanes have less steric hindrance so these are preferentially undergo SN2 reaction.
![]()
Question 6.
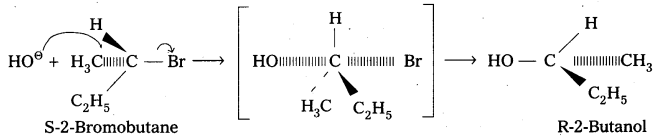
Describe the stereo chemical effect on the hydrolysis of 2-bromobutane.
Answer:
When S-2-Bromobutane is allowed to undergo hydrolysis R-2-butanol is formed with the – OH group occupying the position opposite to what bromide had occupied. This is an example of SN2 – reaction. SN2 reactions of optically active halides are accompanied by inversion of configuration.
Question 7.
What is the criteria for optical activity. Give two examples of chiral molecules.
Answer:
Optical activity: The property of rotating the plane polarized light by a chemical substance is called optical activity.
- If the plane polarised light rotates in clock wise direction then it is dextro rotatory [(+) (or) d-forms].
- If the plane polarised light rotates in anti-clock wise direction then it is laevo rotatory [(-) or /-form].
Crieteria for optical activity:
- Chirality (or) dissymmetry is the necessary and sufficient condition for a molecule to show optical activity.
Chirality : The objects which are non-superimposable on their mirror images are said to be chiral and this property is known as chirality. - Asymmetry (absence of symmetry) of the molecule is responsible for the optical activity of organic compounds.
Examples of chiral molecules :- 2-Butanol
- 2-Chlorobutane
- 2-Bromopropanoic acid.
![]()
Question 8.
Define the following: [A.P. Mar. 16]
i) Racemic mixture
ii) Retention of configuration
iii) Enantiomers.
Answer:
i) Racemic mixture: Equal portions of Enantiomers combined to form an optically inactive mixture. This mixture is called racemic mixture.
- Here rotation due to one isomer will be exactly cancelled by the rotation of due to other isomer.
- The process of conversion of enantiomer into a racemic mixture is called as racemisation.

ii) Retention of configuration: The preservation of the integrity of the spatial arrangement of bonds to an asymmetric centre during a chemical reaction (or) transformation is called Retention of configuration.
General Eg : Conversion of XCabc chemical species into YCabc.
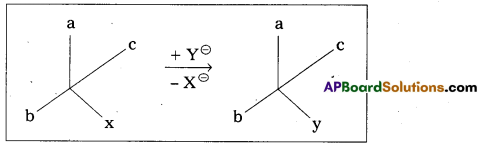
Eg : (-) 2 – Methyl 1 – butanol conversion into (+) 1 – chloro 2. Methyl butane
iii) Enantiomers : The stereo isomers related to each other as non-superimposable mirror images are called enantiomers.
- These have identical physical properties like melting point, boiling points refractive index etc.
- They differ in rotation of plane polarised light.
Question 9.
Write the mechanism of dehydrohalogenation of 2-bromobutane.
Answer:
Dehydrohalogenation of 2 – Bromobutane: 2 – Bromobutane reacts with alc.KOH to form 2 – Butene as major product.
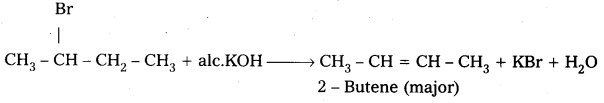
Mechanism:
- 2 – Bromobutane heated with alc.KOH elemination of hydrogen atom from β – carbon and bromine atom from α – carbon takes place. This is called β – Elimination.
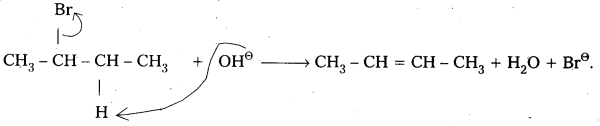
- 2 – Butene is major product formed according to saytzev’s rule. “In dehydrohalogenation reactions the preferred product is that alkene which has the greater no. of alkyl groups attached to double bonded carbon atoms”.
![]()
Question 10.
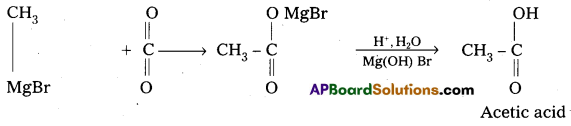
Explain the Grignard reagents preparation and application with suitable example.
Answer:
Alkyl magnesium halides are generally called as Grignard reagenty.
Preparation: These are prepared by the treatment of alkyl halides with magnesium metal in presence of dry ether.
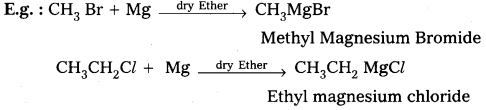
Applications:
Grignard reagents have wide applications in the synthesis of large no. of organic compounds.
- Preparation of alkanes :
Grignard reagents reacts with alcohols and forces alkanes.
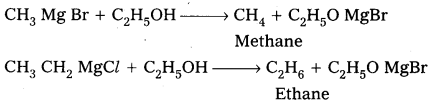
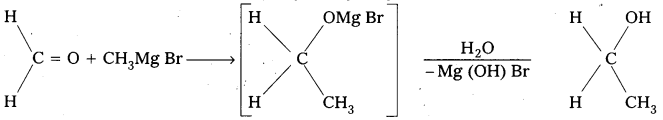
- Preparation of alcohols : Ethylalcohol is obtained by the action of Methyl magnesium bromide on formal dehyde followed by the hydrolysis.
- Preparation of carboxylicacids:
Grignard reagent on carboxylation followed by the hydrolysis to form carboxylic acids.
Question 11.
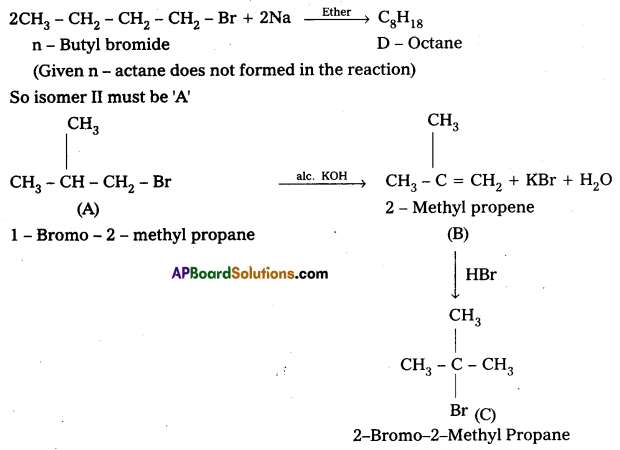
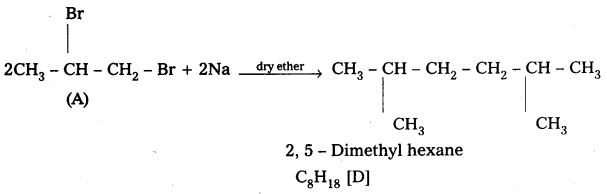
A primary alkyl halide C4H9Br(A) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound B. B on reaction with HBr yields C which is an isomer of A. When A is reacted with sodium metal forms D, C8H8 which is different from the compound formed when n-butylbromide is reacted with sodium. Give the structural formulae of A-D and write equations for all the reactions.
Answer:
Given 1° – alkyl halide molecular formula C4H9Br
Two isomers possible with molecular formula C4H9Br (i- alkyl halides)
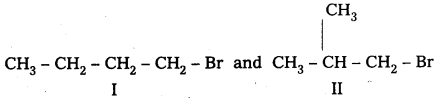
Given that compound ‘A’ when reacted with Na does not forms the same product produced by n — Butyl bromide.
∴ isomer I cannot be ‘A’.
![]()
Question 12.
Account for the following statements:
i) Aryihalides are extremely less reactive towards Nucleophilic substitution reactions.
ii) p-Nitrochlorobenzene and o, p-dinitrochlorobenzene undergo Nucleophilic substitution readily compared to chlorobenzene.
Answer:
i) Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions due to following reasons.
- In aryl halides ‘C’ undergoes SP2 hybridised and it has greater S – character ånd electro negativity So the C – X bond length is shorter.
- In aryl halides resonance effect plays an important role.
The electron pairs on halogen atom are in conjugation with it π – electrons of the ring.
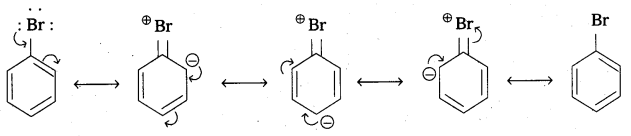
In the above C – Br bond acquires apartial double bond nature due to resonance. This bond cleavage is difficult. - The phenyl cation formed in aryl halides is not stabilised by resonance.
ii) p – nitrochlorobenzene and o, p – dinitro chlorobenzene undergo nucleophillic substitution reachily compared to chlorobenzene due to the following reasons.
- Due to presence of – NO2 group which is an electron with drawing group at ’O’ and ‘P’ – positions in the ring makes the bond breaking easy.
- As the number of NO2 groups increases reactivity of aryl halide also increases. This can be evidended by the following reactions.
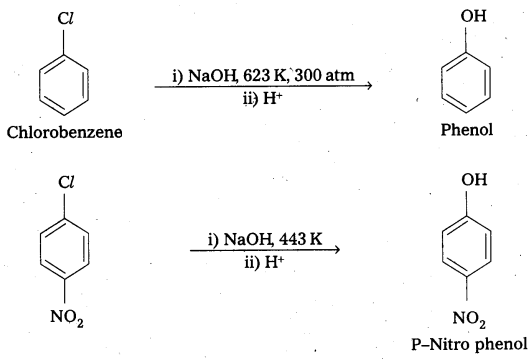
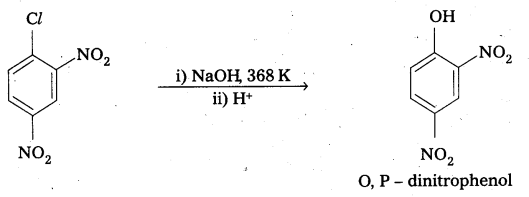
Question 13.
Explain how the following conversions are carried out:
i) Propene to Propanol
ii) Ethanol to but-1-yne
iii) 1-Bromopropane to 2-Bromopropane
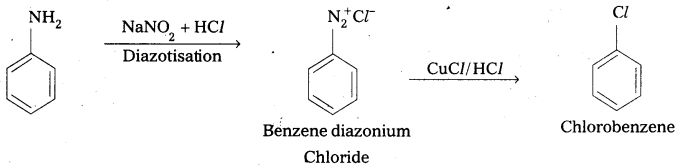
iv) Aniline to Chlorobenzene.
Answer:
i) Propene to propanol
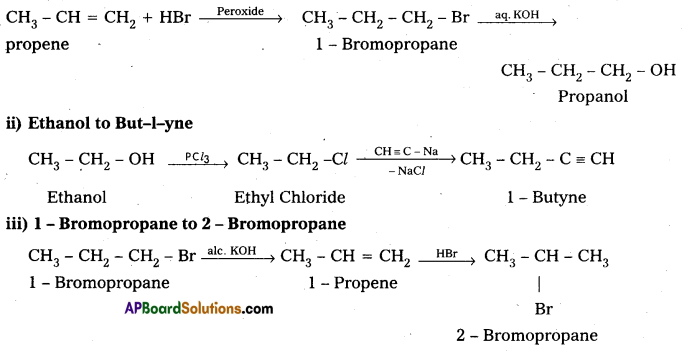
iv) Aniline to chlorobenzene
![]()
Question 14.
What happens when
i) n-butylchloride is treated with alc.KOH.
ii) Bromobenzene is treated with Mg in presence of dry ether.
iii)Methylbromide is treated with sodium in presence of dry ether.
Answer:
i) n-Butylchloride + treated with alc.KOH undergo dehydro halogenation and forms 1-Butene.
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – Cl + alc. KOH → CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2 + kCl + H2O
ii) Bromobenzene is treated with Mg in presence of dry ether forms phenyl magnesium bromide a Grignard reagent.

iii) Methyibromide is treated with sodium in presence of dry ether forms ethane (wurtz reaction)
![]()
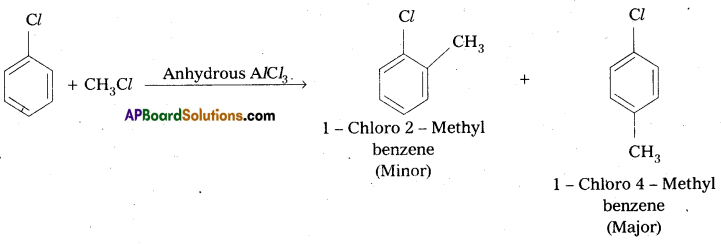
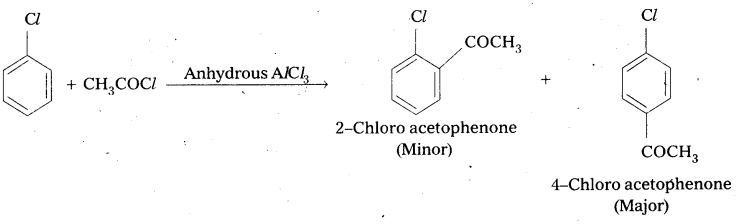
Question 15.
Write the reactions showing the major and minor products when chlorobenzene is reacted with CH3Cl and CH3COCl in presence of AlCl3.
Answer:
i) Friedel crafts alkylation : When chiorobenzene is treated with CH3Cl to form 1 – Chloro – 4 – Methyl benzene (major) and 1 – Chloro 2 – Methylbenzene (minor).
ii) Friedel Craft’s acylation: Chlorobenzene reacts with CH3COCl in presence of Anhydrous AlCl3 to form 2 – Chloro actophenone, (Minor) and 4 – Chloro acetophenone (major).
Textual Examples
Question 1.
Draw the structures of all the eight structural isomers that have the molecular formula C5H11Br. Name each isomer according to IUPAC system and classify them as primary, secondary or tertiary bromide.
Solution:
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2Br 1-Bromopentane (1°)
CH3CH2CH2CH(Br)CH3 2-Bromopentane (2°)
CH3CH2CH(Br)CH2CH3 3-Bromopentane (2°)
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2Br 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane (1°)
(CH3)2CHCHBrCH3 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane (2°)
(CH3)2CBrCH2CH3 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane (3°)
CH3CH2CH (CH3) CH2Br 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane (1°)
(CH3)3CCH2Br 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethyipropane (1°)
![]()
Question 2.
Write IUPAC names of the following:
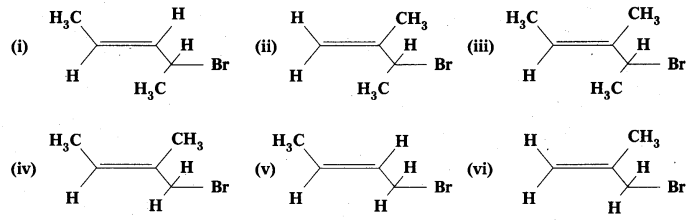
Solution:
- 4-Bromopent-2-ene
- 3-Bromo-2-methylbut-l-ene
- 4-Bromo-3-methylpent-2-ene
- 1-Bromo-2-methylbut-2-ene
- 1-Bromobut-2-ene
- 3-Bromo-2-methylpropene
Question 3.
Identify all the possible monochloro structural isomers expected to be formed on free radical monochlorination of (CH3)2CHCH2CH3.
Solution:
In the given molecule, there are four different types of hydrogen atoms. Replacement of these hydrogen atoms will give the following.
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2Cl
(CH3)2CHCH(Cl)CH3
(CH3)2C(Cl)CH2CH3
CH3CH(CH2Cl)CH2CH3
Question 4.
Write the products of the following reactions
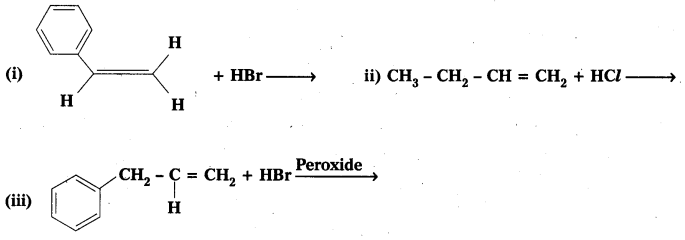
Solution:
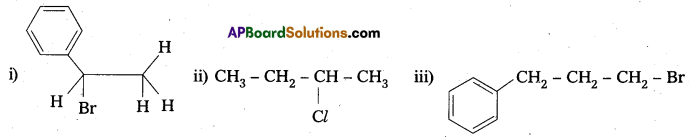
![]()
Question 5.
Haloakanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as main product while AgCN forms isocyanides as the chief product. Explain.
Solution:
KCN is predominantly ionic and provides cyanide ions in solution. Although both carbon and nitrogen atoms are in a position to donate electron pairs, the attack takes place mainly through carbon atom and not through nitrogen atom since C-C bond is more stable than C-N bond. However, AgCN is mainly covalent in nature and nitrogen is free to donate electron pair forming isocyanide as the main product.
Question 6.
In the following of halogen compounds, which would undergo SN2 reaction faster ?
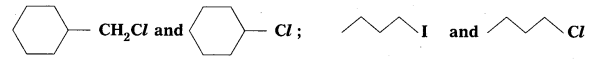
Solution:
 It is primary halide and therefore undergoes SN2 reaction faster.
It is primary halide and therefore undergoes SN2 reaction faster.
![]() As iodine is a better leaving group because of its large size, it will be released at a faster rate in the presence of incoming nucleophile.
As iodine is a better leaving group because of its large size, it will be released at a faster rate in the presence of incoming nucleophile.
Question 7.
Predict the order of reactivity of the following compounds in SN1 and SN2 reactions.
i) The four isomeric bromobutanes
ii) C6H5CH2Br, C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(CH3)Br, C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br
Solution:
i) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br < (CH3)2CHCH2Br < CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3 < (CH3)3CBr (SN1)
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br > (CH3)2CHCH2Br > CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3 > (CH3)3CBr (SN2)
Of the two primary bromides, the carbocation intermediate derived from (CH3)2CHCH2Br is more stable than that derived from CH3CH2CH2CH2Br because of greater electron donating inductive effect of (CH3)2CH-group. Therefore, (CH3)2CHCH2Br is more reactive than CH3CH2CH2Br in SN1 reactions. CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3 is a secondary bromide and (CH3)3 CBr is a tertiary bromide. Hence the above order is followed in SN1. The reactivity in SN2 reactions follows the reverse order as the steric hinderance around the electrophilic carbon increases in that order.
ii) C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5) Br > C6H5CH(C6H5)Br > C6H5CH(CH3)Br > C6H5CH2Br (SN1)
C6H5C(CH3) (C6H5) Br < C6H5CH(C6H5)Br < C6H5CH(CH3)Br < C6H5CH2Br (SN2)
Of the two secondary bromides, the carbocation intermediate obtained from C6H5CH(C6H5)Br is more stable than obtained from C6H5CH(CH3)Br because it is stabilised by two phenyl groups due to resonance. Therefore, the former bromide is more reactive than the latter in SN1 reactions. A phenyl group is bulkier than a methyl group. Therefore, C6H5CH(C6H5)Br is less reactive than C6H5CH(CH3)Br in SN2 reactions.
![]()
Question 8.
Identify chiral molecules in each of the following pair of compounds. (Wedge and Dash representations according to Inter 1 yr., fig. 13.1).
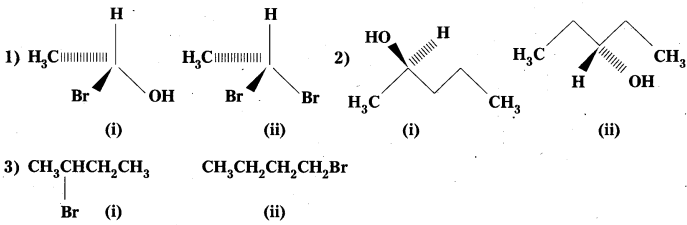
Solution:
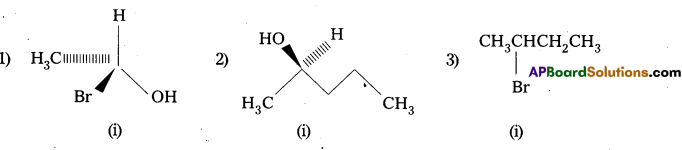
Question 9.
Although chlorine is an electron withdrawing group, yet it is ortho-, para-directing in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Why ?
Solution:
Chlorine withdraws electrons through inductive effect and releases electrons through resonance. Through inductive effect, chlorine destabilises the intermediate carbocation formed during the electrophilic substitution.
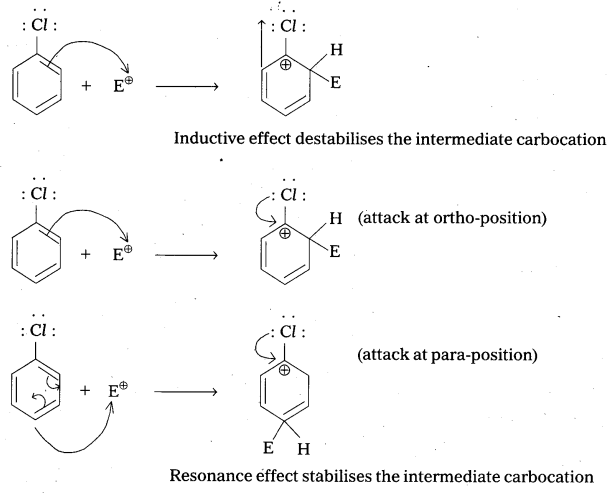
Through resonance, halogen tends to stabilise the carbocation and the effect is more pronounced at ortho-and para-positions. The inductive effect is stronger than resonance and causes net electron withdrawl and thus causes net deactivation. The resonance effect tends to oppose the inductive effect for the attack at ortho-and para-positions and hence makes the deactivation less for ortho-and para-attack. Reactivity is thus controlled by the stronger inductive effect and orientation is controlled by resonance effect.
![]()
Intext Questions
Question 1.
Write structures of the following compounds:
i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
iii) 4-tert. Butyl-3-iodoheptane
iv) 1, 4-Dibromobut-2-ene
v) 1-Bromo-4-sec. butyl-2-methylbenzene.
Answer:
Question 2.
Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI ?
Answer:
H2SO4 cannot be used along with KI in the conversion of an alcohol to an alkyl iodide as it converts KI to corresponding acid, HI which is then oxidised by it to I2.
Question 3.
Write structures of different dihalogen derivatives of propane.
Answer:
- ClCH2CH2CH2Cl
- ClCH2 CHClCH3
- Cl2CHCH2 CH3
- CH3CCl2 CH3
![]()
Question 4.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photo¬chemical chlorination yields.
i) A single monochloride,
ii) Three isomeric monochlorides,
iii) Four isomeric monochlorides.
Answer:
i)
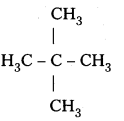
All the hydrogen atoms are equivalent and replacement of any hydrogen will give the same product.
ii) CaH3CbH2CcH2CbH2CaH3
The equivalent hydrogens are grouped as a, b and c. The replacement of equivalent hydrogens will give the same product.
iii)
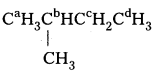
Similarly the equivalent hydrogens are grouped as a, b, c and d. Thus, four isomeric products are possible.
Question 5.
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions.
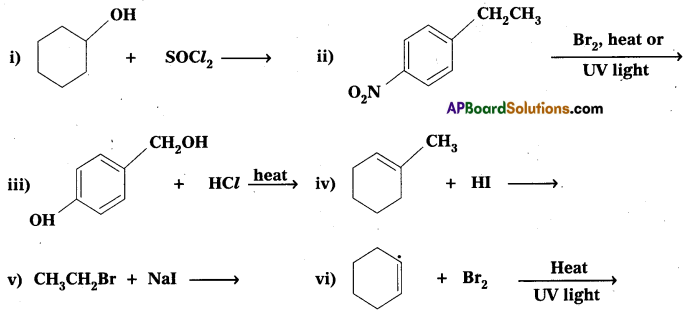
Answer:
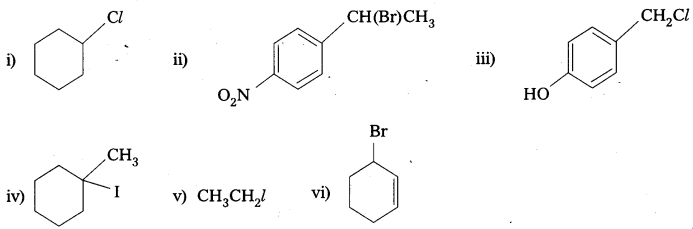
![]()
Question 6.
Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points.
- Bromomethane, Bromoform, Chloromethane, Dibromomethane.
- 1 – Chloropropane, Isopropyl chloride, 1 – Chlorobutane.
Answer:
- Chloromethane, Bromomethane, Dibromomethane, Bromoform. Boiling point increases with increase in molecular mass.
- Isoporpylchloride, 1 – Chloropropane, 1 – Chlorobutane. Isopropylchloride being branched has lower b.p. than 1 – Chloropropane.
Question 7.
Which alkyl halide from the following pairs would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism ? Explain your answer.
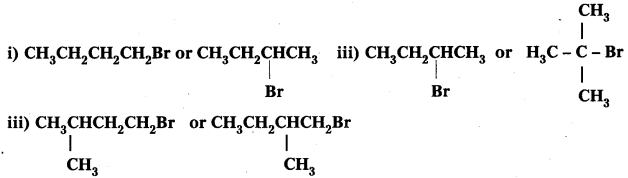
Answer:
i) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br Being primary halide, there won’t be any steric hindrance.
ii)
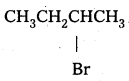
Secondary halide reacts faster than tertiary halide.
iii)
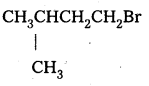
The presence of methyl group closer to the halide group will increase the steric hindrance and decrease the rate.
Question 8.
In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction?
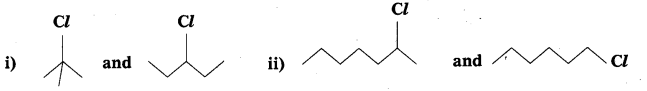
Answer:
i) 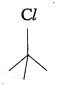 Tertiary halide reacts faster than secondary halide because of the greater stability of tert-carbocation.
Tertiary halide reacts faster than secondary halide because of the greater stability of tert-carbocation.
ii) 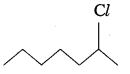 Because of greater stability of secondary carbocation than primary.
Because of greater stability of secondary carbocation than primary.
![]()
Question 9.
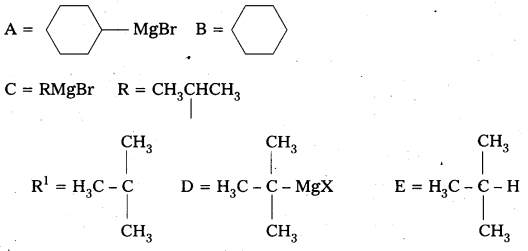
Identify A, B, C, D, E, R and R1 in the following:
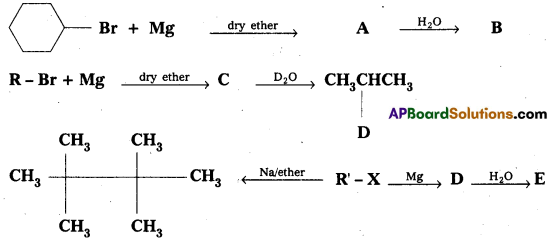
Answer: