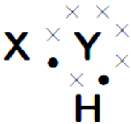AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Chemistry Solutions Chapter 14 Carbon and its Compounds Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Chemistry Solutions 14th Lesson Carbon and its Compounds
10th Class Chemistry 14th Lesson Carbon and its Compounds Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
Name the simplest hydrocarbon. (AS1)
Answer:
The simplest hydrocarbon is alkane called Methane (CH4). It’s an aliphatic, saturated compound of Hydrogen and Carbon.
Question 2.
What are the general molecular formulae of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes? (AS1)
Answer:
General molecular formula of alkane is CnH2n+2.
General molecular formula of alkene is CnH2n.
General molecular formula of alkyne is CnH2n-2.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the carboxylic acid used as a preservative. (AS1)
Answer:
Vinegar with chemical formula CH3COOH is used as preservative. 5 – 8% of solution of acetic acid or ethanoic acid in water is called vinegar and it is used widely as preservative in pickles.
Question 4.
Name the product other than water formed on burning of ethanol in air. (AS1)
Answer:
C2H3OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O + Energy
So, the product other than water formed on burning of ethanol in air is carbon dioxide (CO2).
Question 5.
Give the IUPAC name of the following compounds. If more than one compound is possible, name all of them. (AS1)
i) An aldehyde derived from ethane.
ii) A ketone derived from butane.
iii) A chloride derived from propane.
iv) An alcohol derived from pentane.
Answer:
i) An aldehyde derived from ethane is ethanal. Its formula is CH3CHO.
ii) A ketone derived from butane. Its IUPAC name is Butanone.
Its chemical formula is CH3COCH2CH3
It is also known as methyl ethyl ketone. (Its general name)
iii) A chloride derived from propane.
A) 1-Chloro propane. Its formula is CH3CH2CH2Cl.

iv) An alcohol derived from pentane :
A) 1-Pentanol. Its formula is CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH.
B) 2-Pentanol. Its formula is CH3CHOH CH2CH2CH3
C) 3-Pentanol. Its formula is CH3CH2 CHOH CH2CH3
Question 6.
A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding ; can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used? (AS1)
Answer:
- Ethyne when burnt in the presence of oxygen gives enough heat that can be used for welding.
- Whereas if it is burnt in air which contains nitrogen, CO2 and other inactive gaseous contents, sufficient oxygen is not available for burning ethyne to give the required heat.
Question 7.
Explain with the help of a chemical equation, how an addition reaction is used in vegetable ghee industry. (AS1)
Answer:
- The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydrocarbon is called hydrogenation. The process of hydrogenation takes place in the presence of nickel or palladium metals as catalyst.
- The process of hydrogenation has an important industrial application. It is used to prepare vegetable ghee (or vanaspati ghee) from vegetable oils.
- Vegetable oils are unsaturated fats having double bonds between some of their carbon atoms.
- When a vegetable oil (like groundnut oil) is heated with hydrogen in the presence of finely divided nickel as catalyst, a saturated oil called vegetable ghee (or vanaspati ghee) is formed. This a reaction is called hydrogenation of oils and it can be represented as follows.
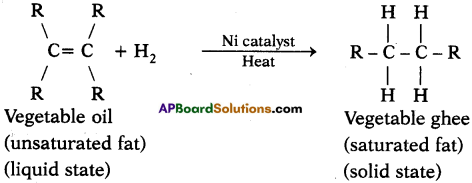
Here vegetable oil is a liquid whereas vegetable ghee is a solid (or a semi solid).
Question 8.
a) What are the various possible structural formulae of a compound having molecular formula C3H6O? (AS1)
b) Give the IUPAC names of the above possible compounds and represent them in structures. (AS1)
c) What is the similarity in these compounds? (AS1)
Answer:
a) They are CH3COCH3and CH3 CH2 CHO
b) i) The IUPAC name of CH3COCH3 is propanone.
ii) The IUPAC name of CH3 CH2 CHO is propanal.
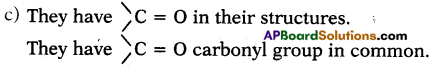
Question 9.
Name the simplest ketone apfl write its molecular formula. (AS1)
Answer:
Acetone is the simplest ketone. Its molecular formula is CH3COCH3 Its IUPAC name is propanone.
Question 10.
What do we call the Self linking property of carbon? (AS1)
Answer:
The property of self combination (or linking) of carbon atoms to form long chains is useful to us because it gives rise to an extremely large number of carbon compounds (or organic compounds). This is known as catenation.
![]()
Question 11.
Name the compound formed by heating ethanol at 443 K with excess of cone. H2SO4. (AS1)
(OR)
What is the compound formed when ethyhalcohol (Ethanol) is dehydrated ? Write the chemical equation of the reaction.
Answer:
1. When ethanol is heated with excess of cone. H2SO4 at 443 K (170° C), it gets dehydrated to form ethene (which is an unsaturated hydrocarbon).
2. During dehydration of ethanol molecules (CH3 – CH2OH), H from the CH3 group and OH from CH2OH group are removed in the form of a water molecule (H2O) regulating in the formation of this molecule (CH2 = CH2).
3. In this reaction concentrated sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent.
Question 12.
Give an example for esterification reaction. (AS1)
Answer:
The reaction between carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of cone. H2SO4 to form a sweet odoured substance, ester with the functional group
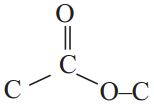
is called esterification.
Ex: Ethanoic acid (carboxylic acid) reacts with Ethanol (alcohol) and forms ethyl acetate.
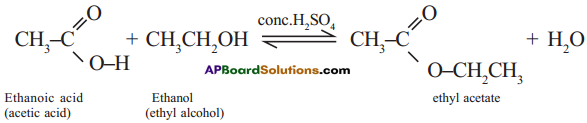
Question 13.
Name the product obtained when ethanol is oxidized by either chromic anhydride or alkaline potassium permanganate. (AS1)
(OR)
If the ethanol is oxidized by either chromic anhydride or alkaline potassium permanganate, what is the product obtained from them?
Answer:
Ethanol (Ethyl alcohol) undergoes oxidation to form the product of Acetaldehyde and finally Acetic acid.
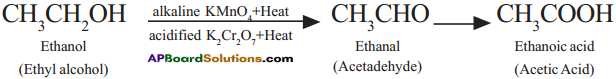
Question 14.
Write the chemical equation representing the reaction of preparation of ethanol from ethane. (AS1)
Answer:
1. Ethane in the absence of air on heating forms ethene
![]()
2. Then Ethanol is prepared on large scale from ethene by the addition of water vapour to it in the presence of catalyst like P2O5, Tungsten oxide at high pressure and temperature.

Question 15.
Write the IUPAC name of the next homologous of CH3OHCH2CH3. (AS1)
Answer:
The IUPAC name of the next homologous of CH3OHCH2CH3 is HO-CH3CH2CH2CH3 1 – butanol.
Question 16.
Define homologous series of carbon compounds. Mention any two characteristics of homologous series. (AS1)
Answer:
1. The series of carbon compounds in which two successive compounds differ by – CH2 unit is called homologous series.
Ex : 1) CH4, C2H6, C3H8, ………………..
2) CH3OH, C2H5OH, C3H7OH, ………………..
2. If we observe above series of compounds, we will notice that each compound in the series differs by – CH2 unit by its successive compound.
3. Characteristics of homologous series :
i) They have one general formula.
Ex : alkanes (CnH2n+2), alkynes (CnH2n-2), alcohols (CnH2n+1) OH, etc.
ii) Successive compounds in the series possess a difference of (-CH2) unit.
iii) They have similar chemical properties.
![]()
Question 17.
Give the names of functional groups
(i) – CHO
(ii) – C = O. (AS1)
(OR)
Write the names of the given functional groups
(i) – CHO
(ii) – C = O
Answer:
i) – CHO → aldehyde
ii) – C = O → ketone
Question 18.
Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding? (AS1)
Answer:
Since carbon atoms can achieve the inert gas electron arrangements only by the sharings of electrons, therefore, carbon always forms covalent bonds.
Question 19.
Allotropy is a property shown by which class substance: elements, compounds or mixtures? Explain allotropy with suitable examples. (AS1)
Answer:
1. Allotropy is a property shown by the elements.
2. The property of an element to exist in two or more physical forms having more or less similar chemical properties but different physical properties is called allotropy.
3. The different forms of the element are called allotropes and are formed due to the difference in the arrangement of atoms.
4. Example for allotropes : Allotropes of carbon.
Allotropes of carbon are classified into two types. They are
1) Amorphous forms,
2) Crystalline forms.
5) Amorphous forms of carbon:
Coal, coke, wood, charcoal, animal charcoal, lampblack, gas carbon, petroleum coke, sugar charcoal.
6) Crystalline forms of carbon :
Diamond, graphite and buckminsterfullerene.
Question 20.
Explain how sodium ethoxide is obtained from ethanol. Give chemical equations. (AS1)
Answer:
As ethanol is similar to water molecule (H2O) with C2H5 group in place of hydrogen, it reacts with metallic sodium to liberate hydrogen and form sodium ethoxide.
![]()
Question 21.
Describe with chemical equation how ethanoic acid may be obtained from ethanol. (AS1)
Answer:
Ethyl alcohol (Ethanol) undergoes oxidation to form the product Acetaldehyde and finally acetic acid (Ethanoic acid).
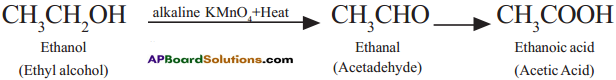
Question 22.
Explain the cleansing action of soap. (AS1)
Answer:
When a dirty cloth is put in water containing dissolved soap, the hydrocarbon ends of the soap molecules in the micelle attach to the oil or grease particles present on the surface of dirty clothes.
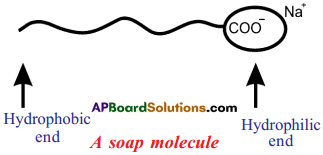
Question 24.
Explain the structure of graphite in terms of bonding and give one property based on this structure. (AS1)
(OR)
Why does graphite act as lubricant?
Answer:
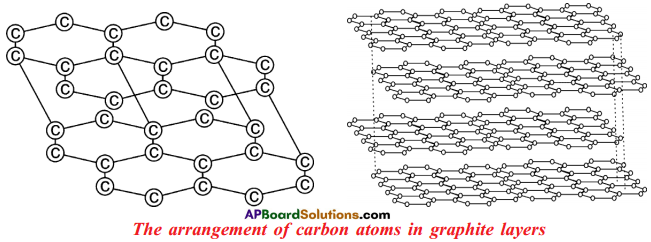
- Graphite forms a two dimensional layer structure with C – C bonds within the layers.
- There are relatively weak interactions between the layers.
- In the layer structure, the carbon atoms are in a trigonal planar environment.
- This is consistent with each carbon atom in sp² hybridisation.
- Interactions between the sp² orbitals (overlaps) lead to the formation of C – C bonds.
- Each carbon atom is with one unhybridised ‘p’ orbital.
- The unhybridised ‘p’ orbitals interact to form a π system that is delocalised over the whole layer.
- The interactions known as London dispersion forces between the layers which are separated by a distance of 3.35 A° are weakened by the presence of water molecules so that it is easy to cleave graphite.
- For this reason graphite is used as lubricant and as the lead in pencils.
Question 25.
Name the acid present in vinegar. (AS1)
Answer:
1) The acid present in vinegar is Ethenoic acid or acetic acid (CH3COOH).
2) 5 – 8% solution of acetic acid in water is called vinegar.
Question 26.
What happens when a small piece of sodium is dropped into ethanol? (AS2)
Answer:
Ethanol reacts with sodium to liberate hydrogen and form sodium ethoxide.
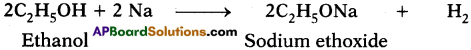
Question 27.
Two carbon compounds A and B have molecular formula C3H8 and C3H6 respectively. Which one of the two is most likely to show addition? Justify your answer. (AS2)
Answer:
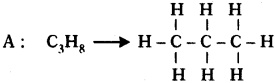
• It is a saturated hydrocarbon. It shows substitution reaction.
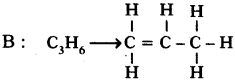
• This is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Hence it shows addition to become saturated. During the reactions, addition of reagent takes place at the double bonded carbon atoms.
Justification :
In the following, C3H6 undergoes addition reaction.

Question 28.
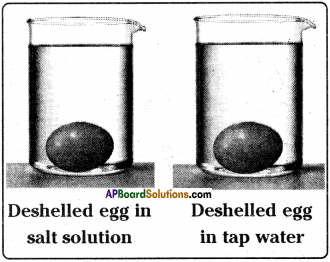
Suggest a test to find the hardness of water and explain the procedure. (AS3)
(OR)
How do you test whether a given water sample is soft or hard?
Answer:
- Take about 10 ml hard water (well water or hand pump water) in a test tube.
- Add five drops of soap solution to it.
- Shake the test tube vigorously.
- We see that no lather is formed at first.
- Only a dirty white curd like scum is formed on the surface of water.
- From this, we conclude that soap does not form lather easily with hard water.
- We have to add much more soap to obtain lather with hard water.
Question 29.
Suggest a chemical test to distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid and explain the procedure. (AS3)
Answer:
- Take ethanol and ethanoic acid in two different test tubes.
- Add nearly 18 g of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) to each test tube.
- Lots and lots of bubbles and foam will be observed from the test tube containing ethanoic acid. This is due to release of CO2.
NaHCO3 + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 - Ethanol will not react with sodium bicarbonate and thus we won’t observe any change in the test tube containing ethanol.
Thus we can separate ethanol from ethanoic acid.
![]()
Question 30.
An organic compound ‘X’ with a molecular formula C2H6O undergoes oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 and forms the compound ‘Y’, that has molecular formula C2H4O2. (AS3)
i) Identify ‘X’ and ‘Y’.
Answer:
X is Ethanol is CH3CH2OH and T is Ethanoic acid, i.e., CH3COOH.
ii) Write your observation regarding the product when the compound X is made to react with compound IT which is used as a preservative for pickles.
Answer:
Ethyl alcohol undergoes oxidation to form the product Acetaldehyde and finally Acetic acid.
![]()
Here CH3COOH is used as preservative for pickles.
When X reacts with Y it forms ethyl acetate and water which is called esterification reaction.
CH3COOH + C2H5OH → CH3COOC2H5 + H2O
Question 31.
Prepare models of methane, ethane, ethene and ethyne molecules using clay balls and matchsticks. (AS4)
Answer:
Stick and ball model :
1) Methane (CH4) :
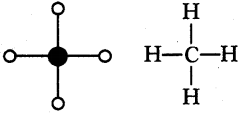
2) Ethane (C2H6):
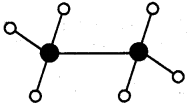
3) Ethene (C2H4):

4) Ethyne (C2H2)
![]()
Question 32.
Collect information about artificial ripening of fruits by ethylene. (AS4)
Answer:
- Seasonal fruits like mango, banana, papaya, sapota and custard apple are often harvested in nature. But due to unripe condition they are subsequently allowed to ripen by natural release of ripening harmone (ethylene) from the fruit.
- However, natural ripening in some fruits is a slow process, which leads to high weight loss, desiccation of fruits and under ripening. With the rapid development of fruit trade, artificial ripening has become essential and the methods practised earlier by small traders are smoking and calcium carbide treatment.
- Fruits ripened with calcium carbide though seem attractive and colourful are inferior in taste, flavour and spoil faster.
- Government of India has banned the use of calcium carbide for artificial ripening of fruits under PFA Act 8-44AA, 1954.
- Artificial ripening of fruits by using the above steps spoils the health of consumers, so we should not use such type of fruits.
- Government has to take serious action on the fruit sellers who are practising the above said methods.
Question 33.
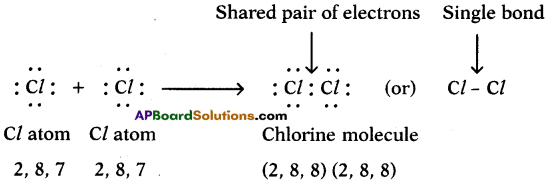
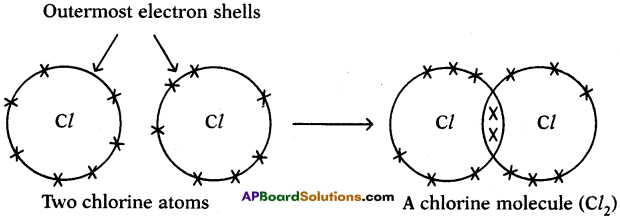
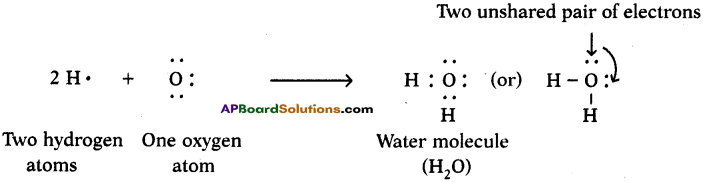
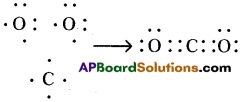
Draw the electronic dot structure of ethane molecule (C2H6). (AS6)
Answer:
C2H6:
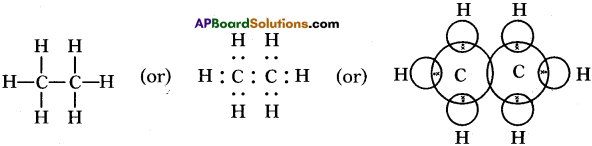
Question 34.
How do you appreciate the role of esters in everyday life? (AS6)
Answer:
- Esters are usually volatile liquids having sweet or pleasant smell.
- They are also said to have fruity smell.
- Esters are used in making artificial perfumes.
- This is because of the fact that most of the esters have a pleasant smell.
- Esters are also used as flavouring agents.
- This means that esters are used in making artificial flavours and essences used in ice-cream, sweets and cool drinks.
- The alkaline hydrolysis of esters is known as saponification (Soap making).
- That’s why we can appreciate the role of esters in everyday life.
Question 35.
How do you condemn the use of alcohol as a social practice? (AS7)
Answer:
- Consumption of alcohol in the form of beverages is harmful to health.
- It causes severe damage to blood circulation system.
- Addiction to alcohol drinking leads to heart diseases and damages the liver.
- It also causes ulcers in small intestines due to increased acidity and damages the digestive system.
- Alcohol which is consumed in raw form under the names liquor, gudumba which is more harmful to health due to adulteration.
- Alcohol mixed with pyridine is called denatured spirit. Consumption of denatured spirit causes blindness and death.
- Hence use of alcohol is a social evil which harms the society.
![]()
Question 36.
An organic compound with molecular formula C2H4O2 produces brisk effervescence on addition of sodium carbonate/bicarbonate.
Answer the following :
a) Identify the organic compound. (AS1)
Answer:
The organic compound is Ethanoic acid (CH3COOH).
b) Write the chemical equation for the above reaction. (AS1)
Answer:

c) Name the gas evolved. (AS2)
Answer:
CO2
d) How will you test the gas evolved? (AS3)
Answer:
1) Pass the evolved gas through lime water in a test tube.
2) We will find that lime water turns milky.
3) Only CO2 gas can turn lime water milky.
e) List two important uses of the above compound. (AS1)
Answer:
1) Dilute ethanoic acid (CH3COOH) is used as a food preservative in the preparation of pickles and sauces.
2) Ethanoic acid is used for making cellulose acetate which is an important artificial fibre.
Question 37.
1 ml glacial acetic acid and 1 m/of ethanol are mixed together in, a test tube. Few drops of concentrate sulphuric acid is added in the mixture are warmed in a water bath for 5 min.
Answer the following:
a) Name the resultant compound formed.
b) Represent the above change by a chemical equation.
c) What term is given to such a reaction?
d) What are the special characteristics of the compound formed?
Answer:
a) Ethyl acetate.
![]()
c) Esterification
d) It has fruity smell or pleasant smell.
Fill In The Blanks
1. Carbon compounds containing double and triple bonds are called ………………….
2. A compound which is basic constituent of many cough syrups ………………………
3. Very dilute solution of ethanoic acid is ………………..
4. A sweet odour substance formed by the reaction of an alcohol and a carboxylic acid is ………………
5. When sodium metal is dropped in ethanol …………………. gas will be released.
6. The functional group present in methanol is …………………….
7. IUPAC name of alkene containing 3 carbon atoms is ………………….
8. The first member of homologous series among alkynes is ……………………
9. The product that is formed by dehydration of ethanol in cone, sulphuric acid is ………………….
10. Number of single covalent bonds in ammonia are ………………..
11. Type of reactions shown by alkanes is ……………….
Answer:
- unsaturated compounds
- ethanol
- vinegar
- ester
- H2
- – OH (Alcohol)
- propene
- ethyne (C2H2)
- ethene (C2H4)
- 3
- substitutional
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the four test tubes containing the following chemicals shows the brisk effervescence when dilute acetic acid was added to them?
i) KOH
ii) NaHCO3
iii) K2CO3
iv) NaCl
A) i & ii
B) ii & iii
C) i & iv
D) ii & iv
Answer:
B) ii & iii
2. Which of the following solution of acetic acid in water can be used as preservative?
A) 5-10%
B) 10-15%
C) 15-20%
D) 100%
Answer:
A) 5-10%
![]()
3. The suffix used for naming an aldehyde is
A) – ol
B) – al
C) – one
D) – ene
Answer:
B) – al
4. Acetic acid, when dissolved in water, it dissociates into ions reversibly because it is a
A) weak acid
B) strong acid
C) weak base
D) strong base
Answer:
A) weak acid
5. Which one of the following hydrocarbons can show isomerism?
A) C2H4
B) C2H6
C) C3H8
D) C4H10
Answer:
D) C4H10
6. Combustion of hydrocarbon is generally accompanied by the evolution of
A) Heat
B) Light
C) Both heat and light
D) Electric current
Answer:
C) Both heat and light
7. 2 ml of ethanoic acid was taken in each of the three test tubes A, B and C and 2 ml, 4 ml and 8 ml water was added to them respectively. A clear solution is obtained in:
A) Test tube A only
B) Test tubes A & B only
C) Test tubes B and C only
D) All the test tubes
Answer:
D) All the test tubes
![]()
8. If 2 ml of acetic acid was added slowly in drops to 5 ml of water then we will notice
A) The acid forms a separate layer on the top of water
B) Water forms a separate layer on the top of the acid
C) Formation of a clear and homogenous solution
D) Formation of a pink and clear solution
Answer:
C) Formation of a clear and homogenous solution
9. A few drops of ethanoic acid were added to solid sodium carbonate. The possible results of the reactions are
A) A hissing sound was evolved
B) Brown fumes evolved
C) Brisk effervescence occurred
D) A pungent smelling gas evolved
Answer:
C) Brisk effervescence occurred
10. When acetic acid reacts with ethyl alcohol, we add cone. H2SO4, it acts as and the process is called
A) Oxidizing agent, saponification
B) Dehydrating agent, esterification
C) Reducing agent, esterification
D) Acid and esterification
Answer:
B) Dehydrating agent, esterification
10th Class Chemistry 14th Lesson Carbon and its Compounds InText Questions and Answers
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 254
Question 1.
Can carbon get helium configuration by losing four electrons from the outer shell?
Answer:
- If carbon loses four electrons from the outer shell, it has to form C4+ ions.
- This requires huge amount of energy which is not available normally.
- Therefore C4+ formation is also a remote possibility.
- Carbon has to satisfy its tetravalency by sharing electrons with other atoms.
- It has to form four covalent bonds either with its own atoms or atoms of other elements.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 255
Question 2.
How do carbon atoms form bonds in so many different ways?
Answer:
As per valence bond theory, the four unpaired electrons in a carbon atom is main cause to form many bonds.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the four unpaired electrons in carbon atom through excited state.
Answer:
Electronic configuration of carbon (ground state):
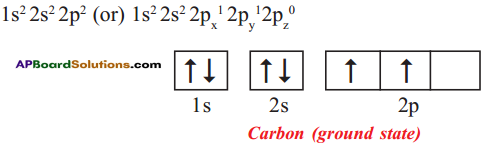
Electronic configuration of carbon (excited state):
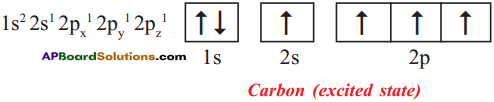
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 256
Question 4.
Where does this energy to excite electron come from?
Answer:
- We have to understand that free carbon atom would not be in excited state under normal conditions.
- When the carbon atom is ready to form bonds with other atoms, the energy required for excitation is taken up from bond energies, which are the liberated energies when bonds are formed between carbon atom and other atoms.
Question 5.
In methane (CH4) molecule all four carbon – hydrogen bonds are identical and bond angle HCH is 109°28′. How can we explain this?
Answer:
In excited state, carbon atom has three unpaired electrons in p-orbitals and one electron in s-orbital. These four valence electrons are with different energies. These orbitals combine to form four identical orbitals. Four hydrogen atoms form four identical C -H bonds with bond angle 109° 28′. This is called hybridisation.
![]()
Question 6.
How do these energetically unequal valence electrons form four equivalent covalent bonds in methane molecule?
Answer:
1) When bonds are formed, energy is released and the system becomes more stable. If carbon forms four bonds rather than two, still more energy is released and so the resulting molecule becomes even more stable.
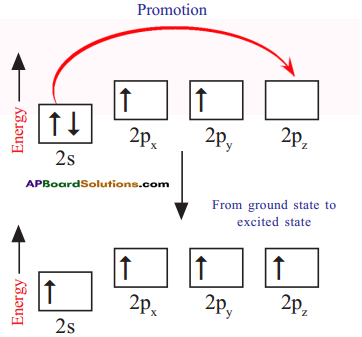
2) The energy difference between the 2s and 2p orbitals is very small. When carbon atom is ready to form bonds it gets a small amount of energy from bond energies and gets excited to promote an electron from the 2s to the empty 2p to give four unpaired electrons.
3) We have got four unpaired electrons ready for bonding, but these electrons are in two different kinds of orbitals and their energies are different.
4) We are not going to get four identical bonds unless these unpaired electrons are in four identical orbitals.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 257
Question 7.
How to explain the four orbitals of carbon containing unpaired electrons as energetically equal?
Answer:
With hybridisation we explai n the four orbitals of carbon containing unpaired electrons are energetically equal.
Ex : Methane (CH4).
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 258
Question 8.
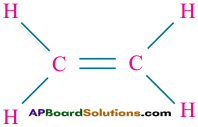
How do you explain the ability of C – atom to form two single covalent bonds and one double bond?
Answer:
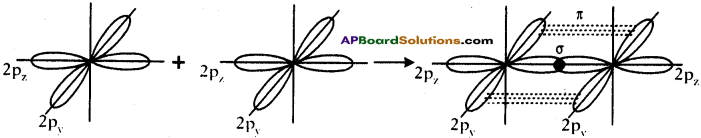
Ethylene (CH2 = CH2) explains the ability of carbon atom to form two single covalent bonds and one double bond.
Ex:
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 259
Question 9.
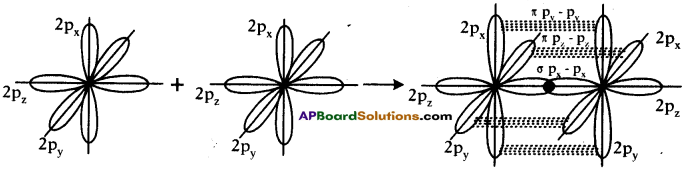
How do you explain the ability of carbon atom to form one single bond and one triple bond?
Answer:
Ethyne (HC [latex]\equiv[/latex] CH) explains the ability of carbon atom to form one single bond between one hydrogen and carbon, and one triple bond between carbon and carbon.
Ex : H – C [latex]\equiv[/latex] C – H.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 260
Question 10.
What are bond angles H[latex]\widehat{\mathbf{C}}[/latex]H in CH4, C2H4 and C2H2 molecules?
Answer:

10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 262
Question 11.
How do you understand the markings (writings) of a pencil on a paper?
Answer:
- When we write with a pencil, the inter layer attractions breakdown and leave graphite layers on the paper.
- It is easy to remove pencil marks from paper with an eraser because, the layers do not bind strongly to the paper.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 265
Question 12.
Allotting completely one special branch in chemistry to compounds of only one element. Is it justified when there are so many elements and their compounds but not with any special branches?
Answer:
- We understand that all molecules that make life possible carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, hormones, and vitamins contain carbon.
- The chemical reactions that take place in living systems are of carbon compounds.
- Food that we get From nature, various medicines, cotton, silk and fuels like natural gas and petroleum almost all of them are carbon compounds.
- Synthetic fabrics, plastics, synthetic rubber are also compounds of carbon.
- Hence, carbon is a special element with the largest number of compounds:
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 266
Question 13.
What are hydrocarbons?
Answer:
The compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen in their molecules are called hydrocarbons.
![]()
Question 14.
Do all the compounds have equal number of C and H atoms?
Answer:
No. All the compounds do not have equal number of C and H atoms.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 269
Question 15.
Observe the following two structures.
a) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
b)
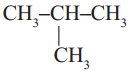
i) How about their structures? Are they same?
Answer:
No, they are not same compounds.
ii) How many carbon and hydrogen atoms are there in (a) and (b) structures?
Answer:
Carbon – 4 ; Hydrogen – 10.
iii) Write the condensed molecular formulae for (a) and (b), do they have same molecular formulae?
Answer:
C4H10; Yes.
Question 16.
Can carbon form bonds with the atoms of other elements?
Answer:
Carbon forms compounds not only with atoms of hydrogen but also with atoms of other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus, halogens, etc.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 272
Question 17.
What do you mean by nomenclature of Organic componds?
Answer:
Nomenclature of organic chemistry is systematic method of naming organic compound.
![]()
Question 18.
What is the basis for nomenclature?
Answer:
The basic of the nomenclature is number of carbons in the parent chain in a compound.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 273
Question 19.
What are the word – root and suffix?
Answer:
Word root:
Word root indicates the number of carbon atoms in the longest possible continuous carbon chain also known as parent chain.
Suffix :
Suffix is added immediately after the word root. It is two types
1) Primary Suffix :
It is used to indicate the degree of saturation or unsaturation of the main chain.
2) Secondary Suffix :
It is used to indicate the main functional group in the organic compound.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 274
Question 20.
What do you mean by the term ‘alkyl’?
Answer:
Alkyl:
Alkyl is a substituent, that is attached to the molecular fragment.
General formula of alkyl is CnH2n + 1
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 278
Question 21.
Can we write the structure of a compound if the name of the compound is given?
Answer:
Yes, we can write the structure of a compound if the name of the compound is given.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 279
Question 22.
Why do sometimes cooking vessels get blackened on a gas or kerosene stove?
Answer:
Because of the inlets of air getting closed, the fuel gases do not completely undergo combustion. Hence, it forms a sooty carbon form which gets coated over the vessels.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 280
Question 23.
Do you know what is a catalyst?
Answer:
A catalyst is a substance which regulates the rate of a given reaction without itself finally undergoing any chemical change.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 281
Question 24.
Do you know how the police detect whether suspected drivers have consumed alcohol or not?
Answer:
- The police officer asks the suspect to blow air into a plastic bag through a mouth piece of the detecting instrument which contains crystals of potassium-di-chromate (K2Cr2O7).
- As K2Cr2O7 is a good oxidizing agent, it oxidizes any ethanol in the driver’s breath to ethanal and ethanoic acid.
- Orange Cr2O72- changes to bluish green Cr3+ during the process of the oxidation of alcohol.
- The length of the tube that turned into green is the measure of the quantity of alcohol that had been drunk.
- The police even use the IR Spectra to detect the bonds C – OH and C – H of CH3 – CH2OH.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 283
Question 25.
What are esters?
Answer:

The compounds which contain the functional group and the general formula R – COO – R’, where R and R’ are alkyl groups or phenyl groups, are known as “Esters”.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 284
Question 26.
What is a true solution?
Answer:
A true solution is that in which the solute particles dispersed in the solvent are less than 1 nm in diameter.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 286
Question 27.
What is the action of soap particles on the greasy cloth?
Answer:
- Soaps and detergents make oil and dirt present on the cloth come out into water, thereby making the cloth clean.
- Soap has one polar end and one non-polar end.
- The polar end is hydrophilic in nature and this end is attracted towards water.
- The non-polar end is hydrophobic in nature and it is attracted towards grease or * . ; oil on the cloth, but not attracted towards water.
- When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to dirt and remove it from the cloth.
- The hydrophobic end of the soap molecules move towards the dirt or grease particles. ’
- The hydrophobic ends attach to the dirt particle and try to pull out.
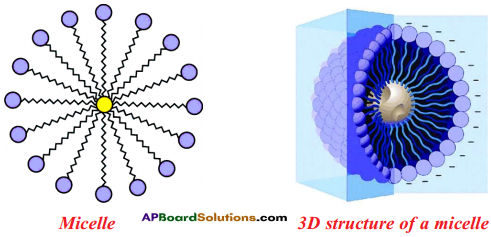
- The molecules of soap surround the dirt particle at the centre of the cluster and form a spherical structure called micelle.
- These micelles remain suspended in water like particles in a colloidal solution.
- The various micelles present in water do not come together to form a precipitate as each micelle repels the other because of the ion-ion repulsion.
- Thus, the dust particles remain trapped in micelles and are easily rinsed away with water.
- Hence, soap micelles remove dirt by dissolving it in water.
10th Class Chemistry Textbook Page No. 280
Question 28.
Why we are advised not to use animal fats for cooking?
Answer:
- Animal fats have recently been implicated as the cause of heart disease and obesity. So, we are advised not to use animal fats for cooking.
- Excess animal fat is stored in lipocytes, which expand in size until the fat is used for fuel.
![]()
Question 29.
Which oil is recommended for cooking? Why?
Answer:
Canola oil :
- A recent entrant into the Indian market Canola is flying off the shelves.
- Canola oil which is made from the crushed seeds of the Canola plant, is said to be amongst the healthiest of cooking oils.
- It has the lowest saturated fat content of any oil.
- It’s seen as a healthy alternative as it’s rich in monosaturated fats and is high in omega-3 and omega a fats.
- It has a medium smoking point and is an oil that works well for fruits, baking, sauteing, etc.
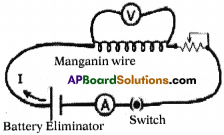
10th Class Chemistry 14th Lesson Carbon and its Compounds Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
Observe the structural formula of the following hydro carbons and write their names in your notebook.
Answer:
1) CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2
Sol. But-l-ene
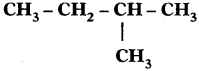
Sol. 2-Methyl butane
3) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
Sol. Hexane
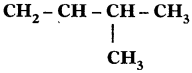
Sol. 3-Methyl, but-l-ene
5)
![]()
Sol. Prop-l-yne
Activity-2
Question 2.
Read the names of the following hydro carbons and draw their structures in your notebook.
1. 2,2-Dimethyl hexane
Sol.

2. But-l-yne
Sol. CH3 – CH2 – C = CH
3. 3-Methyl Pent-2-ene
Sol.
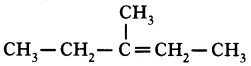
4. But-1.2-diene
Sol. CH3 – CH3 = c = CH2
5. Hept-2 en, 4-yne
Sol.
![]()
Activity – 3
Question 3.
Write an activity to show esterification reactions.
Answer:
The compound formed is ester. The process is called esterification.
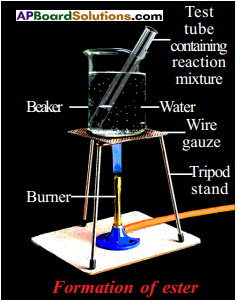
- Take 1 ml of ethanol and 1 ml of glacial acetic acid along with a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid in a test tube.
- Warm it in a water bath or a beaker containing water for at least five minutes.
- Pour the warm contents into a beaker containing 20-50 ml of water and observe the odour of the resulting mixture.
- We will notice that the resulting mixture is sweet odoured subatance.
- This substance is nothing but ethyl acetate, an ester.
- This reaction is called esterification reaction.
Activity – 4
Question 4.
Write an activity to show soap solution separates oil from water.
Answer:
- Take about 10 ml of water each in two test tubes.
- Add a drop of oil to both the test tubes.
- Label them as A and B.
- Add a few drops of soap solution to test tube B.
- Now shake both the test tubes vigorously for the same period of time.
- We can see the oil and water layers separately in both the test tubes immediately after we stop shaking them.
- Leave the test tubes undisturbed for sometime and observe.
- The oil layer separates out first in which test tube we added drops of soap solution.