AP State Syllabus AP Board 8th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Rational Numbers Ex 1.1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 8th Class Maths Solutions 1st Lesson Rational Numbers Exercise 1.1
![]()
Question 1.
Name the properly Involved in the following examples.
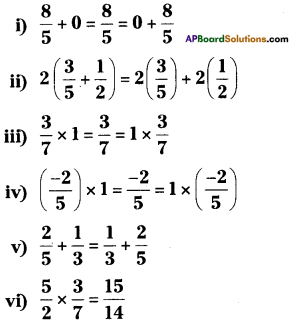
vii) 7a + (-7) = 0
viii) x + [latex]\frac{1}{x}[/latex] = 1(x ≠ 0)
ix) (2 x x) + (2 x 6) = 2 x (x + 6)
Solution:
i) Additive identity
ii) Distributive law
iii) Multiplicative identity
iv) Multiplicative identity
v) Commutative law of addition
vi) Closure law in multiplication
vii) Additive inverse
viii) Multiplicative inverse
ix) Distributive
![]()
Question 2.
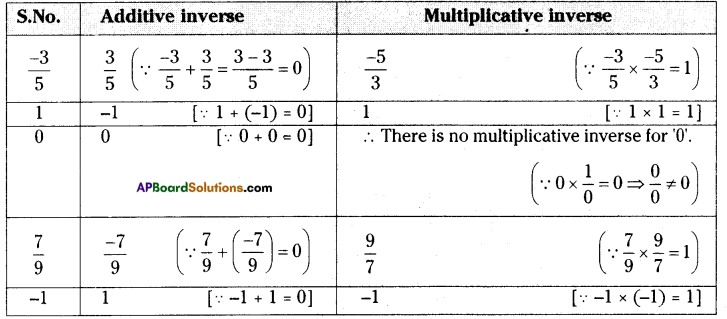
Write the additive and the multiplicative inverses of the following.
i) [latex]\frac{-3}{5}[/latex]
ii) 1
iii) 0
iv) [latex]\frac{7}{9}[/latex]
v) -1
Solution:
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks
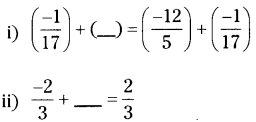

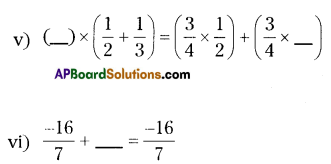
Solution:
i) [latex]\left(\frac{-12}{5}\right)[/latex]
ii) [latex]\left(\frac{4}{3}\right)[/latex]
iii) [latex]\left(\frac{9}{11}\right)[/latex]
iv) [latex]\left(\frac{6}{7}\right)[/latex]
v) [latex]\left(\frac{3}{4}, \frac{1}{3}\right)[/latex]
vi) 0
![]()
Question 4.
Multiply [latex]\frac{2}{11}[/latex] by the reciprocal of [latex]\frac{-5}{14}[/latex]
Solution:
The reciprocal of [latex]\frac{-5}{14}[/latex] is [latex]\frac{-14}{5}[/latex]
( ∵ [latex]\left(\frac{-5}{14}\right) \times\left(\frac{-14}{5}\right)=1[/latex] )
∴ The product of [latex]\frac{2}{11}[/latex] and [latex]\frac{-14}{5}[/latex] is
[latex]\frac{2}{11} \times\left(\frac{-14}{5}\right)=\frac{-28}{55}[/latex]
Question 5.
Which properties can be used computing [latex]\frac{2}{5} \times\left(5 \times \frac{7}{6}\right)+\frac{1}{3} \times\left(3 \times \frac{4}{11}\right)[/latex]
Solution:
The following properties are involved in the product of
[latex]\frac{2}{5} \times\left(5 \times \frac{7}{6}\right)+\frac{1}{3} \times\left(3 \times \frac{4}{11}\right)[/latex]
i) Multiplicative associative property.
ii) Multiplicative inverse.
iii) Multiplicative identity.
iv) Closure with addition
Question 6.
Verify the following
[latex]\left(\frac{5}{4}+\frac{-1}{2}\right)+\frac{-3}{2}=\frac{5}{4}+\left(\frac{-1}{2}+\frac{-3}{2}\right)[/latex]
Solution:
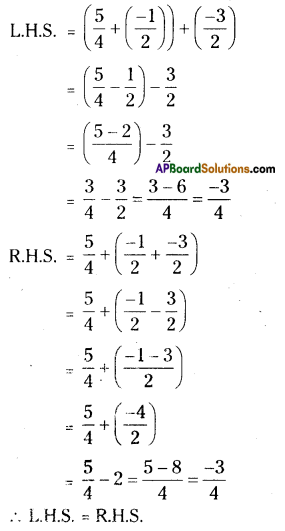
![]()
Question 7.
Evaluate [latex]\frac{3}{5}+\frac{7}{3}+\left(\frac{-2}{5}\right)+\left(\frac{-2}{3}\right)[/latex] after rearrangement.
Solution:
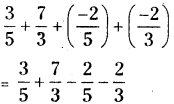
Let x = [latex]1.2 \overline{4}[/latex]
⇒ x = 1.244……. …………………(1)
Here periodicity of equation (1) is 1. So
it should be multiplied by 10 on both
sides.
⇒ 10 x x = 10 x 1.244
10x = 12.44 …………..(2)

![]()
Question 8.
Subtract
(i) [latex]\frac{3}{4}[/latex] from [latex]\frac{1}{3}[/latex]
(ii) [latex]\frac{-32}{13}[/latex] from 2
(iii) -7 from [latex]\frac{-4}{7}[/latex]
Solution:
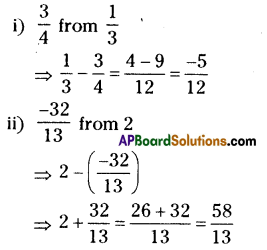
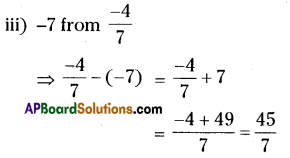
Question 9.
What numbers should be added to [latex]\frac{-5}{8}[/latex] so as to get [latex]\frac{-3}{2}[/latex] ?
Solution:
Let the number to be add ‘x’ say
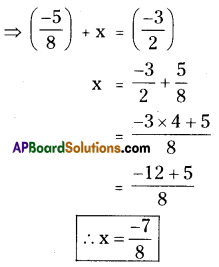
∴ [latex]\frac{-7}{8}[/latex] should be added to [latex]\frac{-5}{8}[/latex] then we will get [latex]\frac{-3}{2}[/latex]
Question 10.
The sum of two rational numbers is 8 If one of the numbers is [latex]\frac{-5}{6}[/latex] find the other.
Let the second number be ‘x’ say
⇒ [latex]x+\left(\frac{-5}{6}\right)=8[/latex]
⇒[latex]8+\frac{5}{6}=\frac{48+5}{6}=\frac{53}{6}[/latex]
∴ The other number (x) = [latex]\frac{53}{6}[/latex]
Question 11.
Is subtraction associative in rational numbers? Explain with an example.
Solution:
Let [latex]\frac{1}{2}, \frac{3}{4}, \frac{-5}{4}[/latex] are any 3 rational numbers.
Associative property under subtraction
a – (b – c) = (a – b) – c
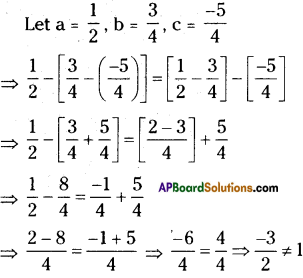
∴ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ a – (b – c) ≠ (a – b) – c
∴ Subtraction is not an associative in rational numbers.
![]()
Question 12.
Verify that – (-x) = x for
(i) x = [latex]\frac{2}{15}[/latex]
(ii) x = [latex]\frac{-13}{15}[/latex]
Solution:
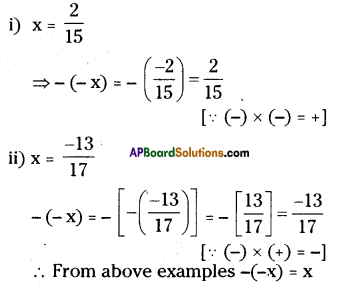
Question 13.
Write-
(i) The set of numbers which do not have any additive identity
(ii) The rational number that does not have any reciprocal
(iii) The reciprocal of a negative rational number.
Solution:
i) Set of natural numbers ’N’ doesn’t possesses the number ‘0’.
ii) The rational number ‘0’ has no multiplicative inverse.
[ ∵ 1/0 is not defined]
iii) The reciprocal of a negative rational number is a negative rational number.
Ex : Reciprocal of [latex]\frac{-2}{5}=\frac{-5}{2}[/latex]