Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions 9th Lesson Biomolecules which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions 9th Lesson Biomolecules
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Carbohydrates.
Answer:
The compounds which are primarily produced by plants and form a very large group of naturally occurring organic compounds are called Carbohydrates.
Eg: Glucose, Fructose, Starch. Carbohydrates are the polyhydroxy aldehydes (or) ketones.
Question 2.
Name the different types of carbohydrates on the basis of their hydrolysis. Give one example for each.
Answer:
On the basis of hydrolysis, carbohydrates are classified as
- Monosaccharides, Eg : Glucose, fructose
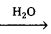 No saccharides
No saccharides - Oligosaccharides, Eg : Sucrose, maltose
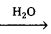 two monosaccharides
two monosaccharides - Polysaccharides, Eg : Starch, cellulose
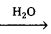 large number of monosaccharides.
large number of monosaccharides.
![]()
Question 3.
How is Glucose prepared ? [IPE – 2014]
Answer:
Glucose is prepared by the hydrolysis of starch in presence of a little acid.
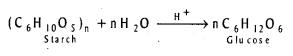
Question 4.
Why are sugars classified as reducing and non-reducing sugars ?
Answer:
- Carbohydrates that reduce Fehling’s reagent, Tollen’s reagent are called reducing sugars.
Eg: Glucose. - Carbohydrates that doesnot reduce Fehling’s reagent, Tollen’s reagent are called non reducing sugars.
Eg : Sucrose.
Question 5.
What do you understand by invert sugars ?
Answer:
During the hydrolysis of sucrose there is a change in the sign of rotation, from dextro (+) to laevo (-) and the product is named as invert sugar.
Question 6.
What do you mean by essential amino acids ? Give two examples for non essential amino acids ? [IPE 2014] [T.S. Mar. 16]
Answer:
Essential amino acids : The amino acids which cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through diet are known as essential aminoacids.
Eg : valine, leucine etc.
Examples of non essential amino acids are Alanine, Glycine, Aspartic acid.
![]()
Question 7.
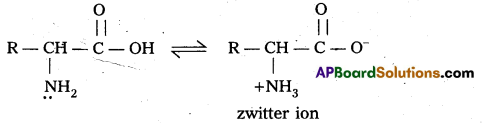
What is zwitter ion ? Give an example. [IPE 2015 (AP)]
Answer:
Zwitter ion: In aqueous solution of amino acids, the carboxyl group can lose a proton and amino acid can accept that proton to form a dipolar ion. This ion is called as zwitter ion.
Question 8.
What are reducing sugars ?
Answer:
Carbohydrates that reduce Fehling’s reagent, Tollen’s reagent are called reducing sugars.
Eg: glucose.
Question 9.
What are proteins ? Give an example.
Answer:
Proteins : A poly peptide with more than hundred amino acid residues, having molecular mass higher than 10,000 units is called a protein.
Eg : keratin, myosin, insulin.
Question 10.
What are the components of a nucleic acid ?
Answer:
- Nucleic acids are long chain polymers of nucleotides i.e., poly nucleotides.
- Nucleic acids are constituted by pentose sugar, phosphoric acid, and nitrogenous hetero cyclic base (purine (or) pyrimidine).
![]()
Question 11.
What are essential and non – essential amino acids ? Give one example for each. [IPE – 2016 (TS)]
Answer:
- Essential amino acids : The amino acids that cannot be synthesised by the body and must be supplied in the diet are called essential amino acids.
Eg : valine, leucine, phenyl alanine etc. - Non-essential amino acids : Other amino acids synthesised by the tissues of the body are called non-essential amino acids..
Eg: Glycine, alanine etc.
Question 12.
Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins.
Answer:
Globular proteins
- In this proteins the chains of poly peptides coil around to give a spherical shape.
- hese are soluble in water.
- Eg : Insulin
Fibrous proteins
- In this proteins the poly peptides run parallel and are held together by hydrogens and disulphite – bonding.
- These are insoluble in water.
- Eg: keratin
Question 13.
Why are vitamin A and vitamin C essential to us ? Give their important sources.
Answer:
Vitamin A and Vitamin C are essential to us.
Explanation :
- Deficiency of vitamin A causes night blindness, redness in eyes, xerophthalnia.
- Deficiency of vitamin C causes pernicious anaemia (RBC deficient in haemoglobin).
Sources:
- Vitamin – A : Fish liver oil, carrots, butter and milk.
- Vitamin – C : Citrous fruits, amla, green leafy vegetables
![]()
Question 14.
What do you understand from the names (a) aldo pentose and (b) ketoheptose ?
Answer:
a) Aldo pentose : If a monosaccharide contains 5 carbon atoms with aldehyde group then it is known as aldo pentose.
b) Ketoheptose : If a monosaccharide contain seven carbons with a ketone group then it is called ketoheptose.
Question 15.
What are anomers ?
Answer:
Anomers : The two isomeric structures of a compound which differ in configuratiofi at C-l only are called Anomers.
Question 16.
What are amino acids ? Give two examples.
Answer:
The organic compounds which contain amino (-NH2) functional group and carboxyl (-COOH) functional group are called amino acids.
Eg : Glycine, Alanine etc.
Question 17.
What are fibrous proteins ? Give examples.
Answer:
When the poly peptide chains run parallel and are held together by hydrogen and disulphide bonds then fibre – like structure is formed. These are called fibrous proteins. These are insoluble in water.
Eg : keratin, myosin.
![]()
Question 18.
What are globular proteins ? Give examples.
Answer:
When the chains of polypeptides coil around to give a spherical shape then globular proteins are formed. These are usually soluble in water.
Eg : insulin and albumins.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the denaturation of proteins.
Answer:
The phenomenon of disorganization of native protein structure is known as denaturation. Denaturation results in the loss of secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. This involves a change in physical, chemical and biological properties of protein molecules.
Agents of denaturation:
Physical agents – Heat, violent shaking, X – rays, UV – radiation.
Chemical gents – Acids, alkalies, organic solvents, urea, salts of heavy metals.
Question 2.
What are enzymes ? Give examples ?
Answer:
The group of complex proteinoid organic compounds, elaborated by living organism which catalyse specific organic reactions are called enzymes.
Eg.: Lipases, Rennin, Maltase, Invertase etc. Practically all biological processes such as digestion, respiration etc., are carried on through the agency of enzymes.
Enzymes may be defined as biocatalysts synthesised by living cells.
The functional unit of enzyme is known as holo enzyme made up at apo enzyme (protein part) and co enzyme (non-protein part).
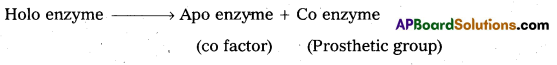
Question 3.
Write notes on vitamins.
Answer:
Vitamin is defined as an “accessory food factor which is essential for growth and healthy maintenance of the body.”
Classification : Vitamins are broadly classified into two major groups.
a) the fat soluble Eg : vitamin A, D, E and K.
b) water soluble Eg : vitamin B – complex and C.
![]()
Question 4.
What are harmones ? Give one example for each. [IPE – 2016 (TS)] [Mar. 14]
- steroid hormones
- Poly peptide hormones and
- amino acid derivatives.
Answer:
Hormones: Hormone is defined as an “organic compound synthesised by the ductless glands of the body and carried by the blood stream to another part of the body for its function”.
Eg : testosterone, oestrogen.
- Example for steroid hormones : Testosterone, oestrogen
- Example for poly peptide hormones: Insulin
- Example for Amino acid derivative : Thyroidal hormones thyroxine.
Question 5.
Write the importance of carbohydrates.
Answer:
Importance of carbohydrates:
- Carbohydrates are essential for life of plants.
- Carbohydrates are used as storage molecules as starch in plants.
- Cell wall of plants is made up of cellulose.
- Carbohydrates are also essential for life of animals. Carbohydrates are used as storage molecules as glycogen in animals.
- Carbohydrate source honey is used for a long time as an instant source of energy.
![]()
Question 6.
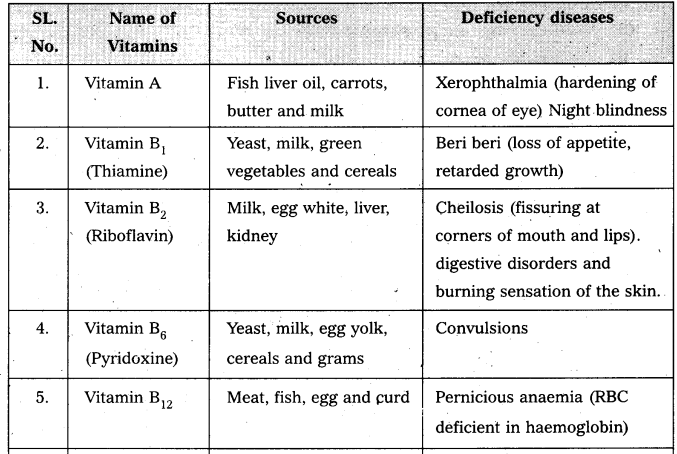
Give the sources of the following vitamins and name the diseases caused by their- deficiency [T.S. Mar. 17] [IPE AP & TS (Mar. 15) BMP, 2016 (AP]
(a) A
(b) D
(c) E and
(d) K
Answer:
Vitamin : A
Sources : Fish oils, liver, kidney
Deficiency diseases : Night blindness, Redness in eyes.
Vitamin : D
Sources : Fish oils, butter, milk, egg
Deficiency diseases : Rickets in children, osteomalacia in adults
Vitamin : E
Sources : Wheat germ oil, egg yolk, green vegetables
Deficiency diseases : Sterility
Vitamin : K
Sources : Green vegetables, Intestinal flora.
Deficiency diseases : Blood coagulation is prevented
Question 7.
Write notes on proteins. [IPE – 2016 (TS)]
Answer:
Proteins are polypeptide chains of amino acids.
Classification of Proteins : Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape.
a) Fibrous Proteins : These are fibre like proteins, the polypeptide chains are parallel which are held together by hydrogen and disulphide bonds. These are insoluble in water.
Ex : Keratin present in hair, wool, silk etc., and myosin present in muscles.
b) Globular proteins: In these proteins, the polypeptide chains coil around to give a spherical shape. These are soluble in water.
Ex : insulin and albumin.
The structure of proteins is explained in four different levels
a) Primary structure
b) Secondary structure
c) Tertiary structure
d) Quaternary structure
Denaturation of proteins : A protein in a biological system with a specific structure and biological activity is called a native protein. The process in which a protein loses its activity when subjected to heating, change in pH, addition of reagents is called denaturation of protein. Denaturation may be reversible or irreversible.
Ex : Coagulation of egg white on boiling is an irresersible denaturation.
Renaturation is the reverse process of denaturation.
![]()
Question 8.
Write about polysaccharides with starch and cellulose as examples.
Answer:
Polysaccharides : The saccharides which on hydrolysis to form large number of monosaccharides are called polysaccharides.
Eg : Starch and cellulose
Starch :
- Starch is the most important dietary source for human beings.
- Vegetables, roots, cereals are important sources of starch.
- It is a polymer ofα – glucose.
- It is constituted by two components Amylose and amylopectin.
Amylose :
- It constitutes 15 – 20% of starch.
- Amylose is water soluble component.
- Amylose is a branched chain with 200 – 1000 α – D – glucose units held by C – 1 to C – 4 glycosidic linkage.
Amylopectin :
- Amylopectin constitutes 80 – 85% of starch.
- It is a branched chain polymer of a – glucose units in which chain is formed by C. – 1 to C – 4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by C – 1 to C – 6 glycosidic linkage.
Cellulose :
- Cellulose occurs in plants and it is the most abundant organic substance.
- It is a major constituent of cell wall of plant cells.
- Cellulose is a straight chain polysaccharide composed only of β – D – glucose units . which are joined by glycosidic linkage between C – 1 of one glucose and C – 4 of the next glucose.
Question 9.
Write notes on the functions of different hormones in the body. [IPE 2014]
Answer:
Functions of Hormones:
- Hormones help to maintain the balance of biological activities in the body.
- Insulin maintains the blood glucose level within the limit.
- Growth hormones and sex hormones play role in growth and development.
- Low level of thyroxine (produced from thyroid gland) causes hypothyroidism. High level of thyroxine causes hyper thyroidism.
- Gluco corticoids control the carbohydrate metabolism, modulates the inflammatory reactions.
- The mineralo corticoids control the level of excretion of water and salt by the kidney.
- Adrenal cortex does not function properly then results in Addison’s disease.
- Hormones released by gonads are responsible for development of secondary sex characters.
- Testosterone is responsible for development of secondary sex hormone produced in male.
- Estradiol is the main female sex hormone responsible for development of secondary female characterstics like control of menstrual cycle.
- Progesterone is responsible for preparing the uterus for implantation of fertiised egg.
![]()
Question 10.
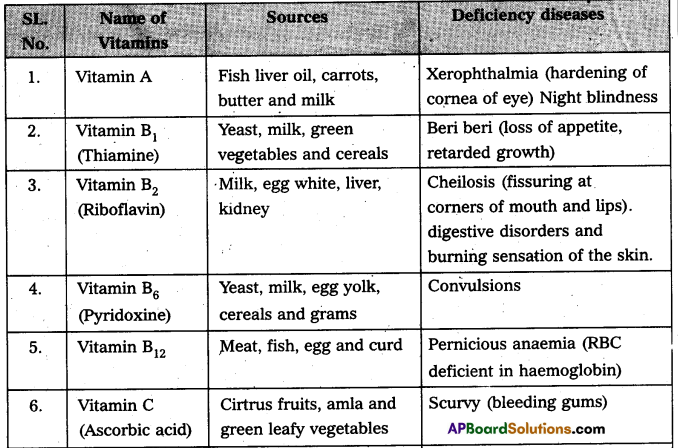
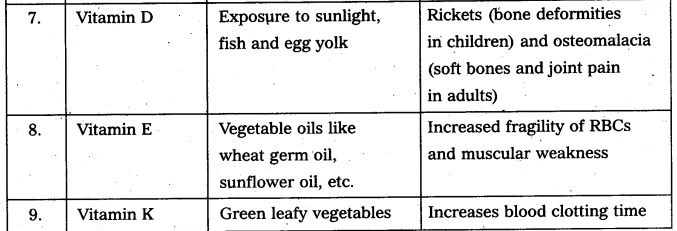
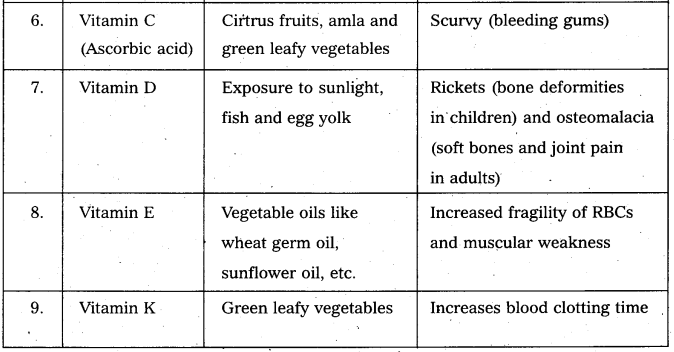
Write the sources of vitamin and diseases due to vitamin deficIency. [AP Mar. 20]
Answer: