AP State Syllabus AP Board 9th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals Ex 8.2 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Maths Solutions 8th Lesson Quadrilaterals Exercise 8.2
Question 1.
In the given figure ABCD is a parallelogram. ABEF is a rectangle. Show that ΔAFD ≅ ΔBEC
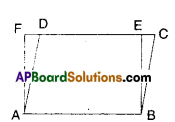
Solution:
Given that □ABCD is a parallelogram.
□ABEF is a rectangle.
In ΔAFD and ΔBEC
AF = BE ( ∵ opp. sides of rectangle □ABEF)
AD = BC (∵ opp. sides of //gm □ABCD)
DF = CE (∵ AB = DC = DE + EC , AB = EF = DE + DF)
∴ ΔAFD ≅ ΔBEC (SSS congruence)
![]()
Question 2.
Show that the diagonals of a rhombus divide it into four congruent triangles.
Solution:
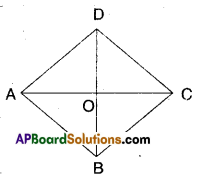
□ABCD is a rhombus.
Let AC and BD meet at O’.
In ΔAOB and ΔCOD
∠OAB = ∠OCD (alt.int. angles)
AB = CD (def. of rhombus)
∠OBA = ∠ODC ………………….(1) (alt. int. angles)
∴ ΔAOB ≅ ΔCOD (ASA congruence)
Thus AO = OC (CPCT)
Also ΔAOD ≅ ΔCOD …………..(2)
[ ∵ AO = OC; AD = CD; OD = OD SSS congruence]
Similarly we can prove
ΔAOD ≅ ΔCOB ……………. (3)
From (1), (2) and (3) we have
ΔAOB ≅ ΔBOC ≅ ΔCOD ≅ ΔAOD
∴ Diagonals of a rhombus divide it into four congruent triangles.
![]()
Question 3.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, the bisector of ∠C and ∠D intersect at O. Prove that ∠COD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (∠A + ∠B) .
(OR)
In a quadrilateral ABCD, the bisectors of ∠A and ∠B are intersects at ‘O’ then prove that ∠AOB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (∠C + ∠D)
Solution:
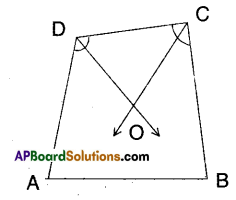
In a quadrilateral □ABCD
∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
(angle sum property)
∠C + ∠D = 360° – (∠A + ∠B)
\(\frac{1}{2}\) (∠C + ∠D) = 180 – \(\frac{1}{2}\) (∠A + ∠B) ………….. (1)
(∵ dividing both sides by 2) .
But in ΔCOD
\(\frac{1}{2}\)∠C + \(\frac{1}{2}\)∠D + ∠COD = 180°
\(\frac{1}{2}\)∠C + \(\frac{1}{2}\)∠D = 180° – ∠COD
∴\(\frac{1}{2}\)(∠C +∠D) = 180° -∠COD………….(2)
From (1) and (2);
180° – ∠COD = 180° – \(\frac{1}{2}\) (∠A + ∠B)
∴ ∠COD = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (∠A + ∠B)
Hence proved.