Practice the AP 10th Class Physical Science Bits with Answers Chapter 1 Heat on a regular basis so that you can attempt exams with utmost confidence.
AP State Syllabus 10th Class Physical Science Bits 1st Lesson Heat with Answers
CONCEPT – I : Heat – Temperature
Question 1.
If you touch a piece of wood and a piece of metal which were kept in the fridge for the same period of time then the result is
A) metal piece is colder than wooden piece
B) wooden piece is colder than metal piece
C) both are at same temperature
D) none
Answer:
A) metal piece is colder than wooden piece
Question 2.
Calorimetry is the measurement of
A) heat
B) temperature
C) pressure
D) mass
Answer:
A) heat
![]()
Question 3.
…………….. flows from a body at higher temperature to a body at lower temperature.
A) Temperature
B) Heat
C) Light
D) Electricity
Answer:
B) Heat
Question 4.
Heat energy will be transferred, when two bodies are placed in thermal contact which are at different temperatures
A) from a body at lower temperature to higher temperature
B) from a body at higher temperature to lower temperature
C) no transfer of heat energy takes place
D) both A and B are correct
Answer:
B) from a body at higher temperature to lower temperature
Question 5.
The degree of hotness or coldness is …………………
A) heat
B) temperature
C) evaporation
D) boiling
Answer:
B) temperature
Question 6.
Elow of heat energy between two bodies or systems requires …………………….
A) pressure difference
B) potential difference
C) temperature difference
D) all of these
Answer:
C) temperature difference
Question 7.
……………… is a measure of thermal equilibrium
A) Temperature
B) Heat
C) Mass
D) None
Answer:
A) Temperature
Question 8.
Three bodies A, B and C are in thermal equilibrium, the temperature of B is 45°C, then the temperature of C is
A) 45° C
B) 50° C
C) 40°C
D) any temperature
Answer:
A) 45° C
Question 9.
An object .A at 10°C and another object B at 10 K are kept in contact, then heat flows from
A) A to B
B) B to A
C) A to A
D) no heat transfer
Answer:
A) A to B
Question 10.
The difference in temperature of a body measured as 27°C. Its corresponding difference in Kelvin scale is ………………..
A) 27 K
B) 300 K
C) 246 K
D) 0 K
Answer:
A) 27 K
![]()
Question 11.
The temperature of a steel rod is 330 K. Its temperature in °C is ……………………..
A) 55° C
B) 59° C
C) 53° C
D) 57° C
Answer:
D) 57° C
Question 12.
Which of the following thermometer scale is also known as absolute scale of temperature?
A) Celsius scale
B) Fahrenheit scale
C) Kelvin scale
D) None
Answer:
C) Kelvin scale
Question 13.
Which one of the following temperature scales can not take negative ?
A) Celsius scale
B) Fahrenheit scale
C) Kelvin scale
D) None
Answer:
C) Kelvin scale
Question 14.
Temperature of a body is directly proportional to
A) potential energy
B) mass
C) density
D) average kinetic energy
Answer:
D) average kinetic energy
Question 15.
Different gases are at same temperature^ Which value remains same for all gases?
A) mass
B) heat
C) linear momentum
D) average kinetic energy
Answer:
D) average kinetic energy
Question 16.
Kinetic energy of molecules is more in
A) ice at 0°C
B) water at 0° C
C) water at 100° C
D) water vapour at 100° C
Answer:
D) water vapour at 100° C
Question 17.
For some change in temperature the amount of heat absorbed by a substance is directly proportional to …………………
A) mass
B) volume
C) both A and B
D) none
Answer:
A) mass
![]()
CONCEPT – II : Specific heat – Method of Mixtures
Question 18.
The amount bf heat requited to raise the temperature of the unit mass of the substance by one unit is called ………………….
A) latent heat
B) 1 Calorie
C) 1 Joule
D) specific heat
Answer:
D) specific heat
Question 19.
The degree of reluctance of a substance to change its temperature
A) latent heat
B) specific heat
C) kinetic energy
D) heat
Answer:
B) specific heat
Question 20.
The rise in temperature is high for a substance, if the maximum share of given heat energy is utilised for increasing its
A) rotational energy
B) potential energy
C) vibrational energy
D) linear kinetic energy
Answer:
D) linear kinetic energy
Question 21.
Internal energy of a system is
A) vibrational energy
B) linear kinetic energy
C) rotational and potential energy
D) all the above
Answer:
D) all the above
Question 22.
The substance with the highest specific heat is
A) mercury
B) gold
C) ice
D) water
Answer:
D) water
Question 23.
The substance with the lowest specific heat is
A) lead
B) mercury
C) kerosene oil
D) water
Answer:
A) lead
Question 24.
‘ Same amount of heat is supplied to two liquids A and B.
The liquid B shows greater rise in temperature. What can you say about the specific heat of B as compared to A?
A) Specific heat of B is less than that of A
B) Specific heat of B is greater than that of A
C) Can’t say
D) Specific heat of B is same as that of A
Answer:
A) Specific heat of B is less than that of A
![]()
Question 25.
Heat store houses on the earth
A) Trees
B) Mountains
C) Oceans
D) Coal
Answer:
C) Oceans
Question 26.
Which of the following is used as coolant?
A) ice
B) water
C) petrol
D) kerosene oil
Answer:
B) water
Question 27.
The S.I unit of specific heat is
A) Cal/g -°C
B) J/kg – K
C) Cal/kg -K
D) J/kg
Answer:
B) J/kg – K
Question 28.
The C.G.S unit of specific heat is
A) Cal/g- °C
B) Cal/kg – K
C) J/kg – K
D) Cal/kg – K
Answer:
A) Cal/g- °C
Question 29.
Specific heat S =
A) Q/Δt
B)Q Δt
C) Q/mΔt
D) mΔt/Q
Answer:
C) Q/mΔt
Question 30.
1 Cal/g -°C =
A) 4.2 × 103J/kg – K
B) 4.2 × 10-3 J/kg – K
C) 4.2 J
D) 4.2 × 106J/kg – K
Answer:
A) 4.2 × 103J/kg – K
Question 31.
If the specific heat is low, the rate of rise or fall in temperature is ………………. for the same quantity of heat supplied.
A) low
B) more
C) equal
D) can’t say
Answer:
B) more
![]()
Question 32.
Which of the following equation is used to determine howmuch heat is needed to raise the temperature of a certain mass of the substance through certain degrees?
A) Q = mL
B) Q = m Δt
C) Q = mS Δt
D) Q = it
Answer:
C) Q = mS Δt
Question 33.
Regarding the specific heat of water which of the following is correct ?
a) Its value in S.I system is 4180 J/kg – K
b) It’s value in C.G.S. system is 1 Cal/g-°C
c) The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of unit mass of substance by one unit
d) Specific heat changes the temperature of the body.
A) a, b
B) a, b, c
C) a, b, c, d
D) only b
Answer:
C) a, b, c, d
Question 34.
Statement I : The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of unit mass of substance through 1 °C is known as specific heat of the substance.
Statement II: The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gm of water through 1°C is 1 calorie.
Which of the above statements is true?
A) Both are true
B) Both are false
C) Statement I is true and II is false
D) Statement I is false and II is true
Answer:
A) Both are true
Question 35.
Mercury is preferred as thermometric fluid because of its
A) high thermal conductivity
B) low specific heat capacity
C) uniform thermal expansion
D) all the above
Answer:
D) all the above
Question 36.
Net heat lost by the hot bodies = Net heat gained by the col d bodies (if heat is noi lost by any other process). This is known as
A) Principle of Pascal
B) Principle of Archimedes
C) Principle of method of mixtures
D) None
Answer:
C) Principle of method of mixtures
Question 37.
The temperature (T) of two samples of the same substance with masses m1 and m2 and temperatures T1 and T2 when added together is
A) \(\frac{\mathrm{m}_{1} \mathrm{~T}_{1}+\mathrm{m}_{2} \mathrm{~T}_{1}}{\mathrm{~m}_{1}+\mathrm{m}_{2}}\)
B) \(\frac{\mathrm{m}_{1} \mathrm{~T}_{1}+\mathrm{m}_{2} \mathrm{~T}_{2}}{\mathrm{~m}_{1}+\mathrm{m}_{2}}\)
C) \(\frac{m_{1} T_{1}+m_{2} T_{2}}{T_{1}+T_{2}}\)
D) m1T1 = m2T2
Answer:
B) \(\frac{\mathrm{m}_{1} \mathrm{~T}_{1}+\mathrm{m}_{2} \mathrm{~T}_{2}}{\mathrm{~m}_{1}+\mathrm{m}_{2}}\)
Question 38.
The temperature of mixture of equal quantities of water at 90°C and water at
60°C when added together is ………………….
A) 60° C
B) 70° C
C) more than 90° C
D) 75° C
Answer:
D) 75° C
![]()
Question 39.
The temperature of mixture of two samples of the same substance is 70°C. One of the samples of 100 ml at 90°C and the other sample at 60°C. Find the quantity of other sample
A) 100 ml
B) 200 ml
C) 300 ml
D) 400 ml
Answer:
B) 200 ml
Question 40.
127° C + 400 K + x = 1000 K. The value of x is …………………
A) 200 K
B) 273 K
C) 473 K
D) 800 K
Answer:
A) 200 K
Question 41.
Which among the following material has specific heat more than that of ice?
A) Water
B) Glass
C) Mercury
D) Copper
Answer:
A) Water
Question 42.
A person is not feeling hot or cold with surroundings then he is in the state of
A) thermal equilibrium
B) high temperature
C) low temperature
D) both high and low temperature
Answer:
A) thermal equilibrium
Question 43.
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gm of water to 1°C is ………….. (in Jouls)
A) 4.186
B) 4. 286
C) 4.108
D) 4. 208
Answer:
A) 4.186
Question 44.
The substance that is having least specific heat from the following …………………
A) Zinc
B) Mercury
C) Water
D) Kerosene
Answer:
B) Mercury
Question 45.
The C.G.S unit of heat from the following is ……………………
A) Joule
B) Calorie
C) Kelvin
D) Celsius
Answer:
B) Calorie
![]()
Question 46.
The S.I unit of heat from the following is …………………….
A) Joule
B) Calorie
C) Kelvin
D) Celsius
Answer:
A) Joule
Question 47.
The S.I unit of temperature from the following is ………………………
A) Joule
B) Calorie
C) Kelvin
D) Celsius
Answer:
C) Kelvin
Question 48.
The final temperature of a mixture of 100g of water at 30°C temperature and 100g of water at 60°C temperature is ………………………
A) 45° C
B) 70° C
C) 90° C
D) 130° C
Answer:
A) 45° C
Question 49.
Specific heat of Cu is 0.095, iron 0.115, brass 0.092 and water 1. Which of the above can be heated quickly when they are kept in sunlight with same masses?
A) Iron
B) Brass
C) Copper
D) Water
Answer:
B) Brass
Question 50.
1 gm of water at 20°C is heated till its temperature raises to 21 °C. The amount of heat energy absorbed by the water is ………………..
A) 1 Joule
B) 1 calorie
C) 1 Kilo calorie
D) 2 Joule
Answer:
B) 1 calorie
Question 51.
1 kg of water at 300 K is heated till its temperature raises to 301K. The amount of heat energy absorbed by the water is …………………..
a) 1 Joule
b) 1 calorie
c) 1 K. calorie
d) 4180 J
A) a, b
B) a,c
C) c,d
D) a, c, d
Answer:
C) c,d
Question 52.
The heat energy required to raise the temperature of 20 kg of water from 25 °C to 75 °C is (in calories) …………………
A) 103
B) 104
C) 105
D) 106
Answer:
D) 106
![]()
Question 53.
The heat absorbed by the substance depends on
A) mass
B) temperature change
C) specific heat
D) all
Answer:
D) all
Question 54.
Evaporation of liquid takes place at the ………………..
A) bottom
B) middle
C) surface
D) edges only
Answer:
C) surface
Question 55.
Water is used in car radiators of engine as coolant because of ………………….
A) its density is more
B) high specific heat
C) high thermal conductivity
D) free availability
Answer:
B) high specific heat
CONCEPT – III : Changes of States
Question 56.
The process of escaping of molecules from the surface of a liquid at any temperature is called ……………………..
A) evaporation
B) condensation
C) boiling
D) melting
Answer:
A) evaporation
Question 57.
Evaporation is a ……………… process.
A) warming process
B) cooling process
C) A and B
D) none
Answer:
B) cooling process
Question 58.
Evaporation is a ………….. phenomenon.
A) bulk
B) hot
C) surface
D) none
Answer:
C) surface
Question 59.
The temperature of a system during evaporation
A) raises
B) remains same
C) falls
D) can’t say
Answer:
C) falls
Question 60.
Evaporation takes place at ………………. temperature
A) 100° C
B) 50° C
C) 28° C
D) any temperature
Answer:
D) any temperature
![]()
Question 61.
The phase change from liquid to gas that occurs at the surface of liquid at any temperature is called ………………………
A) freezing
B) melting
C) boiling
D) evaporation
Answer:
D) evaporation
Question 62.
If the surface of the liquid exposed to air the evaporation process takes place up to ………………….
A) full quantity of liquid evaporates
B) half of the quantity of liquid evaporates
C) \(\frac{1}{3}\)of the quantity of liquid evaporates
D) some quantity of die liquid evaporates
Answer:
A) full quantity of liquid evaporates
Question 63.
Rate of evaporation of a liquid depends on ………………….
A) surface area
B) temperature
C) humidity
D) all
Answer:
D) all
Question 64.
Statement I : The rate of evaporation slows down as the water vapour increases in the air
Statement II : At a given temperature air can hold only fixed amount of water.
A) Statement I is correct, II is incorrect
B) Statement I is incorrect, II is correct
C) Both statements are correct
D) Both statements are incorrect
Answer:
C) Both statements are correct
Question 65.
A fan produces a feeling of comfort during hot season because……………….
A) fan provides cool air
B) it increases humidity
C) of the evaporation of sweat
D) fan cools the surrounding air
Answer:
C) of the evaporation of sweat
Question 66.
During phase change of a substance ……………………
A) temperature remains constant
B) temperature increases
C) temperature decreases
D) temperature may increase or decrease
Answer:
A) temperature remains constant
Question 67.
Among the following phenomenon the evaporation process involved in ……………………..
a) wet clothes dry in the air
b) the floor becomes dry after washing with water
c) sprinkling of the spirit on the skin gives coldness
d) we feel cooling while getting sweat
A) a and b
B) a, b and c
C) a, b, c and d
D) only a
Answer:
C) a, b, c and d
![]()
Question 68.
The rate of evaporation of the liquid is faster in ……………………
A) a cup
B) saucer
C) test tube
D) can’t say
Answer:
B) saucer
Question 69.
The reverse process of evaporation takes place in ……………………….
A) boiling
B) melting
C) freezing
D) condensation
Answer:
D) condensation
Question 70.
The phase change from gas to liquid is called …………………..
A) evaporation1
B) condensation
C) boiling
D) freezing
Answer:
B) condensation
Question 71.
Which of the following is a warming process?
A) evaporatipn
B) condensation
C) boiling
D) all
Answer:
B) condensation
Question 72.
The amount of water vapour present in air is called ………………….
A) boiling
B) pressure
C) humidity
D) heat
Answer:
C) humidity
Question 73.
The water droplets condensed on the surfaces of window – panes, flowers, grass etc are known as ……………………..
A) humidity
B) dew
C) fog
D) none
Answer:
B) dew
Question 74.
Condensed and floating water droplets in the air is called …………………..
A) dew
B) fog
C) ice
D) cloud
Answer:
B) fog
![]()
Question 75.
Dew and fog form due to
A) evaporation
B) melting
C) boiling
D) condensation
Answer:
D) condensation
Question 76.
Water droplets form on the outer surface of the glass tumbler filled with cold water due to
A) evaporation
B) condensation
C) boiling
D) melting
Answer:
B) condensation
Question 77.
Which of the following condensation restricts visibility in the surrounding air?
A) dew
B) fog
C) both
D) none
Answer:
B) fog
Question 78.
‘Which of the following phenomena are reverse of each other ?
A) melting & boiling
B) melting & evaporation
C) boiling & evaporation
D) evaporation & condensation
Answer:
D) evaporation & condensation
Question 79.
A person feels warm when he stays . inside the bathroom after bath because of ……………….
A) evaporation of water
B) condensation of water vapour
C) both A and B
D) neither A nor B.
Answer:
B) condensation of water vapour
Question 80.
Statement I : During evaporation the temperature of the evaporating liquid decreases.
Statement II: During condensation the temperature of the surrounding air increases
A) Both I and II are true
B) I is true, II is false
C) I is false, II is true
D) Both I and II are false
Answer:
A) Both I and II are true
Question 81.
The sultryness in summer days is due to
A) Melting
B) Evaporation
C) Condensation
D) Humidity
Answer:
D) Humidity
![]()
Question 82.
The liquid phase changes to gaseous phase at a constant temperature at a given pressure is called ………………………..
A) evaporation
B) melting
C) boiling
D) condensation
Answer:
C) boiling
Question 83.
The temperature of the liquid while boiling
A) remains constant
B) increases
C) decreases
D) can’t say
Answer:
A) remains constant
Question 84.
If heat is supplied to water continuously, the temperature of water …………………
A) increases continuously
B) decreases
C) increases continuously till it reaches 100° C
D) can’t say
Answer:
C) increases continuously till it reaches 100° C
Question 85.
The heat energy required to change 1gm of liquid to gas at constant temperature is called …………………..
A) specific heat
B) latent heat of vapourization
C) latent heat of fusion
D) calorie
Answer:
B) latent heat of vapourization
Question 86.
The latent heat of vapourization of liquid of “m”gm when the heat energy of “Q” calories is supplied to change its state from liquid to gas is ………………
A) m/Q
B) Q/m
C) Q × m
D) mS Δt
Answer:
B) Q/m
Question 87.
C.G.S unit of latent heat of vapourization is ……………….
A) cal/gm
B) gm/cal
C) calorie
D) cal/gm-°C
Answer:
A) cal/gm
Question 88.
S.I unit of latent heat of vapourization is ………………………
A) kg/J
B) J/Kg
C) J/kg – K
D) Joule
Answer:
B) J/Kg
![]()
Question 89.
1 cal/gm = ………………..
A) 1 J/Kg
B) 4.186 J
C) 4.186 × 103 J/Kg
D) 4.186 × 10-3J/Kg
Answer:
C) 4.186 × 103 J/Kg
Question 90.
The boiling point of water at 1 atm is ………………
A) 100° C
B) 540 cal/gm
C) 373 K
D) both A and C
Answer:
D) both A and C
Question 91.
The latent heat of vapourization of water is ………………..
A) 100° C
B) 80 cal/gm
C) 540 cal/gm
D) 373 K
Answer:
C) 540 cal/gm
Question 92.
The process in which solid phase changes to liquid phase at a constant temperature is called
A) boiling
B) melting
C) condensation
D) freezing
Answer:
B) melting
Question 93.
The melting point of an ice at 1 atm is
A) 0° C
B) 273 K
C) 100° C
D) both A and B
Answer:
A) 0° C
Question 94.
When ice melts its temperature ?
A) remains constant
B) increases
C) decreases
D) cannot say
Answer:
A) remains constant
Question 95.
The heat energy required to convert 1 gm of solid completely into liquid at a constant temperature is called ……………….
A) specific heat
B) 1 calorie
C) latent heat of fusion
D) latent heat of vapourization
Answer:
C) latent heat of fusion
![]()
Question 96.
The latent heat of fusion of ice is …………………
A) 80 cal/gm
B) 540 cal/gm
C) 0°C
D) 100° C
Answer:
A) 80 cal/gm
Question 97.
S.I unit of latent heat of fusion is
A) cal/ gm
B) J/Kg
C) J/Kg – K
D) cal/Kg – K
Answer:
B) J/Kg
Question 98.
C.G.S unit of latent heat of fusion is
A) cal/gm
B) J/kg
C) J/kg – K
D) cal/g – ° C
Answer:
A) cal/gm
Question 99.
How much heat energy is required to convert 1 gm of ice to liquid
A) 540 cal
B) 80 cal
C) 100 cal
D) 373 cal
Answer:
B) 80 cal
Question 100.
The latent heat of fusion of a solid ‘ substance of mass “m” is L. The required amount of heat to change solid phase to liquid phase is ……………… cal.
A) Q = mL
B) Q = mSΔt
C) 80
D) 540
Answer:
A) Q = mL
Question 101.
The amount of heat needed to change from ice to water at 0° C is 80 cal. Find the mass of the substance taken.
A) 100 g
B) 1 g
C) 80 g
D) 20 g
Answer:
B) 1 g
Question 102.
What will be the amount of heat required to convert 50g of water at 100°C to steam at 100° C ?
A) 5400 cal
B) 2,700 cal
C) 400 cal
D) 4000 cal
Answer:
B) 2,700 cal
![]()
Question 103.
What amount of ice can be melted by 4000 cal of heat ?
A) 20 g
B) 30 g
C)40g
D)50g
Answer:
D)50g
Question 104.
Calculate the amount of heat required to convert 5 gm of ice at 0° C to water at 100° C.
A) 900 cal
B) 400 cal
C) 500 cal
D) 100 cal
Answer:
A) 900 cal
Question 105.
Calculate the amount of heat required to convert 50 gm of water at 30° C to water at 100° C.
A) 3, 500 cal
B) 1725 cal
C) 2, 700 cal
D) 4000 cal
Answer:
A) 3, 500 cal
Question 106.
Calculate the amount of heat required to convert 100 g of ice at – 5° C to 0° C.
A) 350 cal
B) 250 cal
C) 400 cal
D) 2,700 cal
Answer:
B) 250 cal
Question 107.
The process in which the substance in liquid phase changes to solid phase is called ………………….
A) melting
B) boiling
C) freezing
D) condensation
Answer:
C) freezing
Question 108.
Freezing of water takes place at ………………
A) 100° C, 1 atm
B) 0° C, 1 atm
C) 80° C, 1 atm
D) 373 K, 1 atm
Answer:
B) 0° C, 1 atm
Question 109.
Statement I : The internal energy of water decreases during freezing.
Statement II : The heat energy given to the ice is totally utilized in breaking the bonds between the water molecules during melting.
A) both statements are correct
B) both statements are incorrect
C) I is correct but II is incorrect
D) I is incorrect but II is correct
Answer:
A) both statements are correct
![]()
Question 110.
When water freezes to form ice, its volume will
A) decrease
B) increase
C) remains same
D) can’t day
Answer:
B) increase
Question 111.
Ice floats on water because
A) density of ice is more then water
B) density of ice is less than water
C) densities of ice and water are equal
D) none
Answer:
B) density of ice is less than water
The graph shows the values of temperature, when 1 g of ice is heated till it becomes water vapour. Observe the graph and answer the following questions. (112 – 125)
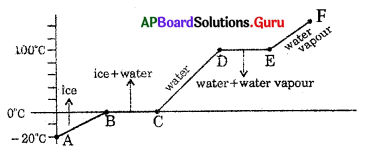
Question 112.
At what temperature ice converts into water ?
A) 0°C
B) -20° C
C) 100°C
D) 50°C
Answer:
A) 0°C
Question 113.
At what temperature water converts into water vapour
A) 0° C
B) -20° C
C) 100° C
D) 50° C
Answer:
C) 100° C
Question 114.
What is the range of temperature of liquid water ?
A) -20° C to 0° C
B) 0° C to 100° C
C) -20° C to 100° C
D) 100°C to >100° C
Answer:
B) 0° C to 100° C
Question 115.
What is the range of temperature of solid ice ?
A) -20° C to 0° C
B) 0°Ctol00°C
C) -20° C to 100° C
D) any range
Answer:
A) -20° C to 0° C
Question 116.
Which part of the graph represents change of state from ice to water ?
A) \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\)
B) \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
C) \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\)
D) \(\overline{\mathrm{DE}}\)
Answer:
A) \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\)
Question 117.
Which part of the graph represents change of state from water to water vapour ?
A) \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\)
B) \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
C) \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\)
D) \(\overline{\mathrm{DE}}\)
Answer:
D) \(\overline{\mathrm{DE}}\)
![]()
Question 118.
Which part of the graph represents only temperature change but not phase change?
A) \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
B) \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\)
C) \(\overline{\mathrm{EF}}\)
D) All
Answer:
D) All
Question 119.
Which part of the graph represents only phase change but not temperature change ?
A) \(\overline{\mathrm{BC}}\)
B) \(\overline{\mathrm{DE}}\)
C) \(\overline{\mathrm{EF}}\)
D) both A and B
Answer:
D) both A and B
Question 120.
The temperature of ice at B
A) -20° C
B) 0° C
C) 100° C
D) 110° C
Answer:
B) 0° C
Question 121.
The temperature of water vapour at E
A) 0° C
B) -20° C 1
C) 100°C
D) more than 100° C
Answer:
C) 100°C
Question 122.
The physical state and temperature of an ice at D
A) liquid, 0° C
B) liquid, 100° C
C) ice,0°C
D) gas, 100° C
Answer:
B) liquid, 100° C
Question 123.
What is the state of ice at E ?
A) solid
B) liquid
C) vapour
D) sublimation
Answer:
C) vapour
Question 124.
What is the value of Q at B ?
A) 10 cal
B) 90 cal
C) 190 cal
D) 730 cal
Answer:
A) 10 cal
![]()
Question 125.
The amount of heat energy absorbed by ice at E
A) 10 cal
B) 90 cal
C) 190 cal
D) 730 cal
Answer:
D) 730 cal
Question 126.
Statement A: Heat is absorbed by a substance during melting and boiling
Statement A : Heat is released from a substance duringfreezing and liquification
A) A is true, B is false
B) A is false, B is true
C) Both are true
D) Both are false
Answer:
C) Both are true
Question 127.
During phase change of a substance ……………………
A) temperature remains constant
B) temperature increases
C) temperature decreases
D) temperature may increase or decrease
Answer:
A) temperature remains constant
Question 128.
X g of water is heated from y° C to z° C. The quantity of heat required in calories …………………….
A) x. (\(\frac{y}{z}\))
B) x (\(\frac{z}{y}\))
C) x(z – y)
D) x (z + y)
Answer:
C) x(z – y)
Question 129.
The liquid which expands during its change of state into solid state is ………………….
A) water
B) alcohol
C) mercury
D) liquid wax
Answer:
A) water
Question 130.
At this temperature water changes into gaseous state, (in Kelvin)
A) 100
B) 373
C) 273
D) 173
Answer:
B) 373
Question 131.
The boiling point of water might be less at this place.
A) Hyderabad
B) Ooty
C) Mumbai
D) Chennai
Answer:
B) Ooty
![]()
Question 132.
The heat energy required to raise the temperature of 20 kg of water from 25° C to 75° C.
A) 103 cal
B) 104 cal
C) 105 cal
D) 106 cal
Answer:
D) 106 cal