AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable Ex 2.5 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 2nd Lesson Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.5
![]()
Question 1.
Solve the following equations.
i) [latex]\frac{n}{5}-\frac{5}{7}=\frac{2}{3}[/latex]
Solution:
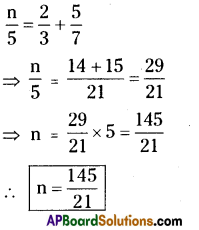
ii) [latex]\frac{x}{3}-\frac{x}{4}=14[/latex]
⇒ [latex]\frac{4 x-3 x}{12}[/latex] = 14
⇒ [latex]\frac{x}{12}[/latex] = 14
⇒ x = 12 × 14 = 168
∴ x = 168
iii) [latex]\frac{z}{2}+\frac{z}{3}-\frac{z}{6}=8[/latex]
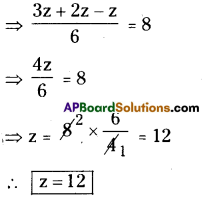
![]()
iv) [latex]\frac{2 p}{3}-\frac{p}{5}=11 \frac{2}{3}[/latex]
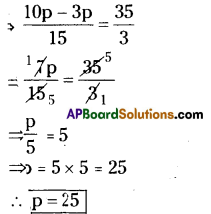
v) [latex]9 \frac{1}{4}=y-1 \frac{1}{3}[/latex]
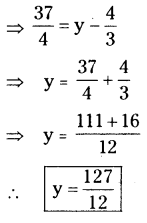
vi) [latex]\frac{x}{2}-\frac{4}{5}+\frac{x}{5}+\frac{3 x}{10}=\frac{1}{5}[/latex]
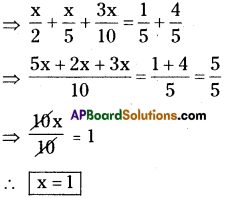
![]()
vii) [latex]\frac{x}{2}-\frac{1}{4}=\frac{x}{3}+\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
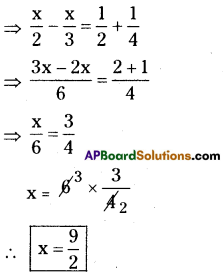
viii) [latex]\frac{2 x-3}{3 x+2}=\frac{-2}{3}[/latex]
⇒ 3(2x – 3) = – 2(3x + 2)
⇒ 6x – 9 = -6x – 4
⇒ 6x + 6x = -4 + 9
⇒ 12x = 5
∴ x = [latex]\frac{5}{12}[/latex]
ix) [latex]\frac{8 p-5}{7 p+1}=\frac{-2}{4}[/latex]
Solution:
⇒ [latex]\frac{8 p-5}{7 p+1}=\frac{-2}{4}[/latex]
⇒ 2(8p – 5) = – (7p + 1)
⇒ 16p – 10 = – 7p – 1
⇒ 16p + 7p = – 1 + 10
⇒ 23p = 9
∴ x = [latex]\frac{9}{23}[/latex]
![]()
x) [latex]\frac{7 y+2}{5}=\frac{6 y-5}{11}[/latex]
⇒ 11 (7y + 2) = 5 (6y-5)
⇒ 77y + 22 = 30y – 25
⇒ 77y – 30y = – 25 – 22
⇒ 47y = – 47
∴ y = [latex]\frac{-47}{47}[/latex]
∴ y = -1
xi) [latex]\frac{x+5}{6}-\frac{x+1}{9}=\frac{x+3}{4}[/latex]
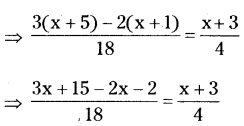
⇒ 4(x + 13) = 18 (x + 3)
⇒ 4x + 52 = 18x + 54
⇒ 4x – 18x = 54-52
⇒ – 14x = 2
⇒ x = [latex]\frac{2}{-1}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{-1}{7}[/latex]
∴ x = [latex]\frac{-1}{7}[/latex]
![]()
xii) [latex]\frac{3 t+1}{16}-\frac{2 t-3}{7}=\frac{t+3}{8}+\frac{3 t-1}{14}[/latex]
Solution:
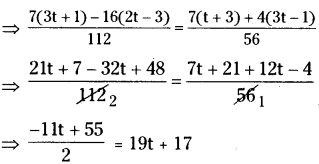
⇒ -11t + 55 = 2(19t + 17) = 38t + 34
⇒ -11t – 38t = 34 – 55
⇒ -49t = – 21
⇒ [latex]\frac{-21}{-49}[/latex] = [latex]\frac{3}{7}[/latex]
∴ t = [latex]\frac{3}{7}[/latex]
Question 2.
What number is that of which the third part exceeds the fifth part by 4?
Solution:
Let the number be ‘x’ say.
[latex]\frac{1}{3}[/latex] rd of a number = [latex]\frac{1}{3}[/latex] x x = [latex]\frac{x}{3}[/latex]
[latex]\frac{3}{7}[/latex] th of a number = [latex]\frac{1}{5}[/latex] x x = [latex]\frac{x}{5}[/latex]
According to the sum
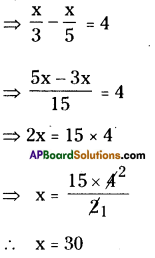
∴ The required number is 30.
![]()
Question 3.
The difference between two positive integers is 36. The quotient when one integer is
divided by other is 4. Find the integers.
(Hint: If one number is ‘X’, then the other number is ‘x – 36’)
Solution:
Let the two positive numbers be x, (x – 36) say.
If one number is divided by second tten the quotient is 4.
∴ [latex]\frac{x}{x-36}=4[/latex]
⇒ x = 4(x – 36) = 4x – 144
⇒ 4x – x = 144
3x = 144
x = 48
∴ x – 36 = 48 – 36 = 12
∴ The required two positive intgers are 48, 12.
Question 4.
The numerator of a fraction is 4 less than the denominator. If 1 is added to both its
numerator and denominator, it becomes 1/2 . Find the fraction.
Solution:
Let the denominator of a fractin be x.
The numerator of a fraction is 4 less than the denominator.
∴ The numerator = x – 4
∴ Fraction [latex]\frac{x-4}{x}[/latex]
If ‘1’ is added to both, its numerator and denominator, it becomes [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
∴ [latex]\frac{1+x-4}{1+x}=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
2 + 2x – 8 = 1 + x
2x – x = 1 + 6 = 7
x = 7
∴ The denominator = 7
The numerator = 7 – 4 = 3
∴ Fraction = [latex]\frac{3}{7}[/latex]
![]()
Question 5.
Find three consecutive numbers such that if they are divided by 10, 17, and 26 respectively,
the sum of their quotients will be 10.
(Hint: Let the consecutive numbers = x, x+ 1, x+ 2, then [latex]\frac{x}{10}+\frac{x+1}{17}+\frac{x+2}{26}=10[/latex])
Solution:
Let the three consecutive numbers be assume that x, (x + 1), (x + 2) respectively.
Given that x, (x + 1), (x + 2) are divided by 10, 17, 26 respectively, the sum of the quotients is 10. Then
⇒ [latex]\frac{x}{10}+\frac{x+1}{17}+\frac{x+2}{26}=10[/latex]
⇒ [latex]\frac{x \times 221+130(x+1)+85(x+2)}{2210}=10[/latex]
⇒ 221x + 130x + 85x + 130 + 170 = 22,100
⇒ 436x + 300 = 22,100
⇒ 436x = 22,100 – 300
⇒ 436x = 21,800
⇒ [latex]\frac{21800}{436}[/latex]
∴ x = 50
∴ The required three consecutive num-bers are x = 50
x + 1 =50+ 1 = 51
x + 2 = 50 + 2 = 52
Question 6.
In class of 40 pupils the number of girls is three-fifths of the number of boys. Find the
number of boys in the class.
Solution:
Let the number of boys = x say.
Total number of students = 40
Number of girls = [latex]\frac{3}{5}[/latex] × x = [latex]\frac{3x}{5}[/latex]
According to the sum 3x
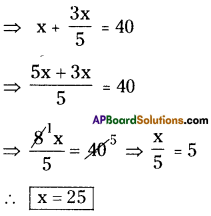
∴ x = 25
∴ Number of boys in the class room = 25
![]()
Question 7.
After 15 years , Mary’s age will be four times of her present age. Find her present age.
Solution:
Let the present age of Mary = x years say.
After 15 years Mary’s age = (x + 15) years
According to the sum
(x + 15) = 4 x x
⇒ x + 15 = 4x
⇒ 4x – x =15
⇒ 3x = 15
⇒ x = 5
∴ The present age of Mary = 5 years.
Question 8.
Aravind has a kiddy bank. It is full of one-rupee and fifty paise coins. It contains 3 times
as many fifty paise coins as one rupee coins. The total amount of the money in the bank is
₹ 35. How many coins of each kind are there in the bank?
Solution:
Number of 1 rupee coins = x say.
Number of 50 – paise coins = 3 x x = 3x
The value of total coins = [latex]\frac{3x}{2}[/latex] + x
[∵50 paisa coins of 3x = ₹[latex]\frac{3x}{2}[/latex]
According to the sum
⇒ [latex]\frac{3x}{2}[/latex] + x = 35
⇒ [latex]\frac{3 x+2 x}{2}[/latex] = 35
⇒ 5x = 2 × 35
⇒ x = 2 × [latex]\frac{35}{5}[/latex]
∴ x = 14
∴ Number of 1 rupee coins = 14
Number of 50 paisa coins = 3 × x = 3 × 14 = 42
![]()
Question 9.
A and B together can finish a piece of work in 12 days. If ‘A’ alone can finish the same work in 20days , in how many days B alone can finish it?
Solution:
A, B can do a piece of work in 12 days.
(A + B)’s 1 day work = [latex]\frac{1}{12}[/latex] th part.
A can complete the same work in 20 days.
Then his one day work = [latex]\frac{1}{20}[/latex]
B’s one day work = (A+B)’s 1 day work – A’s 1 day work
[latex]=\frac{1}{12}-\frac{1}{20}=\frac{5-3}{60}=\frac{2}{60}=\frac{1}{30}[/latex]
∴ Number of days to take B to com¬plete the whole work = 30.
Question 10.
If a train runs at 40 kmph it reaches its destination late by 11 minutes . But if it runs at 50 kmph it is late by 5 minutes only. Find the distance to be covered by the train.
Solution:
Let the distance to be reached = x km say. Time taken to travel ‘x’ km with speed x
40 km/hr = [latex]\frac{x}{40}[/latex] hr.
Time taken to travel ‘x’ km with speed 50 km/hr = [latex]\frac{x}{50}[/latex] hr.
According to the sum the difference between the times

∴ The required distance to be trav¬elled by a train = 20 kms‘.
![]()
Question 11.
One fourth of a herd of deer has gone to the forest. One third of the total number is
grazing in a field and remaining 15 are drinking water on the bank of a river. Find the total
number of deer.
Solution:
Number of deer = x say.
Number of deer has gone to the forest
= [latex]\frac{1}{4}[/latex] × x = [latex]\frac{x}{4}[/latex]
Number of deer grazing in the field
= [latex]\frac{1}{3}[/latex] × x =[latex]\frac{x}{3}[/latex]
Number of remaining deer =15
According to the sum
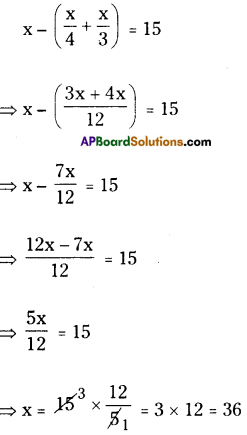
∴ x = 36
∴ The total number of deer = 36
Question 12.
By selling a radio for ₹903, a shop keeper gains 5%. Find the cost price of the radio.
Solution:
The selling price of a radio = ₹ 903
Profit % = 5%
C.P = ?
C.P = [latex]\frac{\mathrm{S.P} \times 100}{(100+\mathrm{g})}[/latex]
= [latex]\frac{903 \times 100}{(100+5)}[/latex]
= [latex]\frac{903\times 100}{105}[/latex]
C.P. = 8.6 × 100 = 860
∴ The cost price of the radio = ₹ 860
![]()
Question 13.
Sekhar gives a quarter of his sweets to Renu and then gives 5 sweets to Raji. He has 7 sweets left. How many did he have to start with?
Solution:
Number of sweets with Sekhar = x say.
Number of sweets given to Renu
= [latex]\frac{1}{4}[/latex] × x = [latex]\frac{x}{4}[/latex]
Number of sweets given to Raji = 5
Till he has 7 sweets left.
x – ( [latex]\frac{x}{4}[/latex] + 5) = 7
⇒ x – [latex]\frac{x}{4}[/latex] – 5 = 7
⇒ x – [latex]\frac{x}{4}[/latex] = 7 + 5 = 12
⇒ [latex]\frac{4 x-x}{4}[/latex] = 12
⇒ [latex]\frac{3x}{4}[/latex] = 12
⇒ x = 12 × [latex]\frac{4}{3}[/latex] = 16
∴ x = 4 × 4 = 16
∴ Number of sweets with Sekhar at the beginning = 16